Glossary of terms
A
Acid neutralization capacity The amount of acid, expressed in mol/kg, required to neutralize a given weight of material to a stable neutral pH.
Activity Number of radioactive decays per unit time. Unit: 1 Bq (Becquerel)=1 decay/s; Old unit: 1 Ci (Curie)=3.7×1010 Bq.
Activity concentration Activity per unit mass.
ADC Analog-to-digital converter.
Alpha (α-) radiation Radiation, which consists of α-particles containing two protons and two neutrons and is identical to an ionized 4He nuclei.
Anion An ion with a negative charge.
Available content The quantity of a constituent that can be leached from a material under conditions that under extreme conditions could be reached in the environment or in the very long term.
B
Base neutralization capacity The amount of base, expressed in mol/kg, required to neutralize a given weight of material to a stable neutral pH.
Batch tests Leaching tests which are carried out on a single portion of material using a single portion of leachant, i.e., there is no renewal of leachant during the test.
Beta (β-) radiation Radiation made up of β-particles that are electrons, with a negative elementary charge, or not so often, positrons both with positive elementary electric charge.
Branching ratio The probability that a nucleus will decay by a certain process (compared to all possible decay processes).
BSS Basic Safety Standard.
Buffer A solution containing both a weak acid and its conjugate weak base whose pH changes only slightly on addition of acid or alkali.
Building A structure, which encloses a space.
Building material Material used in a construction work for the construction of a building
Building product Construction product for incorporation in a permanent manner in a building or parts thereof
C
Carbonation Uptake of carbon dioxide in an alkaline material.
Cation An ion with a positive charge.
Complexation The formation of an ion into a molecular structure consisting of a central atom bonded to other atoms by coordinate covalent bonds.
Construction material Material used in a construction work.
Construction product Any product or kit which is produced and placed in the market for incorporation in a permanent manner in construction works or parts thereof and the performance of which has an effect on the performance of the construction works with respect to the basic requirements for construction works.
Construction work Any work carried out in connection with the construction, alteration, conversion, fitting-out, commissioning, renovation, repair, maintenance, refurbishment, demolition, decommissioning or dismantling of a structure.
Correction factor Factor by which the reading of a measurement device must be corrected when the measurement is not performed at the conditions at calibration.
D
DIC See dissolved inorganic carbon
Diffusion Transfer of matter due to the thermal energy of molecules (a particular case of diffusion is the spontaneous mixing of one substance with another when in contact or separated by a permeable membrane or microporous barrier).
Dissolution Molecular dispersion of a solid in a liquid.
Dissolved inorganic carbon This usually represents carbonate species.
Dissolved organic carbon (or DOC) Natural or artificial organic matter remaining in dissolved state in solution (e.g., humic and fulvic acids).
DL Decision limit.
Dose conversion factor (for radon) Factor by which the radon exposure can be converted into a dose.
E
Effective dose Absorbed radiation energy in tissue weighted by the kind of radiation (radiation weighting factor wR) and targeted tissues/organs (tissue weighting factor wT); the effective dose can be used for the radiation risk estimation.
Effective dose rate Effective dose per unit time.
Efficiency Probability for detecting radiation per unit decay or per unit radiation particle or photon.
Eluate As leachate but usually in the context of a laboratory test.
Emission Release of substances from one environment, medium, or phase to another.
Equilibrium (chemical and physical) Chemical equilibrium is a condition in which a reaction and its opposite or reverse reaction occur at the same rate resulting in a constant concentration of reactants. Physical equilibrium is exhibited when two or more phases of a system are changing at the same rate so the net change in the system is zero.
Equilibrium (secular) The activity of a shorter lived progeny is the same as the activity of the longer lived mother nuclide. Thus, the activity of the progeny decreases with the half-life of the mother nuclide. In case of 222Rn radioactive equilibrium means that the activity of each short-lived progeny is the same as the activity of the longer-lived radon gas.
