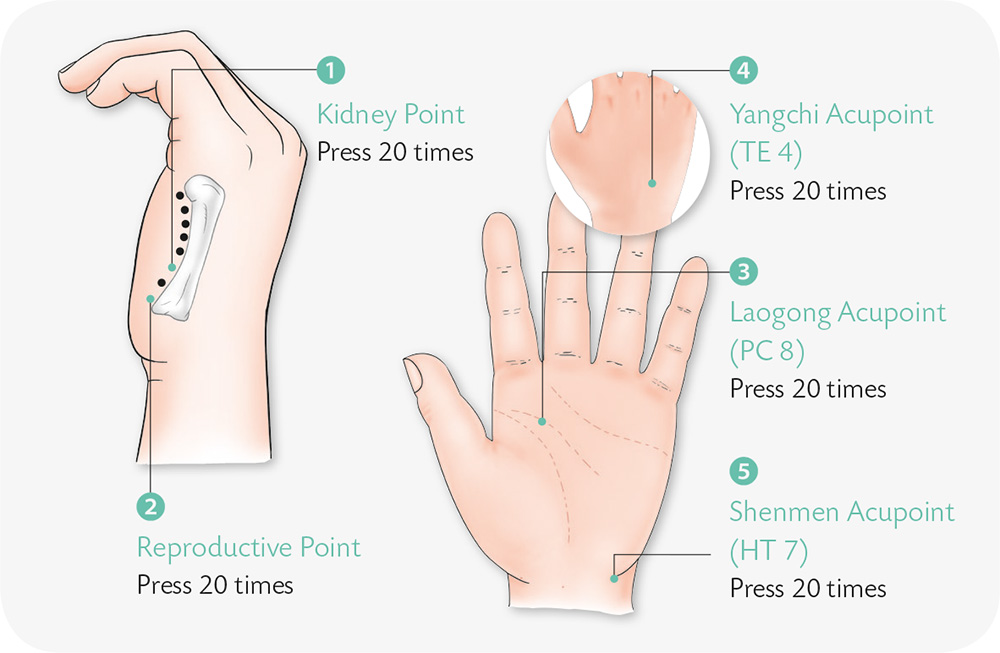
Disorders of the Orthopedic and Genito-Urinary Systems
There are 206 bones in an adult human body. They are connected by joints and ligaments, all of which constitutes the skeleton and gives the human being its basic form. The skeletal system also protects the internal organs and supports the functions of athletic performance. The urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureter, bladder, and urinary tract, functions primarily for the purpose of excretion. The reproductive system, however, serves to continue the human race generation after generation through a variety of biological activities including insemination and conception. This chapter aims at improving the health of your orthopedic, urinary, and reproductive systems.
1. Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is a condition caused by stimulation and pressure on the roots of the nerves.
Chronic wear and tear is believed to be the primary cause of cervical spondylosis. It damages local ligaments, muscles, and joint capsules resulting in local edema and hemorrhage. Then, infection occurs and spurs may develop, affecting the local nerves and blood vessels. Acute and chronic neck injuries after prolonged periods of working with the head down, or incorrect posture, violent impact, cervical deterioration, trauma to the neck, and chronic soreness are all major causes of cervical spondylosis.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Its main symptoms are soreness of the head, neck, shoulders, back, and arms, with a stiff neck restricting movement; a heavy sensation in the shoulders and back; weak arms, numbness of the fingers, and an inability to grasp things firmly. The patient may sometimes experience vertigo and palpitations. If the condition is serious, the patient may experience light-headedness, headache, blurred vision, dry and swollen eyes that are hard to open, clogged ears, tinnitus, loss of balance, racing heart, nervousness, and bloating of the gastro-intestinal tract. Other symptoms include difficulty swallowing and voice loss. If long-term treatment is unsuccessful, the disease may trigger psychological symptoms such as insomnia, irritability, anger, anxiety, and depression.
