
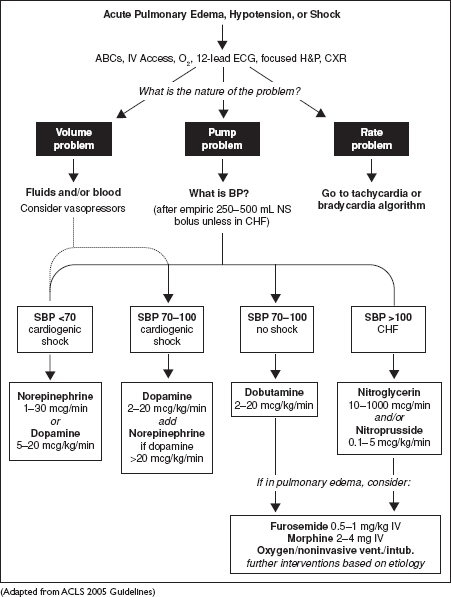
Figure Appendix-1 ACLS pulmonary edema, hypotension or shock algorithm

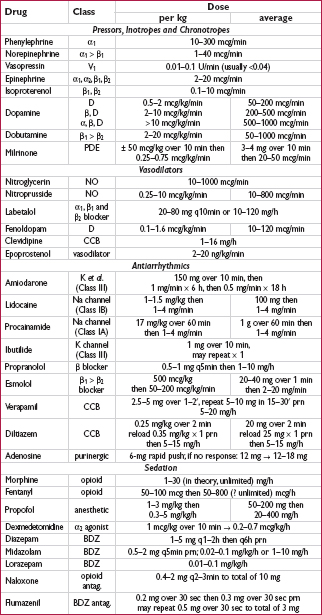
Oxygen consumption (L/min) = CO (L/min) × arteriovenous (AV) oxygen difference
CO = oxygen consumption/AV oxygen difference
Oxygen consumption must be measured (can estimate w/ 125 mL/min/m2 but inaccurate)
AV oxygen difference = Hb (g/dL) × 10 (dL/L) × 1.36 (mL O2/g of Hb) × (SaO2–SMVO2)
SaO2 is measured in any arterial sample (usually 93–98%)
SMVO2 (mixed venous O2) is measured in RA, RV or PA (assuming no shunt) (nl ∼75%)

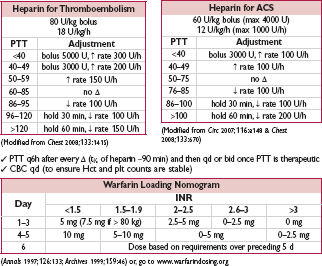
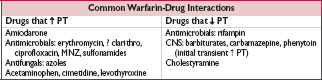
• Indications: when failure to anticoagulate carries ↑ risk of morbidity or mortality (eg, DVT/PE, intracardiac thrombus)
• Rationale: (1) Half-life of factor VII (3–6 h) is shorter than half-life of factor II (60–72 h);
∴ warfarin can elevate PT before achieving a true antithrombotic state
(2) Protein C also has half-life less than that of factor II;
∴ theoretical concern of hypercoagulable state before antithrombotic state
• Method: (1) Therapeutic PTT is achieved using heparin
(2) Warfarin therapy is initiated
(3) Heparin continued until INR therapeutic for ≥2 d and ≥4–5 d of warfarin (roughly corresponds to ∼2 half-lives of factor II or a reduction to ∼25%)