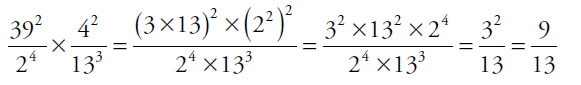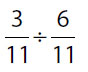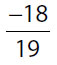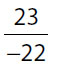Fractions and Decimals
For questions in the Quantitative Comparison format (“Quantity A” and “Quantity B” given), the answer choices are always as follows:
(A) Quantity A is greater.
(B) Quantity B is greater.
(C) The two quantities are equal.
(D) The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
For questions followed by a numeric entry box  , you are to enter your own answer in the box. For questions followed by a fraction-style numeric entry box
, you are to enter your own answer in the box. For questions followed by a fraction-style numeric entry box  , you are to enter your answer in the form of a fraction. You are not required to reduce fractions. For example, if the answer is
, you are to enter your answer in the form of a fraction. You are not required to reduce fractions. For example, if the answer is  , you may enter
, you may enter 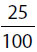 or any equivalent fraction.
or any equivalent fraction.
All numbers used are real numbers. All figures are assumed to lie in a plane unless otherwise indicated. Geometric figures are not necessarily drawn to scale. You should assume, however, that lines that appear to be straight are actually straight, points on a line are in the order shown, and all geometric objects are in the relative positions shown. Coordinate systems, such as xy-planes and number lines, as well as graphical data presentations, such as bar charts, circle graphs, and line graphs, are drawn to scale. A symbol that appears more than once in a question has the same meaning throughout the question.
1.What is the value of 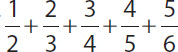 ?
?
Give your answer as a fraction.

| 2. | Quantity A |
Quantity B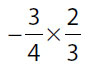 |
3.At a convention of monsters, 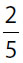 have no horns,
have no horns, 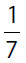 have one horn,
have one horn, 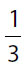 have two horns, and the remaining 26 have three or more horns. How many monsters are attending the convention?
have two horns, and the remaining 26 have three or more horns. How many monsters are attending the convention?
(A)100
(B)130
(C)180
(D)210
(E)260
4.Devora spends  of her money on a textbook, and then buys a notebook that costs
of her money on a textbook, and then buys a notebook that costs  the price of the textbook. If there is no sales tax on the items and she makes no other purchases, what fraction of her original money does Devora have remaining?
the price of the textbook. If there is no sales tax on the items and she makes no other purchases, what fraction of her original money does Devora have remaining?
Give your answer as a fraction.

5.Which of the following are equal to 0.003482?
Indicate all such values.
- –0.003482 × 10–1
- 0.3482 × 10–2
- 34.82 × 104
- 34.82 × 10–4
- 3,482 × 10–6
6.Which of the following are equal to 12.12 × 10–3?
Indicate all such values.
- –1.21 × 103
- 0.012
- 0.00001212 × 103
- 0.01212 × 103
7.5 is how many fifths of 10?
(A) 2.5
(B) 5
(C)10
(D)20
(E)50
| 8. | Quantity A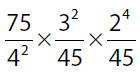 |
Quantity B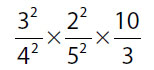 |
9.In a certain class,  of all the students are girls and
of all the students are girls and  of all the students are girls who take Spanish. What fraction of the girls take Spanish?
of all the students are girls who take Spanish. What fraction of the girls take Spanish?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
10.  of all the cars on a certain auto lot are red, and
of all the cars on a certain auto lot are red, and 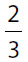 of all the red cars are convertibles. What fraction of all the cars are NOT red convertibles?
of all the red cars are convertibles. What fraction of all the cars are NOT red convertibles?
Give your answer as a fraction.

11. Two identical pies were cut into a total of 16 equal pieces. If one of the resulting pieces was then split equally among three people, what fraction of a pie did each person receive?
(A)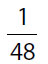
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)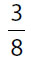
xy ≠ 0
| 12. | Quantity A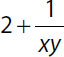 |
Quantity B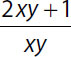 |
| 13. | Quantity A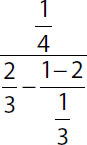 |
Quantity B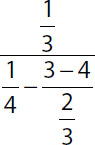 |
At store A, 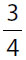 of the apples are red. At store B, which has twice as many apples, 0.375 of them are red.
of the apples are red. At store B, which has twice as many apples, 0.375 of them are red.
| 14. | Quantity A The number of red apples at store A |
Quantity B The number of red apples at store B |
15. A pot of soup was divided equally into two bowls. If Manuel ate  of one of the bowls of soup and
of one of the bowls of soup and 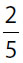 of the other bowl of soup, what fraction of the entire pot of soup did Manuel eat?
of the other bowl of soup, what fraction of the entire pot of soup did Manuel eat?
Give your answer as a fraction.