Hand Exercises
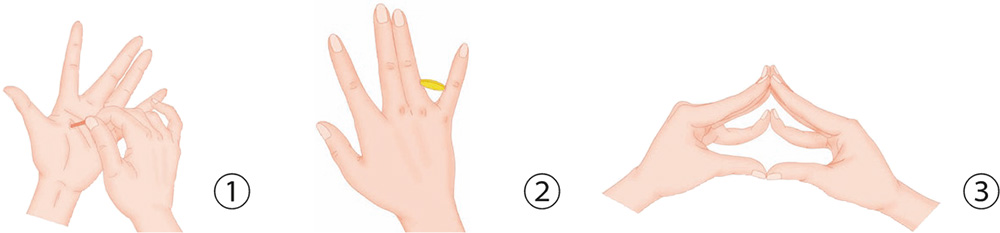
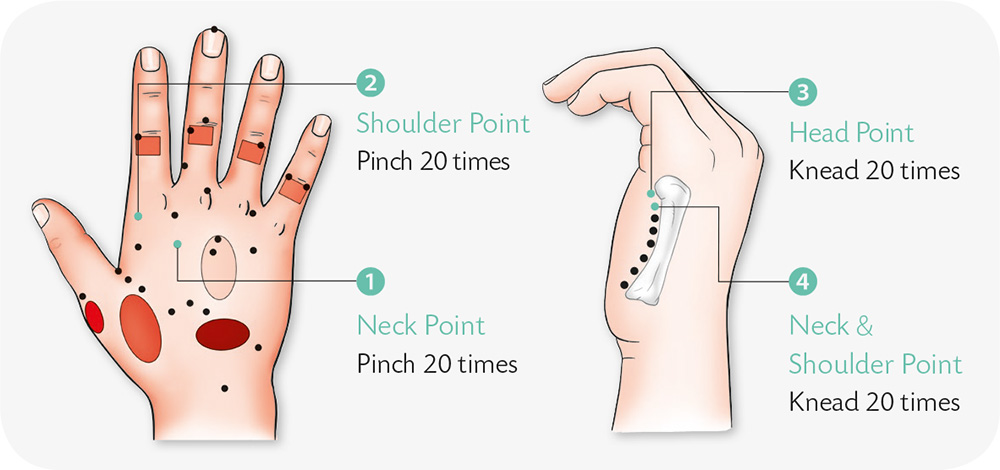
1. With your palm facing inward, spread out the fingers. Use a stick to jab the transverse creases of the thumb evenly from the top down.
2. With your palm facing outward, place a coin horizontally between the proximal phalanges of the little and ring fingers. Hold the coin there with force, and move it up to the fingertip.
3. Press your thumb and four fingers against each other to form an angle, and keep pressing to make it as large as you can through resistance.
Other Methods
1. During breaks at work, do some activities that help relax the cervical spine and prevent cervical spondylosis, such as folding the neck up and down, and turning your head to the left and right. Do this once or twice, and repeat it for 10 minutes every day.
2. Maintain a good sleeping posture. It is best to use a soft contoured pillow to keep the neck in its natural curve. The height of the pillow should be about 10 cm.
3. Maintain a good posture at work. Try to sit in a posture with your head neither tilting up nor lowering down. Move your neck after working for an hour, to give the ligaments and muscles a rest.
Frozen shoulder is a condition characterized by damage and wear and tear to the soft tissues, muscles, ligaments, tendons, synovial bursae, and joint capsules of the shoulders. This age-related deterioration gradually develops into a chronic non-bacterial inflammation around the shoulder’s joint capsules and soft tissues.
Frozen shoulder is often found in people around 50 years of age. The causes are:
1. Prolonged periods of overwork and incorrect posture causing chronic strain injuries.
2. Injury to the upper limbs, meaning that the shoulder has to remain in a fixed position for a long period of time, causing the tissue around the shoulder to shrink and stick together.
3. Sudden injury to the shoulder due to strain, which is left untreated or treated incorrectly.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Shoulder pain is the most evident symptom. A pain begins somewhere in your shoulder, which is clearly related to an action or posture you have taken. As the condition progresses, the area of pain grows to involve the middle part of the upper arm, accompanied by limited movement of the shoulder. When the condition worsens, the affected arm cannot even move to brush the hair or wash the face.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
