Strategy for the Prediction, Control, and Optimization of the Functional Properties of Food Proteins: Using Statistical and Chemometric Tools
* Laboratorio de Bromatología, Facultad de Química, Bioquímica y Farmacia, Universidad Nacional de San Luis, Chacabuco y Pedernera, San Luis, Argentina
** Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CCT—San Luis—CONICET), Instituto de Física Aplicada (INFAP), San Luis, Argentina
† Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica, Centro Atómico Constituyentes, San Martín, Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina
Abstract
Proteins have functional properties that govern their behavior in foods during processing, storage, and consumption. Proteins can have high nutritional quality and not have functional properties suitable for incorporation into determined food systems. Furthermore, a desirable functional attribute for an additive may be undesirable for everyone else. This chapter describes the design of a new strategy to predict, control, and optimize the functional parameters of food proteins hydrolyzed or not, using chemometrics tools. The starting material consists of proteins whose functional properties are desired to modify. Functional properties (e.g., emulsifying and foaming properties) can be simultaneously evaluated by an experimental statistical design, response surface graphics, and multiple linear regressions. This strategy expands the applications of food proteins and allows the following facilities: assess interactions between variables of multivariate systems, evaluate the dependence between functional parameters, and optimize the additive production with tailor-made functional properties for different food systems.
Keywords
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Statistical Design of Experiments
Table 11.1
| ID No. | (E:S) Ratio (mg of Papain/g of Cheese Casein) | pH | Time of Hydrolysis (min) | Temperature (°C) | Amount of Added Buffer (g/g Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 levels | 7 levels | 7 levels | 7 levels | 3 levels | |
| 1 | 0.113 | 7 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 2 | 0.220 | 7 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 3 | 0.166 | 8.73 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 4 | 0.166 | 7.58 | 247.9 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 5 | 0.166 | 7.58 | 174.5 | 66.3 | 20 |
