CHAPTER 7V
BLOOD SYSTEM | CELLULAR SYSTEM
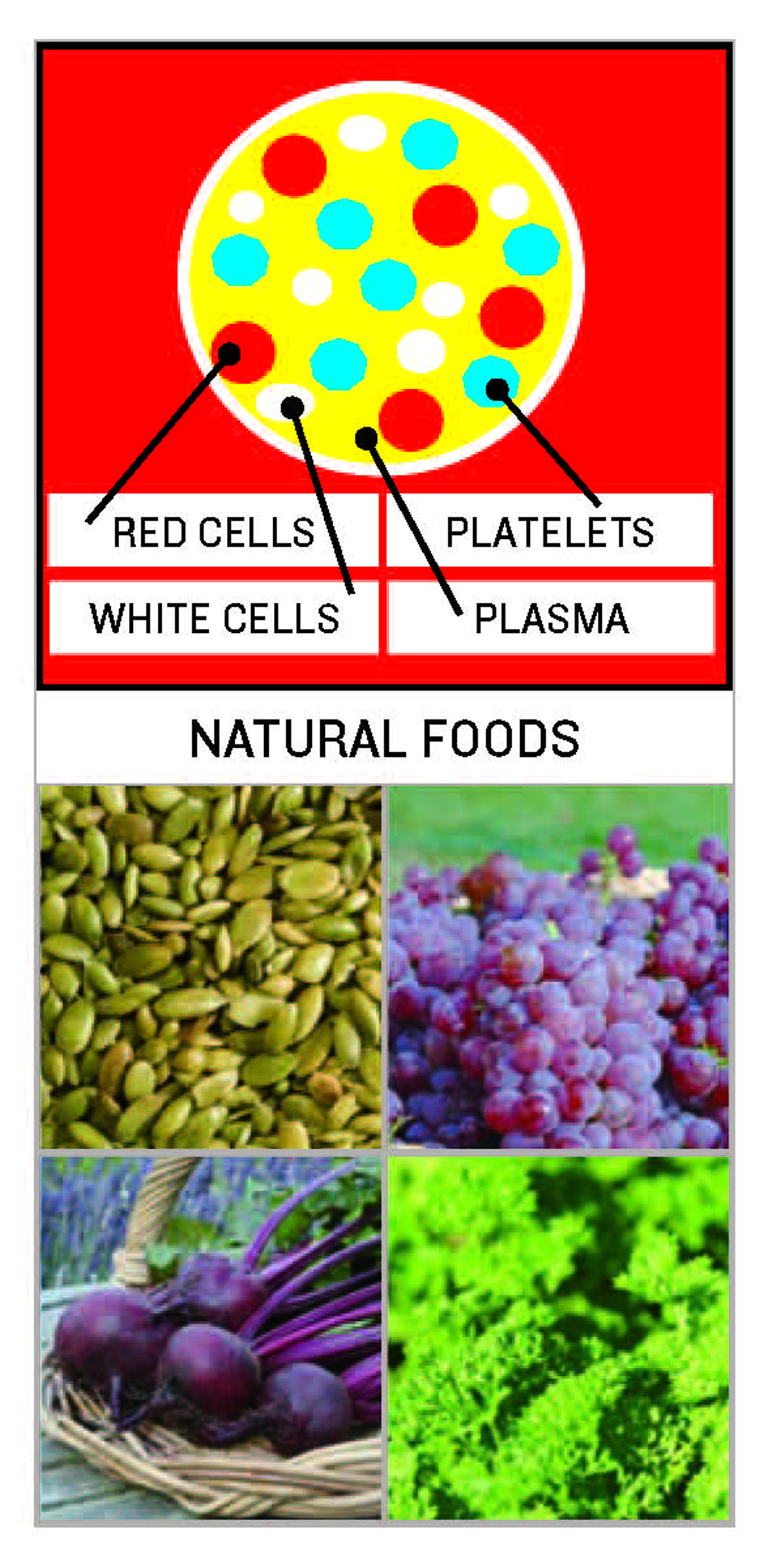
9 BLOOD SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The blood system is the carrier of all nutrients in the form of oxygen, glucose, amino acids, minerals, water, vitamins and enzymes. Blood is our lifeline and over a period of 2 months the entire body’s blood cells are renewed.
The main functions of blood are to:
Blood is composed of 55% plasma, 45% cells. Plasma contains 90% water and 10% solids in the form of minerals and protein. Cells contain 95% red cells, 3% platelets and 2% white cells. Blood contains 16 mineral elements and the average person holds 6 litres of precious blood.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Potassium eliminates blood impurities, reduces high blood pressure, improves blood circulation.
Sodium keeps minerals soluble within the bloodstream and controls blood pressure.
Sulphur provides oxygen to the blood, required for the development of blood haemoglobin.
Chlorine purifies the blood and regulates blood pressure.
Fluorine increases the number of blood cells.
Iron is vital for blood haemoglobin production.
Manganese assists in the formation of red blood cells with iron and copper.
Cobalt maintains red blood cells. Other essential nutrients for the blood system are chromium, vanadium, and vitamins C, F, K, P, and B complex.
10 CELLULAR SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The diagram on the right shows the six main types of cells. A cell is defined as a small mass of protoplasm containing a nucleus with the following abilities:
Protoplasm consists of the following substances: organic compounds as protein, fatty substances, carbohydrates, inorganic salts and water
Within the structure of every living cell there is a code stored in the DNA molecule with the unique ability to issue instructions for the reproduction of identical new cells via the RNA (ribonucleic acid) at the outer boundary of cells. There is a constant flow of nutrients within each cell that occurs millions of times a day within the body. All cells require a combination of glucose, minerals, vitamins, oxygen and water.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Sodium regulates fluids from either side of cell walls.
Sulphur cell respiration, new cells.
Chlorine cell membranes.
Fluorine increases red blood cells.
Iron nucleus of every cell and transports oxygen to muscle cells.
Magnesium activates protein and carbohydrates within cells.
Silicon vital for cell growth with the hair, skin and eyes, promotes red blood cell and bone development.
Cobalt maintains body cells.
Chromium movement of glucose (blood sugar) into cells.
Vitamin A skin, digestive, respiratory, bone and urinary cells; also transfer of genetic material.
Vitamin C vital for skin cells.
Vitamin E promotes cell life and cell respiration.
Vitamins F, K and B complex.

