AP Biology Practice Exam 2: Section I
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Time–1 hour and 30 minutes
For the multiple-choice questions to follow, select the best answer and fill in the appropriate letter on the answer sheet.
1. A baby duck runs for cover when a large object is tossed over its head. After this object is repeatedly passed overhead, the duck learns there is no danger and stops running for cover when the same object appears again. This is an example of
A. imprinting.
B. fixed-action pattern.
C. agonistic behavior.
D. habituation.
2. In a population of giraffes, an environmental change occurs that favors individuals that are tallest. As a result, more of the taller individuals are able to obtain nutrients and survive to pass along their genetic information. This is an example of
A. directional selection.
B. stabilizing selection.
C. sexual selection.
D. disruptive selection.
3. The relatives of a group of pelicans from the same species that separated from each other because of an unsuccessful migration are reunited 150 years later and find that they are unable to produce offspring. This is an example of
A. allopatric speciation.
B. sympatric speciation.
C. genetic drift.
D. gene flow.
4. A cell is placed into a hypertonic environment and its cytoplasm shrivels up. This demonstrates the principle of
A. diffusion.
B. active transport.
C. facilitated diffusion.
D. plasmolysis.
5. Which of the following is a biotic factor that could affect the growth rate of a population?
A. Volcanic eruption
B. Glacier melting
C. Destruction of the ozone layer
D. Sudden reduction in the animal food resource
6. Which of the following is not a way to form recombinant DNA?
A. Translation
B. Conjugation
C. Specialized transduction
D. Transformation
7. Chemiosmosis occurs in
I. Mitochondria
II. Nuclei
III. Chloroplasts
A. I only
B. II only
C. III only
D. I and III
8. Which of the following theories is based on the notion that mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from prokaryotic cells?
A. Fluid mosaic model
B. Endosymbiotic model
C. Taxonomic model
D. Respiration feedback model
9. Which of the following is not known to be involved in the control of cell division?
A. Cyclins
B. Protein kinases
C. Checkpoints
D. Fibroblast cells
10. Which of the following statements about posttranscriptional modification is incorrect?
A. A poly-A tail is added to the 3′ end of the mRNA.
B. A guanine cap is added to the 5′ end of the mRNA.
C. Introns are removed from the mRNA.
D. Posttranscriptional modification occurs in the cytoplasm.
11. In a certain pond, there are long-finned fish and short-finned fish. A horrific summer thunderstorm leads to the death of a disproportionate number of long-finned fish to the point where the relative frequency of the two forms has drastically shifted. This is an example of
A. gene flow.
B. natural selection.
C. genetic drift.
D. stabilizing selection.
12. During the central dogma, transcription occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells by transcribing the cells’ DNA. Located thousands of base pairs away from the promoter region is the transfer-affecting region on the DNA. What is that region called?
A. Enhancer
B. Repressor
C. Operator
D. Promoter
13. Which of the following statements about photo-synthesis is incorrect?
A. H2O is an input to the light-dependent reactions.
B. CO2 is an input to the Calvin cycle.
C. Photosystems I and II both play a role in the cyclic light reactions.
D. O2 is a product of the light-dependent reactions.
14. If a couple has had three sons and the woman is pregnant with their fourth child, what is the probability that child 4 will also be male?
A. ½
B. ¼
C. ⅛
D. 1⁄16
15. Which of the following is an incorrect statement about gel electrophoresis?
A. DNA migrates from positive charge to negative charge.
B. Smaller DNA travels faster.
C. The DNA migrates only when the current is running.
D. The longer the current is running, the farther the DNA will travel.
16. You are told that in a population of guinea pigs, 4 percent are black (recessive) and 96 percent are brown. Which of the following is the frequency of the heterozygous condition?
