Diseases of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
A network of ducts and vessels throughout the human body, the circulatory system includes the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. The former circulates blood, while the latter circulates lymph fluid. The respiratory system is the general term for the organs that exchange the air inside the body with that of the external world: We breathe out carbon dioxide and breathe in fresh oxygen. The respiratory system consists of respiratory ducts (nasal, larynx and pharynx, trachea and bronchus) and the lungs. This chapter aims to help you improve the health of these two systems.
1. Hypertension
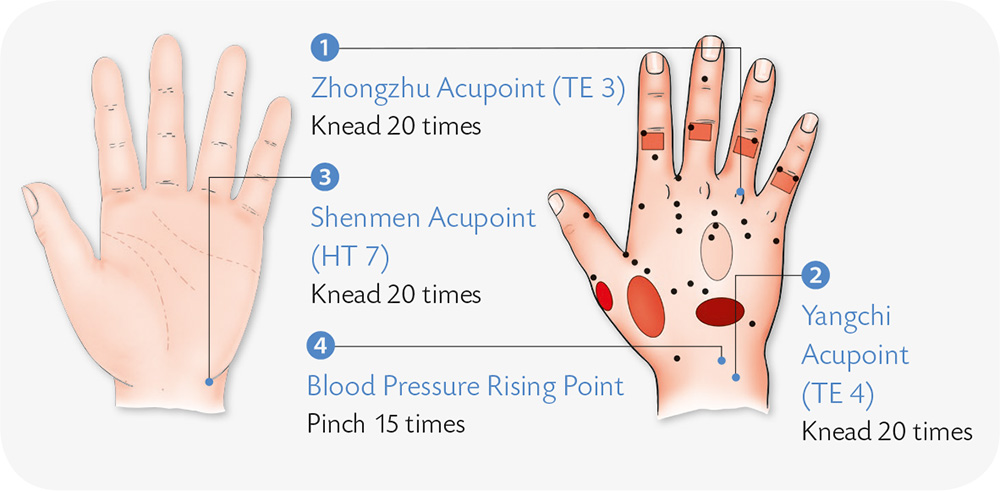
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is one of the most common diseases in the world, and also one of the biggest risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. It may trigger complications such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, and chronic kidney diseases. The risk of hypertension increases as you age. Women, who have a lower risk of hypertension than males in general, are confronted with a rapidly increasing risk after menopause, which may be even higher than the risk faced by men. In places of higher latitude where it is colder, the prevalence of hypertension is greater than at lower latitudes where it is warmer. Its prevalence at high altitudes is greater than in low altitudes. Hypertension is also related to dietary habits. The more your intake of salt and saturated fat, the higher your blood pressure and the greater the risk of hypertension.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Hypertension has the following symptoms:
Tinnitus: Perception of ringing in both ears, lasting for a prolonged period of time.
Shortness of breath and palpitations: High blood pressure can cause cardiomyopathy, an enlarged heart, and heart failure, which all lead to shortness of breath and palpitations.
Headache: If a patient often has a headache, sometimes severe, accompanied by nausea and vomiting, this could be a sign of hypertension.
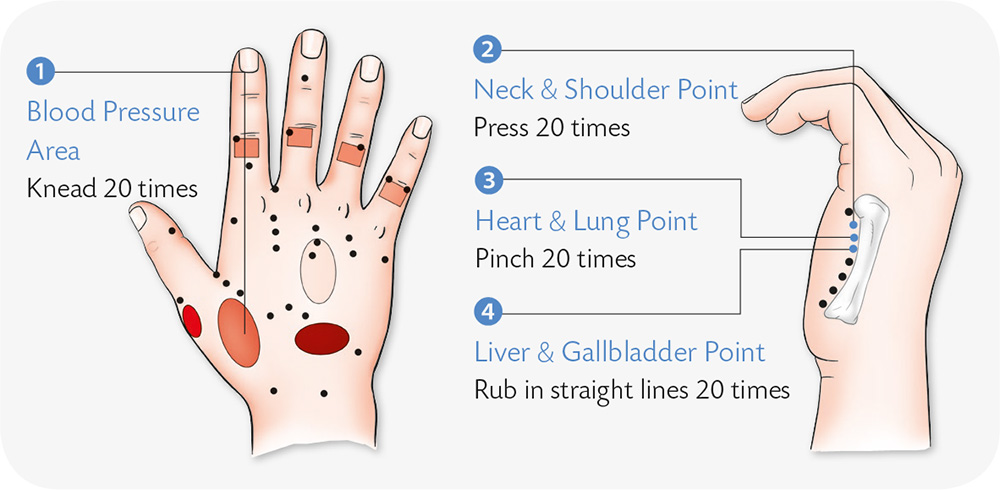
Hand Exercises
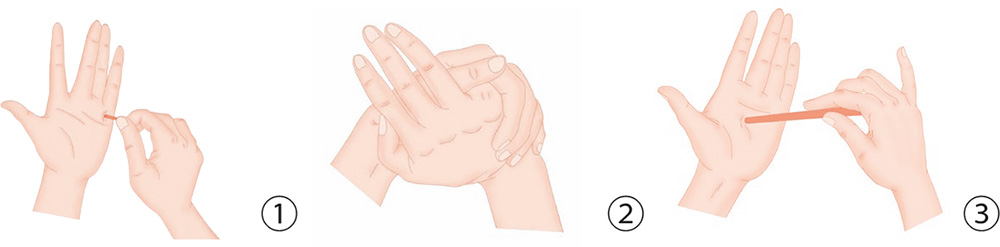
1. Use a stick to jab in evenly-spread dots the transverse creases (creases found when you bend your fingers) of the ring finger with force.