16. Which of the following is equal to 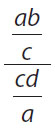 for all non-zero values of a, b, c, and d?
for all non-zero values of a, b, c, and d?
(A)ac
(B)bd
(C)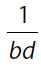
(D)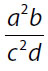
(E)
17. Which of the following is equal to 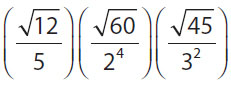 ?
?
(A)
(B)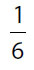
(C)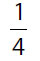
(D)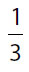
(E)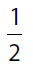
18. Which of the following is equal to  ?
?
(A)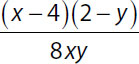
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)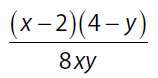
x is a digit in the decimal 12.15x9, which, if rounded to the nearest hundredth, would equal 12.16.
| 19. | Quantity A x |
Quantity B 4 |
20. What is the value of  ?
?
Give your answer as a fraction.

21. In a decimal number, a bar over one or more consecutive digits means that the pattern of digits under the bar repeats without end. What fraction is equal to 7.583?
Give your answer as a fraction.

| 22. | Quantity A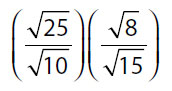 |
Quantity B |
23. What is the value of  ?
?
(A)
(B)
(C)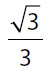
(D)
(E)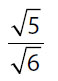
24. In a certain box of cookies,  of all the cookies have nuts and
of all the cookies have nuts and 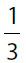 of all the cookies have both nuts and fruit. What fraction of all the cookies in the box have nuts but no fruit?
of all the cookies have both nuts and fruit. What fraction of all the cookies in the box have nuts but no fruit?
(A)
(B)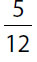
(C)
(D)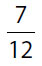
(E)
25.  of all the juniors and
of all the juniors and 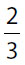 of all the seniors of a certain school are going on a trip. If there are
of all the seniors of a certain school are going on a trip. If there are 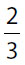 as many juniors as seniors, what fraction of the junior and senior students are not going on the trip?
as many juniors as seniors, what fraction of the junior and senior students are not going on the trip?
(A)
(B)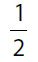
(C)
(D)
(E)
26.  of the women and
of the women and  of the men in a group speak Spanish. If there are 40% as many men as women in the group, what fraction of the group speaks Spanish?
of the men in a group speak Spanish. If there are 40% as many men as women in the group, what fraction of the group speaks Spanish?
Give your answer as a fraction.

abcd ≠ 0
| 27. | Quantity A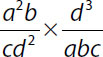 |
Quantity B |
m ≠ 0
| 28. | Quantity A |
Quantity B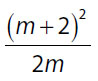 |
29. Which two of the following numbers, when added together, yield a sum between 1 and 2?
Indicate two such numbers.
30. Which three of the following numbers, when multiplied by each other, yield a product less than –1?
Indicate three such numbers.
31. What is the value of (3 –  )2 + (3 +
)2 + (3 +  )2 ?
)2 ?
(A)
(B)
(C)36
(D)
(E)162
32. If  = 1, what is the value of m?
= 1, what is the value of m?
(A)–2
(B)–1
(C) 0
(D) 1
(E) 2
rs = 
| 33. | Quantity A |
Quantity B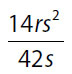 |
| 34. | Quantity A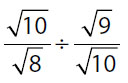 |
Quantity B |
35. Which of the following fractions has the greatest value?
(A)
(B)
(C)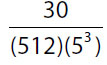
(D)
(E)
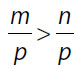
| 36. | Quantity A m |
Quantity B n |
37. If 2x ≠ y and 5x ≠ 4y, then what is the value of  ?
?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)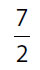
(E)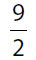
38. What is the value of  ?
?
(A)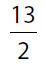
(B)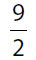
(C)
(D)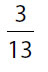
(E)
Fractions and Decimals Answers
1.  (or any equivalent fraction). Sum the fractions by finding a common denominator, which is a multiple of 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. The smallest number that works is 60.
(or any equivalent fraction). Sum the fractions by finding a common denominator, which is a multiple of 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. The smallest number that works is 60.