NOTE: d.v. refers to the daily value for women 25–50 years, refer to RDI chart for adult male and child values.
11 ELIMINATION SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
There are two main parts to the elimination system: the digestive system and excretory fluids system. After the process of digestion within the stomach and small intestine, the remaining food chyme passes into the large intestine. This is approx.1.5m long and has five main parts: the caecum, the transverse colon, descending colon, pelvic colon and the rectum. Digestive elimination requires a fair portion of roughage to function efficiently. Such foods as fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains are ideal foods to assist the elimination system.

The excretory fluids system includes the kidneys, skin, liver and lungs. The kidneys remove excess urea (protein) via the urine. The skin removes excess moisture. The liver removes nitrogen, old red blood cells and toxic substances. The lungs expel carbon dioxide and water. Mucus is produced within the body to expel toxins from the respiratory system and from the digestive system. Fasting is beneficial.

NATURAL FOODS
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Sodium eliminates carbonic acid from the lungs and waste inorganic elements from the body.
Chlorine removes toxins from the liver, blood and respiratory system.
Sulphur eliminates toxins from digestion and the skin and blood.
Iron in combination with copper eliminates waste from the blood.
Silicon cleanses the skin, removes uric acid from the blood.
Potassium assists the colon and the kidneys and skin to remove waste.
Magnesium removes kidney stones.
Manganese removes excess sugar from the blood, via the urine.
Phosphorus assists the kidneys and the elimination of excess acids.
Choline eliminates excess fats.
12 GROWTH SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The growth system has numerous main stages:


NATURAL FOODS
1. A single cell to 3 months when all cells are formed. 2. In the first year the baby will triple in weight and double in height and brain size. 3. From 2–10 years, the child grows in height, on average 7.5cm per year. 4. From 11–20 years the rapid growth stage occurs, with approx.8cm height increase in boys in the first few years, with a height increase for girls of approx.6cm per year during adolescence.
The pituitary gland is the most important controller of growth. It produces a hormone, somatotropin, for body growth and other hormones to stimulate the growth of the thyroid gland, thyrotrophic hormone, thereby increasing the body’s metabolism rate. The adrenal glands and the sex glands are stimulated by various hormones produced by the pituitary gland. The thymus gland functions from birth till approx.the age of 7, for development of the reproductive and immune systems.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Calcium is the main growth mineral;, however, it requires numerous other minerals and vitamins to function efficiently. Calcium is required for growth of bones, skin, teeth, blood and hormone development.
Phosphorus is required in a two and a half parts calcium to one part phosphorus ratio for growth of bones and nerves.
Potassium for muscle growth.
Iodine is essential for the thyroid gland which controls both body and mental growth.
Fluorine assists strong bone growth.
Magnesium assists the development of strong bones, teeth and nerves.
Iron for blood haemoglobin growth. Other essential factors are the daily supply of protein, vitamin A and sunlight.
NOTE: All amounts in this book are measured in milligrams (mg) per 100 grams, unless stated otherwise.
13 IMMUNE SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The immune system is constantly on the alert for any invading germs, bacteria, viruses and infections. The first line of defence are the white cells of the blood, also known as phagocytes, which multiply rapidly to destroy the infection, bacteria or virus. The second line of defence comes from the lymphatic system which produces lymphocyte cells. These produce antibodies that attempt to prevent bacteria and viruses from reproducing. The phagocytes ingest the captured bacteria and dispose of them. The spleen plays a major role: it produces antibodies, lymphocytes and destroys worn-out blood cells. The most common ways for bacteria and viruses to enter the body are through diet, water and inhaled air. The lymphatic system consists of a wide ranging network of lymph nodes in the neck, groin, armpits, digestive system and also within the spleen. The lymph nodes are like filters, collecting infections which the white cells and antibodies destroy.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Iron strengthens the immune system by replacing worn-out blood cells in combination with copper and the mineral manganese.
Potassium assists the kidneys to remove fluid waste and infections. Calcium increases the body’s ability to fight infections.
Chlorine removes toxic waste.

NATURAL FOODS
Vitamin A promotes the immune system’s ability to fight infections and increases resistance to toxins.
Sulphur prevents infections.
Vitamin C protects against toxins and infections by increasing the supply of white blood cells.
Vitamin P activates vitamin C.
Vitamin D activates all nutrients.
Vitamins B5 and B6 assist in the production of antibodies.

14 JOINT SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The joint system performs an incredible variety of movements. The three main types of joints are: fixed joints (skull bones); slightly moveable (pelvis, collarbone); and freely moveable (hands, feet, knees, spine, hip, neck, shoulders, wrist, elbows, jaw and ankles).
The most common problem with the joint system is the condition of arthritis. There are two main types of arthritis: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis causes a loss of cartilage linings around the moving joints, often caused by years of wear and tear, incomplete nutrition, insufficient rest, work under stessful conditions and excess body acidity. Rheumatoid arthritis causes the joints to become inflamed and painful, the exact cause is uncertain but conditions of prolonged emotional stress, anger and resentment may trigger the condition.
Excess intake of refined foods may cause inorganic calcium to build up around joints and replace tissues, which results in the deterioration of joint flexibility.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Sodium (celery), not table salt, keeps calcium soluble in the blood, preventing a build-up of calcium. It also reduces acidity in the blood.
Potassium helps to balance the acid– alkaline levels of the blood.
Chlorine maintains healthy joints as it purifies the blood of toxic waste.
Sulphur eliminates body toxins.
Vitamin C is essential for production of collagen and synovial fluid, plus it protects against inflammation.

NATURAL FOODS
Vitamin E repairs damaged tissues, improves circulation, cell nourishment and body flexibility.
Vitamin F repairs damaged tissues.
Vitamin S repairs damaged tissues and promotes cellular growth.
Salicylic acid in grapefruit reduces the build-up of inorganic calcium.

NOTE: d.v. refers to the daily value for women 25–50 years, refer to RDI chart for adult male and child values.
15 OPTIC SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The optic system provides the view to the world and the incredible range of colours, shapes and objects. Light enters the eyes through the cornea (lens) which focuses and passes light through the pupil. This regulates the amount of light within the iris, the coloured part of the eye.