2. With the center of the right palm facing up, withdraw the little finger; your left palm covers your right palm, and presses it while squeezing the little finger of the right hand.
3. Use a pen to jab the center of the palm evenly.
Other Methods
1. Reduce your sodium salt intake. Sodium salt contributes to rising blood pressure, and increases the risk of its occurring. Potassium salt, however, may counteract raised blood pressure caused by sodium salt.
2. Stop smoking. Smoking is one of the major contributing factors to cardiovascular diseases.
3. Limit alcohol intake. Long-term alcohol consumption may lead to hypertension. Reducing your intake can drastically reduce your risk of hypertension.
4. Exercise regularly. Regular physical exercise can reduce blood pressure.
5. Lose weight. Reduced body fat will lower your blood pressure.
6. Reduce emotional stress and keep a balanced state of mind. Negative emotions will increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Take proactive measures to prevent and reduce your emotional stress. Also, try to correct an unhealthy state of mind, and give it treatment if needed.
2. Hypotension
There is no universal diagnostic standard yet for low blood pressure. In general, an adult is considered to have hypotension if their blood pressure reads below 90/60 mmHg in a limb artery.
Based on the manner of its onset, low blood pressure can either be acute or chronic. Acute low blood pressure refers to a sudden and obvious drop from normal or higher blood pressure, which may be caused by unusual physical weakness. It often happens to young women with very fragile and slender constitutions. Chronic low blood pressure is consistently lower than the normal range.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Symptoms of low blood pressure are faintness, giddiness, feebleness, palpitations, and cognitive impairment. Hypotension often happens in the morning when the affected person gets up from bed. When standing up, they will feel dizziness, weakness in the legs, vertigo, or faintness accompanied by a pale complexion, sweating, nausea, and a change in their pulse rate.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
1. Put a ring on the middle phalanx of the ring finger and turn it to stimulate the finger.
2. Use a toothbrush to brush the palm side of the ring finger back and forth 15 times.
3. Strap a wristwatch on your index finger and last two fingers, and leave your middle finger above the strap.
Other Methods
People with hypotension should maintain a diet that helps to lift the heart and nourish the brain. This includes longan, lotus seeds, dates, and mulberries. Avoid raw and cold food and food that unlock qi, such as spinach, radish, and celery, as well as cold drinks and ice cream. Particularly avoid corn, as it tends to reduce blood pressure.
Do more exercise, and improve your overall physical fitness. You can do the following every day: Lie on your back, pull your arms up and interlock your fingers, then make them push and pull against each other for resistance; pull when inhaling; release when exhaling. Repeat this 3 or 4 times, then pull your arms away from the sides of your body to above your head; hold the hands together, and slowly straighten your fingers as you breathe. Then pull back your arms to the sides of your body while inhaling. Repeat as many times as you see fit.
3. Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary atherosclerosis is the primary cause of coronary heart disease. Other factors causing the disease include gender and age, family history, abnormal level of lipids, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, being overweight, obesity, gout, and lack of exercise.
The types of coronary heart disease are as follows:
Angina pectoris: It manifests itself as a squeezing or fullness from behind the chest bones and is often accompanied by anxiety. It lasts 3 to 5 minutes, often emanating to the left side of the hips, shoulders, larynx and pharynx, the back, and the right arm.
Myocardial infarction: Prodrome symptoms often occur a week in advance, such as chest pain while resting or doing light manual labor, accompanied by evident discomfort and fatigue.
Sudden cardiac death: The patient suffers sudden cardiac death as the existing atherosclerosis progresses. When a coronary artery spasm or clog occurs, myocardial infarction will follow, resulting in a local electrophysiological disorder and temporary severe abnormal heart rhythms.
Symptomless myocardial ischemia: Many patients with extensive coronary artery blockage do not feel chest pain. Some may not even experience pain at the time of death.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
Hand Exercises
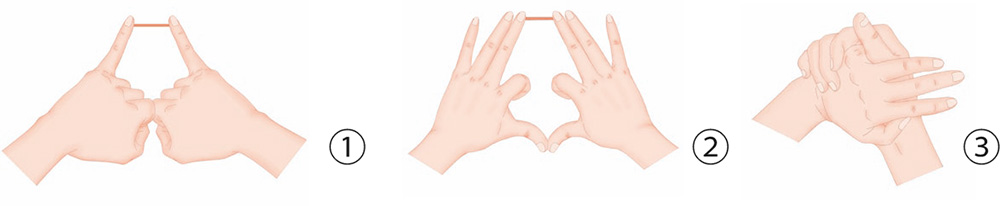
1. Hold a stick between the tips of your little fingers and press it with the force of the two fingers.
2. Hold a stick with the tips of your middle fingers, while you withdraw the two index fingers and press the thumbs against each other.
3. With your right palm holding on to the left palm, press the withdrawn little finger of the left hand, while the remaining three fingers of the left hand touch and press the back of the right hand.