2. (A). In Quantity A, use a common denominator to add:

In Quantity B, multiply straight across both top and bottom (common denominators are only needed for addition and subtraction). Cancel where possible:

Quantity A is greater. (Be careful with negatives! The closer to 0 a negative is, the greater it is.)
3. (D). This is a common GRE setup—the question presents several fractions and one actual number. First find what fraction of the whole that number represents, then solve for the total (call the total m). Notice that all the denominators are primes, so they don’t share any factors. Therefore, the common denominator is their product: 5 × 7 × 3 = 105.

The remaining 26 monsters represent 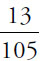 of the total monsters at the convention:
of the total monsters at the convention:
| 26 | = | 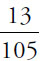 m m |
 × 26 × 26 |
= | m |
| 105 × 2 | = | m |
| 210 | = | m |
4. 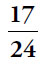 (or any equivalent fraction). The textbook costs
(or any equivalent fraction). The textbook costs  of Devora’s money. The notebook costs
of Devora’s money. The notebook costs  of that amount, or
of that amount, or  of Devora’s money. Thus, Devora has spent
of Devora’s money. Thus, Devora has spent  of her money. Subtract from 1 to get the fraction she has left:
of her money. Subtract from 1 to get the fraction she has left: 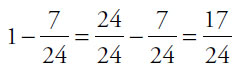 .
.
Alternatively, pick a value for Devora’s money. (Look at the denominators in the problem—4 and 6—and pick a value that both numbers go into evenly.) For instance, say Devora has $120. She would spend  , or $30, on the textbook. She would spend
, or $30, on the textbook. She would spend 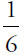 of that amount, or $5, on the notebook. She would have spent $35 and would have $85 left, and thus
of that amount, or $5, on the notebook. She would have spent $35 and would have $85 left, and thus  of her money left. Reduce
of her money left. Reduce  to get
to get 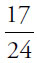 , or enter
, or enter  in the boxes.
in the boxes.
5. 0.3482 × 10–2, 34.82 × 10–4, and 3,482 × 10–6 only. Note that the first answer is negative, so it cannot be correct. For the second answer, move the decimal 2 places to the left: 0.3482 × 10–2 = 0.003482 (correct). For the third answer, move the decimal 4 places to the right (since the exponent is positive)—this move makes the number much greater and cannot be correct. For the fourth answer, move the decimal 4 places to the left: 34.82 × 10–4 = 0.003482 (correct). For the fifth answer, move the decimal 6 places to the left: 3,482 × 10–6 = 0.003482 (correct).
6. 0.00001212 × 103 only. First, simplify 12.12 × 10–3 = 0.01212. Now, test which answers are equal to this value. The first answer is negative, so it cannot be correct. The second answer is 0.012 and is therefore incorrect (the end has been “chopped off,” so the number is not the same value). The third answer is 0.00001212 × 103 = 0.01212 and is correct. The fourth answer is 0.01212 × 103 = 12.12 and is not correct.
7. (A). Translate the words into math. If x means “how many,” then “how many fifths” is  :
:
| 5 | = |  × 10 × 10 |
| 5 | = | 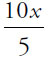 |
| 25 | = | 10x |
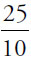 |
= | x |
| x | = | 2.5 |
8. (A). Simplify each quantity by breaking down to primes and canceling factors:
Quantity A: 
Quantity B: 
Since  , Quantity A is greater. You can compare these fractions by making a common denominator, by cross-multiplying, or by comparing the decimal equivalents 0.333 (repeating infinitely) and 0.3.
, Quantity A is greater. You can compare these fractions by making a common denominator, by cross-multiplying, or by comparing the decimal equivalents 0.333 (repeating infinitely) and 0.3.
If there are identical factors in each quantity in the same position (e.g., 32 on top or 42 on bottom), then you can save time by canceling those factors first from both quantities.
9. (D). This question is not asking for  of
of  . Rather,
. Rather,  and
and  are fractions of the same number (the number of students in the whole class). A good way to avoid this confusion is to plug in a number for the class. Pick 12, as it is divisible by both 4 and 12 (the denominators of the given fractions).
