Skin Conditions and Diseases of the Nose, Eyes, Throat, and Teeth
The skin is the largest organ in the human body. It prevents the internal organs and tissues from being attacked physically, mechanically, chemically, and by pathogenic microorganisms. The skin functions as a barrier to the outside world in two ways: It prevents the loss of bodily fluids, electrolytes, and other substances, and stops the invasion of external harmful substances. It retains the internal stability of the body, provides biological protection, and participates in the metabolic process. The health of the skin and the facial organs is not only crucial to the overall health of a human being, but is also related to the aesthetics of external appearance. By understanding the hand reflexology and acupressure in this chapter, you will learn how to improve the health of your skin and your facial organs, for internal and external vibrancy.
1. Eczema
Eczema is one of the most common inflammatory skin diseases, and can either be acute or chronic.
The causes of eczema can be internal and external.
External triggers: Chemical irritants such as dyes, medicine, paint, soap, detergent, cosmetics; sunlight, UV rays, extremely low temperatures, extreme heat, dryness and humidity, and physical irritants such as animal hair, feathers, and glass fibers.
Internal triggers: Chronic diseases such as gastrointestinal disorders, intestinal parasites, chronic alcohol intoxication, metabolic dysfunction, and endocrine disorders, and emotional problems such as nervousness, insomnia, and fatigue.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Primary manifestations include intense itching, and multiple forms of skin lesions that are symmetrical in distribution with a tendency to ooze. The course of the disease is long, and it can reoccur from time to time.
Acute Eczema: Skin patches with red papule; papule with pus-filled blisters, with clear dots or small patches of erosion that weep fluid and form scabs. Acute eczema results in skin lesions of multiple forms, and can recur, which may lead to chronic eczema.
Chronic Eczema: Inefficient treatment and repeated recurrence of acute and sub-acute eczema can result in chronic eczema. Skin lesions turn dark red, brownish red, or maculopapular. The patches often merge and thicken, becoming moss-like with scales, scratches, and blood crust on the skin surface. It is usually dotted with papules and sporadic maculopapulae. Itching can sometimes be unbearable, and the condition often worsens after taking a bath, drinking alcohol, overheating in bed, and emotional stress. It can sometimes affect a patient’s sleep. Patches of chronic eczema are self-limiting, with clear edges. They are moist, and thicken over time.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
Hand Exercises
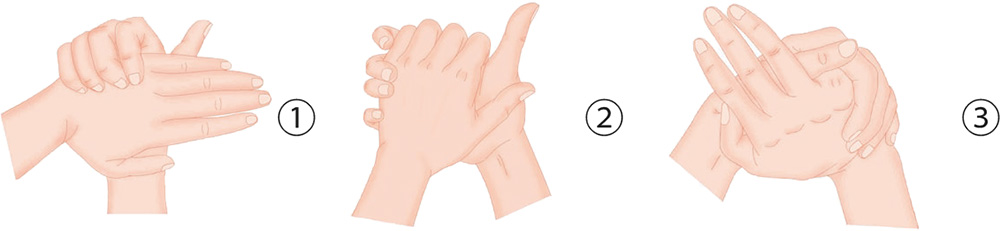
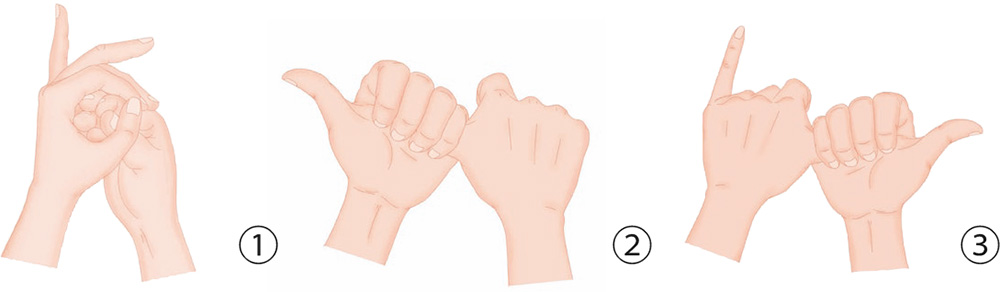
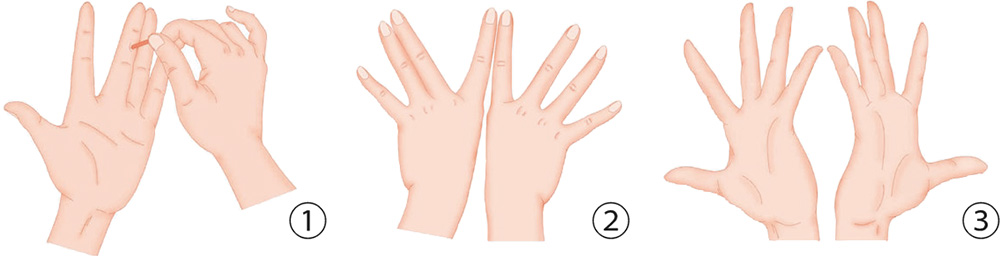
1. With your right hand, clasp the left palm positioned horizontally. With the four fingers of the right hand, clasp the back of the left palm, jabbing and pressing.
