-WONDERFOOD-
TOMATOES
An integral part of the Mediterranean diet, tomatoes are a great source of health-promoting vitamins A and C. They also contain a powerful antioxidant called lycopene, which may improve heart health and protect against a number of cancers. Better still, cooking seems to boost the lycopene-related benefits of tomatoes, as does serving them with a little fat, for example olive oil.
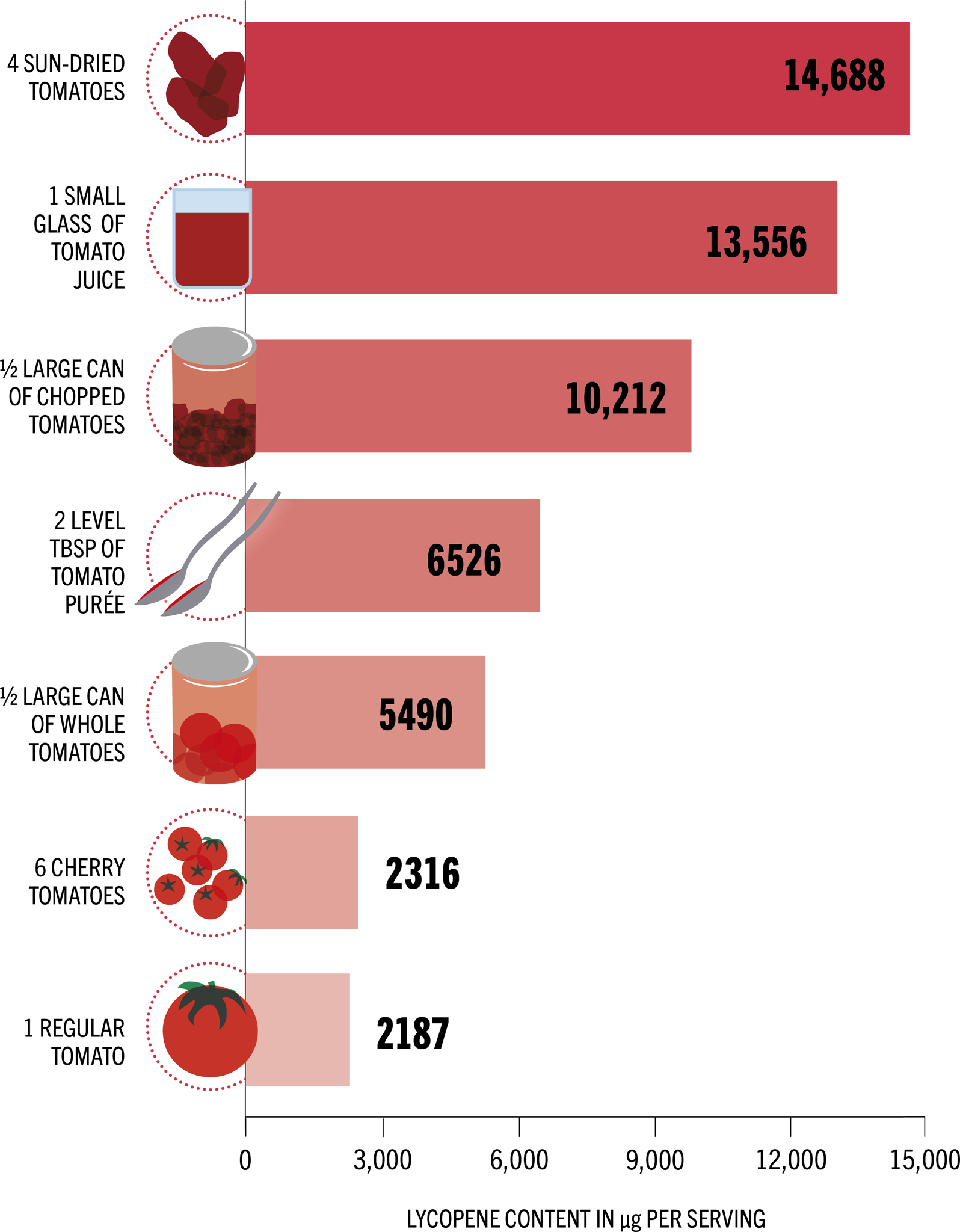
All tomatoes are packed with health-promoting vitamins, but these tomatoes and tomato products are particularly high in the beneficial antioxidant lycopene.
Regular tomatoes
- contain high levels of vitamin C, which is important for the immune system.
Cherry tomatoes
- are rich in beta-carotene, which benefit the eyes and immunity.
Chopped or whole canned tomatoes
- are a great source of lycopene due to the heat treatment used during processing.
Tomato purée
- is a great provider of beta-carotene, which the body uses to make vitamin A.
Sun-dried tomatoes
- are higher in most nutrients as drying concentrates the vitamins and minerals.
Tomato juice
- is extremely high in lycopene, which has many anticancer and heart-boosting effects.
Leave tomatoes on your work surface to ripen. Once ripe, keep them in a cool place away from sunlight but don’t refrigerate: cold temperatures damage their cells, affecting the tomatoes’ flavour permanently.
Eat both raw and cooked tomatoes; but note cooking and processing tomatoes actually boosts their lycopene content.
A daily serving of tomatoes or tomato products is ideal. However, consuming tomatoes only a few times a week still offers many health benefits.
1 serving equals
- 1 whole regular tomato
- 6 cherry tomatoes
- 200g (7oz) chopped canned tomatoes
- 2 canned plum tomatoes
- 4 sun-dried tomatoes
- 1 small glass of tomato juice
- 2 level tablespoons of tomato purée
When buying fresh, choose ripe, dark red tomatoes as they contain the most lycopene. Canned, sun-dried, and puréed tomato products are good choices as they have high levels of lycopene, but look out for hidden salt in any processed products.
Perfect partners
Tomatoes’ benefits are enhanced by other foods. Fat helps the body absorb carotenoids such as lycopene, and one study found adding avocado to a tomato salsa boosted lycopene absorption by four times. Another great partnership, which studies have found may prevent cancer, is eating tomatoes with broccoli.
 52%
52%
reduction in size of prostate cancer tumour in lab-based tests when broccoli and tomatoes were eaten together.
Fights cancer
Lycopene may protect against many cancers, including those of the lung, pancreas, stomach, mouth, colon, and breast. The most compelling evidence is its effect on prostate cancer, the second most common cancer in men – a review of 26 studies found higher lycopene intakes are generally linked to a lower incidence of this disease.
Heart health
Many studies suggest tomatoes – and in particular the lycopene they contain – help keep the heart healthy. Research shows higher intakes of tomatoes and tomato products reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol, increase HDL (good) cholesterol, and may lower blood pressure. One review of studies also found lycopene decreased the risk of stroke by 19 per cent. Discover how different tomatoes and tomato products compare in terms of their lycopene content, below, to see how to get your daily supply.