Diseases of the Digestive System
The digestive system consists of the digestive tract and digestive glands. The digestive tract includes the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. It also includes auxiliary organs such as the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. The system ingests, transports, and breaks down food into smaller components so nutrition can be absorbed into the body. Waste from digestion is ejected from the body through defecation. Therefore, the system is of vital importance. A healthy digestive system is related to diet, and promotes a sense of happiness. In this chapter, hand reflexology will assist you in alleviating the symptoms of digestive discomfort and improving the health of your digestive system.
1. Chronic Gastritis
Chronic gastritis is a long-term inflammation of the stomach’s mucosa caused by a variety of diseases. It may be triggered or worsened by long-term and excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, irregular eating habits, ingesting food that is too cold, too hot, too coarse, or too hard, and drinking strong tea and coffee. Chronic gastritis is hard to cure when the mucosa is infected by helicobacter pylori.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Many patients have no obvious symptoms. A common symptom is discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen after a meal, or irregular, intermittent, or constant pain in the upper abdomen. If necessary, the patient may undergo a gastric biopsy with gastroscopy to determine whether there is inflammation.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
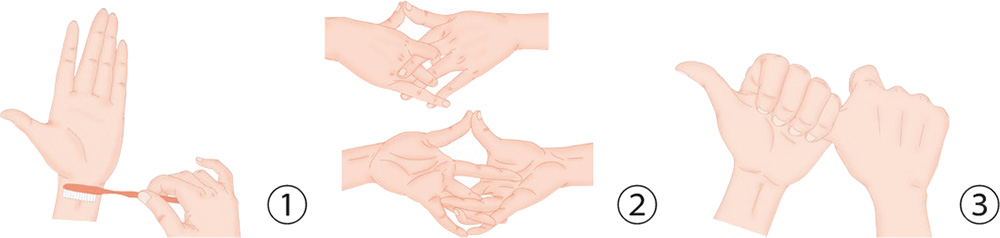
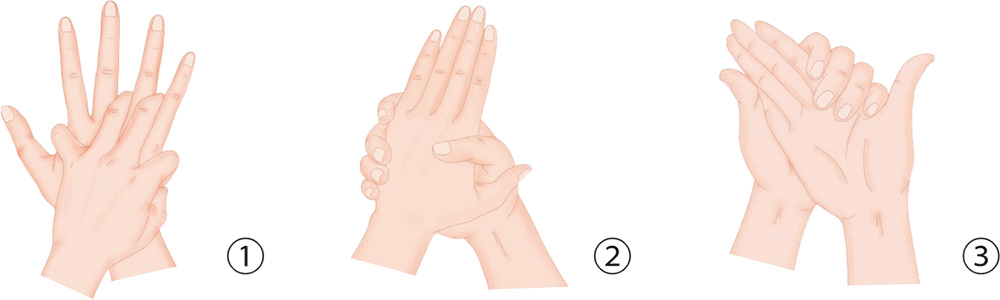
1. Brush the arm side of your wrist crease to the left and right with a toothbrush 30 times.
2. Press your thumbs against each other; hold onto the left middle finger with your right index finger; hold onto the left ring finger with your right middle finger, and press your right little finger against the left little finger.
3. Wrap the four fingers of your left hand around your right thumb by the root, and pull it away forcefully but slowly.
Other Methods
Those suffering from chronic gastritis should maintain a healthy lifestyle and good eating habits:
1. Maintain a controlled diet, avoiding overeating and irregular meal schedules.
2. Be vigilant about food hygiene; make sure external microorganisms cannot attack your mucosa.
3. Try to eat food that is refined, easy to digest, and nutritious.
4. Stay psychologically healthy, because depression, extreme tension, and fatigue can result in the dysfunction of pyloric sphincter, causing bile reflux that eventually leads to chronic gastritis.
The following measures should be taken to prevent chronic gastritis:
1. Avoid smoking and alcohol. Harmful chemicals in tobacco will stimulate the secretion of gastric acid, which erodes the mucosa. Excessive smoking will cause bile reflux. Excessive alcohol intake or long-term drinking of strong liquor will cause gastric mucosal congestion and edema, or even erosion, increasing the risk of chronic gastritis.
2. Medicine abuse (because of other diseases) may harm the mucosa, eventually triggering chronic gastritis or gastric ulceration. Only use drugs as prescribed.
