Food Processing for Increasing Consumption: The Case of Legumes
Abstract
Food is a basic necessity of life. However, over the past few decades food quality and safety issues have caused serious concern among consumers on account of their direct association with human health. Unsafe food poses serious risk to the health of consumers, particularly in the developing countries where food contamination is high on account of indiscriminate use of food contaminants and food protectants. The presence of harmful antinutrients and pesticide residues in legumes limits the bioavailability of the essential nutrients. Organic farming and other approaches are effective in dealing with pesticide contamination, but it would take significant time for them to be adopted worldwide. Therefore, a simple, as well as effective solution in the transitional phase is offered by domestic processing techniques. Domestic food processing methods, such as washing, cooking, milling, parboiling, and storage, may provide a simple and effective solution in this context. The nature of the processing operation (viz., physical, chemical, or thermal) plays an important role in this; usually, the processes that utilize the higher temperatures have greater effects on dissipation of antinutrients and pesticide residues. It is concluded that a combination of processing techniques renders food grains safe for human consumption.
Keywords
1. Food Legumes: A Boon to Human Nutrition
2. Antinutrients in Legumes and Their Removal
2.1. Enzyme Inhibitors
2.1.1. α-Amylases
2.1.2. Trypsin inhibitors
2.1.3. Protease inhibitors
2.2. Cyanogenic Glucosides
2.3. Lectins
2.4. Tannins
2.5. Oxalates
2.6. Phytates
2.7. Saponins
2.8. Alkaloids
3. Processing Techniques to Reduce Antinutritional Factors
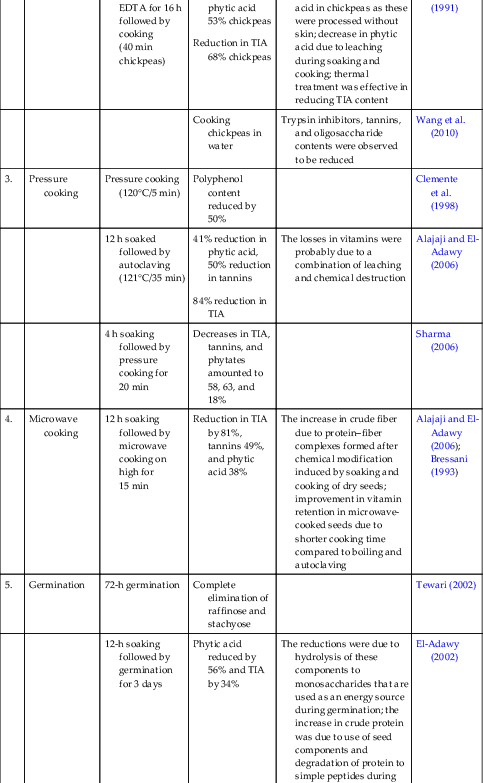
Table 1.1
| S. No. | Processing Techniques | Detailed Methods | Effects on Antinutrients | Reasons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soaking | Soaking 12 h | Phytic acid content showed loss of 20% due to soaking | El-Tinay et al. (1989) | |
| Soaking for 9 h | Decreases in α-galactosides; 27% (distilled water), 17% (citric acid),16% (NaHCO3) | Frias et al. (2000) | |||
| 2. | Boiling | 19 h soaking followed by 90-min boiling | Decrease amounting to 99% in phytic acid and 82.27% in TIA | The losses in vitamins were probably due to a combination of leaching and chemical destruction | Alajaji and El-Adawy (2006) |
| 4 h soaking followed by 90-min boiling | Decreases in TIA, tannins, and phytates amounted to 36, 30, and 23% | Sharma (2006) | |||
| 12 h soaked seeds were cooked | Possible hydrolysis of starch and oligosaccharides to monosaccharides on cooking resulting in increased concentration of sugars in cooked legumes; cooking may cause rupturing of starch granules followed by amylolysis that leads to a decreased amount of starch | Jood et al. (1988) | |||
| Soaking (9 h) in citric acid, distilled water, or 0.07% sodium bicarbonate solution followed by boiling for 35 min | Losses in α galactosides Complete elimination of TIA |
||||
| Soaking (12 h) followed by boiling in water for 60 min | 30% loss in phytic acid | El-Tinay et al. (1989) | |||
| Soaking in 0.03% EDTA for 16 h followed by cooking (40 min chickpeas) | Reduction in phytic acid 53% chickpeas Reduction in TIA 68% chickpeas |
Greater reduction in phytic acid in chickpeas as these were processed without skin; decrease in phytic acid due to leaching during soaking and cooking; thermal treatment was effective in reducing TIA content | Estevez et al. (1991) | ||
