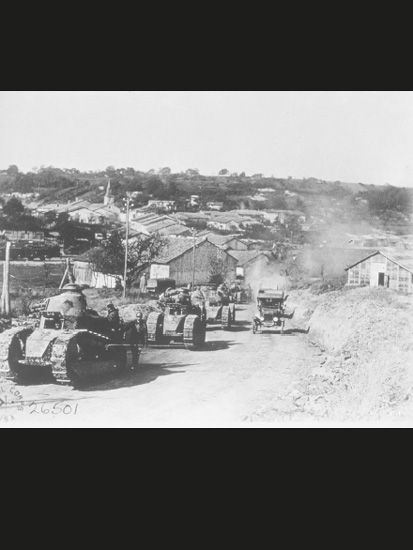

World War I began in Europe three years before the United States entered the war. These French tanks are passing through the village of Rampant, likely on their way to battle.
March 4 |
Woodrow Wilson is sworn in as the 28th president of the United States. |
June 28 |
Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire, is assassinated by a Serbian nationalist in Sarajevo, Bosnia. |
July 28 |
Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia. |
July 30 |
Russia begins mobilizing troops to fight Austria-Hungary and its ally, Germany. |
August 1 |
Germany declares war on Russia. |
August 3 |
Germany declares war on France, Russia’s ally. |
August 4 |
Germany invades neutral Belgium on its way to France; Britain declares war on Germany in response to Belgian invasion. |
August 19 |
President Wilson declares to the U.S. Senate that the United States will remain neutral as Europe fights. |
Sept. 6–12 |
First Battle of the Marne; France and Britain stop German advance into France. |
November 3 |
Britain begins to mine North Sea to prevent German trade. |
January 10 |
Woman’s Peace Party is organized, with activist Jane Addams as its head. |
February 4 |
Germany declares that the sea around Britain is a war zone, where ships can be torpedoed by German submarines. |
March |
The British navy builds up a total blockade to keep ships from delivering supplies to Germany. The blockade will prove very effective, nearly starving the German people as the war goes on. |
Italy agrees to join the war on the Allied side, largely to fight Austria-Hungary, whose land it borders. |
|
May 7 |
A German submarine, U-20, sinks the passenger ship Lusitania, with the loss of 128 American lives. |
May 10 |
Instead of declaring war on Germany, Wilson makes a speech that says the United States will not join the fight. |
May 13 |
The United States sends a diplomatic note to Germany asking the Germans to call off submarine warfare in neutral waters. |
June 9 |
The United States sends a second diplomatic note to Germany. |
July 21 |
The United States sends a firm third note to Germany, saying that it will consider any more torpedoing of ships headed to Britain “deliberately unfriendly.” |
August 10 |
The first military training camp for civilians opens in Plattsburgh, New York. |
August 19 |
A German submarine sinks the Arabic, killing two Americans. |
September 1 |
Germany pays for the damage and deaths caused when the Arabic sank. It agrees to limits on submarine warfare. |
November 1 |
The pacifist Anti-Preparedness Committee organizes. |
November 4 |
President Wilson asks Congress to enlarge the U.S. Army and Navy. |

American soldiers load a mobile railroad gun, which shoots shells that measure more than one foot in diameter. They are at the Argonne front in Baleycourt, France, in November 1918.
During the third Liberty Loan campaign, these members of “the Liberty Loan Choir” sing on the steps of City Hall in New York City. Crowds of Americans came to be entertained and to buy Liberty bonds.