Equilibrium equivalent concentration (EEC) Computed radon concentration in radioactive equilibrium with the same potential alpha energy concentration (PAEC) as observed: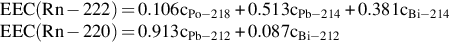
Equilibrium factor Ratio of the EEC to the radon activity concentration (or ratio of the potential alpha energy concentration of short-lived radon decay products in a given volume of air to the potential alpha energy concentration of these decay products if these are in radioactive equilibrium with radon in the same volume of air).
Exhalation rate, E Radon activity transferred from either a mass (Em—free mass radon exhalation rate, unit: Bq/kg/s) or a surface (Es—free surface radon exhalation rate, unit: Bq/m2/s) to the ambient air per unit time.
Exposure Contact to radiation, either measured in dose units (or equivalent units) or as a product of activity's concentration and time.
Extraction A separation operation that may involve three types of mixture: (1) a mixture composed of two or more solids (2) a mixture composed of a solid and a liquid—as in this context (3) a mixture of two or more liquids. One or more components of such a mixture are removed (extracted) by exposing the mixture to the action of a solution or solvent in which the component to be removed is soluble.
F
Fluence Number of particles or photons passing through unit area.
FWHM Full width at half maximum.
G
Gamma (γ-) radiation Radiation composed of high-energy photons (electromagnetic waves) coming from the nucleus.
H
Half-life Time until a nuclide has reduced to half its initial value when no further production of this nuclide take place (e.g., in radioactive decay chains).
HPGe High-purity germanium (detector).
I
Index I or I-index Activity concentration index
Infiltration The movement of water (usually rainwater) into and through a solid material.
Inorganic Chemicals that are generally considered to include all substances except hydrocarbons and their derivatives or all substances which are not compounds of carbon with the exception of carbon oxides and carbon disulfide.
Ionic strength A measure of the concentration of ions in solution.
Isotopes Nuclides with equal number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Most chemical elements consist of different isotopes. These isotopes behave chemically (nearly) identically.
L
Leachant Liquid in contact with or which will be brought in contact with a solid which extracts soluble components of the solid.
Leachate Liquid containing soluble components extracted from a solid (usually linked to field conditions, e.g., landfill leachate).
Leaching The process by which the soluble components of one phase (usually a solid) are transferred to another phase (usually a liquid).
Liquid to solid ratio The liquid to solid ratio relates to the amount of liquid used in a batch leaching test to extract a given amount of solid. Abbreviation: L/S Unit: L/kg.
LLD Lower level of detection.
M
Marinelli beaker A plastic container with a cylindrical recess in the bottom for detector installation for analyzing moderate to low activity level of radioactive samples in powder or liquid form directly for gamma ray emitting isotopes.
MCA Multichannel analyzer.
Montecarlo calculation A technique used to model the probability of different outcomes in a process that cannot easily be predicted due to the intervention of random variables.
MS Members states (of the EU)
N
Naturally occurring radioactive material (or NORM) Radioactive material containing no significant amounts of radionuclides other than naturally occurring radionuclides (NOR), for a detailed discussion of the concept see Chapter 2.
NOR Naturally occurring radionuclides.
NORM by-product By-products from a process and either comprises or is contaminated by NORM.
NORM residue Material that remains from a process and comprises or is contaminated by NORM.
NORM waste NORM for which no further use is foreseen.
O
Organic Chemicals that are generally considered to include all compounds of carbon except carbon oxides and sulfides.
Oxidation/reduction potential A measure of the ability of a system to cause oxidation or reduction reactions. Oxidation and reduction are reactions in which electrons are transferred. Oxidation and reduction always occur simultaneously (redox reactions). The substance that gains the electrons is termed the oxidizing agent and the substance that loses the electrons is termed the reducing agent.
P
Partitioning The distribution of molecules in different states or phases in a system for example as solid, liquid, or gas.
pE A measure of the redox potential
Percolation The movement of a liquid through a solid.
pH A value taken to represent the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution.
Photopeak Relative maximum in the energy spectrum of a gamma emitter which is caused by the deposition of the full energy of a photon (full energy peak).
pH static leach test A leaching test consisting of a number of individual extractions of subsamples of the same material at pH values fixed by addition of acid or base as required.