A. 16 percent
B. 32 percent
C. 40 percent
D. 48 percent
17. Which of the following is known to be involved in the photoperiodic flowering response of angiosperms?
A. Auxin
B. Cytochrome
C. Phytochrome
D. Gibberellins
18. Which of the following tends to be highest on the trophic pyramid?
A. Primary consumers
B. Herbivores
C. Primary carnivores
D. Primary producers
19. A form of species interaction in which one of the species benefits while the other is unaffected is called
A. parasitism.
B. mutualism.
C. commensalism.
D. symbiosis.
20. The transfer of DNA between two bacterial cells connected by sex pili is known as
A. specialized transduction.
B. conjugation.
C. transformation.
D. generalized transduction.
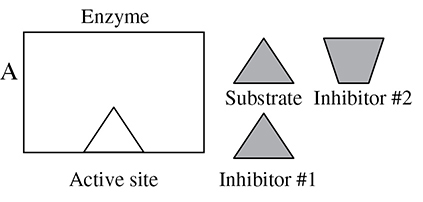
For questions 21–22, please use the preceding diagram:
21. If inhibitor 1 is able to bind to the active site and block the attachment of the substrate to the enzyme, this is an example of
A. noncompetitive inhibition.
B. competitive inhibition.
C. a cofactor.
D. a coenzyme.
22. Which of the following is not a change that would affect the efficiency of the enzyme shown above?
A. Change in temperature
B. Change in pH
C. Change in salinity
D. Increase in the concentration of the enzyme
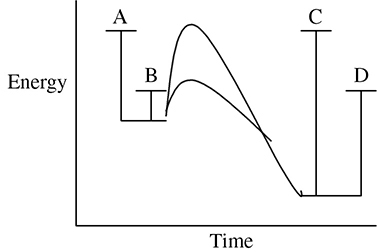
23. Which of the following points on the preceding energy chart represents the activation energy of the reaction involving the enzyme?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
24. When an animal is harmless but has a similar appearance of a more dangerous animal, that animal is exhibiting what type of defense mechanism?
A. Aposomatic coloration
B. Batesian mimicry
C. Deceptive markings
D. Cryptic coloration
25. Twenty people decide to start a new population, totally isolated from anyone else. Two of the individuals are heterozygous for a recessive allele, which in homozygotes causes cystic fibrosis. Assuming this population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what fraction (expressed as a decimal) of people in this new population will have cystic fibrosis?
A. 0.05
B. 0.005
C. 0.0025
D. 0.25
26. During meiosis, trisomy 21 can result from what chromosome abnormality?
A. An extra chromosome 21 from a mutation
B. An extra chromosome 21 from nondisjunction
C. An autosomal dominant disorder
D. A missing chromosome 21 from nondisjunction
27. The semiconservative model of DNA produces what complementary strand to the sequence 5′ – TTAACGAACG – 3′ during DNA replication?
A. 5′ – UUAAGCUUGC–3′
B. 5′ – AATTGCTTGC–3′
C. 3′ – AATTGCTTGC 5′
D. 3′ – UUAAGCUUGC5′
28. A local scientist has been re-creating Mendel’s experiments and recently produced an equal number of true breeding yellow (Y), smooth (R) pea plants, and true breeding green (y), wrinkled (r) pea plants. What is/are the expected F2 genotype(s)?
A. YYrr
B. YyRr; YYRr; yyrr
C. YyRr
D. YYRR; YyRr; yyRR; yyrr
29. Describe the outcome when a carrot with an osmolarity of 0.25 M is placed in a solution of 0.45 M saltwater.
A. The saltwater will enter the cell until equilibrium is reached.
B. The saltwater and carrot are isotonic, resulting in no movement.
C. Water will enter the cell until equilibrium is reached.
D. Water will leave the cell until equilibrium is reached.
30. A certain mutation found in fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) is hypothesized to be autosomal recessive. The experimenter crossed two Drosophila flies that were heterozygous for the trait. The next generation produced 70 wild-type males, 65 wild-type females, 36 males with the mutation, and 40 mutant females. Calculate the chi-squared value for the null hypothesis that the mutation is autosomal recessive.