2. With your right palm, clasp the left palm horizontally. With the five digits of both hands, press the back of the other palm with force.
3. With your right palm up, withdraw the little finger; your left hand covers the right palm from above. Press the back of the right hand and squeeze the withdrawn little finger.
Avoid local irritation such as scratching, soap, hot baths, wiping with force, and inappropriate treatment. Avoid spicy and irritating food and alcohol. In the course of an acute outbreak, do not undergo immunization; an infant should not be vaccinated if suffering from eczema.
For young children suffering from eczema, the following measures are recommended:
1. Avoid using overheated water for baths, and do not use soap.
2. Avoid excessive exposure to the sun.
3. Avoid direct contact with clothes made from coarse cotton or synthetic fabrics, otherwise the condition could worsen.
4. Take sedative medicine as prescribed by the doctor before going to bed, as itching will affect sleep.
5. Trim children’s fingernails, and wrap their fingers with gauze so they don’t scratch themselves.
6. Avoid the chickenpox vaccine until the eczema has healed.
2. Urticaria
Urticaria is a common skin allergy. Clinically, it is divided into common urticaria, cold urticaria, and sunlight urticaria.
Many things can trigger this dermatologic condition: food such as fish, shrimps/prawns, crab, and eggs; allergies, self-immune problems, allergens in the air, infection, physical irritation, bug bites, and even some spicy condiments. Medicines such as penicillin and sulphanilamide may also trigger urticaria via the patient’s immune system. Infections by viruses, bacteria, fungus, and parasites may also cause it.
Manifestations and Symptoms
The clinical manifestation of the disease is the sudden appearance of patches or groups of skin wheals that are unusually itchy, accompanied by fever, swollen joints, headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and palpitations.
Wheals are of different shapes and sizes. They can be bright red or pale, and may disappear on their own. An individual wheal will not exist for more than 36 hours. No traces are left when they subside. If urticaria occurs in the throat, it may cause breathing trouble; if it is in the stomach and intestines, it may cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Hand Exercises
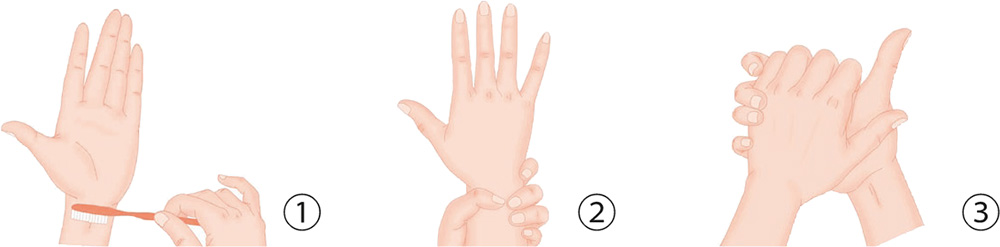
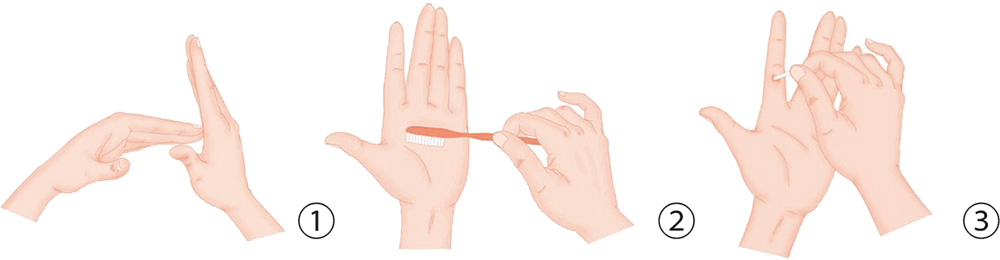
1. Brush your wrist crease with a toothbrush to the left and right, 30 times.
2. Stretch your right palm out, facing against you. Your left hand holds the right wrist horizontally to keep it in place, and then turn your right palm clockwise and counter-clockwise 10 times each.
