Data is the new currency or oil. It can be found in your shopping pattern, emails, online banking, food ordering and in many places besides. Every year, we continue to encounter issues such as cyber threats, illegal surveillance (Wikileaks), and anti-privacy advocacy that targets these areas. In a connected world like the internet, security and privacy is a must when it comes to protecting data. As an end user, it's impossible to have an end-to-end visibility on public internet infrastructure that we use day to day. Fortunately, we have virtual private networks (VPN), a type of shield which forms a secure tunnel between two or more VPN supported devices. VPN helps to protect data traffic from snooping or man-in-the-middle attacks. However, to pick the best VPN service out there, we first need to understand the different VPN types and their use cases.
There are many use cases for VPNs. One very common reason why a VPN might be used for secure communication for mobile users or between branches and head offices is because it provides secure access for corporate IT resources:

Your local ISP acts as a gateway for internet access and your activity can be tracked via this. In the same way as when you attempt to access any resources, the resource provider can also track your location based on your IP address. This is going to be another use case where you hide your identity by using third-party VPNs. In the following diagram, you can see that a user sitting in Manila can connect to a global resource, that might be blocked for the local ISP in Manila:
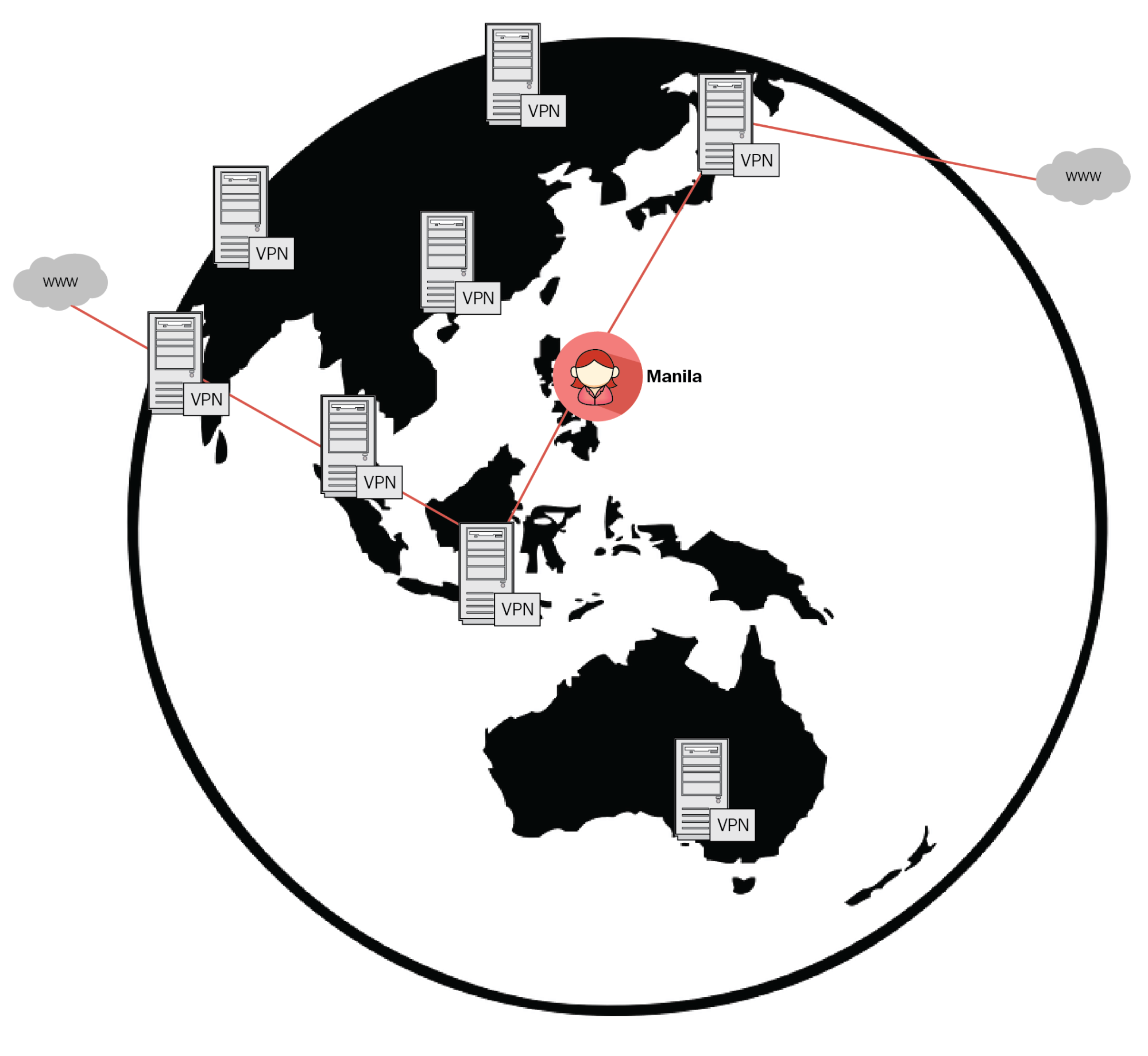
These VPNs are available either in app format or are inbuilt within the browser. Some organizations also provide full tunnel capabilities. Here, once you are connected to a corporate VPN, your exit point to the internet would be your organization's internet gateway.