A. 3.35
B. 9.98
C. 13.33
D. 6.64
31. A recent levy has been breached, causing flooding in a local community with saltwater. A local farmer is trying to determine if his crops can survive the flooding. The saltwater has a water potential of −8.73 MPa. The farmer’s crops have a molar concentration of 0.25 M with a pressure potential of −1.0 MPa at 27°C. What will happen to the crops?
A. The crops will maintain turgid pressure due to the crop’s water potential being −7.23 MPa and the saltwater being −8.73 MPa.
B. The crops will become flaccid and eventually die due to the crop’s water potential being −7.23 MPa and the saltwater being −8.73 MPa.
C. The pressure potential of the plant will cause the crops to gain water from the flooding saltwater.
D. The pressure potential of the plant will push the sugar out of the crops into the flooding saltwater.
32. A cell is in equilibrium with its surroundings. The molarity of the surrounding solution at 20°C is 0.8 M. Calculate the solute potential of the surrounding solution.
A. -3.90
B. -39.0
C. -19.5
D. -1.95
Questions 33–36 refer to the following pedigree.
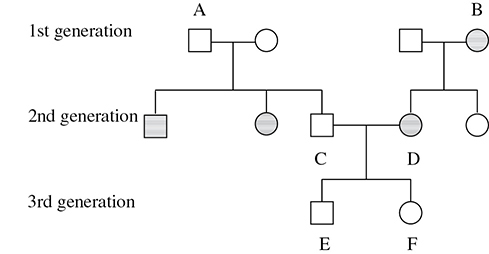
33. What kind of inheritable condition does this pedigree appear to show?
A. Autosomal dominant
B. Autosomal recessive
C. Sex-linked dominant
D. Sex-linked recessive
34. What is the probability that couple C and D will produce a child that has the condition?
A. 0
B. 0.125
C. 0.250
D. 0.333
35. Which of the following conditions could show the same kind of pedigree results?
A. Cri-du-chat syndrome
B. Turner syndrome
C. Albinism
D. Hemophilia
36. If child E does in fact have the condition, what is the probability that child F will also have it?
A. 0
B. 0.250
C. 0.500
D. 0.750
Questions 37–39: An experiment involving fruit flies produced the following results:
Vestigial wings are wild type; crumpled wings are mutant.
Gray body is dominant; black body is mutant.

37. From the data presented above, one can conclude that these genes are
A. sex-linked.
B. epistatic.
C. holandric.
D. linked.
38. What is the crossover frequency of these genes?
A. 10 percent
B. 20 percent
C. 30 percent
D. 35 percent
39. How many map units apart would these genes be on a linkage map?
A. 5 map units
B. 10 map units
C. 20 map units
D. 30 map units
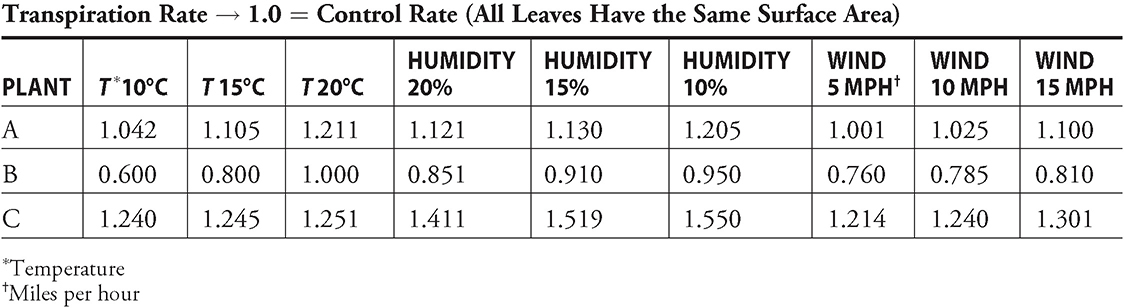
Questions 40–42: A laboratory procedure -involving plants presents you with the data found in the following two charts:
40. From the transpiration rate data, it appears that transpiration rate rises as
A. temperature ↑, wind speed ↓, humidity ↓
B. temperature ↑, wind speed ↑, humidity ↓
C. temperature ↑, wind speed ↑, humidity ↑
D. temperature ↓, wind speed ↑, humidity ↑
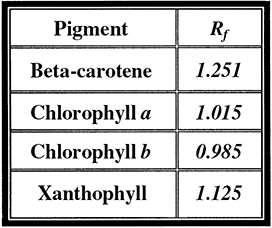
41. According to the Rf values given in the preceding smaller table, which pigment would migrate the fastest on chromatography paper?