3. Your right palm clasps the left palm horizontally. With the five digits of both hands, tightly clasp the back of the other palm, and press hard.
Other Methods
Patients with urticaria should avoid scratching the affected area. Do not apply warm compression in the affected area either. Follow a diet with few or no artificial additives. Eat fresh vegetables and fruit, including grapes, seaweed, tomatoes, sesame, cucumbers, carrots, bananas, and green beans. Wear a mask when going out to prevent other infections.
The following measures can be taken to prevent recurrence after the disease is cured:
1. Keep a fixed bedtime and time to get up. In spring and summer, go to bed late and get up early; in the fall, go to bed early and get up early; in winter, go to bed early but get up late.
2. Avoid keeping pets such as cats and dogs at home. Keep the house and carpets clean. Those who have a history of allergies should stay away from flowers and plants to avoid being affected by pollen.
3. For those whose urticaria may be triggered by contact, try to avoid soap containing perfumes, and avoid contact with chemical materials such as rubber and dye.
3. Acne
Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a chronic skin condition caused by sebaceous follicles. It usually occurs on the face, chest, and back, characterized by pimples, bumps, papules, nodules, and cystic lesions. It happens most commonly among young people.
There are many causes of acne. Traditional Chinese Medicine holds that it happens when the heat-wind passing the lung meridian is blocked by the skin. Pathogens include the patient’s hormone levels, excessive sebum secretion, proliferation of propionibacterium acne, and inflammation and abnormal keratoses of the pilosebaceous ducts. Sometimes, excessive intake of rich, oily, and spicy food results in the rise of damp-heat in the body, causing an outbreak on the face. In addition, characterized by the rising yang-heat in the body, young blood fights wind-cold; however, when yang-heat is blocked in the skin, acne can occur.
Manifestations and Symptoms
First, a skin lesion appears, either whiteheads or blackheads. They are neither red nor raised above the skin, and too few in numbers to be visible. Open plugged pores have tips of a yellowish white color, but can turn black due to pigmentation. The spot has a black head, but when squeezed, its end appears as a semi-transparent white fat bolt. Pimples are the initial damage to the skin before they turn into acne. When the situation deteriorates, they become inflamed papules, and appear as red papules, pustules, nodules, abscesses, cysts, and scar.
Skin lesions often happen on the face, particularly on the forehead, cheeks, and chin. They also occur on the chest, back, and shoulders where sebum glands are numerous. Skin lesions usually appear symmetrically. Occasionally they also grow on other parts of the body. Acne lesions have no symptoms, but the patient may feel pain when the infection becomes more evident.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
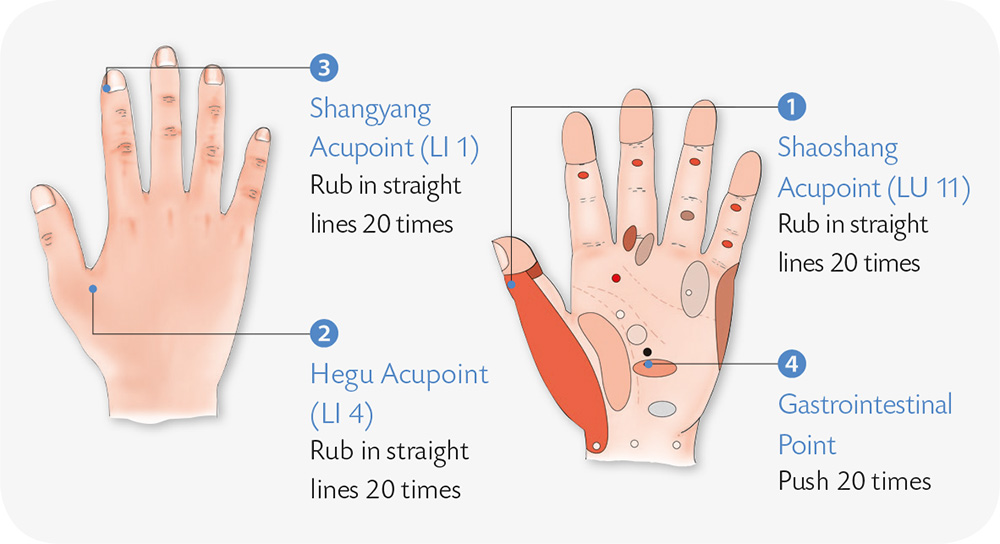
Hand Exercises

1. With your palms facing down, spread the fingers out. Interlock them, and press them against one another with force.
2. With your palms facing each other, bend both thumbs and index fingers; with the middle fingers facing each other, interlock the ring finger and the little fingers; press the tips of the middle fingers hard against each other.
3. With your right palm facing up, lock your left hand into the right hand from behind; with both hands, use the force of the fingers to press against each other; the right palm pulls forward and the left pulls back.
1. Try not to stay up late. Make sure you have plenty of sleep. Unhealthy lifestyles and late nights will exacerbate acne.
2. Maintain a cheerful mood, and avoid anxiety and mood swings.
3. Wash your face twice or three times a day with mild soap and warm water. There is no need for special soap during treatment, but when the condition becomes severe, use a medicinal liquid prescribed by your doctor to wash the affected area.
4. If the affected has oily skin, more care should be taken, because active secretion of sebum demands that the skin be left untouched; massage will only encourage the secretion of sebum.
5. Wash your hair frequently. Do not have bangs, and do not let your hair touch your face. This will cause a build-up of acne-causing grease.
6. Do not use foundation or cosmetics to cover facial acne. It will only block the pores and worsen the condition.
4. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition characterized by patches of red skin and shining silvery scales.
Its primary causes are as follows:
1. Genetics: Those with a family history of psoriasis have a greater risk of being affected.
2. People who have suffered from tonsillitis, otitis media, and colds are also at higher risk of developing psoriasis.
3. Sometimes infections in the gastrointestinal, respiratory, sinus and genito-urinary systems may exacerbate psoriasis.
4. Emotional stress, anxiety, depression, and fear can also trigger or exacerbate psoriasis. The disease will worsen a few weeks or months after an episode of emotional stress.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Psoriasis often appears on the scalp, torso, and backside of the limbs as red patches that gradually grow and merge into scaly patches or plaques with clear borders. At the base of the affected area, there is moist skin. On the surface of the skin are thick, irregular silvery scales. When removing a scale you will see a red membrane, and when removing the membrane you will see petechiae. Features of this disease are white scales, shiny membranes, and punctuated red spots.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
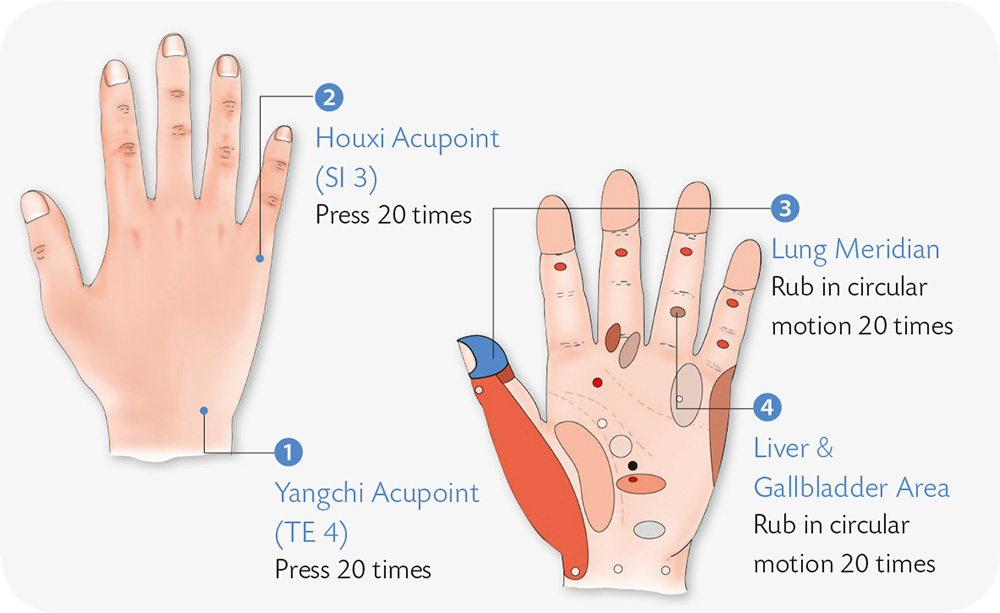
Hand Exercises
1. Use a stick to jab the middle finger evenly, from the fingertip downward.
2. With your palms facing down, withdraw both thumbs and align both hands side by side. Stretch out the remaining four fingers abruptly. The motion should have a strong impact.
3. With your palms facing up, spread the fingers and stretch both thumbs outward. Align the ulnar sides of the hands as an axis, and turn the palms downward as much as you can.
Other Methods
1. Prevent infection. Local infection, particularly tonsillitis, is a major trigger of psoriasis. It is crucial that wounds and inflammation be cleaned promptly in the case of suppurative tonsillitis and similar illnesses.
2. Learn to adjust your emotions and stay optimistic; remain peaceful and calm.
3. Take enough rest and do adequate exercise to strengthen your physical fitness against diseases.
4. Keep healthy dietary habits. Try not to consume alcohol and smoke; avoid spicy and irritating food, and do not eat seafood and lamb.
5. Regularly take folic acid, and Vitamins A, C, and B12.
5. Tonsillitis
Modern medical science holds that tonsillitis is the result of delayed treatment of acute tonsillitis, which is a non-specific acute inflammation of the palatine tonsils that is often found in children and adolescents but is rare among people who are 50 and above.
With excessive fatigue, smoking or alcohol, or cold and damp conditions, the body may lose its resistance to diseases, and the tonsil is thus likely to be affected by bacteria and inflammations.
Sometimes, after the onset of infectious diseases such as scarlet fever, diphtheria, measles, and flu, the condition may gradually become chronic. Bacteria such as staphylococcus and streptococcus pneumoniae may also trigger tonsillitis. Among them, the most common is Group A hemolytic streptococci.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Acute onset, severe chills, and high fever with the temperature reaching 39 to 40℃. With young children, their temperature could be so high as to cause seizures, vomiting, coma, poor appetite, constipation, and systemic soreness and feebleness; evident pain in the throat, particularly when swallowing. When severe, the pain may radiate to the ear. Young children may cry and scream when trying to swallow. Children may suffer sleep disruption, because swollen tonsils block their airways.
Hand Exercises
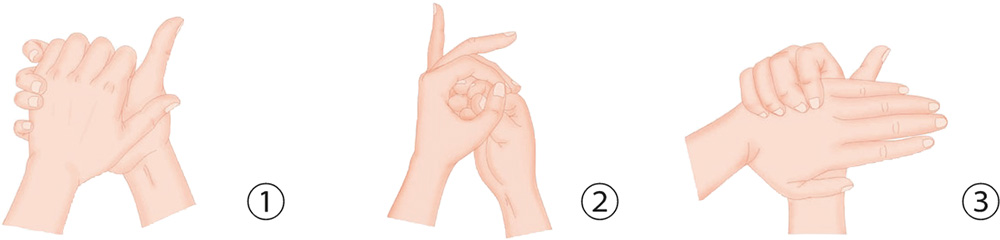
1. Your right palm holds onto your left palm horizontally; the five digits clasp the back of the other palm tightly and press hard.
2. Bring the five digits of your right hand together and wrap them with your left palm; repeatedly squeeze them and then release.
3. With your right hand, clasp your left palm positioned horizontally; with the four right fingers, clasp the back of the left palm, and jab and press down.
Other Methods
Do more exercise to strengthen your physical fitness and improve the body’s resistance to diseases. Wear more clothes when temperatures are low. As chronic tonsillitis is contagious and may trigger chronic infections in the ear, nose, and throat, as well as arthritis, nephritis, and rheumatic heart disease, a tonsillectomy may be necessary.
6. Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is a hypersensitive reaction to certain allergens by people with particular constitutions, often the young.
It is mainly caused by pollen as the seasons change, e.g., from trees, wild grass, and agricultural crops. Perennial allergic rhinitis, however, is related to the perennial allergens in daily life, such as dust and dust mites in the house, fungi, animal hair and dander, feathers, and cotton fibers. Meanwhile, patients with atopic constitutions are usually found to have a family history of such allergies.
Manifestations and Symptoms
1. Red, itchy, and watery eyes.
2. Itchy nose. People who are allergic to pollen may also experience itchy eyes, ears and throat. Increased nasal discharge, mostly watery (sometimes dripping involuntarily). With inflammation, the nasal discharge thickens.