Muscles within the eye (ciliary muscles) cause the lens to bulge or flatten and transfer light to the retina. Within the retina, millions of light receptors called cones (for colour) and rods (for black and white) build an image which is then transferred to the brain for final evaluation, via the optic nerve. The eyes are protected by the eyelid. Blinking keeps the eye moist and clean, eyebrows keep sweat from the eyes and eyelashes keep dust away from the eyes. The optic system can become strained by poor lighting or excess use of computers, television screens and excess ultraviolet sunlight. Protection of the eyes is vital to maintain good vision for many years.

NATURAL FOODS
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Vitamin A is essential for correct peripheral (side) vision, colour vision and night vision. It protects against eye infections and a prolonged deficiency can lead to blindness.
Fluorine assists the function of the iris and promotes a sparkle to the eye.
Silicon repairs damaged tissues.
Zinc is stored within the eyes and a deficiency can lead to poor sight.
Calcium assists to prevent cataracts.
Vitamin C is essential for the lens of the eyes and nourishment of eyes.
Vitamin P assists vitamin C functions.
Vitamin B2 promotes clear vision.
Vitamin B5 nourishes the eyes.
Vitamin B6 protects against eye strain and cataracts.
Choline protects from glaucoma.
16 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The reproductive system develops during puberty for boys (12–15) and girls (12–14). From birth till the age of seven, the thymus gland initiates the development of the reproductive organs. At puberty, the pituitary gland produces a hormone (GTH) which stimulates the production of the male hormone (testosterone) and the female hormone (oestrogen).

The female is born with all the eggs (ova) that are required during the reproductive years. It takes about 46 days for the male sperm to mature and millions are produced every day.
The combination of the male sperm and female egg create a transformation of life from 23 chromosomes into 46 chromosomes, producing a fertilised egg. Once pregnancy has occurred, it takes approx.37 weeks before the baby is born.
The reproductive life for the male can last for 70 to 80 years, but for the female, the onset of menopause during the late forties will be the end to the reproductive cycle.

NATURAL FOODS
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Chlorine assists in the distribution of the reproductive hormones. Iron is essential during pregnancy and menstruation.
Manganese is vital for the glands of the reproductive system and for production of milk, sex hormones, and for menstrual cycles.
Zinc is essential for the reproductive organs and protects against sterility and prostate problems.
Chromium assists cell growth.
Selenium enhances vitamin E.
Vitamin E is the life vitamin; it is essential for cell division at conception and protects against sterility, miscarriage and premature birth.
Vitamin A is required for the transfer of hereditary characteristics.
B complex vitamins are vital, refer to section entitled as VITAMIN B1 – Thiamine.
NOTE: All amounts in this book are measured in milligrams (mg) per 100 grams, unless stated otherwise.
17 SKIN SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The skin supports a number of important functions by providing a protective layer to the body which keeps out bacteria, water and sunlight. The skin has sensitivity to heat, cold, pain and pressure, thereby providing a warning signal and temperature gauge. The outer layer of skin (epidermis) contains no blood vessels and is in fact dead skin. The next layer (dermis) is living skin and consists of fibrous and connective tissues, sweat glands, nerve fibres, oil glands (sebaceous) and blood vessels. The sebaceous glands produce sebum which keeps the skin supple and the hair oiled. The body has approx.3 million sweat glands which balance body temperature via sweating (pores open) which cools the body, and when cold, the sweat glands contract due to the blood vessels and muscles contracting. Vitamin D is the only nutrient that is available without food intake, as the skin surface via a substance called ergosterol can absorb vitamin D and transform it into a useable form within the body.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Phosphorus is part of every skin cell and it is vital for skin repair.
Sulphur cleanses the skin.
Chlorine rejuvenates the skin.
Fluorine preserves a healthy skin and hair condition.

NATURAL FOODS
Silicon eliminates toxins from the dermis layer, repairs damaged skin and removes dead skin.
Copper is required for skin and hair pigment.
Iron promotes a healthy complexion.
Selenium preserves skin elasticity and assists the action of vitamin E.
Vitamin E assists in the growth and repair of skin.
Vitamins C, P and F help to develop collagen.
Vitamin E promotes healthy skin life, essential for healing of skin tissues.