Other Methods
1. Patients with coronary heart disease should keep warm. Particularly in winter when extreme cold sets in with a strong wind, they should take precautions by wearing a facemask and avoiding walking against the wind. This is because in low temperatures, the heart requires a greater supply of blood, but the contracting coronary artery reduces the supply. As a result, the heart muscle cannot get enough blood, which triggers angina pectoris.
2. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by following a regular daily routine. Go to bed early and get up early, and avoid working late.
3. Keep a balanced diet and eat fresh and light food that are easy to digest. Eat vegetables and fruit to make sure you get enough vitamins.
4. Be active and do exercise based on your ability. Design or select appropriate sports and games to facilitate the circulation of qi and blood and alleviate the burden on the heart.
4. Anemia
Anemia is a common clinical condition caused by a decreased number of circulating red blood cells per unit volume. Owing to a variety of causes, anemia is classified as anemia by blood loss, destruction of red blood cells, and decreased or faulty red blood cell production.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Clinically, the patient is described as having pale skin, a lusterless complexion, and rough skin. The patient may have mucocutaneous ulceration as the condition progresses to severity.
Anemia may cause shortness of breath or even trouble breathing when it is severe. Long-time anemia, an excessive workload of the heart, coupled with an insufficient supply of oxygen, may lead to anemic heart disease that manifests as a change of heartbeat accompanied by abnormal heart rhythms and heart failure.
Anemia may also do harm to the nervous system, causing lightheadedness, tinnitus, headache, insomnia, frequent and vivid dreams, memory problems, and an inability to concentrate.
In addition, anemia may cause conditions such as an unusually rapid heartbeat, poor appetite, diarrhea, amenorrhea, and decreased sexual desire. If an infant is anemic, they are susceptible to more crying and irritability. Worse still, it may affect brain development.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
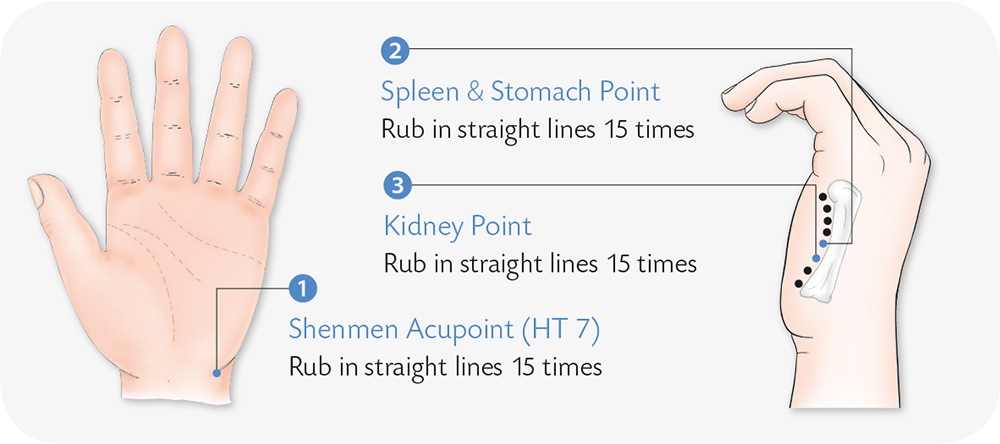
Hand Exercises
1. Open your palm, spread out the fingers, and use a stick to jab the center of the palm in evenly-spread dots.
2. Use a toothbrush to brush up and down the center of the palm. Repeat 30 times.
3. Place a ball in the center of the palm, spread the fingers, and use the mobility of the roots of the fingers to roll it clockwise and counter-clockwise 10 times respectively.
1. Maintain a balanced diet. Eat regular meals of an appropriate size. Avoid excessive drinking and eating. Choose food of many varieties, and avoid biases in dietary components.
2. Eat food rich in iron, such as pig’s liver and blood, lean meat, dairy products, beans, rice, apples, and green vegetables.
3. Drink more tea, which supplements folic acid and vitamin B12 and is conducive to the treatment of megaloblastic anemia. However, for those with iron-deficiency anemia, do not drink tea that may hinder the absorption of iron, and eat more acidic food instead.
4. Avoid spicy, raw, and cold food, as they are not easy to digest.
5. Cold
Cold is an illness that goes away after running its course. There are two types: Common cold and influenza. Common cold is a common respiratory illness caused by a cold-causing virus, whereas influenza is an acute contagious respiratory epidemic caused by flu viruses.
Colds are caught primarily because exogenous negative qi attacks the body via the skin, mouth, and nose when the system is weak and has decreased resistance to diseases, and when it is unable to adapt to drastic weather changes.
Manifestations and Symptoms
According to TCM, there are three types of cold: wind-cold, wind-heat, and damp-heat.
Wind-cold: In addition to the general symptoms of a stuffy nose, sneezing, coughing, and headache, the patient has an aversion to cold, a low-grade temperature but no sweat, sore muscles, clear and watery nose discharge, thin white phlegm, a painful and swollen throat, absence of thirst or a penchant for hot drinks, and sparse white tongue coating.
Wind-heat: In addition to the general symptoms of a stuffy nose, runny nose, coughing, and headache, the patient runs a high temperature, has thick, sticky yellow phlegm, and a sore throat (usually starting before other cold symptoms); sputum is usually yellow or dark, and the patient may experience constipation.