February 8 |
Germany again authorizes its submarines to torpedo armed merchant ships. |
February 21 |
Battle of Verdun begins. It lasts until December 18. |
March–April |
Britain tightens its naval blockade around Germany. |
March 9 |
Pancho Villa’s Mexican troops attack Columbus, New Mexico. |
March 15 |
The United States sends 11,000 soldiers into Mexico under General John J. Pershing to capture Villa. |
March 24 |
A German submarine sinks the French ship Sussex. Some Americans are hurt. |
April 24 |
Irish nationalists rebel against British rule in Ireland in the Easter Rebellion. Britain represses the rebellion. Many Irish Americans are upset and become anti-British. |
June 3 |
Congress passes the National Defense Act, which increases the size of the U.S. Army. |
July 1 |
Battle of the Somme begins. It ends on November 18. |
July 30 |
An explosion in New Jersey destroys huge numbers of weapons waiting to be shipped to the Allies. German agents and German Americans are suspected. |
August 29 |
Congress passes the Naval Act, which calls for building new battleships and destroyers. |
Woodrow Wilson wins election to a second term as president of the United States. He wins on the slogan “He kept us out of war.” |
|
December 18 |
President Wilson calls on the warring countries on both sides to say what terms they would require for peace. |
January 10 |
The National Women’s Party, the more militant of suffragist organizations, begins picketing the White House to demand votes for women. |
January 22 |
President Wilson makes a speech calling for “peace without victory,” meaning the war could stop before one side or the other in Europe was completely destroyed. |
January 31 |
Germany declares that it will pursue unrestricted submarine warfare, making any ship, neutral or not, a target. |
February 3 |
The United States, no longer neutral, breaks off diplomatic relations with Germany. |
February 5 |
The U.S. Army leaves Mexico, having failed to capture Pancho Villa. But American troops gain some experience in warfare that will be useful when they enter World War I. |
February 28 |
President Wilson informs the American press of the Zimmermann Telegram from the Foreign Secretary of Germany to Mexico, calling on the country to ally with Germany. |
March 12 |
President Wilson orders that all U.S. merchant ships be armed with weapons. |
April 2 |
President Wilson asks Congress to declare war on Germany. |
April 6 |
Congress declares war on Germany. |
April 13 |
The federal government establishes the Committee on Public Information (CPI), headed by George Creel. |
May 10 |
British and American ships begin a convoy system; several ships—some armed—travel together to protect themselves from German submarines. |
May 12 |
President Wilson appoints General John Pershing to head the American Expeditionary Force (AEF), the army that the United States sends to France. |
President Wilson signs the Selective Service Act, calling for registration and drafting of young men. Registration begins on June 5. |
|
June 15 |
Congress passes the Espionage Act, giving the federal government censorship powers. |
June 20 |
The first Liberty loan drive is launched. |
June 26 |
The first American soldiers arrive in France. |
July 1 |
The Civil Liberties Bureau is founded. It will become the American Civil Liberties Union, which is still active today. |
July 12 |
Striking copper miners in Bisbee, Arizona, are arrested and sent by train to the desert. |
July 31 |
Battle of Passchendaele begins. It is over on November 6. |
August 23 |
Black troops attack white civilians in Houston, Texas, enraged by segregation practices. |
September 5 |
The federal government begins raids on the offices of the radical union the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW). |
October 24 |
Battle of Caporetto begins, pitting Italians against German and Austro-Hungarian troops. It ends in November with Italy’s defeat. Italy calls on the other Allies for help. |
November 7 |
Communists assume power in Russia. |
January 8 |
President Wilson delivers his “Fourteen Points” speech to Congress. |
March 3 |
Russia and Germany sign the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, ending their war. |
March 11 |
First reports of the Spanish influenza outbreak are issued in Fort Riley, Kansas. |
April 1 |
The German army begins an offensive attack against the Allies along the Somme River. |
April 5 |
German immigrant Robert Prager is lynched in Illinois; he is believed to be a spy. He is not. |
May 16 |
Congress passes the Sedition Act, which establishes grounds for censorship and imprisonment, in addition to those listed in the Espionage Act. |
This American officer rides in the basket of an observation balloon in April 1918. He flies over enemy territory near the front lines to report back on German army movement and activities.