A. Xanthophyll
B. Chlorophyll a
C. Chlorophyll b
D. Beta-carotene
42. From the transpiration rate data presented in the larger table, which of the following plants appears to be most resistant to transpiration?
A. Plant A
B. Plant B
C. Plant C
D. Plants B and C are similarly resistant.
Questions 43–45: A population of rodents is studied over the course of 100 generations to examine changes in dental enamel thickness. Species that are adapted to eat food resources that require high levels of processing have thicker enamel than do those that eat softer, more easily processed foods. Answer the following questions using this information and the curves that follow.
43. How is average enamel thickness changing in this population?
A. There is no real change.
B. The color and size are changing.
C. It is increasing.
D. It is decreasing.
44. You randomly pick one data point from all three sets of data (all three generations), and the individual’s enamel thickness score is 15. Which of the following can be inferred?
A. The individual comes from generation 1.
B. The individual comes from generation 50.
C. The individual comes from generation 100.
D. The individual could be from any of these generations.
45. What inference can you make about this species’ diet?
A. Its food resources are getting softer and easier to process.
B. Its food resources are getting harder and more difficult to process.
C. The population is growing.
D. The population is shrinking.

Questions 46–49: A student sets up a lab experiment to study the behavior of slugs. She sets up a large tray filled with soil that measures 1 square meter and has four sets of conditions, one in each quadrant:
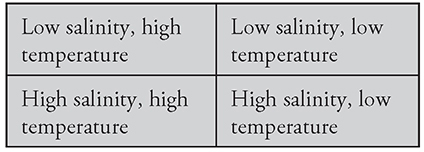
She places 20 slugs in the tray, 5 in each quadrant. Use this information to answer the following questions:
46. What is this lab setup called?
A. A gel sheet
B. A choice chamber
C. A potometer
D. An incubation chamber
47. After 5 minutes, there are 5 slugs in each quadrant. Which of the following is not a viable explanation for this finding?
A. The slugs haven’t had time to move yet.
B. The slugs have no preference for temperature or salinity conditions.
C. The slugs can’t move from one area of the tray to another.
D. The slugs do not like to live in high-temperature areas.
48. After 20 minutes, 20 slugs are in the high- temperature, low-salinity quadrant. What kind of animal behavior has this experiment displayed?
A. Kinesis
B. Taxis
C. Survival
D. Feeding
49. A classmate has set up a similar experiment in the following manner:

Of the 20 slugs that she puts in her tray, 18 move to the high-salinity, high-temperature section within one hour, while the other 2 move to the low-salinity, low-temperature section. She concludes that slugs prefer conditions of high salinity and temperature. What is wrong with this conclusion?
A. She didn’t specify what the two temperatures or salinities were.
B. The slugs may not have been able to move where they wanted.
C. Crowding may have affected the behavior of the slugs, causing the two others to move to the other section.
D. She is measuring two variables at once with no control, and therefore can’t conclude anything about slug tastes.
50. Viral transduction is the process by which viruses carry bacterial DNA from one bacterial cell to another. In what way does this process play a role in bacterial evolution?
A. By making the bacterial cell more resistant to predators
B. By directly creating new species of bacteria
C. By increasing genetic variation of the bacteria
D. By selecting for viruses better able to infect bacteria
51. ADH is a hormone secreted by the kidneys that reduces the amount of water excreted in the urine. ADH is released in times of dehydration. This is an example of
A. innate behavior.
B. maintaining homeostasis.
C. failure to respond to the environment.
D. positive feedback.
For questions 52–54, refer to the information and graph that follows.