| Cooking chickpeas in water | Trypsin inhibitors, tannins, and oligosaccharide contents were observed to be reduced | Wang et al. (2010) | |||
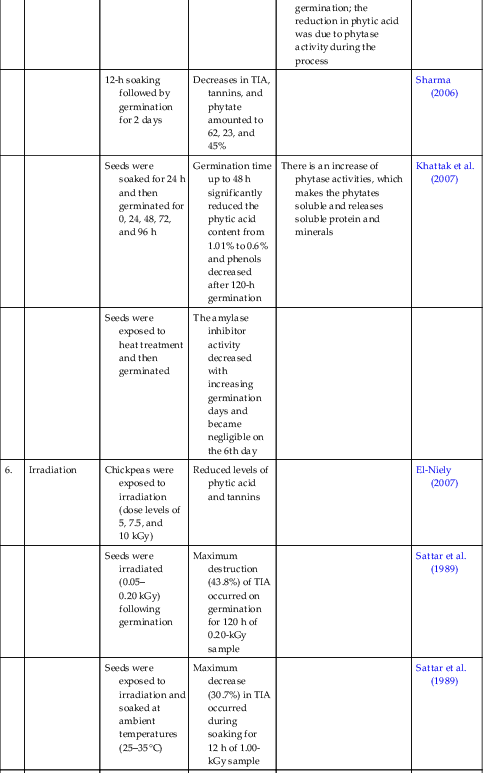
| 3. | Pressure cooking | Pressure cooking (120°C/5 min) | Polyphenol content reduced by 50% | Clemente et al. (1998) | |
| 12 h soaked followed by autoclaving (121°C/35 min) | 41% reduction in phytic acid, 50% reduction in tannins 84% reduction in TIA |
The losses in vitamins were probably due to a combination of leaching and chemical destruction | Alajaji and El-Adawy (2006) | ||
| 4 h soaking followed by pressure cooking for 20 min | Decreases in TIA, tannins, and phytates amounted to 58, 63, and 18% | Sharma (2006) | |||
| 4. | Microwave cooking | 12 h soaking followed by microwave cooking on high for 15 min | Reduction in TIA by 81%, tannins 49%, and phytic acid 38% | The increase in crude fiber due to protein–fiber complexes formed after chemical modification induced by soaking and cooking of dry seeds; improvement in vitamin retention in microwave-cooked seeds due to shorter cooking time compared to boiling and autoclaving | Alajaji and El-Adawy (2006); Bressani (1993) |
| 5. | Germination | 72-h germination | Complete elimination of raffinose and stachyose | Tewari (2002) | |
| 12-h soaking followed by germination for 3 days | Phytic acid reduced by 56% and TIA by 34% | The reductions were due to hydrolysis of these components to monosaccharides that are used as an energy source during germination; the increase in crude protein was due to use of seed components and degradation of protein to simple peptides during germination; the reduction in phytic acid was due to phytase activity during the process | El-Adawy (2002) | ||
| 12-h soaking followed by germination for 2 days | Decreases in TIA, tannins, and phytate amounted to 62, 23, and 45% | Sharma (2006) | |||
| Seeds were soaked for 24 h and then germinated for 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h | Germination time up to 48 h significantly reduced the phytic acid content from 1.01% to 0.6% and phenols decreased after 120-h germination | There is an increase of phytase activities, which makes the phytates soluble and releases soluble protein and minerals | Khattak et al. (2007) | ||
| Seeds were exposed to heat treatment and then germinated | The amylase inhibitor activity decreased with increasing germination days and became negligible on the 6th day | ||||
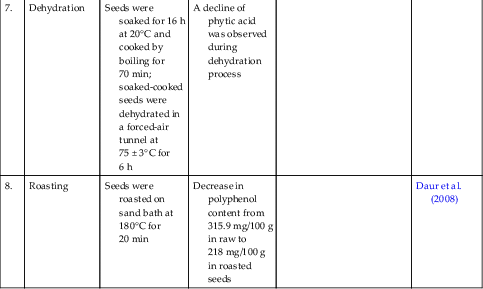
| 6. | Irradiation | Chickpeas were exposed to irradiation (dose levels of 5, 7.5, and 10 kGy) | Reduced levels of phytic acid and tannins | El-Niely (2007) | |
| Seeds were irradiated (0.05–0.20 kGy) following germination | Maximum destruction (43.8%) of TIA occurred on germination for 120 h of 0.20-kGy sample | Sattar et al. (1989) | |||
| Seeds were exposed to irradiation and soaked at ambient temperatures (25–35°C) | Maximum decrease (30.7%) in TIA occurred during soaking for 12 h of 1.00-kGy sample | Sattar et al. (1989) | |||
| 7. | Dehydration | Seeds were soaked for 16 h at 20°C and cooked by boiling for 70 min; soaked-cooked seeds were dehydrated in a forced-air tunnel at 75 ± 3°C for 6 h | A decline of phytic acid was observed during dehydration process | ||
| 8. | Roasting | Seeds were roasted on sand bath at 180°C for 20 min | Decrease in polyphenol content from 315.9 mg/100 g in raw to 218 mg/100 g in roasted seeds | Daur et al. (2008) |

EDTA, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; TIA, trypsin inhibitor activity.