Damp-heat: Aversion to cold, feverish sensation, no taste in the mouth, headache, distending sensation in the head, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
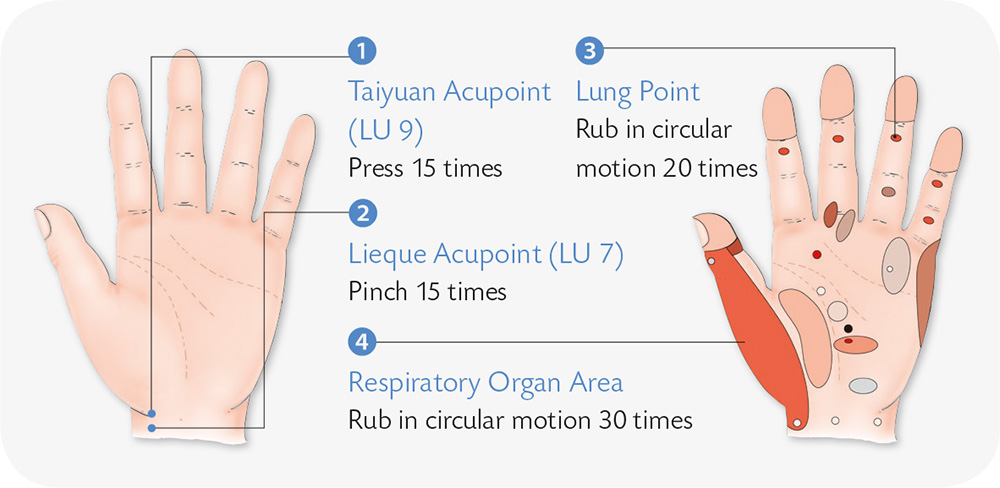
Hand Exercises
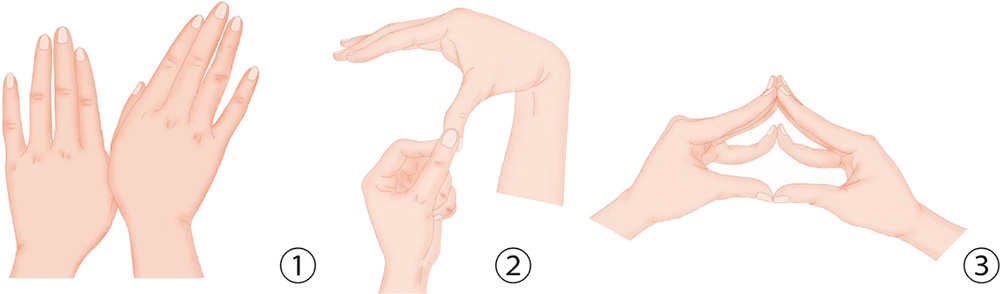
1. Bend the fingers slightly, align your thumb with the middle finger, and press the tips of the two fingers against each other.
2. Use your thumb and the index finger to press and rub the center of the other palm.
3. With your right thumb and index finger, pull and pinch the skin on the back of the ring finger at its root.
Other Methods
1. Tips for cold prevention: Wash hands often, open windows often for fresh air, avoid bodily contact with the affected, take adequate rest, drink plenty of water, and keep a regular daily schedule.
2. In the early stage of cold, use a blow dryer on temples for 3 to 5 minutes a few times daily, to help relieve the symptoms.
3. In addition to getting timely treatment, a balanced diet will help you recuperate. Avoid salty food, which tends to cause the diseased mucous membrane to constrict, thus exacerbating nasal congestion and throat discomfort. Besides, overly salty food can induce more phlegm due to local irritation, and can thus worsen a cough. Avoid sweet and oily food too, as sweetness is conducive to dampness, and oily food is hard to digest. Therefore, stay away from all kinds of candy, sugary drinks, and fatty meat when you have a cold. Avoid spicy food and food containing hot energy, because they are likely to drain your body’s fluid, encourage heat, and generate phlegm that is hard to spit out.
4. Soak your feet in warm water for 15 minutes every night, with the water covering your instep. Your feet should turn red after soaking.
6. Pharyngitis
This is an upper respiratory tract disease. Based on the time since its onset and its various symptoms, it can be acute or chronic.
Acute pharyngitis is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. It often happens in winter and spring, and is secondary to acute rhinitis, acute sinusitis, and acute tonsillitis. It is often a complication of contagious diseases such as measles, flu, and scarlet fever.
Chronic pharyngitis is often the result of ineffective treatments of episodes of acute pharyngitis. It can also be the result of other nasal disorders, nasal obstructions, long-term mouth breathing, and irritation of the pharynx due to physical and chemical factors, as well as chemotherapy in the neck.
The illness is often secondary to chronic conditions such as constipation, anemia, cardiovascular disease, and chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Primary symptoms are pain and itchiness in the pharynx, trouble swallowing, and a feverish sensation. When compounded with laryngitis, the patient will experience hoarseness of the voice if not severe, and loss of the voice if severe.
Adults mainly suffer symptoms in the pharynx. Early signs include dryness and itchiness, and a burning sensation. It then progresses to pain, which exacerbates when swallowing, excessive secretion of saliva, and ear pain on the inflamed side of the pharynx.