3. Maintain an appropriate diet, avoiding strongly acidic and spicy food, as well as food that is cold and raw. These types of food will irritate the stomach, and are not conducive to the prevention and treatment of chronic gastritis.
Gastroptosis is the downward displacement of the stomach below the normal range, usually around or even below the iliac crest. The disease is caused by a deficiency in diaphragm suspension, or by the declining function and loosening of the gastrohepatic and gastrocolic ligaments, a decline in intra-abdominal pressure, and abdominal muscle relaxation. Coupled with the patient’s constitution and build, the stomach drops down in the shape of an open fishhook. This is what is referred to as “tensionless stomach” in the case of gastroptosis.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Those affected with slight downward displacement may not experience any symptoms.
Those affected with more evident downward displacement may experience discomfort and fullness in the upper abdomen. Symptoms after meals include burping and belching, anorexia, and constipation. Sometimes the patient will feel a dull pain deep in the stomach, which is exacerbated after meal, when standing up, and when tired.
Those affected with the condition in the long term may suffer weight loss, feebleness, and palpitations, as well as perpetual constipation. The unpleasantness of many of the symptoms may lead to mental stress, which causes insomnia, headaches, dizziness, apathy, and depression.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
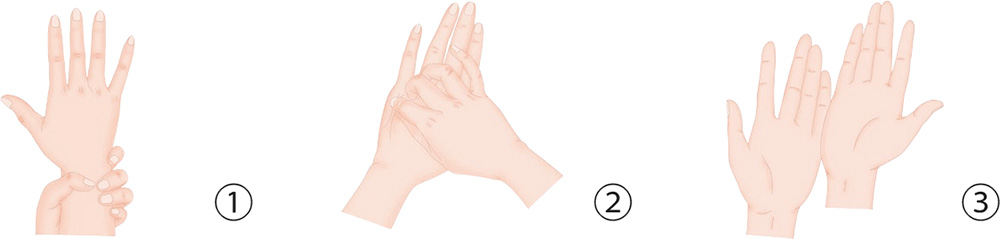
1. With your right palm stretched out facing against you, hold your right wrist in place with your left hand; then, turn your right palm clockwise and counter-clockwise 10 times respectively.
2. With your right thumb and index finger, pinch the skin along the metacarpal bone of the little finger until you reach the wrist crease.
3. With your palms facing up, press the heels of the palms against each other, and rub up and down; repeat it as many times as you want.
Other Methods
The key to the treatment of gastroptosis is to enhance your physical fitness, improve the nutritional components in your diet, and do more exercise that uses the abdominal muscles.
Develop healthy dietary habits: Eat smaller portions but more often, 4 to 6 times a day; chew carefully before swallowing to stimulate gastric movement and accelerate the gastric emptying rate, thus alleviating abdominal discomfort. Reduce the intake of spicy and irritating food, e.g., chili peppers and ginger. Limit your consumption of alcohol and coffee; maintain a balanced food intake of various nutrients.
Exercises: Practice qigong and medical exercises, accompanied by walking, jogging, massage, and taiji. When practicing qigong, lie on your back in bed. Movements should be gentle and slow, with relaxed muscles, and should take place in a quiet ambiance. qigong can improve the overall health of the body. It can also increase primordial qi in the spleen and stomach, promote gastrointestinal movements, and benefit digestion and absorption, resulting in increased appetite.
3. Peptic Ulcer
A peptic ulcer is a chronic ulceration of the digestive tract and tissues by gastric juice, which contains acid and pepsin. Clinical research has found that over-secretion of gastric acid, helicobacter pylori infection, and the declining protective ability of mucosa are primary factors.
The main features of peptic ulcers are:
1. Chronic, cyclic, and rhythmic onset of upper and middle abdominal pain; an onset typically happens 1 to 2 hours after meal and lasts 1 to 2 hours. The pain subsides when the stomach is empty.
2. A duodenal ulcer often happens on an empty stomach. The symptoms are exacerbated after meals.
3. Other gastrointestinal symptoms include increased secretion of saliva, heartburn, gastric reflux, acid reflux, belching, nausea, and vomiting.