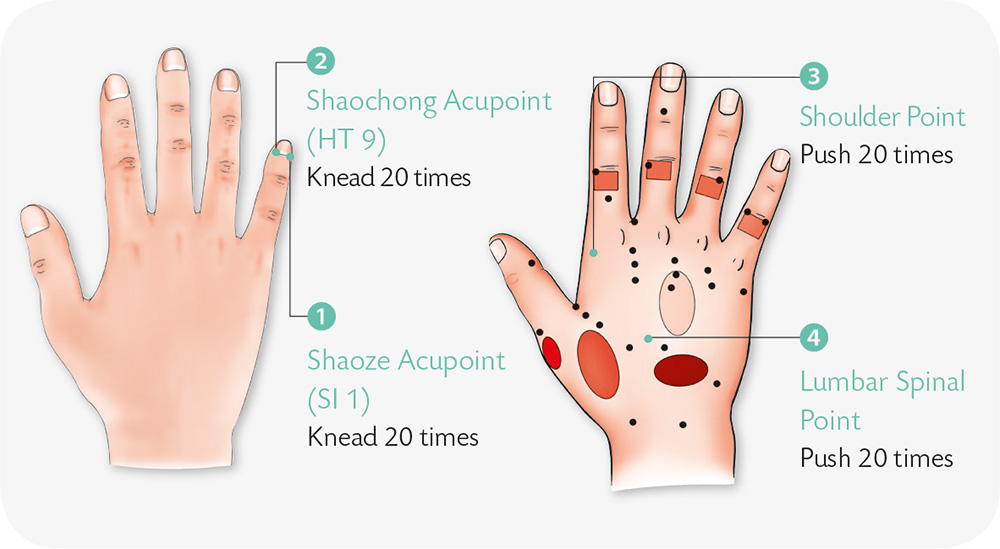
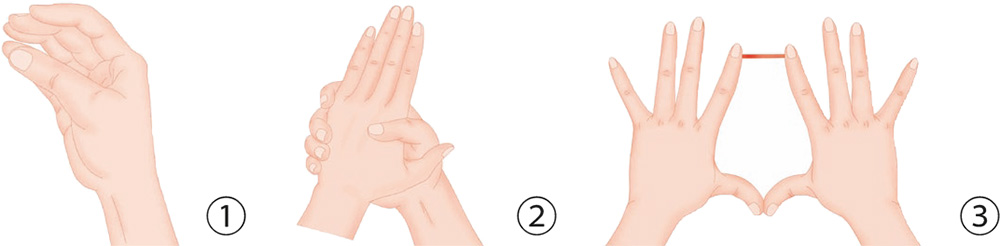
1. Bend the thumb and the fingers of your right hand slightly, forming a hollow fist, with the thumb and the little finger pinching each other.
2. With your right hand, hold onto your left hand horizontally, with the tips of the four fingers jabbing and pressing the skin of the left hand, while the left palm presses against the right hand.
3. Hold a stick with the tips of the index fingers and hold it there firmly. In the meantime, press the thumbs against each other.
Other Methods
Keep warm and avoid letting the shoulder catch cold. If you sit working at desk, or if your shoulders remain in the abduction position for a long time, adjust your posture from time to time to avoid chronic wear and tear and accumulative injuries.
Do exercises during work breaks to relax the shoulders and neck:
• Stand up straight; keep your hands down naturally, place your feet shoulder-width apart, and lean your head as far back as possible, while keeping your eyes fixed on one object for 15 seconds.
• Use your thumbs to press and knead the back of your neck 15 times.
• Move your head to the front, back, left, and right; then do it the opposite way; do this clockwise and counter-clockwise 10 times each.
• Interlock your fingers and put your palms behind the neck; push forward with the force of your hands while your neck goes backward, the two forces resisting each other, while turning your head left and right 5 times.
If you are diabetic, or have cervical spondylosis, injuries to the shoulders and the arms, and neurological diseases, or if you have recently had an operation on the chest, be very careful if you experience any pain in your shoulder.
Lumbar disc herniation is a common illness that occurs when the inner nucleus pulposus ruptures from the annular tear and presses the nerve roots, causing a clinical syndrome characterized primarily by sciatica.
The deterioration of the lumbar disc usually starts when a person is in their 20s, compounded by accumulative injuries from daily life and work. When the disc is subject to repeated pressure, it buckles and twists, and the back of the annulus is likely to rupture. With repeated pressure, the rupture grows where the annulus becomes increasingly thinner. Any additional trauma can cause it to break, resulting in pain in the lower back radiating to the leg, or even causing neurological impairment.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Radiating pain that travels along the sciatic nerve, from the lower back and buttocks to the thigh, the leg, and the surface of the foot. The event of coughing, sneezing, bowel movements, and bending can exacerbate the pain. The pain increases when the patient is in motion, but will subside after rest. It occurs repeatedly.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
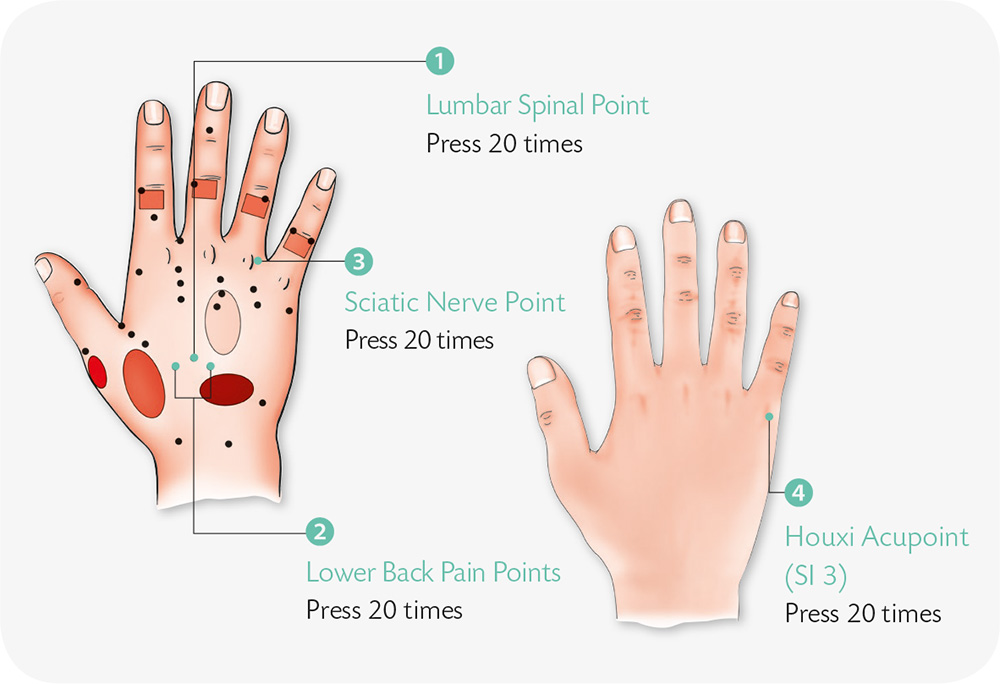
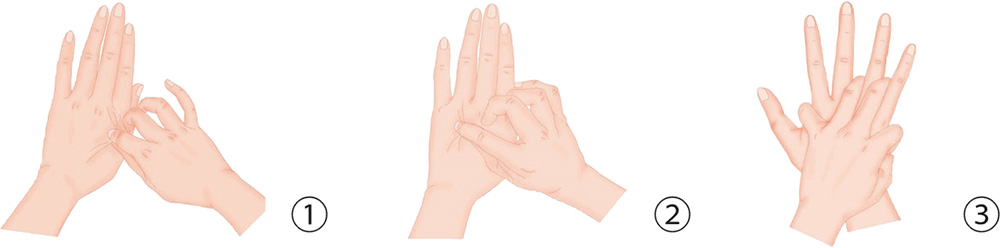
1. With your right thumb and index finger, pinch and pull the skin on the back of the left hand along the metacarpal bone of the index finger.
2. With your right thumb and index finger, pinch and pull the skin below the end of the proximal phalanx of the left ring finger.
3. With your right palm facing down, lock the fingers of your left hand into those of the right hand, and press and squeeze as you please.
Other Methods
1. Alternate work with rest; avoid staying in the same posture and repeating the same movement over an extended period of time.
2. People whose work requires bending at the waist or working at a desk for a prolonged period of time should adjust the height of their desk and chair to change posture. A 15-minute exercise session is recommended after 45 minutes of working sitting down.
3. People who have to bend very often should move regularly to stretch their back and open their chest, and should wear a wider belt.
4. Keep a healthy lifestyle; maintain regular meal times and bed times; avoid staying up late.
5. Exercise is a good way of prevention and cure, e.g., swimming and aerobics. Also, lie on your chest, lift up your head, arms, legs, and feet as high as you can; lift them up and put them down as one round, and do four groups of eight rounds each time, once or twice every day. This will help to prevent lumbar disc herniation.
4. Urinary Stones
Urinary stones indicate the presence of hard particles or deposits in the urinary system due to high urine concentration. The stones are found in the kidneys, ureter, and anywhere in the urinary tract.
Clinical manifestations may vary due to the different locations of the stones. Kidney stones and ureteral stones are typically characterized by renal colic and blood in the urine. At the onset, the patient will feel intense pain, either constant or intermittent, in the lower back, radiating along the ureter to places such as the iliac fossa, perineum, and scrotum. Before the onset, the patient usually has no symptoms, but suddenly experiences an intense bursting pain on one side of the lower back due to intense exercise, physical labor, or long-distance travel. It is often accompanied by fullness of the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, blood in the urine, pyuria, difficultly urinating, or interrupted urine flow.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
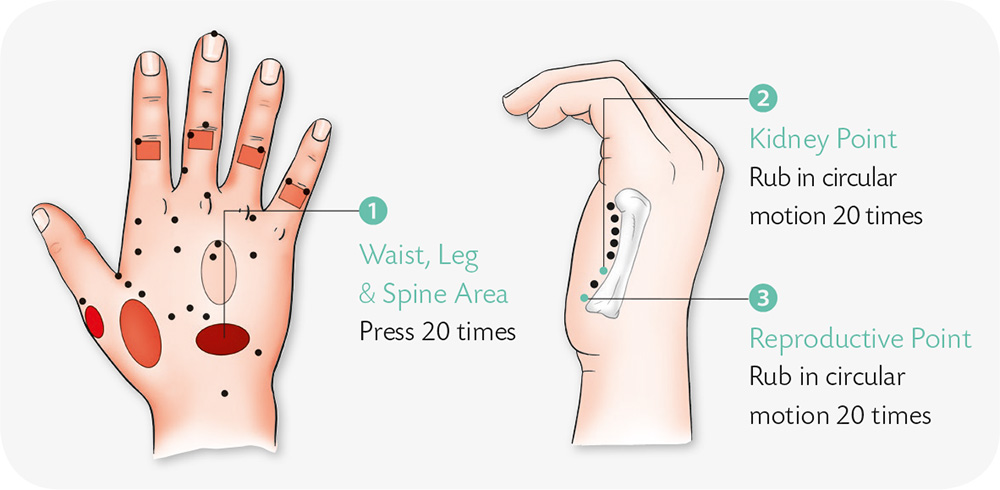
Hand Exercises
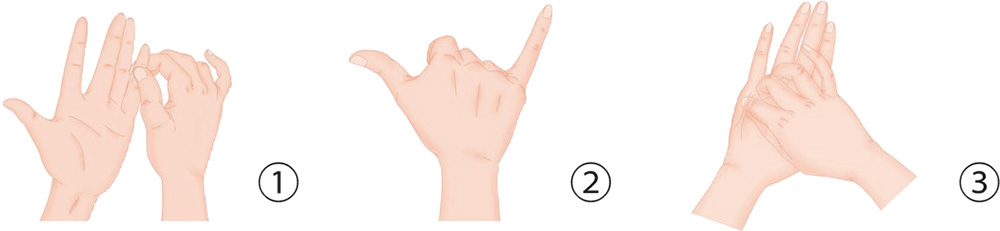
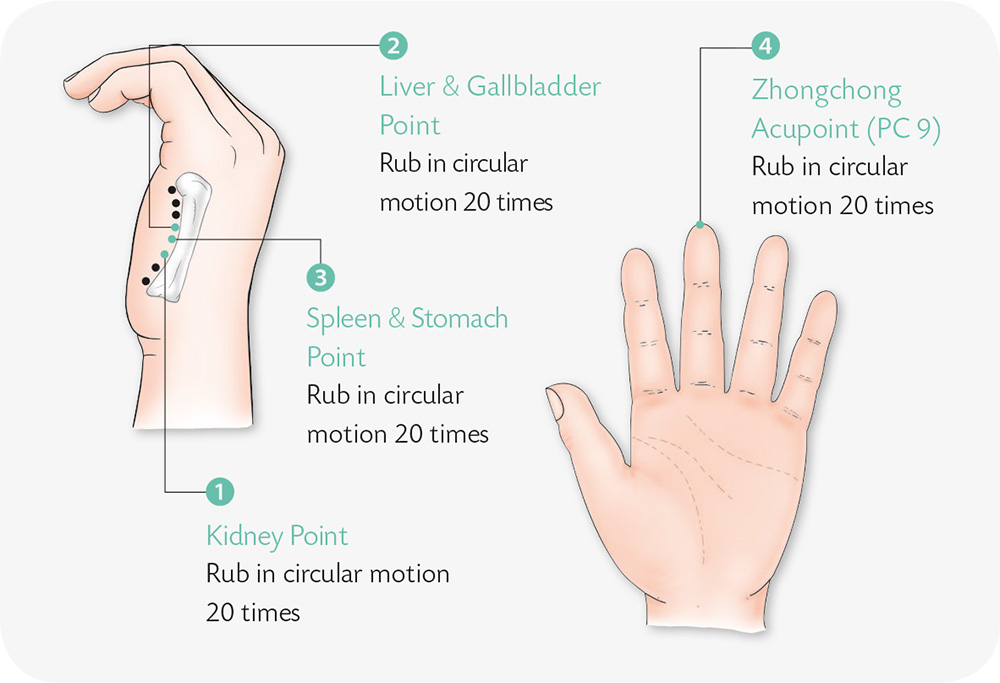
1. With your thumb and index finger, twist and press the little finger of the other hand in spiral rotation from the bottom up.
2. With your palm facing outwards, quickly contract the three fingers in the middle, making the Chinese finger-counting sign for “6.” Do it six times.
3. With your right thumb and index finger, pinch the skin of the little finger along its metacarpus to the wrist crease.
In daily life, people with urinary stones should:
1. Lower their intake of animal protein, e.g., meat and offal.
2. Lower their intake of salt and maintain a light diet.
3. Drink light tea or water instead of strong tea.
4. Refrain from drinking milk less than 4 hours before sleep. The formation of kidney stones is due to a sudden increase of calcium in the urine. The peak time for calcium to exit the body is 2 to 3 hours after drinking milk. If you are sleeping at this time, the urine becomes concentrated and more calcium stays in the kidneys, increasing the likelihood that stones will form.
5. Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infection refers to an inflammation of the urinary system due to an attack of bacteria (and very occasionally by fungus, protozoa, or viruses). The most common is E. coli, but possible contributing bacteria also include bacillus coli communior, bacillus proteus, and staphylococcus.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Urinary tract infection may cause acute and chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis, and urethritis.
Acute pyelonephritis: Systemic symptoms include sudden onset, chills, shaking, feverish sensation, discomfort across the body, headache, fatigue, poor appetite, nausea, vomiting, lower back pain, and discomfort in the kidney area. Symptoms in the urinary system include bladder inflammation leading to urinary urgency, frequent or painful urination, lower back pain, and/or lower abdominal pain.
Chronic pyelonephritis: Manifestations may be similar to acute pyelonephritis but much less severe, with no fever, systemic discomfort, or headache. Signs of urinary tract infection: Only a small number of patients have intermittent symptoms of pyelonephritis, but more common is the presence of intermittent symptomless bacteria in the urine and/or intermittent urine urgency, frequent urination, discomfort in the lower back, and/or intermittent low-grade fever. Chronic interstitial nephritis-related manifestations are hypertension, frequent urination, increased urination at night, higher occurrence of dehydration. Chronic kidney disease-related signs are a puffy face in the morning, frequent urination at night, and back pain.
Cystitis and urethritis: Manifestations are primarily frequent, urgent, and painful urination, as well as pain in the bladder area.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
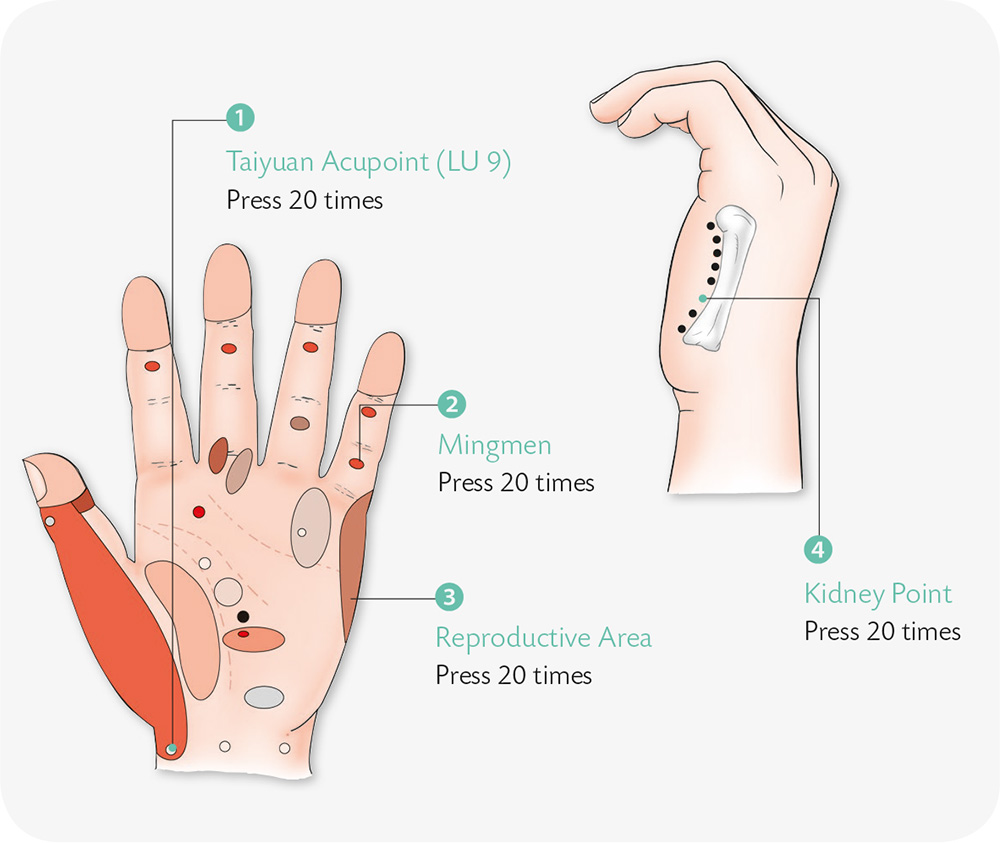
Hand Exercises
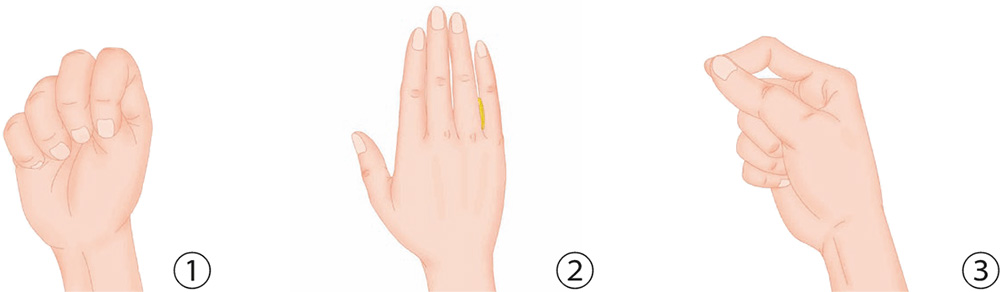
1. Make a fist with the palm faces inward. Withdraw the thumb to tuck it between the ring finger and the little finger, and contract and squeeze the remaining four fingers with force.
2. Place a coin vertically between the proximal phalanges of the little finger and the index finger.
3. Bend the five digits of your right hand slightly, forming a hollow fist, and align your thumb and index finger to make the tips jab each other.
Other Methods
1. Avoid negative emotions and keep a positive outlook.
2. Do more exercise, such as jogging and walking, to strength your physical fitness and improve your resistance to disease, thus reducing the risk of bacterial infection.
3. For women, make sure your private parts are always clean. For men, a long foreskin is likely to cause urinary tract infections, so maintaining good hygiene is important; wash your private parts every day.
6. Nephritis
There are many types of nephritis. Based on the initial causes, they are broadly divided into congenital glomerulonephritis and secondary glomerulonephritis. Another classification is based on duration: acute nephritis and chronic nephritis.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Early symptoms: Most sufferers will have experienced other infection about a month before its onset, e.g., suppurative tonsillitis. The onset can be sudden, accompanied by high fever. It can also be gradual and can go unnoticed.
Hypertension: One of the most typical signs of nephritis.
Swelling: About half of those affected experience swelling when urination decreases. The swelling is more evident in the face and the lower extremities, and is difficult to alleviate once it has begun.
Symptoms in the neurological system: The primary signs are headache, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and decreased thinking ability. In serious cases, the sufferer may experience visual impairment, or even amaurosis, fainting, and seizures.
Anemia: Sufferers of nephritis are often found to have anemia, and may experience fatigue and dizziness.
Hand Exercises
1. Use the five digits of your right hand to pull away the proximal phalanx of the left little finger slowly 15 times.
2. With your thumb and index finger, hold the proximal phalanx of the little finger of the other hand, and twist and pull it in a spiral rotation.
3. Open your palm and abruptly retract your middle finger toward the thumb while keeping the index, ring, and little fingers straight.
Other Methods
Patients should regulate their life schedule and cultivate a healthy lifestyle:
1. Keep a regular schedule and maintain a healthy lifestyle; do not overwork, as excessive fatigue is likely to worsen the condition.
2. Do aerobics and exercises for physical fitness.
3. Maintain a pleasant mood.
4. Avoid smoking and alcohol.
5. Avoid cold winds and try not to catch a cold, as this can exacerbate the condition.
Clinical surveys show that about 70% of kidney disease cases are related to working too much over a long period of time. Therefore, you should see a doctor if you experience excessive fatigue over a period of time, feel pain in your waist and back, experience increased foam in your urine, increased urination at night, decreased volume of urine, bloody urine, increased proteinuria, puffiness of the eyelids and lower extremities, or dizziness.
7. Prostatitis
Prostatitis has many names due to its different causes. They include non-specific bacterial prostatitis, idiopathic bacterial prostatitis, specific prostatitis, non-specific granulomatous prostatitis, prostate by other pathogens, and prostate congestion.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Often accompanied by urgent and frequent urination, and pain in the private parts when urinating. The condition may manifest as chills and high fever, accompanied by constant and evident lower urinary tract infection, dribbling urination, cloudy urine, and inflamed discharge from the urinary tract, as well as lethargy and fatigue, and aversion to cold in the lower back and knees. Illnesses such as acute cystitis may occur at the same time.