are fractions of the same number (the number of students in the whole class). A good way to avoid this confusion is to plug in a number for the class. Pick 12, as it is divisible by both 4 and 12 (the denominators of the given fractions).
Class = 12
Girls = 5
Girls who take Spanish = 3 (which is  of all the students in the class)
of all the students in the class)
The question asks for the number of girls who take Spanish over the number of girls. Thus, the answer is 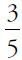 .
.
10.  (or any equivalent fraction). If
(or any equivalent fraction). If 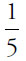 of all the cars are red, and
of all the cars are red, and  of those are convertibles, then the fraction of all the cars that are red convertibles =
of those are convertibles, then the fraction of all the cars that are red convertibles = 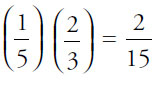 . Since you want all of the cars that are NOT red convertibles, subtract
. Since you want all of the cars that are NOT red convertibles, subtract 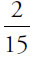 from 1 to get
from 1 to get  .
.
11. (B). If two pies are cut into 16 parts, each pie is cut into eighths. Thus,  of a pie is was divided among three people. “One-third of one-eighth” =
of a pie is was divided among three people. “One-third of one-eighth” = 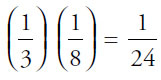 .
.
12. (C). Transform Quantity B by splitting the numerator:
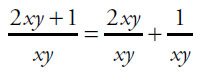
Next, cancel the common factor xy from top and bottom of the first fraction:
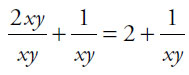 , which is the same as Quantity A.
, which is the same as Quantity A.
Alternatively, you can transform Quantity A by turning 2 into a fraction with the same denominator (xy) as the second term.
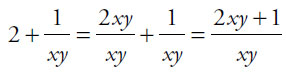 , which is the same as Quantity B. Thus, the quantities are equal.
, which is the same as Quantity B. Thus, the quantities are equal.
13. (B). Simplify each quantity from the inside out.
Quantity A: 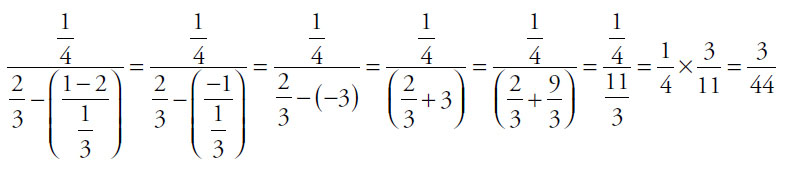
Quantity B: 
Since Quantity B has a greater numerator and a smaller denominator, it is greater than Quantity A. This rule works for any positive fractions. You could also use the calculator to compute the decimal equivalents.
14. (C). Whether you choose fractions or decimals, put  and 0.375 in the same form to more easily compare. Either way, 0.75 is double 0.375 (or
and 0.375 in the same form to more easily compare. Either way, 0.75 is double 0.375 (or  is double
is double  ). Since store B has twice as many apples, 0.375 of store B’s apples is the same number as 0.75 of store A’s apples.
). Since store B has twice as many apples, 0.375 of store B’s apples is the same number as 0.75 of store A’s apples.
Alternatively, pick numbers such that store B has twice as many apples. If store A has 4 apples and store B has 8 apples, then store A would have  (4) = 3 red apples and store B would have (0.375)(8) = 3 red apples. The two quantities are equal.
(4) = 3 red apples and store B would have (0.375)(8) = 3 red apples. The two quantities are equal.
15.  (or any equivalent fraction). Manuel ate
(or any equivalent fraction). Manuel ate  of one-half of the entire pot of soup and then
of one-half of the entire pot of soup and then 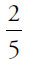 of the other half of the entire pot of soup. As math:
of the other half of the entire pot of soup. As math:
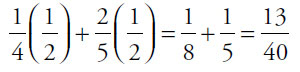
Alternatively, pick numbers, ideally a large number with many factors. For example, say there are 120 ounces of soup. Each bowl would then have 60 ounces. Manuel ate  of one bowl (15 ounces) and
of one bowl (15 ounces) and 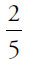 of the other bowl (24 ounces). In total, he ate 39 ounces out of 120. While
of the other bowl (24 ounces). In total, he ate 39 ounces out of 120. While  would be counted as correct, reducing
would be counted as correct, reducing  (by dividing both numerator and denominator by 3) yields
(by dividing both numerator and denominator by 3) yields  , the answer reached via the other method above.
, the answer reached via the other method above.
16. (D). To divide by a fraction, multiply by its reciprocal:

17. (C). Pull squares out of the square roots and cancel common factors:
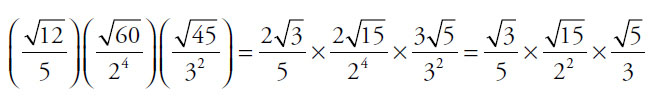
Since  ,
,
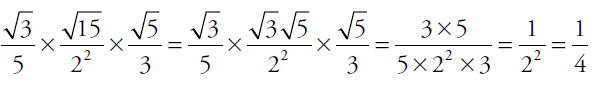
Alternatively, in the calculator multiply 12 × 60 × 45 = 32,400, then take the square root to get 180 for the numerator. The denominator is 5 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 = 720. Finally, calculate  = 0.25, which is
= 0.25, which is  .
.
18. (C). Combine the four fractions by finding a common denominator (8xy, which is also suggested by the answer choices):

Now the key is to factor the top expression correctly:
xy – 4y – 2x + 8 = (x – 4)(y – 2)
It is a good idea to FOIL the expression on the right to make sure it matches the left-hand side. Or, FOIL the numerators of the choices to see which matches the distributed form of the numerator above.
Finally,  .
.
19. (A). Since the decimal rounds to 12.16, the thousandths digit x must be 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9. All of these possibilities are greater than 4.
20. 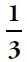 (or any equivalent fraction). One option is to punch the whole numerator and the whole denominator into the calculator and submit each product. If you’re very careful, that will work. However, it might be wise to try canceling some common factors out of the fraction, to save time and to avoid errors. It’s fine to switch to the calculator whenever the cancelations aren’t obvious:
(or any equivalent fraction). One option is to punch the whole numerator and the whole denominator into the calculator and submit each product. If you’re very careful, that will work. However, it might be wise to try canceling some common factors out of the fraction, to save time and to avoid errors. It’s fine to switch to the calculator whenever the cancelations aren’t obvious:

21.  (or any equivalent fraction). First, turn the decimal into a sum of two pieces, to separate the repeating portion:
(or any equivalent fraction). First, turn the decimal into a sum of two pieces, to separate the repeating portion:
7.583 = 7.58 + 0.003
Deal with each piece in turn. Like any other terminating decimal, 7.58 can be written as a fraction with a power of 10 in the denominator:

The repeating portion is similar to 0.3 = 0.3333 … =
So 0.003 is just  , moved by a couple of decimal places: 0.003 = (0.3)(0.01) =
, moved by a couple of decimal places: 0.003 = (0.3)(0.01) =  .
.
Finally, write the original decimal as a sum of fractions, and then combine those fractions:
7.583 = 7.58 + 0.003 = 
Enter  unreduced, or you can reduce it to
unreduced, or you can reduce it to  .
.
22. (A). Both quantities are positive square roots, so just compare the underlying numbers.
Quantity A:  = 1.33
= 1.33
Quantity B: 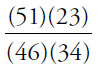 = 0.75
= 0.75
The square root of 1.33 (or  ) is greater than the square root of 0.75 (or
) is greater than the square root of 0.75 (or 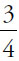 ).
).
23. (B). The square root of a fraction is the square root of the top over the square root of the bottom:
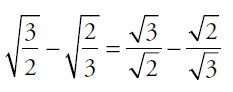
Then make a common denominator:  .
.