3.1. Nonheat Processing
3.1.1. Soaking
3.1.2. Germination/sprouting
3.1.3. Fermentation
3.2. Heat Processes
3.2.1. Cooking
3.2.2. Roasting
3.3. Modern Methods, Including Radiation-Based Technology
3.3.1. Microwave cooking
3.3.2. Irradiation
4. Food Safety and Quality Issues
5. Significance of Paradigm Shift
6. Pesticides: Types, Application, Environmental Impacts, and Human Health Effects
6.1. Pesticides: Types and Application
6.2. Environmental Impacts of Pesticides
6.3. Health Impacts of Pesticides
6.4. Not-to-Be-Used Pesticides
6.5. Pesticide Residues in Food
6.6. Sustainable Methodology for Food Safety Within the Transitional Phase
6.7. Domestic Processing Techniques and Food Safety (Pesticide Residues)
6.8. Food Processing
Table 1.2
| S. No. | Processing | Commodities | Pesticides | Residue Dissipation (%) | Reasons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bread making | Wheat flour | Endosulfan Deltamethrin Malathion Propiconazole Chlorpyrifos Hexaconazole |
70 63 60 52 51 46 |
Bread making involves yeast-mediated fermentation and baking, causing pesticide degradation | Sharma et al. (2006) |
| 2. | Milling and storage for 1 year | Wheat | Phoxim methyl | 8–10 | During milling, residues accumulation occurs in bran fractions and reduction in white flour | Alnaji and Kadoum (1979) |
| 3. | Milling | Whole grain | Deltamethrin | 42.39 | Marei et al. (1995) | |
| 4. | Milling | Wheat | Malathion | 95 | Uygun et al. (2005) | |
| 5. | Parboiling | IR 20 paddy | Ekalux 25 EC 0.05% Dursban 25 EC 0.05% Lebaycid 100 EC 0.05% |
49 51 68 |
Reduction due to inactivation or degradation of the pesticides at high temperature | Krishnamurthy and Sreeramulu (1982) |
| 6. | Parboiling | Rough rice | Malathion | 99 | Cogburn et al. (1990) | |
| 7. | Storage for 6 months at 26.7°C | Wheat Maize sorghum |
Malathion | 85% of total residue remained on outside of grain after 24 h, residues increased inside the grain and decreased markedly on the outside during the first month, and residues disappeared more rapidly from the outside than from the inside during the remaining storage time | Kadoum and LaHue (1974) | |
| 8. | 12 months of storage in an open basket | Maize grains Beans |
Malathion | 64 47 |
High losses due to volatilization and possible settling of pesticide dust formulation to the bottom and on the sides of basket during storage in the open and windy tropical laboratory | Lalah and Wandiga (2002) |
| 9. | Milling and storage for 4 and 36 weeks, respectively | Wheat grain | Chlorpyrifos methyl Etrimfos Fenitrothion Malathion Methacrifos Pirimiphos methyl |
2.7 0.08 63.33 50 50 32.35 |
Wilkin and Fishwick (1981) | |
| 10. | Storage around 6 months | Barley | Malathion | 65–72 | Uygun et al. (2007) | |
| 11. | Cooking without and with NaCl | Maize grains Beans |
Malathion | 56.7 and 69.7 64.2 and 75 |
Lalah and Wandiga (2002) | |
| 12. | Washing (twice) | Soybeans | Dichlorvos Malathion Chlorpyrifos Captan |
80–90 | Sprayed pesticides remain as microparticles on soybeans and are easily removed by mechanical stirring in water | Miyahara and Saito (1994) |
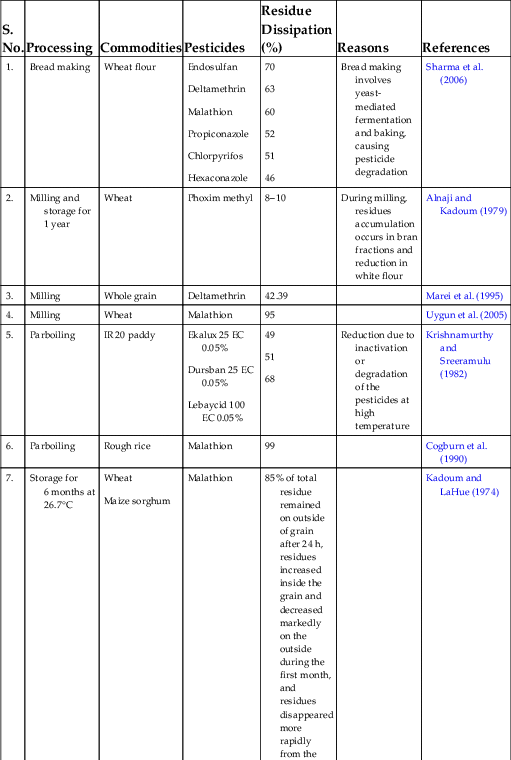

Source: From Kaushik, G., Satya, S., Naik, S.N., 2009. Food processing a tool to pesticide residue dissipation–a review. Food Res. Int. 42 (1), 26–40.