4. Even if a normal appetite is maintained, fear of pain may lead to reduced food intake, causing weight loss.
5. Systemic symptoms may include neurosis such as insomnia, a slow pulse, and excessive sweating.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
Hand Exercises
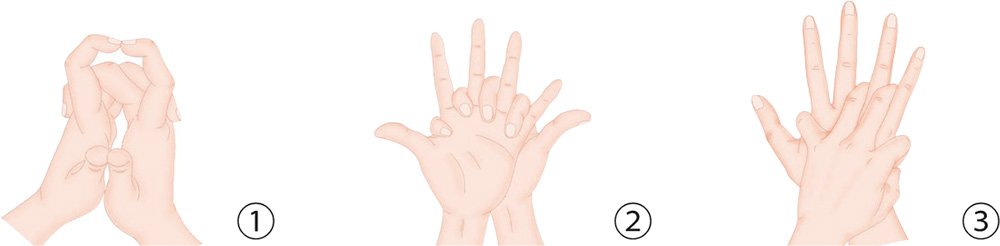
1. Press your index fingers and the thumbs against each other at the tip, and interlock the remaining fingers. Press the palms against each other with equal force to create strong resistance.
2. With your left palm facing up, spread the fingers out; interlock your right hand with the fingers of the left hand from behind, and use the force of the fingers to pinch and press the left hand.
3. With your right palm facing down, lock the fingers of the left hand into those of the right hand from the back whichever way you want, and press with force.
Other Methods
Good care should be taken in daily life:
1. Mental health: Ulcers are more likely to develop if you are experiencing stress, depression, anxiety, or traumatic events. Therefore, having a positive attitude to life is key to the prevention of peptic ulcers.
2. Avoid excessive fatigue: Excessive fatigue will hinder the supply of gastrointestinal blood. Over-secretion of acid and decreased secretion of mucus may damage the mucosa and result in peptic ulcers.
3. Avoid excessive drinking and smoking: Alcohol can be harmful to the protective wall of the gastric mucosa, and may trigger cirrhosis and chronic pancreatitis, thus exacerbating stomach conditions. Smoking can stimulate the secretion of gastric acid and pepsin, which deepens the damage to the mucosa.
4. Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers
It is generally believed that spasms of the blood vessels and muscles of the stomach and duodenum cause the lining of the gastric and duodenum walls to receive inadequate nutrition. This leads to reduced resistance against erosion of the gastrointestinal mucosa by gastric juices.
Healthy people have strong gastrointestinal mucosa that can ward off erosion by gastric acid and pepsin, but when problems occur in any part of the whole chain, ulceration will develop.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Tarry stools and hematemesis (spitting blood): Spitting blood often signals gastric tract bleeding above the duodenum, but tarry stools can be a result of bleeding anywhere in the gastric tract. Spitting blood is invariably accompanied by tarry stools.
Shock: Excessive blood loss will result in shock, a pale complexion, and thirst.
Anemia: Heavy bleeding will lead to reduced counts of hemoglobin, red blood cells, and hematocrit.
Hand Exercises
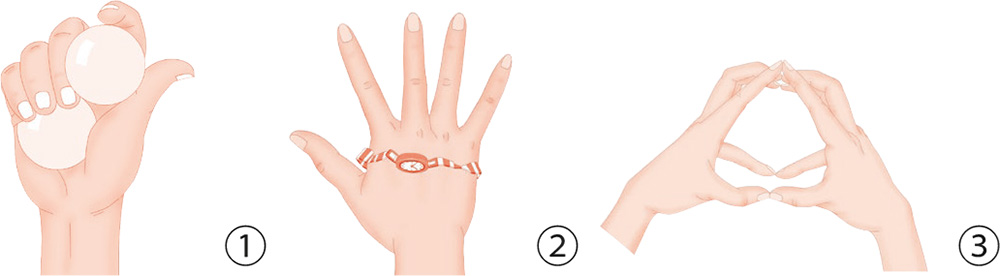
1. Place two balls in your palm, and use the mobility of your fingers to turn them, keeping them apart.
2. Strap a wristwatch or an elastic band on your palm, and stretch your hand so the strap of the watch or the elastic band will stretch or contract as your hand does.
3. With your palms facing each other, press the tips of the five digits to form a hollow ball. Press the tips of the fingers against each other with force.