Frail adults or young children may manifest general symptoms such as fever, aversion to cold, headache, poor appetite and sore limbs.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
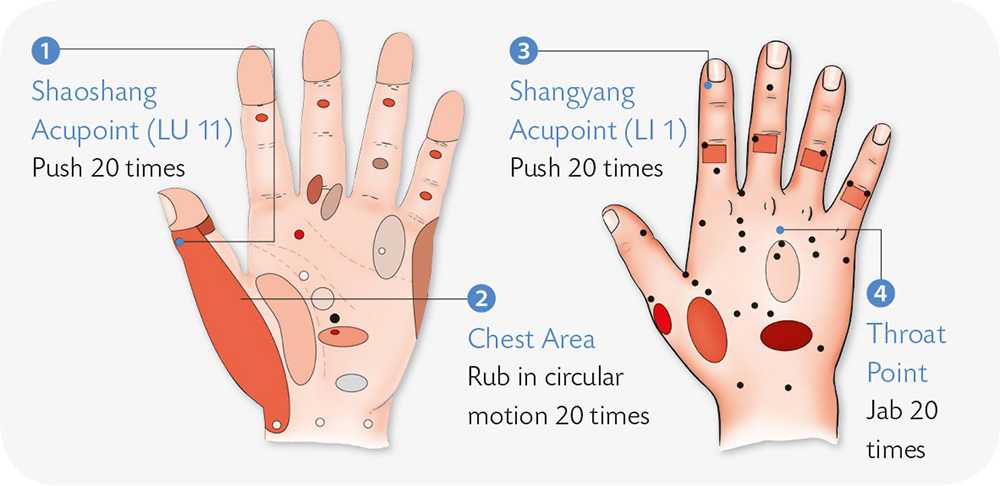
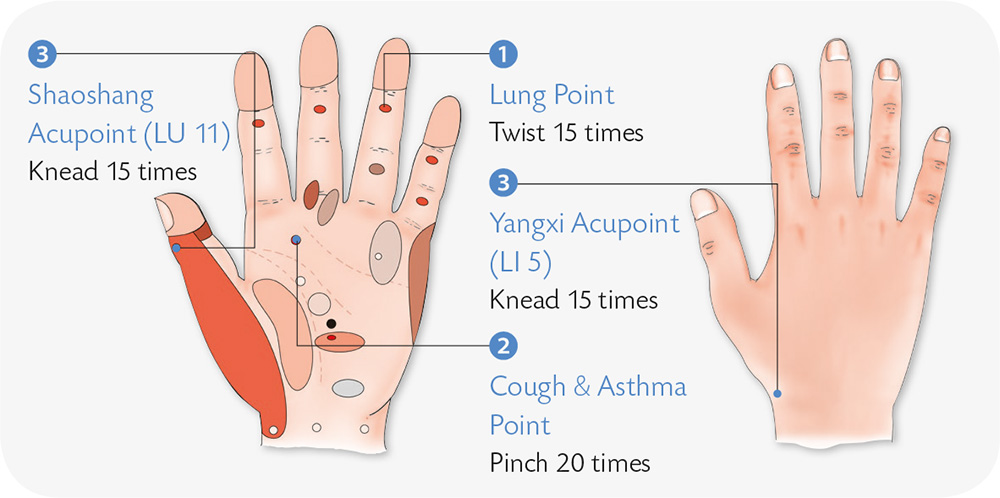
Hand Exercises
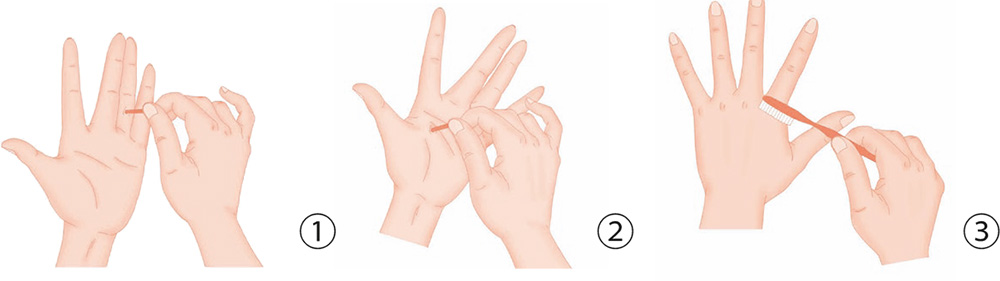
1. Use a stick to jab the ring finger in evenly-spread dots, starting from the fingertip downward; at the same time take deep breaths.
2. With the palm facing inward, spread the five digits, and use a stick to jab the transverse creases of the thumb forcefully in evenly spread dots.
3. Brush the Hegu acupoint up and down with a toothbrush.
Other Methods
An appropriate diet may help the patient recuperate:
Congee with goji berries: Wash sticky rice and goji berries, and then soak them in water for 30 minutes. Cook on gentle heat and simmer until the congee is ready. Eat a bowl of it every day. The congee nourishes yin and moistens the throat, and is good for chronic laryngitis and dry throat.
Sugar cane and radish drink: Cook lily bulbs until they are mushy, then mix with sugar cane juice and white radish juice. Drink one glass before going to bed at night. It nourishes yin and reduces heat, which is good for voice fatigue and chronic laryngitis.
7. Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammation of the airways, the mucosa around the trachea, and the bronchus and surrounding tissues, usually caused by infection and other physio-chemical factors. A weakened immune system plays an important role in the formation and development of chronic bronchial asthma.
Contributing factors to chronic bronchial asthma are:
Air pollution: Chlorine, nitric oxide, and sulphur dioxide in the air can irritate the mucosa of the bronchus and may do damage to the epithelial tissue of the airways, weakening the filtering ability of the airways.
