DIAGNOSTIC EXAM: AP BIOLOGY: SECTION I
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Time—1 hour and 30 minutes
For the multiple-choice questions that follow, select the best answer and fill in the appropriate letter on the answer sheet.
1. A pH of 10 is how many times more basic than a pH of 7?
A. 10
B. 100
C. 1,000
D. 10,000
2. Destruction of microfilaments would most adversely affect which of the following?
A. Cell division
B. Cilia
C. Flagella
D. Muscular contraction
3. Imagine that for a particular species of moth, females are primed to respond to two types of male mating calls. Males who produce an in-between version will not succeed at obtaining a mate and will therefore have low reproductive success. This is an example of
A. directional selection.
B. stabilizing selection.
C. artificial selection.
D. disruptive selection.
4. Crossover occurs during
A. prophase of mitosis.
B. prophase I of meiosis.
C. prophase II of meiosis.
D. prophase I and II of meiosis.
5. Which of the following is a specialized feature of plants that live in hot and dry regions?
A. Stomata that open and close
B. Transpiration
C. Photophosphorylation
D. C4 photosynthesis
6. A virus that carries the reverse transcriptase enzyme is a
A. retrovirus.
B. prion.
C. viroid.
D. DNA virus.
7. Ants live on acacia trees and are able to feast on the sugar produced by the trees. The tree is protected by the ants’ attack on any foreign insects that may harm the tree. This is an example of
A. parasitism.
B. commensualism.
C. mutualism.
D. symbiosis.
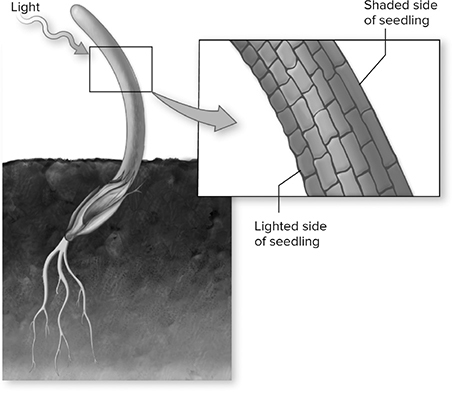
8. What process is taking place in the plant to cause its behavioral and physiological response?
A. Phototropism
B. Gravitropism
C. Photomorphogenesis
D. Circadian rhythms

9. The vine in the figure above is exhibiting what behavioral response?
A. Gravitropism
B. Phototropism
C. Thigmotropism
D. Photoperiodism
10. A reaction that breaks down compounds by the addition of water is known as
A. a hydrolysis reaction.
B. a dehydration reaction.
C. an endergonic reaction.
D. an exergonic reaction.
11. Sickle cell anemia is a mutation in hemoglobin that affects the shape of red blood cells during periods of low oxygenation. Sickle cell anemia displays recessive inheritance. An expecting mother and father visit a geneticist for counseling. Both parents are carriers of the sickle cell trait. Calculate the likelihood that their child is a carrier.
A. 0.75
B. 0.50
C. 0.25
D. 0.65
12. Dwarfism is an autosomal dominant disease. A couple has sought out genetic counseling as they prepare to start a family. They want to have two biological children. One parent has been diagnosed with dwarfism (Dd); the second parent is healthy (dd). Calculate the probability that both children have dwarfism.
A. 0.25
B. 0.50
C. 0.75
D. 0.15
13. A population of mice is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The recessive phenotype is found in 1 out of every 2,500 mice. Calculate the percentage of the heterozygous phenotype.
A. 0.02
B. 0.04
C. 0.98
D. 0.40
14. Which of the following is an example of aneuploidy?
A. Cri-du-chat syndrome
B. Chronic myelogenous leukemia
C. Turner syndrome
D. Achondroplasia
15. Among the following choices, which one would most readily move through a selectively permeable membrane?
A. Small, uncharged polar molecule
B. Large, uncharged polar molecule
C. Glucose
D. Sodium ion
16. Which of the following is not a lipid?
A. Steroid
B. Fat
C. Phospholipid
D. Glycogen
17. Which of the following hormones is not released by the anterior pituitary gland?
A. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
B. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
C. Growth hormone (GH or STH)
D. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
18. Which of the following is the least specific taxonomic classification category?
A. Division
B. Order
C. Family
D. Genus
19. Which cells control the opening and closing of a plant’s stomata?
A. Guard cells
B. Collenchyma cells
C. Parenchyma cells
D. Mesophyll cells
20. Imagine that 9 percent of a population of anteaters have a short snout (recessive), while 91 percent have a long snout (dominant). If this population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what is the expected frequency (in percent) of the hetero-zygous condition?
A. 30.0
B. 34.0
C. 38.0
D. 42.0
21. The situation in which a gene at one locus alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at another locus is known as
A. incomplete dominance.
B. codominance.
C. pleiotropy.
D. epistasis.
22. The oxygen produced during the light reactions of photosynthesis comes directly from
A. H2O.
B. H2O2.
C. C2H3O2.
D. CO2.
23. A population of fruit flies is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The allele for black eyes (B) is dominant to the red allele (b). The recessive phenotype is seen in 36 percent of the population. Calculate the frequency of the dominant allele.