Other Methods
Daily care for those suffering from gastric and duodenal ulcers involves the following:
1. Healthy cooking: Healthy cooking methods include steaming, boiling, pan-frying, and stewing. Eat lightly, with ginger and pepper to warm the stomach and help protect the mucosa. Food prepared by deep-frying, frying, and smoking are not as digestible, and will impede the healing of the ulcer.
2. Avoid spicy and irritating food, including food that stimulates the secretion of gastric acid, e.g., meat soup, raw green onion, raw garlic, coffee, alcohol, and strong tea, or frozen and extremely hot food, which will irritate the ulcers and worsen the condition.
3. Maintain a nutritious diet with varied ingredients that are easy to digest, and rich in protein, calories, and vitamins. Also, vitamin-rich vegetables and fruit will help expedite the healing of ulcers.
4. Eat food that lubricates the bowels, such as honey, oats, and celery, to prevent dry stools.
5. Calculus of Gallbladder
Calculus of the gallbladder, also known as gallstones, refers to hardened deposits within the bile ducts, and is one of the most common diseases of the digestive system. Clinical manifestations include sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the abdomen, and acute inflammation.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Early gallstones do not usually have any symptoms. Most are detected through normal physical examination. Sometimes people with gallstones may feel slight discomfort that may be mistaken for gastric disease and not treated in a timely manner.
Some people develop only one stone, while others may have multiple. Sometimes, stones exist freely in the gallbladder. They do not lodge in any specific location, and have no symptoms, hence being called symptomless gallstones.
Small stones may be lodged at the neck of the gallbladder. Symptoms may worsen when one eats oily food that causes the organ to constrict, or when one changes position during sleep. When the gallstone is stuck in the neck of the gallbladder blocking the duct, pressure will grow. Bile cannot be emptied through the neck and duct, leading to a clinical symptom known as biliary colic, which manifests as continued and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right abdomen, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. If the stone is stuck somewhere and stops moving, the gallbladder can swell and become infected, which will eventually progress to acute cholecystitis.
Hand Exercises
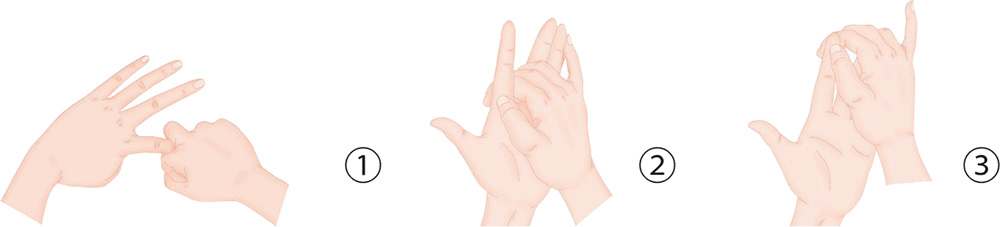
1. With your right index finger and middle finger, clutch the left index finger by its root and pull away slowly but forcefully.
2. With the thumb and index finger of one hand, pinch and press the root of the index finger of the other where the metacarpal bone meets the index finger.
3. With the thumb and index finger of one hand, pinch and press the tip of the index finger of the other hand.
Other Methods
Those affected with gallstones should maintain a healthy lifestyle and dietary habits:
1. Eat meals at regular times to help evacuate old bile and secrete new.
2. Maintain a varied diet including both meat and vegetables, a good proportion of refined grains, and coarse food grains; food intake should also comply with your physical characteristics; eat more fresh vegetables and fruit, and reduce the intake of high-calorie food.
3. Avoid crash diets.
4. Engage in sporting activities to strengthen the functions of your internal organs and prevent bile stasis.
Acute cholecystitis is caused by chemical irritants and bacterial infection. Chronic cholecystitis is a pathological change in chronic inflammation of the gallbladder that comes and goes, often lasting for up to ten years. Some patients may suffer biliary colic and acute attacks.
Most cases of cholecystitis are caused by gallstones, a condition often found in obese and middle-aged women. Some patients are affected due to attacks of E. coli, aerobacter aerogenes, and pseudomonas aeruginosa. A small number of acute cholecystitis cases are caused by trauma and chemical irritants.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Acute cholecystitis: Patients primarily experience sudden upper-right abdomen pain, fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting; some also experience jaundice and even shock.