Acute inflammation may turn chronic either because the condition becomes more serious or before the treatment can run its course and cure the problem. In the case of acute prostatitis turning chronic, the primary signs are pain in the pelvis and abnormal urination. Chronic pain lasts for an extended period of time and cannot be healed. The affected may experience declining quality of life, and further problems such as sexual dysfunction, anxiety, depression, insomnia, and memory problems.
Hand Exercises
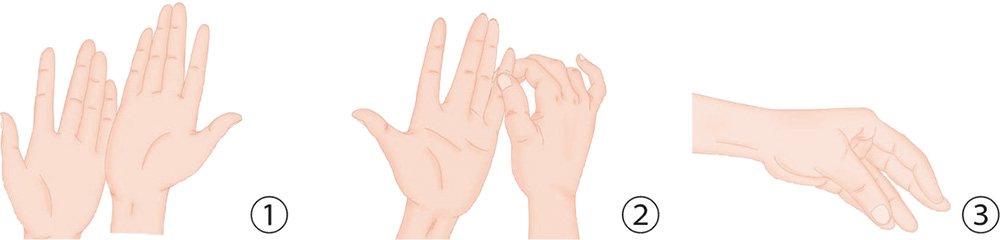
1. With your palms facing up and the heels of the palms pressing against each other, rub them back and forth as many times as you want.
2. With your thumb and index finger, hold the proximal phalanx of the little finger of the other hand, and press and twist it in a spiral rotation.
3. Bend the fingers of your left hand slightly, forming a hollow fist, then pinch the tips of your thumb and little finger together.
Other Methods
If you experience urgent and frequent urination, you should see a doctor as soon as you can during the acute onset. Void your bowels regularly, drink more water, and urinate more often.
Pay attention to the following in your daily life to avoid triggering prostatitis: Excessive sexual activity, forced termination of sexual intercourse, excessive masturbation, an over-restrained sex life, and prolonged voluntary sexual arousal.
Prolonged direct pressure on your private parts, such as cycling, horse riding, and sitting, are likely to cause repeated damage and may lead to a congested prostate, resulting in prostatitis. Also, unhealthy life habits such as alcoholism and indulgence in oily food will likely generate systemic damp-heat in your reproductive organs, causing prostatitis.
8. Male Sexual Dysfunction
Male sexual function includes five components: Sexual arousal, getting an erection, penetration, maintaining an erection, and ejaculation. Any of these components can be dysfunctional, and disorders are collectively known as male sexual dysfunction.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Common dysfunctions include low libido, sexual aversion, hyper-arousal and sexual desire disorders, and dysfunctional erection, penetration, and ejaculation. Ejaculation dysfunction includes premature ejaculation, inhibited ejaculation, and retrograde ejaculation.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
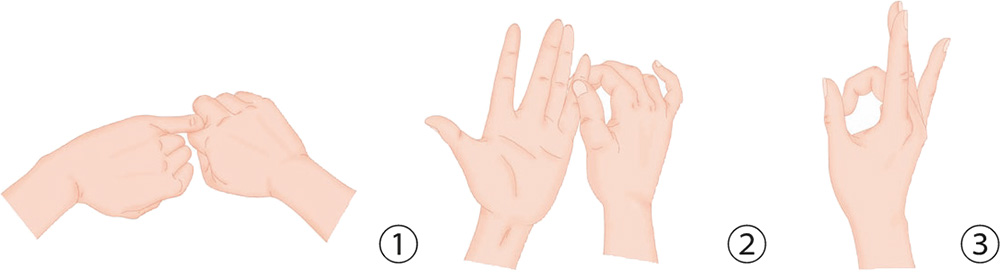
1. With the five digits of your right hand, pull the proximal phalanx of the left little finger slowly 15 times.
2. With the five digits of your left hand, pull the proximal phalanx of the right little finger slowly 15 times.
3. Bend the digits of your right hand slightly, forming a hollow fist. Press the thumb and the index finger against each other so that the tips pinch each other.
Other Methods
Maintain emotional balance. When stressed, stay calm and think rationally. Learn to relax and adjust tension at all times, and avoid anxious or depressive moods.
Steer clear of unhealthy lifestyles and diets. Avoid unnecessary socializing and alcoholism, and control your food intake; understand dangers of smoking, and make a concerted effort to quit. Be focused while having intercourse; sleep in separate beds for a while to avoid too much sexual stimulation and allow your nervous system and sex organs to rest. Research shows that these measures are an effective way of preventing and treating sexual dysfunction. Eat more food that tonifies yang, such as lamb, sparrow, and walnuts, as well as food that contains arginine, e.g., Chinese yam, ginkgo seeds, frozen tofu, eel, sea cucumber, squid, and octopus.