| 6 | 0.166 | 7.58 | 174.5 | 55.3 | 27.7 |
| 7 | 5.5 × 10−3 | 7 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 8 | 0.059 | 5.27 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 9 | 0.059 | 6.42 | 52.1 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 10 | 0.059 | 6.42 | 125.5 | 38.7 | 20 |
| 11 | 0.059 | 6.42 | 125.5 | 49.7 | 12.2 |
| 12 | 0.166 | 5.27 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 13 | 0.166 | 6.42 | 52.1 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 14 | 0.166 | 6.42 | 125.5 | 38.7 | 20 |
| 15 | 0.166 | 6.42 | 125.5 | 49.7 | 12.2 |
| 16 | 0.059 | 8.73 | 150 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 17 | 0.113 | 8.15 | 52.1 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 18 | 0.113 | 8.15 | 125.5 | 38.7 | 20 |
| 19 | 0.113 | 8.15 | 125.5 | 49.7 | 12.2 |
| 20 | 0.059 | 7.58 | 247.9 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 21 | 0.113 | 5.84 | 247.9 | 52.5 | 20 |
| 22 | 0.113 | 7 | 223.4 | 38.7 | 20 |
| 23 | 0.113 | 7 | 223.4 | 49.7 | 12.2 |
| 24 | 0.059 | 7.58 | 174.5 | 66.3 | 20 |
| 25 | 0.113 | 5.84 | 174.5 | 66.3 | 20 |
| 26 | 0.113 | 7 | 76.6 | 66.3 | 20 |
| 27 | 0.113 | 7 | 150 | 66.3 | 12.2 |
| 28 | 0.059 | 7.58 | 174.5 | 55.3 | 27.7 |
| 29 | 0.113 | 5.84 | 174.5 | 55.3 | 27.7 |
| 30 | 0.113 | 7 | 76.6 | 55.3 | 27.7 |
| 31 | 0.113 | 7 | 150 | 41.4 | 27.7 |

2.3. Free Amine Nitrogen and Total Soluble Nitrogen
2.4. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.5. Solubility
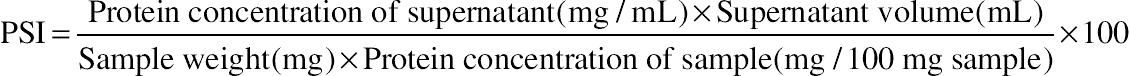 (11.1)
(11.1)2.6. Water-Holding Capacity
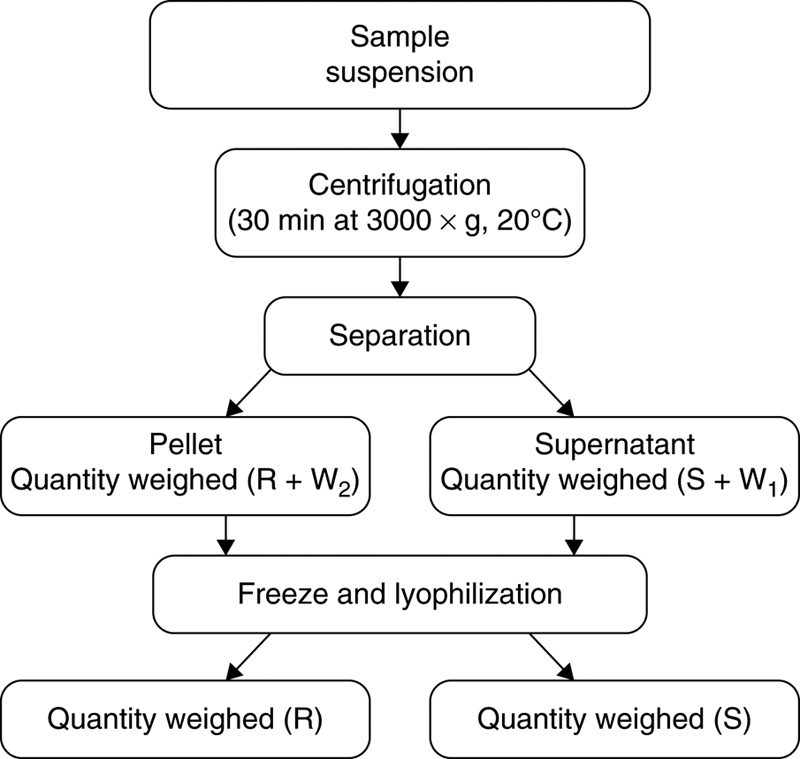
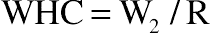 (11.2)
(11.2)2.7. Held Water
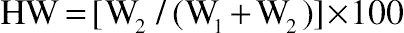 (11.3)
(11.3)2.8. Emulsifying Activity Index and Emulsifying Stability Index
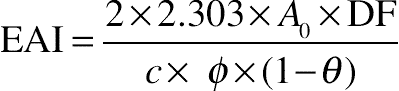 (11.4)
(11.4)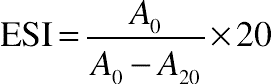 (11.5)
(11.5)2.9. Viscosity (η)
2.10. FTIR Spectroscopy
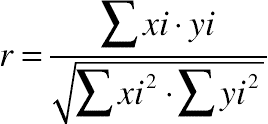 (11.6)
(11.6)2.11. HPLC-MS Analysis
2.12. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.13. Foaming Capacity and Foam Stability (FS)
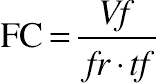 (11.7)
(11.7) (11.8)
(11.8)2.14. Chemometrical Analysis