Chronic cholecystitis: Clinical signs are not evident except for abdominal fullness of varying degrees, discomfort in the upper abdomen or upper-right abdomen, constant dull pain or pain in the right shoulder blade, and symptoms of indigestion such as heartburn, burping and belching, and acid reflux. The symptoms may be exacerbated after eating oily food.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
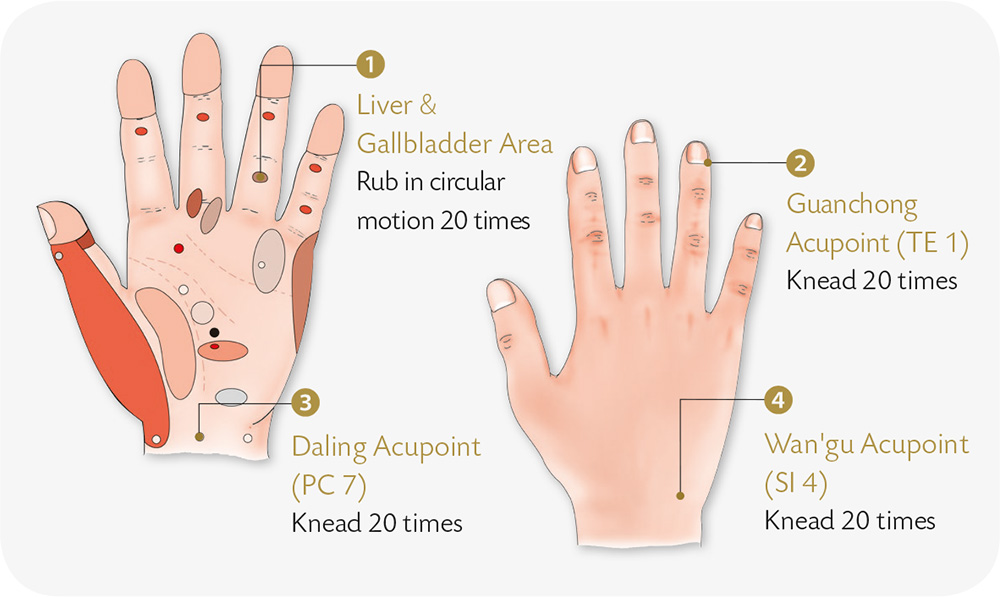
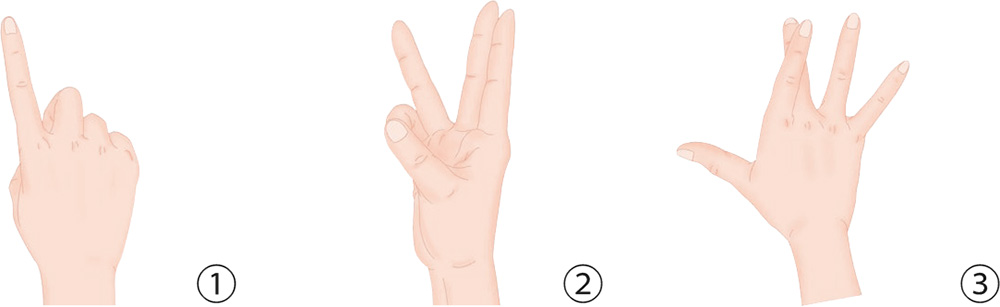
1. With your palm facing outward, abruptly withdraw the thumb and the middle, ring, and little fingers, leaving only the index finger, as if signaling the number “1.”
2. Straighten the index and the middle fingers to form a finger-counting sign for the number “2” (Note: all other fingers bend inward, as in a fist) and then quickly stretch out the ring finger. Repeat 10 times.
3. Cross your index finger over the middle finger, and press the middle finger down with as much force as you can.
Other Methods
A healthy lifestyle will help prevent the condition from deteriorating, and will improve your overall physical fitness:
1. Rich intake of vitamins, particularly Vitamins A, C, and E.
2. Appropriate intake of dietary fiber to stimulate intestinal movement and prevent the onset of cholecystitis.
3. Eat small portions often, which will stimulate the contraction of the gallbladder to empty bile and promote its flow.
4. Healthy cooking methods, such as boiling, roasting, steaming, blanching, braising, and stewing; avoid high-temperature stir-frying, deep frying, or frying, as hot oil is likely to irritate the bile duct, causing acute spasms.