24. (B). Since 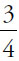 of the cookies have nuts and
of the cookies have nuts and  of the cookies also have fruit, subtract
of the cookies also have fruit, subtract 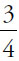 from
from  to get all the cookies with nuts but no fruit:
to get all the cookies with nuts but no fruit:

Alternatively, pick numbers. Since you will be dividing by 4 and 3, pick a number divisible by 4 and 3. If there are 12 cookies, then 9 have nuts and 4 of them have nuts and fruit, so 5—and thus  of the total—would have nuts but no fruit.
of the total—would have nuts but no fruit.
25. (B). If a question refers to fractions of different numbers that are also related by a fraction, try plugging in numbers. Since there are  as many juniors as seniors, some convenient numbers are:
as many juniors as seniors, some convenient numbers are:
Juniors = 20
Seniors = 30
Juniors going on trip =  (20) = 5
(20) = 5
Seniors going on trip = 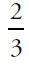 (30) = 20
(30) = 20
Out of 50 total students, 25 are going on the trip, so 25 are NOT going on the trip. The answer is  =
=  .
.
26. 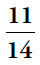 (or any equivalent fraction). If a question refers to fractions of different numbers that are also related by a fraction or percent, try plugging in numbers. Since there are 40% as many men as women, some convenient numbers are:
(or any equivalent fraction). If a question refers to fractions of different numbers that are also related by a fraction or percent, try plugging in numbers. Since there are 40% as many men as women, some convenient numbers are:
Men = 40
Women = 100
Women who speak Spanish = 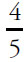 (100) = 80
(100) = 80
Men who speak Spanish =  (40) = 30
(40) = 30
The group has 140 total people and 110 Spanish speakers. The answer is  (you are not required to reduce, as long as your answer is correct and fits in the box).
(you are not required to reduce, as long as your answer is correct and fits in the box).
27. (D). Cancel factors on top and bottom of each product:
Quantity A: 
Quantity B: 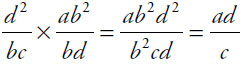
The two quantities differ in the denominators: Quantity A has c2, while Quantity B has c. It cannot be determined which quantity is greater, because for some values (e.g., c = 2) c2 is greater than c, and for others (e.g., c = 0.5) c2 is less than c.
28. (C). Multiply out Quantity A by FOILing.

Make a common denominator (2m) to sum these terms (also, note that this makes Quantity A similar in form to Quantity B):

Since the quantities now have the same denominators and (m + 2)2 = m2 + 4m + 4, the two quantities are equal.
29.  and
and  only. To start, compute each value:
only. To start, compute each value:
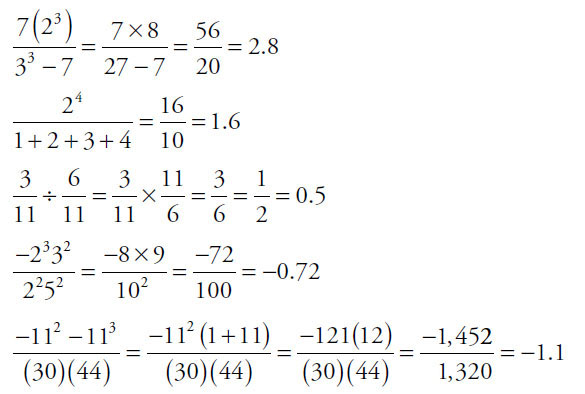
The question asks for exactly two values that sum to a number between 1 and 2.
No two of the positive numbers sum to a number between 1 and 2. So the answers must be a positive and a negative. The only two possibilities that work are 2.8 and –1.1.
30. 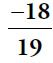 ,
, 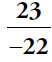 , and
, and 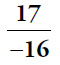 only. The product of three of the numbers must be less than –1. You can brute-force the calculation by trying all possible products, but use the relative size of the numbers to reduce the effort.
only. The product of three of the numbers must be less than –1. You can brute-force the calculation by trying all possible products, but use the relative size of the numbers to reduce the effort.
Notice that the four answer choices are all very close to –1, but some are greater than –1, and others are less than –1. To get the exact order, you can use the calculator, or you can think about the difference between each fraction and –1:
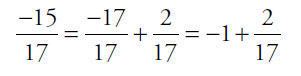
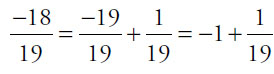 , which is less than the previous number (since
, which is less than the previous number (since  )
)