May 27 |
The German army launches an attack along the Aisne River. By May 31, it will reach the Marne River, within potential striking distance of Paris. |
May 28 |
The U.S. Army experiences its first battle at Cantigny. |
June 3–4 |
Americans participate in their first major action, helping to stop the Germans at Château-Thierry. |
June 6–26 |
American soldiers and marines take part in extensive fighting at Belleau Wood. |
June 16 |
In Ohio socialist Eugene Debs gives a speech that includes remarks against the imprisonment of antiwar demonstrators. Two weeks later he is arrested under the Espionage Act, and in September he is sentenced to ten years in jail. (The sentence is commuted in 1921.) |
July 18 |
The Allied armies, including 310,000 American troops, launch the Aisne-Marne offensive attack. The offensive ends on August 6. |
The first American troops arrive in Vladivostok, Russia. |
|
Sept. 12–15 |
U.S. and French troops attack and capture the Saint-Mihiel salient. |
September 26 |
U.S. forces launch the Meuse-Argonne offensive. |
October 16 |
Congress passes the Immigration Act, making it easier to deport suspected immigrant radicals. |
November 5 |
In the congressional elections, the Republicans win a majority. They will oppose President Wilson’s peace settlement plans. |
November 9 |
Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicates as leader of Germany and flees to neutral Netherlands. (He dies there in 1941.) |
November 11 |
An armistice is declared between the Allies and Germany. |
January 18 |
The Peace Conference opens in Paris. President Wilson attends. |
February 15 |
President Wilson returns to the United States for several weeks. |
June 4 |
Congress passes the 19th Amendment to the Constitution, giving women the right to vote. It is finally ratified by enough states and goes into effect August 26, 1920. |
June 28 |
Germany, France, and Britain sign the Treaty of Versailles, ending war between them. President Wilson also signs, but the treaty is not valid until ratified by the Senate. |
July 9 |
The German government ratifies the treaty. |
July 10 |
President Wilson presents the treaty to the U.S. Senate. The Senate needs to approve it by a two-thirds majority vote for it to go into effect. |
August 21 |
President Wilson shuts down the Committee on Public Information. |
September 3 |
Wilson begins a speaking tour of the United States to promote ratifying the Treaty of Versailles and joining the League of Nations. |
September 25 |
President Wilson collapses while in Colorado and returns to Washington. |
October 2 |
Wilson has a stroke. His health will be poor throughout the rest of his term as president. |
November 19 |
The U.S. Senate rejects the Treaty of Versailles. This is the first time in the Senate’s history that it rejects a peace treaty. |
January 2 |
Government officials round up an estimated 3,000–10,000 suspected radicals, including communists and labor agitators. |
March 19 |
The U.S. Senate rejects the Treaty of Versailles for a second time. |
November 2 |
Republican Warren Harding is elected U.S. president. He will take over in March 1921. |
December 10 |
Woodrow Wilson is awarded the 1919 Nobel Peace Prize. |
December 13 |
Congress repeals the Sedition Act. |
July 2 |
A joint resolution by the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives declares that the war with Germany and Austria-Hungary is over. |
October 18 |
The U.S. Senate ratifies separate treaties between the United States and Germany and Austria. |
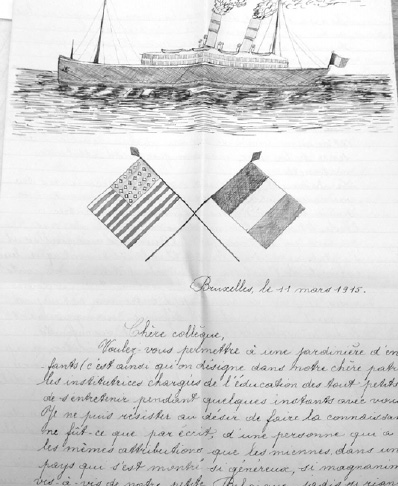
A Belgian child wrote this letter to President Wilson in 1915 to thank Americans for sending food and other aid to Belgium after Germany invaded. It shows a ship that carries goods and the American and Belgian flags crossed in friendship.