Smoking: This is the primary trigger of the disease. Irritating smoke causes the constriction of smooth muscle and encourages active glandular secretion, impeding airflow in the airways.
Infection: Respiratory infection is another important factor that can trigger the onset and worsening of asthma.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of bronchial asthma are:
• Long-term repeated coughing episodes: Mainly coughing in the morning, but also bouts of coughing and spitting of sputum when sleeping. As the disease progresses, coughing can become perennial.
• Expectoration: Usually a white viscous or serous frothy phlegm, occasionally containing blood.
• Panting: When panting is evident, it is known as asthmatic bronchitis.
The early symptoms of chronic bronchial asthma are not obvious. It often occurs in winter and subsides in spring when the weather is warm; inflammation worsens in the late stages when the symptoms persist regardless of seasonal changes. As the condition progresses, it can trigger complications such as emphysema, pulmonary hypertension, and an enlarged right side of the heart.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
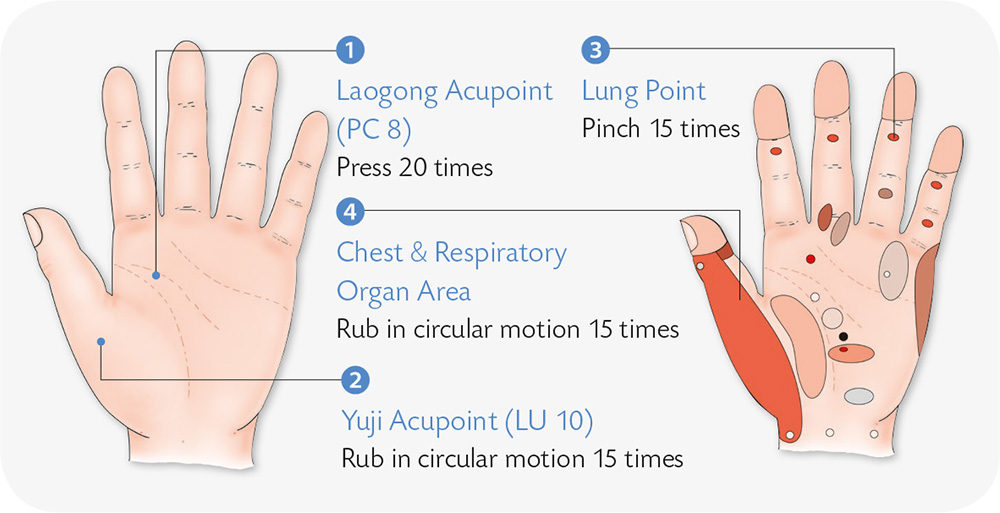
Hand Exercises
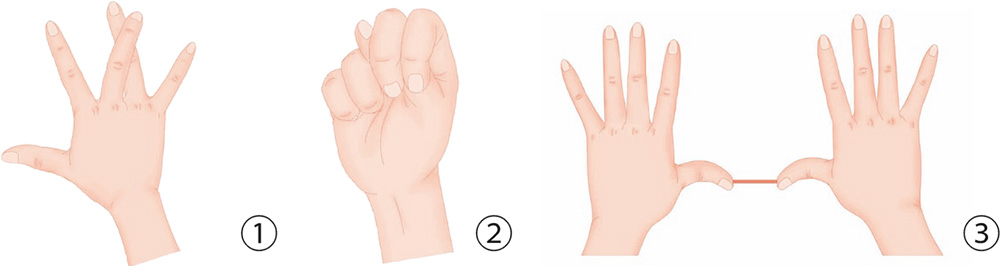
1. Place your palm flat and let your middle finger cross over to hold onto the ring finger. Move from the top down to press the ring finger with force.
2. Tuck your thumb between your middle finger and index finger, and contract the other four fingers with force to press the thumb.
3. Hold a stick with the tips of both thumbs and press it hard with the force of the thumbs.
Other Methods
People with chronic bronchial asthma should follow a good diet to keep healthy:
1. Eat more protein, such as eggs, lean meat, milk, animal liver, fish, and soy products.
2. On days when the temperature is unusually low, eat more food with high calories and warm energy to maintain heat, e.g., meat; also eat plenty of fresh vegetables and fruit to ensure adequate Vitamin C intake.
3. Avoid frozen food and ice cream in summer. Ice crystals (from the water content) are likely to irritate the oral cavity when you eat frozen food, which further reduces the temperatures of the taste buds, periodontal nerves, and salivary glands, triggering inflammation of the throat.
8. Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infection
This is an acute alveolar inflammation caused by streptococcus pneumoniae. Symptoms include the sudden onset of chills, high fever, chest pain, and coughing. Young and healthy people between the ages of 20 and 40 are at high risk of contracting it, particularly in winter and spring.
When the body’s immune system is normal, streptococcus pneumoniae are regular bacterium in the oral cavity, nose, and throat. Streptococcus pneumoniae infection often happens in winter and early spring. They become toxic when ordinarily healthy people catch cold, are caught in the rain, or are tired or drunk. It also occurs when the immune system is weakened by a viral infection.