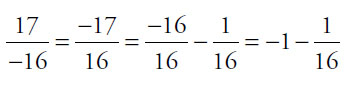 , a greater decrease from –1 than the previous number
, a greater decrease from –1 than the previous number
So the order of the original numbers relative to each other and to –1 is this:  < –1 <
< –1 < 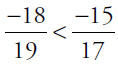 .
.
Try multiplying the three lowest numbers first, since they will produce the lowest product. Only one product of the three numbers can be less than –1 (or there would be more than one right answer), so the three numbers must be as follows, as you can check on the calculator:
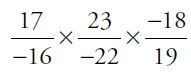 ≈ –1.052 … < –1
≈ –1.052 … < –1
31. (B). First, simplify inside the parentheses. Then, square and add:

The answer is 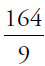 .
.
32. (D). If the left-hand side of the equation is equal to 1, then the numerator and denominator must be equal. Thus, the denominator must also be equal to 3:
 + 1 = 3
+ 1 = 3 = 2
= 2
m + 1 = 2m
1 = m
Alternatively, plug in each answer choice (into both instances of m in the original equation), and stop as soon as one of them works.
33. (B). Cancel common factors in each quantity and substitute in for rs:
Quantity A: 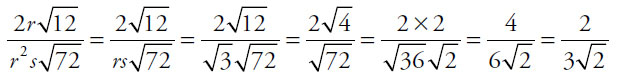
Quantity B: 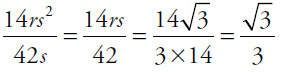
At this point, use the calculator, or compare the two quantities with an “invisible inequality”:

Since everything is positive, it is safe to cross-multiply:
2 × 3 ?? 3
Now square both sides. Since everything is positive, the invisible inequality is unaffected:
(2 × 3)2 ?? 32 × 2 × 3
36 ?? 54
Since 36 < 54, Quantity B is greater.
34. (A). To divide fractions, multiply by the reciprocal:
Quantity A: 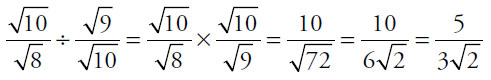
Quantity B: 
Square both quantities to get rid of the square roots:
Quantity A: 
Quantity B: 
At this point, use the calculator. Quantity A is approximately 1.389, whereas Quantity B is approximately 1.344.
35. (A). To determine which fraction is greatest, cancel common terms from all five fractions until the remaining values are small enough for the calculator. Note that every choice has at least one 5 on the bottom, so cancel 51 from all of the denominators.
Note also that every fraction has a power of 2 on the bottom, so convert 16, 32, 512, 46, and 211 to powers of 2. Since 16 = 24, 32 = 25, 512 = 29, and 46 = (22)6 = 212, the modified choices are:
(A)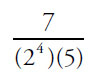
(B)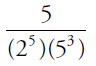
(C)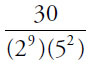
(D)
(E)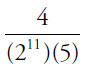
Since every choice has at least 24 on the bottom, cancel 24 from all 5 choices:
(A)
(B)
(C)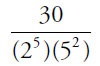
(D)
(E)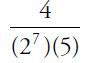
Note that the numerators also have some powers of 2 and 5 that will cancel out with the bottoms of each of the fractions. In choice (C), 30 = (2)(3)(5):
(A)
(B)
(C)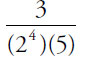
(D)
(E)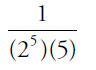
These values are now small enough for the calculator. Note that the GRE calculator does not have an exponent button—to get 28, you must multiply 2 by itself 8 times. This is why you should memorize powers of 2 up to 210, and powers of 3, 4, and 5 up to about the 4th power.
(A)1.4
(B)0.02
(C)0.0375
(D)0.01953125
(E)0.00625
Alternatively, you might notice in the previous step that only the choice (A) simplified fraction is greater than 1; in all the others, the denominator is greater than the numerator.
36. (D). Without knowing the signs of the variables, do not assume that m is greater than n. While it certainly could be (e.g., m = 4, n = 2, and p = 1), if p is negative, the reverse will be true (e.g., m = 2, n = 4, and p = –1).
37. (A). This expression is complicated, but the answer choices are just numbers, so the variables must cancel. This, and the relative lack of constraints on the variables, suggests that you can plug in values for x and y and then solve.
Try x = 2 and y = 3. For these numbers, 2x ≠ y and 5x ≠ 4y as required. Any other numbers that also follow those constraints would yield the same result below:

38. (E). To divide fractions, multiply by the reciprocal of the divisor:

Now break down to primes and cancel common factors: