Gynecological Diseases and Disorders
Problems with the female reproductive system are known as gynecological diseases and disorders. They are common, and often cause great discomfort to women. Due to limited knowledge of such matters, many women do not have adequate resources to take care of their bodies. Unhealthy lifestyles make things even worse. Many women are riddled with illnesses of various kinds, and suffer the consequences of long and ineffective treatments, resulting in inconveniences in their life and work. This chapter aims to improve women’s health through the practice of hand reflexology and acupressure.
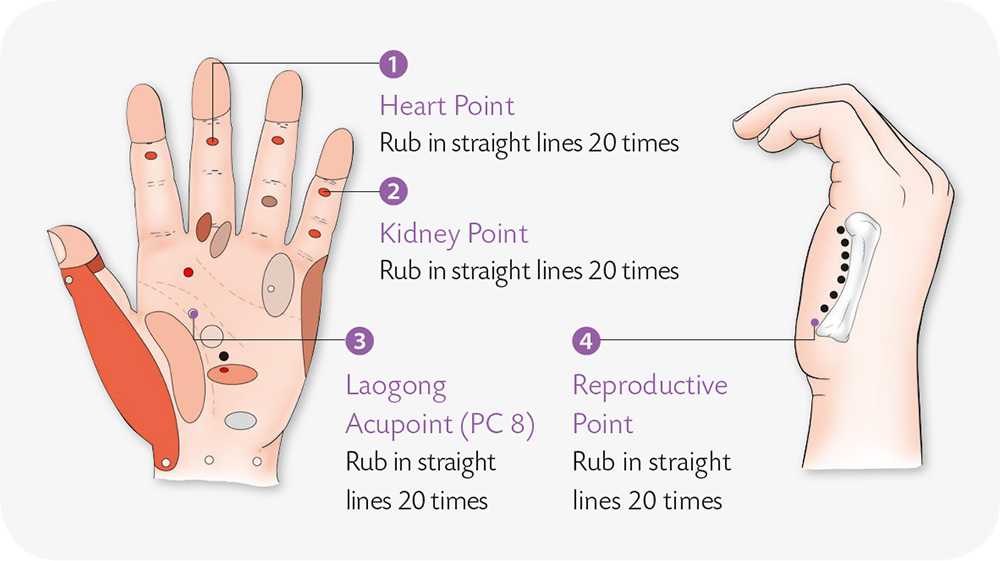
1. Mammary Gland Hyperplasia
Mammary gland hyperplasia is a pathological process in which the glandular tissues and the middle and end parts of the lactiferous ducts expand, grow too much, and experience cystic change.
Modern medical science holds that one of the primary causes of mammary gland hyperplasia are infertility among older women, irregular sexual intercourse, termination of pregnancy, and unhealthy lifestyles such as excessive intake of high-fat and high-calorie food, alcoholism, and smoking. Other factors include external living environments and genetic inheritance.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Lumps in the breast: Tough, cyst-like nodules of various sizes, which move around and are not attached to the skin or the tissues deeper in the breast. The lumps may grow on one side or both sides, and can be single or multiple. They usually appear in the outer, upper quadrant of the breast. These lumps change form with the menstrual cycle: They are bigger and tougher prior to menstruation, and smaller and softer afterwards.
Armpits: The patient usually experiences sore and swelling sensations, but the lymph nodes in the armpit do not swell or grow.
Nipple discharge: Occasional nipple discharge of yellow or greenish yellow fluid, or colorless serous effusion. If the discharge turns reddish or brownish, you should see a doctor.
Hand Exercises
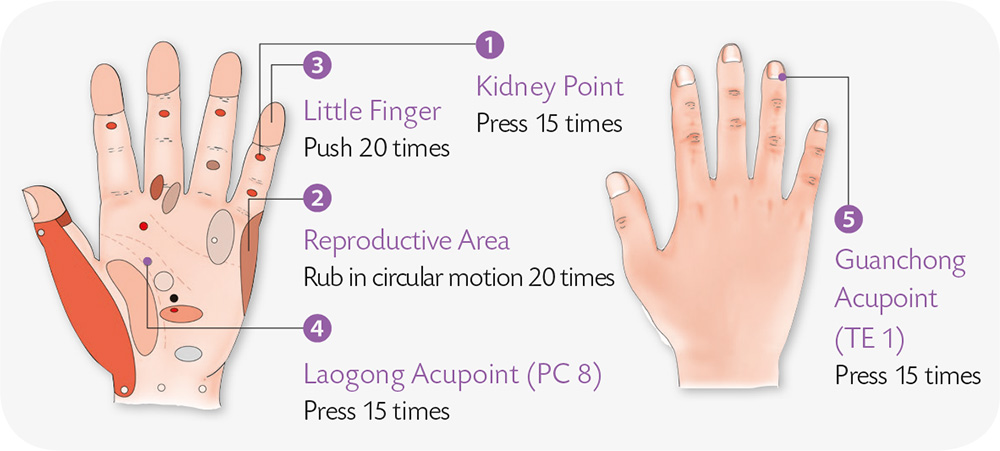
1. Hold a stick between the tips of both middle fingers. Press the thumbs of both hands against each other, with both index fingers withdrawn.
2. With your left palm up, spread out the five digits. Interlock the fingers of your right hand with those of the left hand from behind, pressing and jabbing the left hand with force.
3. With your right palm, hold onto your left palm horizontally and press the withdrawn left little finger underneath the right palm; attach the other three fingers of your left hand to the back of your right hand and press it.
Other Methods
Women suffering from mammary gland hyperplasia should be vigilant in all of the following situations: A long history of mammary gland hyperplasia; overgrowth of nodules (which are many and evident) if touched; aged between 40 and 60 (an age bracket with a high incidence of cancer); a family history of breast cancer.
Special attention should be paid to painless lumps. Breast cancer lumps may not be painful in the early stage. However, once you feel pain, the cancer may have entered the middle or later stages. Go to a specialized hospital for examination to rule out the possibility of cancer.
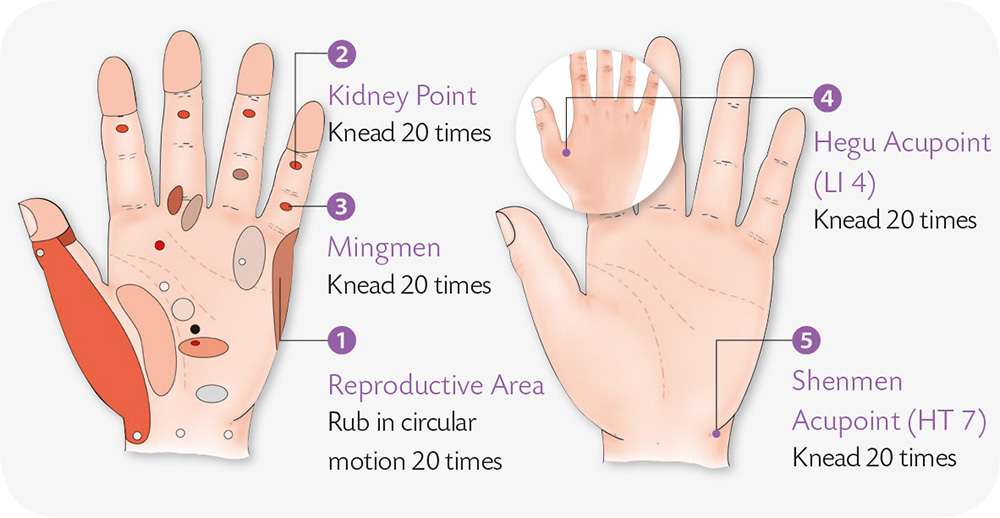
2. Abnormal Menstruation
Abnormal menstruation refers to longer or shorter menstrual cycles than usual, heavier or lighter menstrual flow than usual, or changes in the nature of the discharge, sometime accompanied by discomfort.
It is caused by the following:
• Neuroendocrine dysfunction: Unstable function or deficiency of the posterior pituitary-ovarian axis results in abnormal periods.
• Long-term depression, anger, or severe emotional and psychological trauma could also cause abnormal menstruation or period cramps and amenorrhea.
• Organic diseases: Local inflammation of the reproductive organs, tumors and abnormal development, malnutrition, disorders of the brain, liver and blood diseases.
Manifestations and Symptoms
The condition is characterized by disorders in menstruation cycles and the volume of blood discharge:
1. Irregular uterine bleeding: Excess period discharge or extremely long periods, often found with uterine fibroids, endometrial polyps, and endometriosis.
2. Functional uterine bleeding: Disorders of the endocrine system, but no signs of physical diseases of the reproductive organs.
3. Vaginal bleeding after menopause: This refers to bleeding six months after menstruation has ceased. It is often caused by malignant tumor or inflammation.
4. Amenorrhea: Females over 18 years of age who have never had periods are considered as having congenital amenorrhea; menstruation stops any time after the first period and before menopause (excluding pregnancy or breastfeeding), with a duration of six months or longer; these people are considered to have secondary amenorrhea.
Hand Exercises
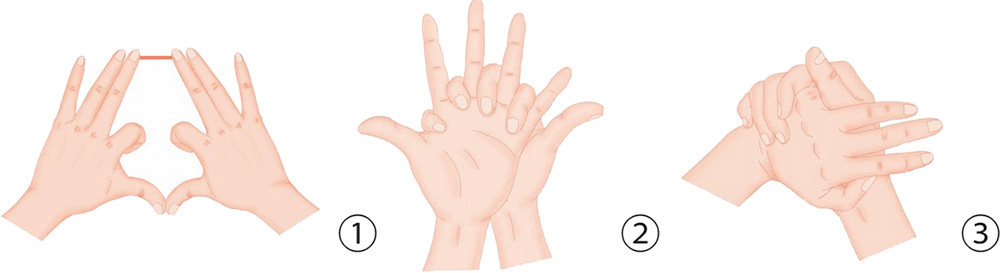
1. With your palm facing outward, place a coin horizontally between the proximal phalanges of your middle and ring fingers. Keep it there firmly, and then move it upward.
2. With your palm facing outward, place a coin between the proximal phalanges of the ring and little fingers. Keep it there firmly, and then move it up and down without it falling off.
3. Put a ring on the middle phalanx of the ring finger, and use your middle or little finger to turn it, stimulating the finger.
Other Methods
Sufferers of abnormal menstruation should do the following:
1. Keep warm, and prevent cold from getting into the body.
2. Pay attention to your diet and avoid raw and cold food, as coldness tends to congeal the blood and thus exacerbate period cramps.
3. Take more rest and avoid fatigue.
4. Keep your emotions in check and avoid violent mood swings. Maintain a good mood.
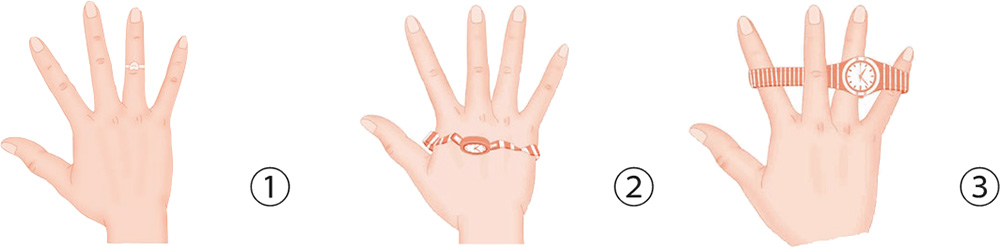
Uterine fibroids are among the most common benign tumors of the female reproductive organs, consisting of lumps that grow in the uterus due to smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Many clinical observations and experiments show that the growth of uterine fibroids depends on female hormones. Patients often have ovarian hyperemia, swelling of the ovaries, and an excess of endometrial hyperplasia. All these signs indicate an abnormally high level of female hormones.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Uterine fibroids typically manifest as:
1. Excessively heavy periods and secondary anemia; prolonged duration of periods, and shorter intervals between periods; irregular or non-stop flow of blood.
2. Lumps in the lower abdomen, and increased leucorrhea discharge.
3. Fibroids in the front wall of the uterine may suppress the bladder, causing a more frequent and urgent need to urinate.
4. They may also cause conditions such as difficult urination, urinary retention, a heavy and distended lower abdomen, and constipation. In severe cases, infertility and miscarriage are likely.
Some people ignore the existence of uterine fibroids, believing that they are benign tumors. However, they may trigger gynecological infections such as adnexitis and pelvic inflammatory disease. Uterine fibroids can have complications primarily caused by torsion of the pedicle in ovarian tumors, or acute endometritis.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
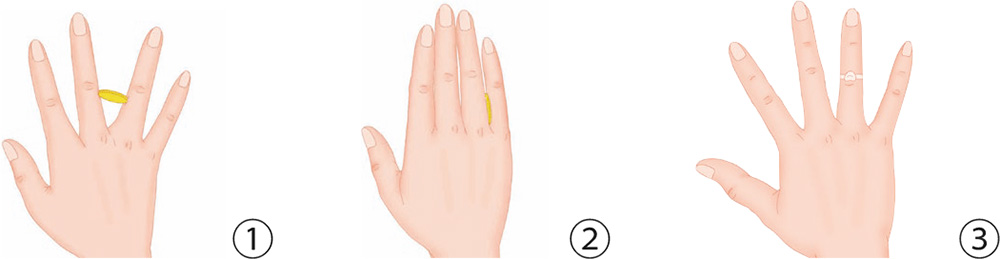
1. Put a ring on the middle phalanx of the ring finger, and turn it with your hand to stimulate the finger.
2. Put a wristwatch or an elastic band on your palm, and stretch and contract your hand.
3. Put a wristwatch or an elastic band on the index, ring, and little fingers, leaving the middle finger above the strap. Stretch your fingers as far as you can.
Other Methods
Special care should be given to your daily diet:
1. Eat light food with low salt and oil; avoid lamb, shrimps, prawns, crab, eel, salted fish, and snakehead fish, as they can trigger certain diseases and conditions.
2. Avoid irritating food and drinks such as chili pepper, Sichuan pepper, raw scallions, and liquor.
3. Avoid food such as longan, dates, gelatine from donkey skin, and royal jelly, as they contain heat and hormones, and cause congealing.
In addition, have regular checkups and seek appropriate treatment based on the progression of the disease. Terminating a pregnancy may damage the uterus and cervix, and thus increase the risk of uterine fibroids. Therefore, proper contraception should be used. Take good care of yourself during menstruation. This will alleviate heavy menstrual discharge for those suffering from uterine polyps, and decrease the risk of serious complications.
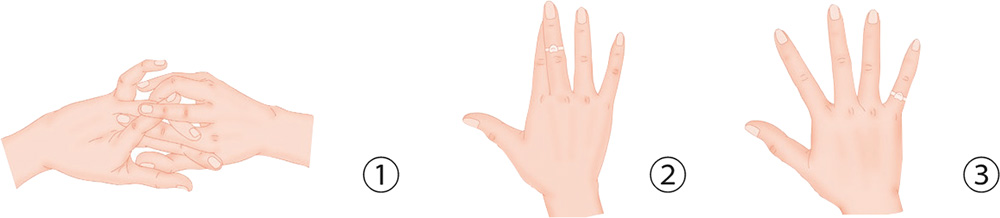
4. Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea refer to pains in the lower abdomen in the course of menstruation.
Those who suffered from dysmenorrhea when their periods first a b c started but whose reproductive organs show no signs of organic disease are considered to have congenital dysmenorrhea. When dysmenorrhea occurs because of physiological pathogens in the reproductive organs, this is called secondary dysmenorrhea. Reproductive diseases include uterine hypoplasia, cervical stenosis, and endometriosis. Dysmenorrhea may also result from mental or physiological factors, such as excessive stress, nervousness, chronic diseases, and anemia.
Manifestations and Symptoms
In the first two days of menstruation, the patient may feel throbbing or cramping pain in the lower abdomen. The pain may radiate to the patient’s vulva, anus, and lower back, and is usually accompanied by nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, pale complexion, sweating, and cold hands and feet. The pain will disappear when the period ends.
Dysmenorrhea is only one of many signs of gynecological diseases, and may conceal the existence of other issues. Seek proper medical treatment, and don’t allow your condition to deteriorate. In general, fever during menstruation accompanied by cramping pain in the lower abdomen usually suggests that you have pelvic inflammatory disease. If your menstrual blood is light brown, or has an abnormal odor, accompanied by rising temperature and lower abdominal pain, it is likely that you have endometritis. Likewise, if your period pains grow longer and more severe, you may have endometriosis.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
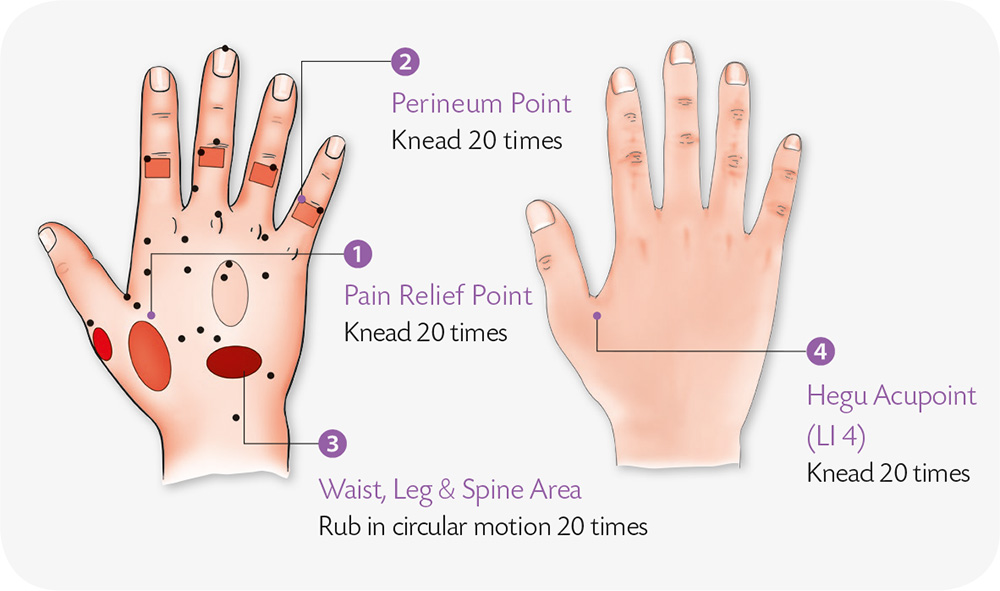
1. Attach both thumbs and little fingers to each other, and lock the remaining fingers into one another.
2. Put a ring on the middle phalanx of your middle finger, and use the other hand to move it up and down.
3. Put the ring on the proximal phalanx of your little finger and move it up and down.
Other Methods
Exercises can help restore the uterus to its normal position:
1. Lie on your back with your legs together. Raise your knees slightly, and keep them there while doing diaphragmatic breathing 20 times. Do this two to three times daily. Diaphragmatic breathing is a style of deep breathing in which inhalation does not expand the chest but raises the abdomen, and exhalation contracts the abdomen instead of the chest.
2. Stand up straight, lift up your heels, and then drop them down. Repeat this 20 times. Do this exercise three times every day.
5. Female Infertility
If a woman is not able to get pregnant after more than two years of unprotected sex with her spouse (who has normal reproductive function), this is considered to be primary infertility. If a woman cannot conceive more than two years after giving birth, abortion, or miscarriage, this is called secondary infertility.
Many factors can cause female infertility. They include conditions such as congenital absence of ovaries, polycystic ovaries, salpingitis, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, cervical inflammation, and cervical stenosis. Psychological factors may also affect a woman’s chances of getting pregnant. Therefore, it is of critical importance that you remain psychologically and emotionally healthy.
Manifestations and Symptoms
A healthy woman trying to conceive for more than two years is not able to get pregnant.
Hand Exercises
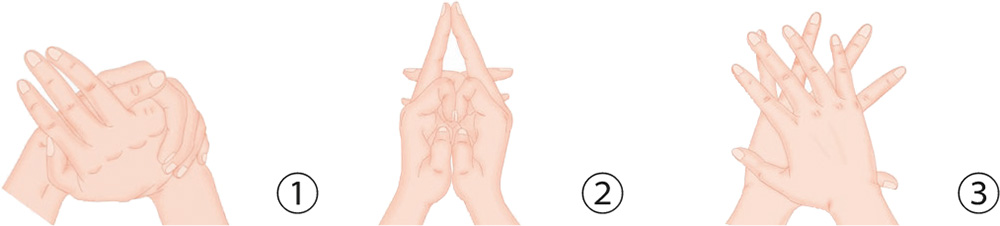
1. With your right palm up, bend the little finger inward. With your left hand, cover the right palm from above, pressing the little finger of the right hand.
2. With your palms facing each other, bend both thumbs and index fingers. Interlock the ring fingers and little fingers, and the fingertips of both hands press or squeeze the points they touch with force.
3. With your left palm down, spread out the five digits. With your right hand, press the left palm, and spread out the five digits and rub the left hand in a circular motion 20 times.
Other Methods
1. Increase dietary nutrition by taking multivitamins such as Vitamins A, B, C, and E, to prepare your body for pregnancy.
2. Avoid unhealthy environments, and take preventative measures when you are in a profession that may have adverse effects on pregnancy.
3. The female reproductive tract is susceptible to infection and blocked fallopian tubes after curettage. Curettage is also likely to damage the uterus and kidneys, leading to endocrine disorders and thus affecting your chances of pregnancy. Lack of rest after curettage can make it harder to get pregnant.
4. Women with infertility issues may also suffer from emotional distress, and should be treated with love and care.