Five dialysis bags, made from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to glucose, were filled with various concentrations of glucose and placed in separate beakers containing 0.5 M glucose solution. The bags were weighed every 10 minutes and the percent change in mass for each bag was graphed:
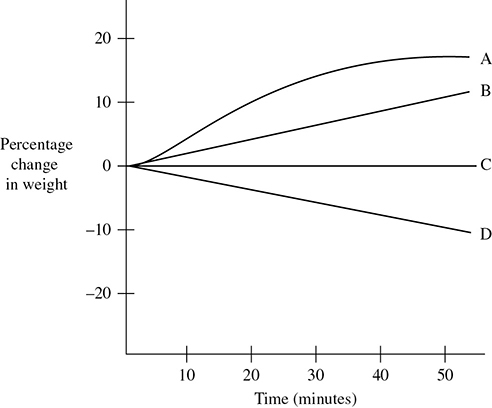
52. Which line represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.5 M solution?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
53. Which line represents the bag with the highest initial concentration of glucose?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
54. Which line or lines represent bags that contain a solution that is hypertonic at 50 minutes?
A. A and B
B. B
C. C
D. D and E
55. A mutation in a bacterial enzyme changed a previously polar amino acid into a nonpolar amino acid. This amino acid was located at a site distant from the enzyme’s active site. How might this mutation alter the enzyme’s substrate specificity?
A. By changing the enzyme’s pH optimum
B. By changing the enzyme’s location in the cell
C. By changing the shape of the protein
D. An amino acid change away from the active site cannot alter the enzyme’s substrate specificity.
Use the following picture of DNA to answer questions 56 and 57:
template strand 5′ ___________ 3′
complementary strand 3′ ___________ 5′
56. Based on the preceding picture, which direction would RNA polymerase move?
A. 3′ → 5′ along the template strand
B. 3′ → 5′ along the complementary strand
C. 5′ → 3′ along the template strand
D. 5′ → 3′ along the complementary strand
57. If the DNA segment is a transcriptional unit, where would the promoter be located?
A. To the left of the complementary strand
B. To the right of the template strand
C. To the left of the template strand
D. To the right of the complementary strand
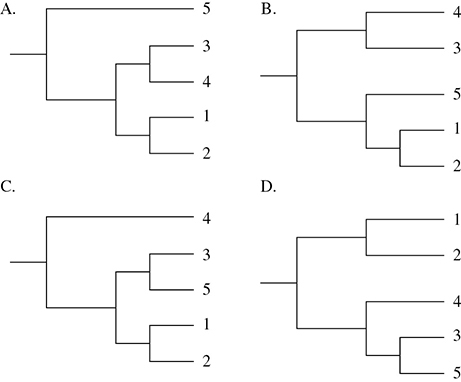
58. A single gene from five related species of -leafhoppers was compared, and the nucleotide differences between the genes are as shown in the table:
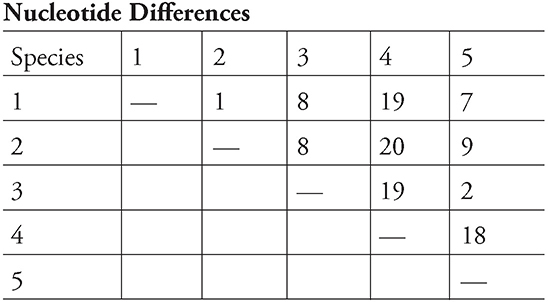
Which of the following phylogenetic trees best shows the correct evolutionary relationship between the leafhoppers?
Answer questions 59 and 60 based on the following cladogram:
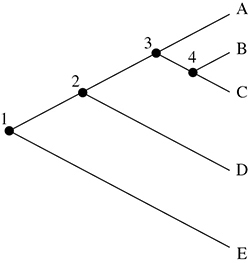
59. What is the common ancestor for B and E?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
60. Which two species are most closely related?
A. A and E
B. A and B
C. B and C
D. D and E