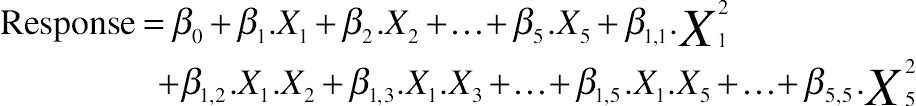 (11.9)
(11.9)2.15. Desirability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Free Amine Nitrogen Content
 (11.10)
(11.10)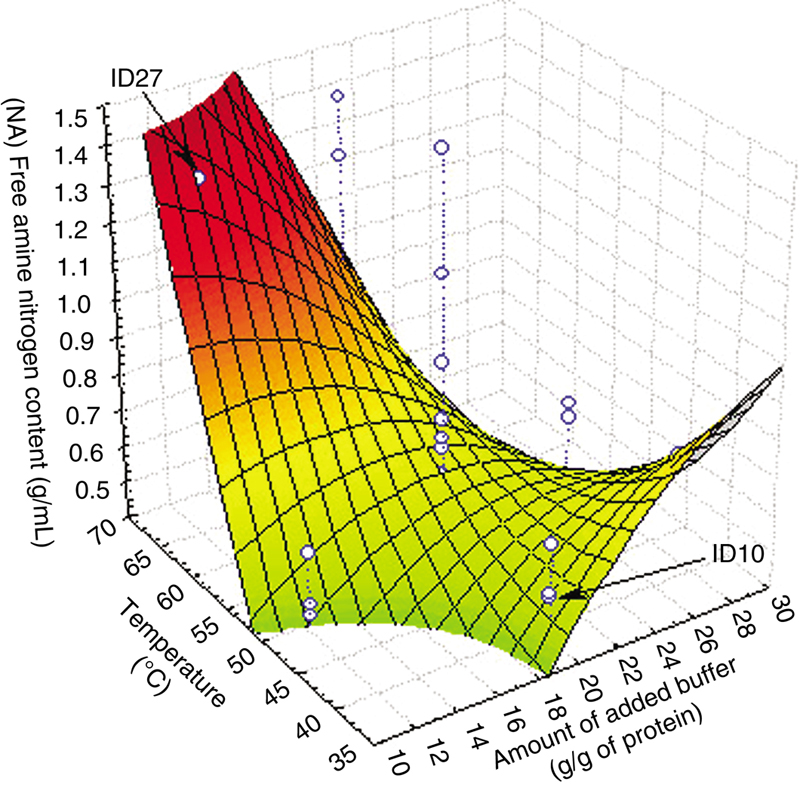
 (11.11)
(11.11)3.2. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Total Soluble Nitrogen Content
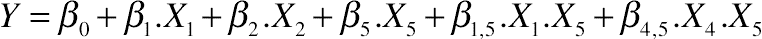 (11.12)
(11.12)
Interactive effects between (A) temperature and amount of added buffer, (B) ratio (E:S) and amount of added buffer for hydrolyzed goat cheese proteins.
3.3. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Protein Solubility Index
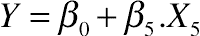 (11.13)
(11.13)3.4. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Water-Holding Capacity
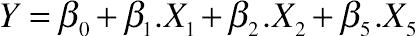 (11.14)
(11.14)
(A) pH and ratio (E:S), (B) ratio (E:S) and amount of added buffer, (C) amount of added buffer and pH for hydrolyzed goat cheese proteins.
3.5. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Held Water
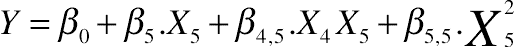 (11.15)
(11.15)
3.6. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Emulsifying Activity Index
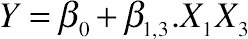 (11.16)
(11.16)
(A) Emulsifying activity index (EAI) and the interactive effect between the time of hydrolysis and ratio (E:S), (B) emulsifying stability index (ESI) and the interactive effect between the ratio (E:S) and temperature for hydrolyzed goat cheese proteins.
3.7. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Emulsifying Stability Index
 (11.17)
(11.17)3.8. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Viscosity (η)
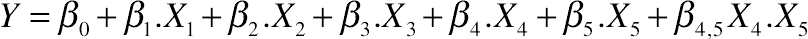 (11.18)
(11.18)

Samples ID No. 10 and ID No. 27) after the subtraction of blanks without papain.
Table 11.2
| Bands | Frequency (± 2 cm−1) | Relative Areas | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID 10 | ID 27 | ||
| β—Sheet | 1636 | 0.00485 | 0.00197 |
| 1689 | |||
| 1698 | |||
| α—Helix | 1660 | 0.00257 | 0.00058 |
| Random | 1647 | 0.0048 | 0.0019 |
| 1653 | |||
| β—Turn | 1669 | 0.00383 | 0.00263 |
| 1674 | |||
| 1683 | |||
| Side chains | 1622 | 0.00078 | 0.00291 |
| 1615 | |||
| 1608 | |||
| Total area | (1600–1700) | 0.01683 | 0.00999 |


Sample ID No. 10 (A) and Sample ID No. 27 (B), and their blanks without papain.