Manifestations and Symptoms
This disease usually has premonitory symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection. The onset is sudden, accompanied by high fever, chills, and sore muscles all over the body. The sufferer’s temperature can reach as high as 39 to 40℃ within a few hours, peaking in the afternoon or early evening, with an acceleration of the pulse. Sufferers typically have flushed cheeks, nasal flaring, dry hot skin, and herpes simplex in the corners of the mouth and around the nose. Some patients may have chest pain on the affected side, which can emanate to the shoulder or abdomen; pain increases as coughing or deeper breathing occur; there is little phlegm, but blood or rust-colored secretions may be seen in it. The patient may also have occasional nausea, abdominal pain or diarrhea, which could lead to misdiagnosis as acute abdomen syndrome.
Hand Exercises
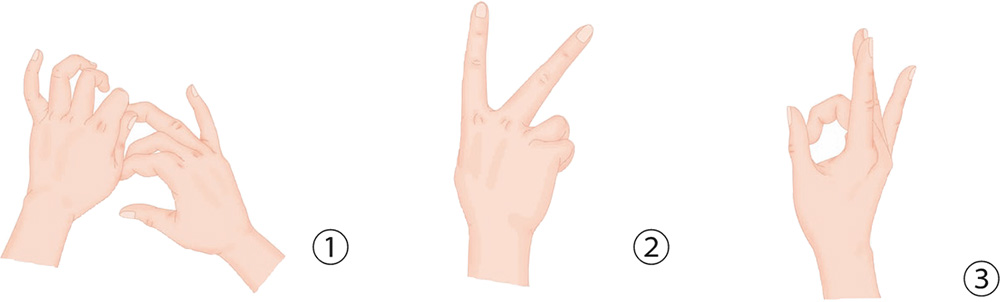
1. Use the thumb and index finger of one hand to twist and press the ring finger of the other hand in spiral rotation, starting from the root to the fingertip.
2. Stretch out your index and middle fingers and keep them attached side by side. Then, abruptly move the index finger away to form a “V” sign.
3. Place your palm flat out; bring your middle finger toward the thumb while keeping the index, ring, and little fingers straight.
Other Methods
Follow a healthy diet to promote the results of medical treatment and improve the body’s resistance to the disease:
1. Eat plenty of nutritious food that is high in calories and protein, to nourish the body’s energy after high fever.
2. An imbalance of acid and alkaline is a common sign of pneumonia. Eat more fresh vegetables and mineral-rich fruit to reverse water and electrolyte disorders.
3. Eat food that is rich in iron, such as meat and egg yolk; eat food rich in copper such as animal liver and sesame paste, as well as high-calcium food like small dried shrimps and dairy products.
9. Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is an infectious respiratory disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis. Most patients contract it through the respiratory system. Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be latent for months in dim and damp environments. When sufferers spit out phlegm, the bacteria can become air-born, infecting healthy people.
Manifestations and Symptoms
The onset is typically slow, but the disease can be long-lasting. The main symptoms include:
Systemic: Systemic toxic symptoms are a low fever in the afternoon (around 37.4 to 38°C), which can last for weeks; some patients may have recurring hot flushes on the cheeks, centers of the palms, and soles of the feet. Other symptoms include fatigue, unintentional weight loss, and night sweats.
Respiratory: Dry cough, or a cough with just a little mucus, which is usually white. When there is a secondary infection, the bronchial tract expands and the patient coughs up yellow sputum, with varying degrees of blood in it. When the patient has pleural effusion and pneumothorax, breathing can be difficult.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
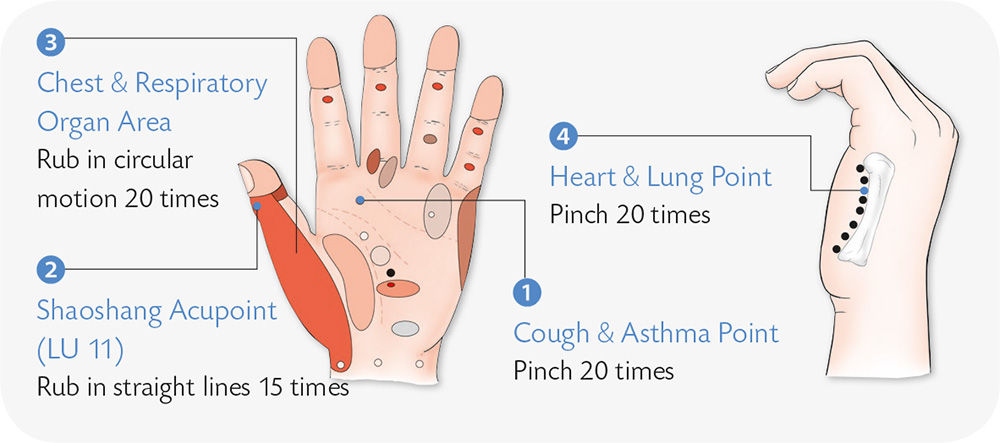
1. With the palms facing down, attach the radial sides of the heels of the palms side by side; withdraw the thumbs and rub the metacarpal sides against each other.
2. With the right palm facing down, use your left thumb and the index finger to pinch the right thumb and pull it vertically downward.
3. Align your fingertips face to face, and press them with force so that they form the biggest possible angle.
Other Methods
Treatment and recuperation from tuberculosis take a long time. The patient should be prepared to fight the disease and maintain good spirits. They should exercise regularly and incrementally to stay physically fit. They should also take good care of themselves, and cooperate with the treatment to ensure a full recovery.