B complex vitamins B2, B3, B5 and PABA.
18 URINARY SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The urinary system filters and eliminates waste liquids. The kidneys, a pair of highly efficient filters, cleanse approx.1 litre of blood per minute (adults). Blood enters the kidneys via the renal artery which transfers blood via millions of capillaries (glomerulus) under high pressure into a capsule (Bowman’s). Red and white cells, fat and protein molecules and platelets are too large to pass into the Bowman’s capsule; they bypass and re-enter the bloodstream via the renal vein.
Plasma containing water, amino acids, glucose, salts and urea can pass into the capsule and then through the long system of tubes (tubule), the next filtration stage of the kidneys. Nearly 99% of the water and all the nutrients are re-absorbed into the bloodstream. The remaining substances are mainly water (96%); solids (2%), chlorides, phosphates, sulphates and oxalates; and urea (2%), the end product of protein digestion. All these substances plus toxins and some drugs are passed from the kidneys via the urine.
BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Potassium cleanses the kidneys, regulates the body’s water balance.
Magnesium maintains minerals in a soluble state, preventing kidney stones.

NATURAL FOODS
Sodium also regulates the body’s water balance with potassium.
Manganese for the formation of urea.
Vitamin A protects against inflammation of the prostate gland and kidney stones.
Vitamin B6 protects against kidney stone formation.
Choline for healthy kidneys.
Vitamin C protects against inflammation of the urinary system caused by phosphatic crystals, as it can dissolve the crystals.
Vitamin E stimulates the elimination of urine and may benefit reduction of oedema.

NOTE: d.v. refers to the daily value for women 25–50 years, refer to RDI chart for adult male and child values.
19 BRAIN SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The brain is the control centre for actions, reactions and sensations. The brain has two main parts: the higher centre and the lower centre. The cortex or cerebral hemisphere is the main part of the brain (80%); it consists of grey matter, or 10 million nerve cells, the centre of thoughts, intelligence, memory, speech, hearing, vision and the direction of physical actions. The lower centre (cerebellum) controls unconscious actions such as balance, posture and movement. The brain stem controls respiration, heart rate, blood vessel size, swallowing, production of saliva and digestive enzymes. Also within the brain are three main glands. The pituitary produces growth hormones, sex hormones, milk hormones and, as the ‘master gland’, controls other glands: thyroid, adrenal, pancreas and sex glands. The pineal gland is the spiritual centre of the brain. The thalamus gland is responsible for feelings of pain. The hypothalamus gland regulates body temperature, blood, water and salt balance.

NATURAL FOODS

BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Phosphorus transfers nerve impulses and is essential for brain function.
Magnesium is required for memory, nourishment and regulating the white nerve fibres of the brain and spinal cord and for steady nerves.
Manganese nourishes the nerves and brain and promotes memory.
Iodine is essential for speech and mental functioning and during pregnancy it promotes mental and physical development of the child.
Bromine protects against mental depression and emotional stress.
Vitamin T promotes a good memory and concentration.
Vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, B12, B15 and folic acid promote memory, concentration, mental stability, sleep and emotional stability.
20 REPAIR SYSTEM
MAIN BODY FUNCTION
The repair system is constantly working to rebuild damaged liver cells, cuts, abrasions and the various internal organs. The body is usually able to repair when adequate time is allowed plus suitable treatment (depending on the severity of the condition), and the supply of essential healing nutrients. Generally speaking, all the body systems are in a constant state of repair and for some conditions that have developed over many years of hard living and lack of suitable nutrition, the benefit from increased nutrition, rest and proper treatment will provide relief and sometimes completely cure the condition. For children, healing occurs at a faster rate compared to adults, provided they are given a proper diet. The human body has a genuine interest and ability to repair: even if nobody else cares, your body will relish proper daily repair nutrition. Refer to the ailment charts for help on healing specific body parts. Let nature be your true healer.

NATURAL FOODS

BENEFICIAL NUTRIENTS
Calcium assists bone repair in combination with vitamins D, A and C, plus the minerals phosphorus, magnesium, fluorine and zinc.
Iron repairs the blood.
Fluorine strengthens bone repairs.
Zinc is vital for repair of burns or wounds as it combines with white cells to remove injured tissues.
Copper is essential for repair of bones, skin, muscles and nerves.
Vitamin A is essential for repair of damaged skin, tissues and bones.
Vitamin C is vital for repair of wounds, varicose veins, bruises, fractures, acne and all tissues.
Vitamin D is essential for general body repair and bone fractures.
Vitamin E is vital for skin, tissue and general repairs.
NOTE: All amounts in this book are measured in milligrams (mg) per 100 grams, unless stated otherwise.