3.9. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Surface Hydrophobicity
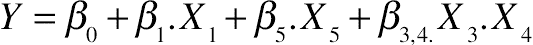 (11.19)
(11.19)
3.10. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Foaming Capacity
3.11. Effect of Protein Hydrolysis of Goat Cheese on Foam Stability
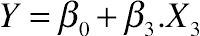 (11.20)
(11.20)3.12. Desirability
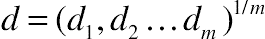 , i = 1 to m.
, i = 1 to m.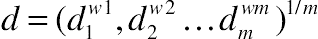 , where 0 ≤ wi ≤ 1 are weights, which hold the condition Σwi = 1. The weights allow us to establish relative importance to the responses.
, where 0 ≤ wi ≤ 1 are weights, which hold the condition Σwi = 1. The weights allow us to establish relative importance to the responses. (11.21)
(11.21)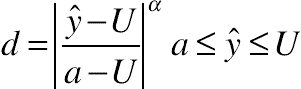 (11.22)
(11.22)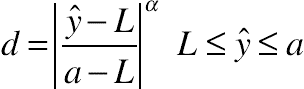 (11.23)
(11.23)Table 11.3
| Responses | Minimum | Maximum | Low Range | Intermediate Range | High Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | 0.41 | 1.364 | 0.41–0.645 | >0.645–1.129 | >1.129–1.364 |
| NT | 1.11 | 7.025 | 1.11–2.588 | >2.588–5.544 | >5.544–7.025 |
| PSI | 14.14 | 91.035 | 14.14–33.36 | >33.36–71.81 | >71.81–91.035 |
| WHC | 0.55 | 3.08 | 0.55–1.182 | >1.182–2.447 | >2.447–3.08 |
| HW | 9.34 | 27.33 | 9.34–13.84 | >13.84–22.73 | >22.73–27.33 |
| EAI | 66.435 | 223.71 | 66.435–105.75 | >105.75–184.4 | >184.39–223.7 |
| ESI | 27.33 | 85.45 | 27.33–41.86 | >41.86–70.9 | >70.9–85.45 |
| η | 1.265 | 1.74 | 1.265–1.384 | >1.384–1.62 | >1.62–1.74 |
| So | 0.955 | 15.64 | 0.955–4.626 | >4.626–11.97 | >11.97–15.64 |
| FC | 0.025 | 0.67 | 0.025–0.186 | >0.186–0.508 | >0.508–0.67 |
| FS | 0.14 | 1.48 | 0.14–0.475 | >0.475–1.145 | >1.145–1.48 |
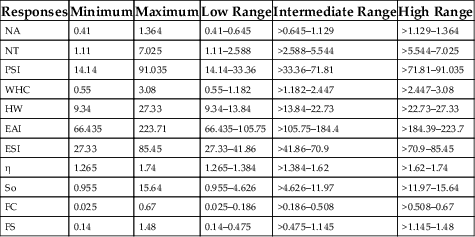
- • Additive for sauces and soups.
- • Additive for bakery products.
- • Additive for accelerate the maturation of hard cheeses.
- • Additive for cheesecake.

Desirability functions as the result of factors (A) E:S ratio and amount of added buffer, (B) pH and time of hydrolysis, and (C) temperature and time of hydrolysis.

Desirability functions as the result of factors (A) E:S ratio and amount of added buffer, (B) pH and time of hydrolysis, and (C) temperature and time of hydrolysis.