Porosity The relative volume of void space to the total volume occupied by a material.
Potential alpha energy concentration (PAEC) Sum of all α-energies from the short living Rn-progeny deposited in unity air volume. Units: J/m3 or MeV/m3. PAEC can be converted into EEC and vice versa.
Precipitation The settlement of small particles out of a liquid or gaseous suspension by gravity or as the result of a chemical reaction.
Progeny Chain of decay products (of radon)—formerly called radon daughter products.
Q
QA Quality assurance.
QC Quality control.
R
Radiation The emission of energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic particles, especially high-energy particles that cause ionization.
Radioactive equilibrium The activity of a short-lived progeny is the same as the activity of the longer living mother nuclide.
Radioactive material Material designated under national law or by a regulatory body as being subject to regulatory control because of its radioactivity.
Radioactivity A process by which nuclides spontaneously decay by the emission of radiation.
Radionuclide Isotope which undergoes radioactive decay
Radon diffusion coefficient The radon activity permeating in a homogeneous media due to molecular diffusion through unit area of the elementary layer of unit thickness per unit time at unit radon activity concentration gradient on the boundaries of this layer.
Radon diffusion length The distance of radon transport in a homogeneous medium due to molecular diffusion, at which the radon flow rate or its activity concentration decreases to 1/e≈0.37 (factor e≈2.72), while the transport is considered in conditionally infinite medium without the influence of edge effects.
Radon emanation The process of radon generation and further removal from the bulk of the solid phase into the pore space by the recoil process resulting from the alpha decay of the radium parent. Atoms of radon found in the pore space that have the ability to migrate into open pores are called free radon. Radon atoms held in the solid phase and which are not able to migrate are called bound radon.
Radon emanation coefficient The ratio of free radon activity to the total activity (free and bound) of radon in the material under the radioactive equilibrium between radon and the radium parent.
Radon exhalation The process of releasing a free radon from the material surface into the surrounding medium (air).
Radon exhalation rate The activity of radon atoms that leave a material per unit surface (or mass) of the material per unit time (also see exhalation rate, E).
Radon exposure Radon activity concentration multiplied by the time of exposure.
Redox See oxidation/reduction potential.
Redox potential (EH) A measure of the oxidation reduction potential. See oxidation/reduction.
S
Scintillator A material that fluoresces when struck by a charged particle or high-energy photon.
Self-attenuation Radiation shielding inside of a sample caused by the sample itself.
Short-lived decay products (short-lived progeny) Radioactive progeny of radon (218Po, 214Pb, 214Bi, 214Po) and thoron (216Po, 212Pb, 212Bi, 212Po, 208Tl).
Solubility The ability or tendency of one substance to blend uniformly with another, e.g., solid in liquid, liquid in liquid, gas in liquid, gas in gas. Solids vary from 0% to 100% in their degree of solubility in liquids depending on the chemical nature of the substances.
Sorption A surface phenomenon that may be either absorption, adsorption, or a combination of the two. The term is often used when the specific mechanism is not known.
Speciation Determination of the precise chemical form of a substance present in a solid material, in a liquid, or in a gas.
Standard A documented method or specification to which activities should conform.
Structure Anything that is constructed.
Structures include buildings, towers, pipelines, structures for transport/communication infrastructure (roads, overpasses, tunnels, parkings), any component and part of a structure.
T
Traceability The ability to refer to a primary standard by an unbroken chain of comparisons.
TS Technical specification.
U
Uncertainty (of measurement) A parameter associated with the result of a measurement, that characterizes the dispersion of the values that could reasonably be attributed to the measurand.
W
Waste A material for which no further use is foreseen
Working level (WL) Any combination of short-lived radon decay products in 1 L of air that will result in the ultimate emission of 130,000 MeV of potential alpha energy. (Old definition: total alpha energy released from the short-lived decay products in equilibrium with 100 pCi of 222Rn per liter of air.)
Working level month (WLM) 170 h exposure to 1 WL.