Patients in the advanced stage are usually very fragile and need a higher dietary intake of protein, calories, and fiber to strengthen the immune system. During this period, patients should stay in bed, especially those who are feverish, coughing up blood, or suffering pulmonary insufficiency in the compensatory mechanisms. Those who do not have obvious toxic symptoms can engage in general exercises, but should restrict themselves to a moderate level.
From remission to stabilization, the patient should increase the intensity of exercise, but must not over-exercise to avoid the possibility of a relapse.
Patients with tuberculosis generally have a weakened immune system and should avoid contracting respiratory infections.
Bronchial asthma, also known simply as asthma, is a chronic inflammation of the airway in response to eosinophils and mast cells. This inflammation will trigger varying degrees of reversible airway obstruction.
There are three causes of bronchial asthma: Irritants in the air, infection, and food allergens. Irritants in the air are either specific or non-specific. The former includes pollen, fungus, animal hair, and dander, whereas the latter includes chemicals such as sulphuric acid, sulphur dioxide, and chloramine. The development and onset of asthma is related to repeated infections of the respiratory airway. It is not uncommon that some food may trigger asthma attacks.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Asthma manifests itself as a sudden difficulty breathing, accompanied by wheezing, rapid breathing, and foamy sputum. Inhaling is relatively easy, but exhaling is hard. During an attack, the patient can hear his or her own wheezing. Onsets most often occur at night or early in the morning. Asthma attacks come and go. Most will subside on their own. In some cases, an attack can last 24 hours, resulting in more serious conditions such as cyanosis, when the patient’s lips and extremities turn bluish.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
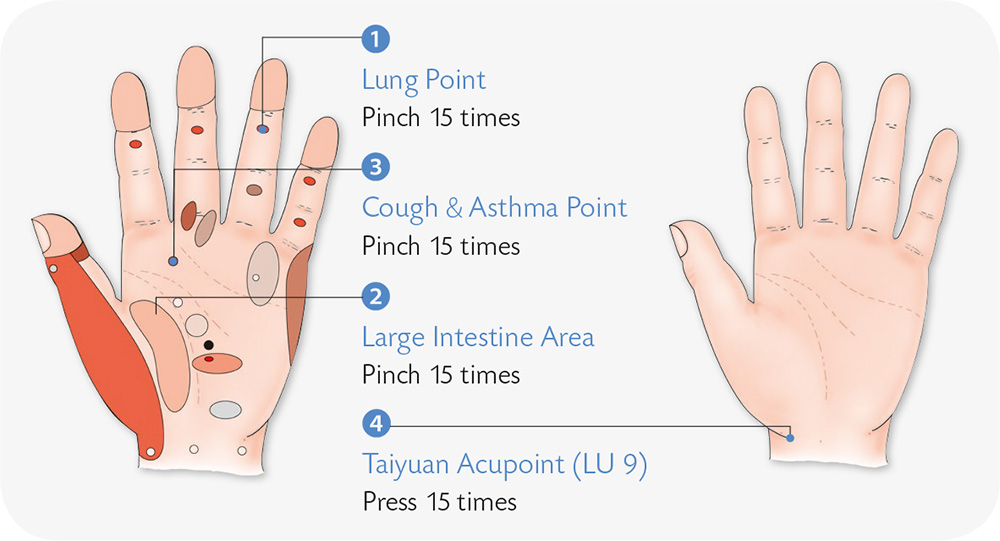
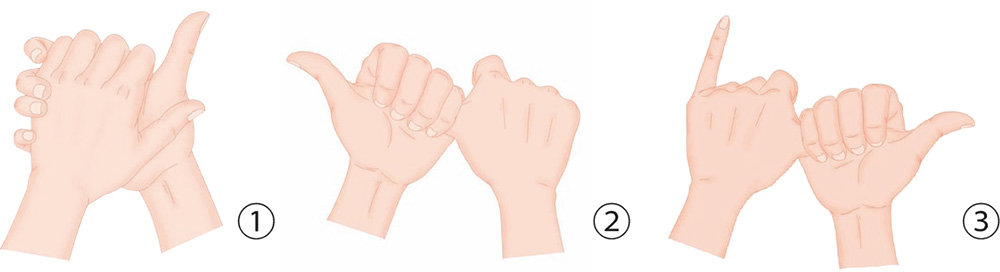
1. Hold your right palm with the left; with your fingers, firmly clasp the back of your other hand, and press and squeeze with force.
2. With the four fingers of the left hand, clasp the thumb of the right hand by its root and pull it outward slowly but forcefully.
3. Wrap the four fingers of the right hand around the left thumb by its root and pull the thumb outward slowly but forcefully.
Other Methods
Do more exercise to improve physical fitness and strengthen the immune system. Stay away from allergens. These measures will help to prevent bronchial asthma attacks.
You should also eat fresh, light food containing plenty of protein and iron.
1. Avoid spicy and irritating food, especially fish, shrimps, and prawns, which are considered likely to trigger asthma.
2. Avoid fatty meat and similar food, as oil tends to generate dampness in the body.
3. Avoid food that generates wind in your body, such as chives and sweet potatoes.
4. Eat more lean meat, animal liver, tofu, and soy milk.
5. Eat plenty of fresh vegetables and fruit. Fresh vegetables not only provide the human body with a variety of vitamins and inorganic salt, but also help to clear phlegm and remove fire; fruit not only helps to clear phlegm and relieve coughing, but also invigorates the spleen and nourishes the lungs.