5. Fasting is recommended when the patient is experiencing acute biliary colic, but an IV injection can be given as a nutritional supplement.
7. Enteritis
Enteritis is divided into two kinds according to the course of the illness: Acute and chronic.
Shigella is the most common bacteria that causes enteritis. Other factors include eating inedible items, contaminated or stale food, chemical irritants, exposure to toxic amounts of heavy metals, as well as some allergies and the overuse of antibiotics.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Digestive tract symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea are the main symptoms.
Systemic symptoms: Usually not obvious, but if it is more serious, the patient may experience fever, dehydration, acid poisoning, and shock.
Physical signs: None in the early stage, or if the disease is not serious. The patient may experience slight pain when pressing the upper abdomen or around the belly button, with progressive gurgling sounds. The course of the disease for an average patient is usually short, and cases will clear up on their own within a few days.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
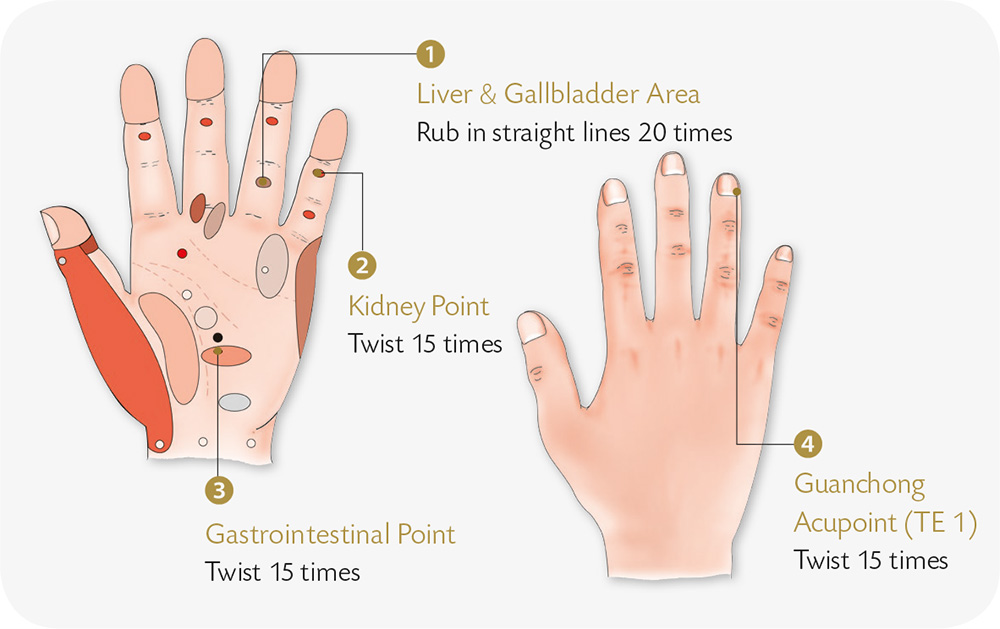
Hand Exercises

1. With your palms facing each other, press the tips of all the fingers against each other to form a hollow ball.
2. Use the middle and index fingers of the left hand to clutch the middle finger of your right hand. Pull away slowly and forcefully.
3. With your right thumb and middle finger, pinch and twist the left middle finger in spiral rotation.
Other Methods
Patients should pay attention to the following:
1. Maintain a diet that is low in oil and fiber, and eat only light fluid food at the onset of the disease.
2. When the number of bowel movements decreases, stay on a full liquid diet such as meat soup, milk, soy milk, and egg soup. Then, move on to a light semi-fluid diet.
3. When diarrhea stops completely, add soft food such as egg custard, slices of fish, ground lean meat, and vegetable paste. Control the total amount of food you eat every day to avoid indigestion.
As the condition improves, the patient may start a course of food therapy to aid recuperation:
Coix Seed Congee: Coix seeds and short grain rice (30 g to 50 g each) and some sugar. Wash the coix seeds and short grain rice clean. Add water to the mixture and cook until tender; then add some sugar. After the sugar melts, it is ready to eat.
Lotus Seed Congee: Lotus seeds and short grain rice (30 g each), roasted lentils (10 g), 10 small dates, and some sugar. Wash the rice, put all the ingredients together, and cook them. When it is done, add sugar and eat.
8. Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are clusters of varicose veins at the end of the rectum and anal canal. The condition is often found in adults. Due to the varying locations of the growths, hemorrhoids are classified as external, internal, and mixed.
They have many causes.
Anatomical reasons: When a person stands or sits, the rectum and the anus are pulled by gravitational force and the pressure from the organs. This makes the upward flow of blood in the veins difficult, and therefore blood vessels may expand due to blood stagnation.
Occupational reasons: Some people often stand or sit for a long time, or carry heavy objects for long trips. This hinders the flow of blood back to the heart, slowing circulation in the pelvic area or causing congestion of the organs in the abdomen. As a result, the veins at the rectum swell and stretch to excess.
Local irritation and unrestrained eating and drinking: Cold or hot stimulation, constipation, diarrhea, excessive drinking, and eating too much pungent and spicy food are all likely to irritate the anus and rectum, causing the blood vessels to swell, affecting the reverse flow of blood in the veins and resulting in excessive stretching of the veins.
Manifestations and Symptoms
External hemorrhoids do not have obvious symptoms, but sufferers will experience a gritty or swollen feeling if they stand or walk for a long time.
Internal hemorrhoids do not cause any discomfort, but the main symptom is bleeding. With early-stage hemorrhoids, there may be a small amount of blood after bowel movements, or simply stools with blood streaks, blood accompanying stools, sprays or drips of bright red blood, or blood on the toilet paper.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
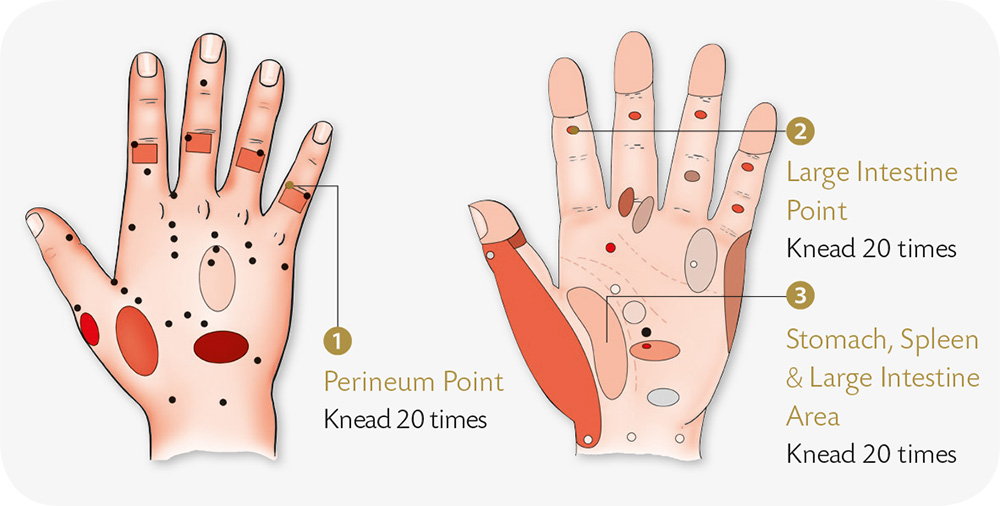
1. With your right palm facing down, lock the fingers of your left hand into those of the right hand; squeeze and press as much as you like.
2. With your right hand, hold onto your left hand horizontally; press the tips of the four fingers of the right hand onto the skin on the back of the left hand; in the meantime, press your left palm against your right palm as hard as you can.
3. Place the back of your right hand above your left palm, and bend the four fingers of your left hand to squeeze your right palm; in the meantime, press your right palm against your left hand.
Other Methods
For people affected with hemorrhoids, good dietary habits and a healthy lifestyle are important:
1. Eat more fresh vegetables and fruit rich in fibers and vitamins, and avoid spicy and irritating food.
2. Go to see a doctor and get appropriate treatment if you have persistent constipation; do not take laxatives or use enemas over an extended period of time, as doing so may desensitize the mucosa of the rectum, incapacitate the bowel, and worsen your constipation, eventually resulting in hemorrhoids.
Due to the high recurrence of hemorrhoids, measures should be taken to prevent them:
1. Take exercise, and increase the body’s resistance to diseases.
2. Maintain a healthy lifestyle, such as avoiding alcohol and pungent and spicy food; eat more vegetables and fruit, and develop a fixed time for bowel movements.