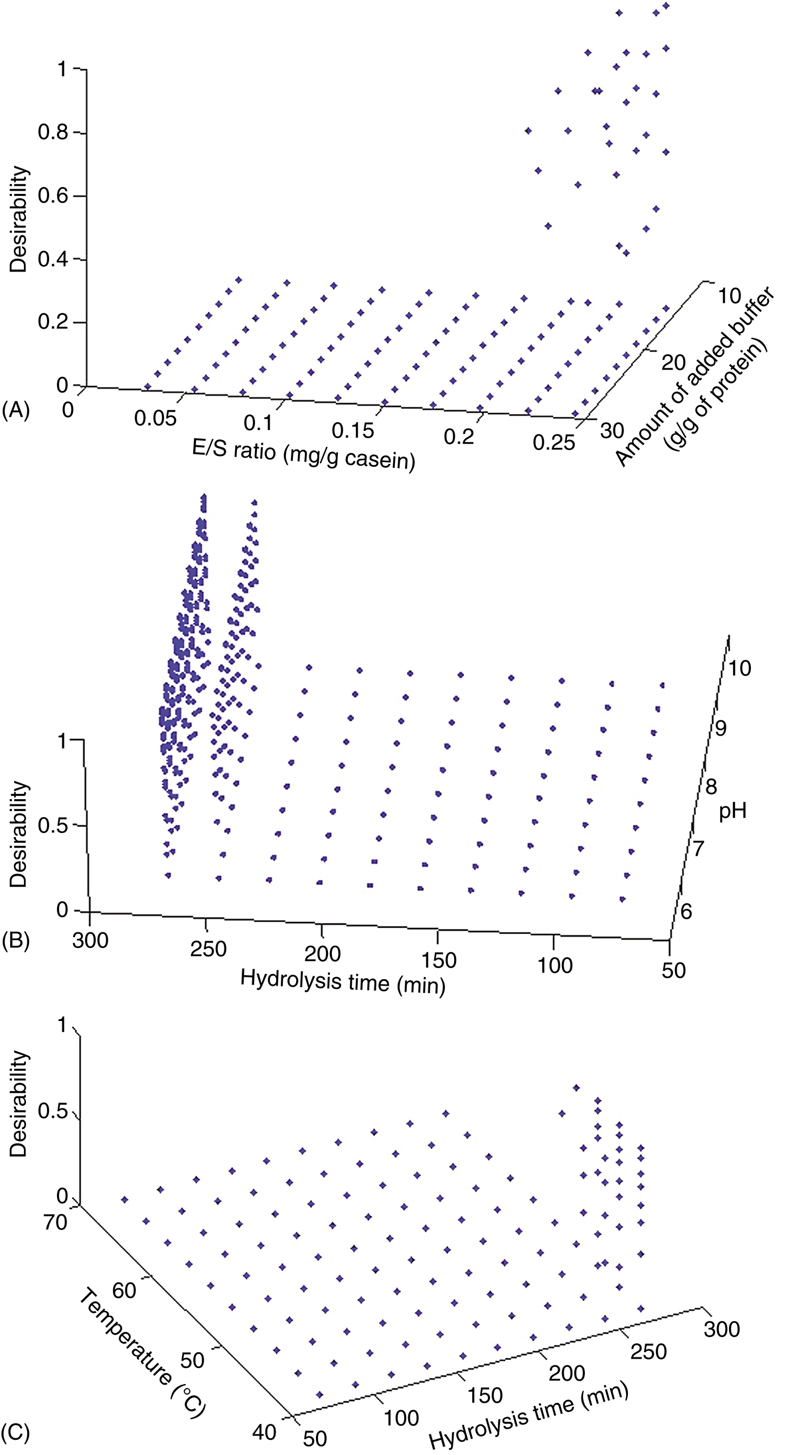
Desirability functions as the result of factors (A) E:S ratio and amount of added buffer, (B) pH and time of hydrolysis, and (C) temperature and time of hydrolysis.
Table 11.4
| Product | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time of Hydrolysis (min) | Enzyme: Substrate Ratio (mg/g of Cheese Casein) | Amount of Added Buffer (g/g Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additive for sauces and soups | 5–9 | 50–70 | 75–270 | Full range | 13–22 |
| Additive for bakery products | 8–9 | 40–50 or 60–70 | 50–100 or 175–270 | 0.12–0.22 | 20–30 |
| Additive to accelerate the maturation of hard cheeses | 6–9 | 45–52 | 270 | 0.20–0.25 | 10–20 |