A. 0.40
B. 0.36
C. 0.60
D. 0.18
24. The presence of which of the following organelles or structures would most convincingly indicate that a cell is a eukaryote and not a prokaryote?
A. Plasma membrane
B. Cell wall
C. Lysosome
D. Ribosome
25. Traits that are similar between organisms that arose from a common ancestor are known as
A. convergent.
B. homologous.
C. vestigial.
D. divergent.
26. The process by which a huge amount of DNA is created from a small amount of DNA in a very short amount of time is known as
A. cloning.
B. transformation.
C. a polymerase chain reaction.
D. gel electrophoresis.
27. A compound contains a COOH group. What functional group is that?
A. Carbonyl group
B. Carboxyl group
C. Hydroxyl group
D. Phosphate group
28. Which of the following forms of cell transport requires the input of energy?
A. Diffusion
B. Osmosis
C. Facilitated diffusion
D. Active transport
29. Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes that
A. are found only in identical twins.
B. are formed during mitosis.
C. split apart during meiosis II.
D. resemble one another in shape, size, and function.
30. Which of the following is an incorrect statement about DNA replication?
A. It occurs in the nucleus.
B. It occurs in a semiconservative fashion.
C. Helicase is the enzyme that adds the nucleotides to the growing strand.
D. DNA polymerase can build only in a 5′-to-3′ direction.
31. Warning coloration adopted by animals that possess a chemical defense mechanism is known as
A. cryptic coloration.
B. deceptive markings.
C. aposematic coloration.
D. Batesian mimicry.
32. In a large pond that consists of long-finned fish and short-finned fish, a tornado wreaks havoc on the pond, killing 50 percent of the fish population. By chance, most of the fish killed were short-finned varieties, and in the subsequent generation there were fewer fish with short fins. This is an example of
A. gene flow.
B. bottleneck.
C. balanced polymorphism.
D. allopatric speciation.
33. Which of the following structures would not have developed from the mesoderm?
A. Muscle
B. Heart
C. Kidneys
D. Liver
34. In a certain breed of dog, the allele for red-colored tongue (T) is dominant to the allele for purple tongue (t). A researcher collected data on 48 dogs bred from a cross between a red-tongued dog and a purple-tongued dog. Of the 48 offspring, 36 had red tongues, and 12 had purple tongues. Calculate the chi-squared value for the null hypothesis, assuming that the red-tongued dog was heterozygous for the tongue-color gene.
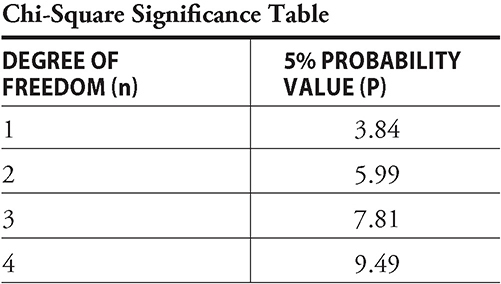
A. 24
B. 48
C. 12
D. 6
35. The cyclic pathway of photosynthesis occurs because
A. the Calvin cycle uses more ATP than NADPH.
B. it can occur in regions lacking light.
C. it is a more efficient way to produce oxygen.
D. it is a more efficient way to produce the NADPH needed for the Calvin cycle.
36. Which of the following conditions is an X-linked condition?
A. Hemophilia
B. Tay-Sachs disease
C. Cystic fibrosis
D. Sickle cell anemia
37. The uptake of foreign DNA from the surrounding environment is known as
A. generalized transduction.
B. specialized transduction.
C. conjugation.
D. transformation.
38. Most of the digestion of food occurs in the
A. esophagus.
B. stomach.
C. small intestine.
D. large intestine.
39. You have just come back from visiting the redwood forests in California and were amazed at how wide those trees were. What process is responsible for the increase in width of these trees?
A. Growth of guard cells
B. Growth of collenchyma cells
C. Growth of apical meristem cells
D. Growth of lateral meristem cells
40. The trophoblast formed during the early stages of human embryology eventually develops into the
A. placenta.
B. embryo.
C. hypoblast.
D. morula.
41. What biome is known for having the greatest diversity of species?
A. Taiga
B. Temperate grasslands
C. Tropical forest
D. Savanna
42. In hypercholesterolemia, a genetic condition found in humans, individuals who are HH have normal cholesterol levels, those who are hh have horrifically high cholesterol levels, and those who are Hh have cholesterol levels that are somewhere in between. This is an example of
A. dominance.
B. incomplete dominance.
C. codominance.
D. epistasis.
43. The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the
A. nucleus.
B. cytoplasm.
C. thylakoid membrane.
D. stroma.
44. Which of the following is a characteristic of an R-selected strategist?
A. Low reproductive rate
B. Extensive postnatal care
C. Relatively constant population size
D. J-shaped growth curve
45. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct?
A. Mitosis makes up 30 percent of the cell cycle.
B. The order of mitosis is prophase, anaphase, metaphase, and telophase.
C. Single-cell eukaryotes undergo mitosis as part of asexual reproduction.
D. Cell plates are formed in animal cells during mitosis.
46. A vine that wraps around the trunk of a tree is displaying the concept known as
A. photoperiodism.
B. thigmotropism.
C. gravitropism.
D. phototropism.
47. Which hormone is known for assisting in the closing of the stomata and inhibition of cell growth?
A. Abscisic acid
B. Cytokinin
C. Ethylene
D. Gibberellin
48. During the humoral immune response, the following sequence takes place. An antigen invader → B cell meets antigen → B cell differentiates into plasma cells and memory cells → plasma cells produce antibodies → antibodies eliminate antigen. What role does the antigen play in activation and communication with the cells of the immune system?
A. Signal
B. Receptor
C. Signal transduction
D. Cellular response
49. Which reaction occurs in the mitochondria and involves the formation of ATP from NADH and FADH2?
A. Glycolysis
B. Oxidative phosphorylation
C. Chemiosmosis
D. Fermentation
50. Which process couples the movement of electrons down the electron transport chain with the formation of ATP, using the driving force provided by the proton gradient?
A. Formation of acetyl CoA
B. Chemiosmosis
C. ATP synthase
D. Glycolysis
51. Which reaction occurs outside the mitochondria, whether oxygen is present or not, to produce 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate?
A. Glycolysis
B. Oxidative phosphorylation
C. Chemiosmosis
D. Fermentation
52. Cells must be able to produce usable energy regardless of oxygen being present. Which reaction is performed by cells in an effort to regenerate the NAD+ required for glycolysis to continue when oxygen is not present?
A. Glycolysis
B. Oxidative phosphorylation
C. Chemiosmosis
D. Fermentation
53. What is the learning behavior exhibited by an organism as it reasons through a problem the first time with no prior experience?
A. Associative learning
B. Insight learning
C. Imprinting
D. Altruistic behavior
54. In interspecific interactions, organisms form relationships with other species in a community. When an organism helps another, even at its own expense, which is the learning behavior for the organisms?
A. Associative learning
B. Insight learning
C. Imprinting
D. Altruistic behavior
55. When an animal substitutes one stimulus for another in order to get the same result, the process is referred to as
A. associative learning.
B. insight learning.
C. imprinting.
D. altruistic behavior.
56. During the critical early life period for an organism, what innate behavior is learned?
A. Associative learning
B. Insight learning
C. Imprinting
D. Altruistic behavior
For questions 57–60, please use the information from the following laboratory experiment:
You are working as a summer intern at the local university laboratory, and a lab technician comes into your room, throws a few graphs and tables at you, and mutters, “Interpret this data for me . . . I need to go play golf. I’ll be back this afternoon for your report.”
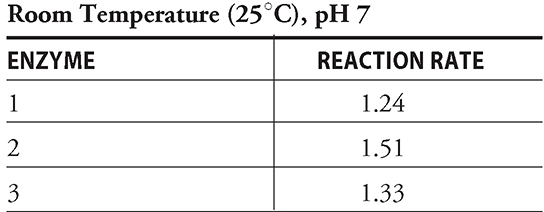
Analyze the data this technician so kindly gave to you, and use it to answer questions 57–60. The reaction rates reported in the tables are relative to the original rate of the reaction in the absence of the enzymes. The three enzymes used are all being added to the same reactants to determine which should be used in the future.
57. If you had also been given a graph that plotted the moles of product produced versus time, what would have been the best way to calculate the rate for the reaction?
A. Calculate the average of the slope of the curve for the first and last minute of reaction.
B. Calculate the slope of the curve for the portion of the curve that is constant.
C. Calculate the slope of the curve for the portion where the slope begins to flatten out.
D. Add up the total number of moles produced during each time interval and divide by the total number of time intervals measured.
58. Over the interval measured, at what temperature does enzyme 2 appear to have its optimal efficiency?
A. 10°C
B. 15°C
C. 20°C
D. 25°C
59. Which of the following statements about enzyme 3 is incorrect?
A. At a pH of 6 and a temperature of 25°C, it is more efficient than enzyme 2 but less efficient than enzyme 1.
B. It functions more efficiently in the acidic pH range than the basic pH range.
C. At 30°C and a pH of 7, it is less efficient than both enzymes 1 and 2.
D. Over the interval given, its optimal temperature at a pH of 7 is 10°C.
60. Which of the following statements can be made from review of these data?
A. Enzyme 1 functions most efficiently in a basic environment and at a lower temperature.
B. Enzyme 1 functions more efficiently than enzyme 2 at 10°C and a pH of 7.
C. The pH does not affect the efficiency of enzyme 3.
D. All three enzymes function more efficiently in an acidic environment than a basic environment.