3. Blockage of the nasal canal. This happens intermittently or constantly, on one or both sides, with uneven degrees of severity.
4. Muffled hearing.
5. Sneezing. Bouts of sneezing happen more than three times daily, often in the morning or at night, or right after contact with the allergen.
6. Dark circles under the eyes.
7. A decreased sense, or even complete loss of smell.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
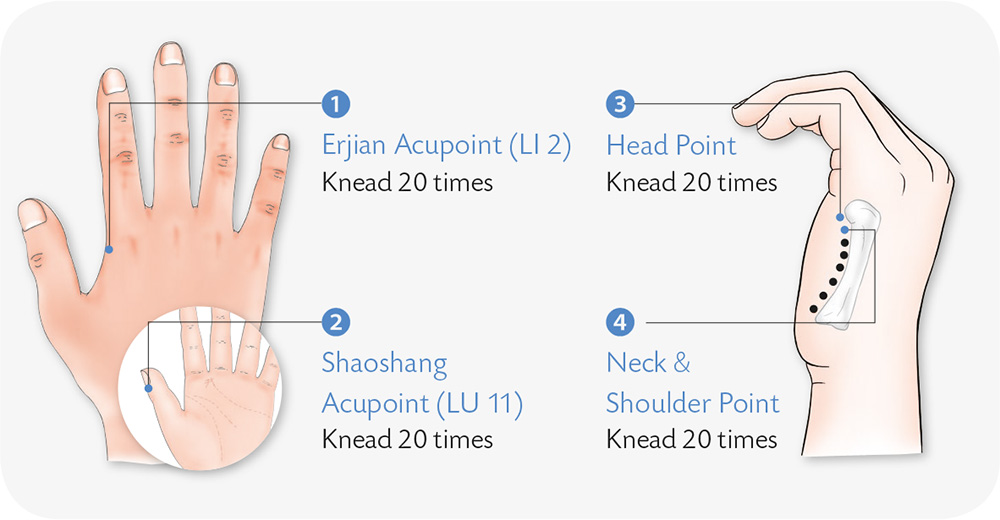
1. Bring the five digits of your right hand together and wrap them with the palm of your left hand. Squeeze and release them repeatedly.
2. Your left hand holds onto your right thumb, and pull it away slowly and with force.
3. The four fingers of the right hand hold onto the left thumb, and pull it away slowly and with force.
Other Methods
Patients with allergic rhinitis should pay attention to what they eat:
Avoid the following food: Unusually cold food, which will reduce your immune system and cause irritation in the respiratory tract; pungent and spicy food such as chili pepper and wasabi, which will irritate the respiratory mucosa; processed or refined food; artificial coloring, particularly Yellow No. 5.
Eat more: Food rich in Vitamins C and A, such as spinach, cabbage, bok choy, and radish; food containing hot energy, such as ginger, garlic, chives, cilantro, sticky rice, Chinese yam, dates, lotus seeds, coix seeds, brown sugar, and longan.
7. Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye problem characterized by elevated pressure in the eye, accompanied by a blood-shot cornea, dilated pupil, severely reduced vision, headaches, and nausea.
Congenital glaucoma occurs in those who have anatomical problems such as small eyeballs, short axial length, hyperopia, and shallow anterior chamber. If coupled with emotional swings, uncontrolled consumption of food, extreme physical strain, insufficient a b c sleep, excessively long periods in dim light, and excessively long periods of reading with the head lowered down, glaucoma is likely to develop.
Secondary glaucoma is mostly caused by trauma, inflammation, hemorrhage, and tumors, which damage the angle of the eye chambers so that the drainage system does not function properly, resulting in increased pressure in the eye.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Acute angle-closure glaucoma: Blurred vision and the appearance of rainbow-colored circles around bright lights; pain in the eye and the head, nausea and vomiting, constipation, and rising blood pressure. Such systemic symptoms are easily confused with symptoms of other diseases such as gastritis, encephalitis, enteritis, and tension headaches. If left untreated, the patient may lose vision within 24 to 48 hours.
Chronic glaucoma: Slow progress, with eye pressure rising gradually. When the pressure is high, the patient may experience a slight headache, as well as soreness and swelling of the eyes. In addition to the shrinking of the optic nerve head, advanced glaucoma also manifests as a dilated pupil and cloudy cornea.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
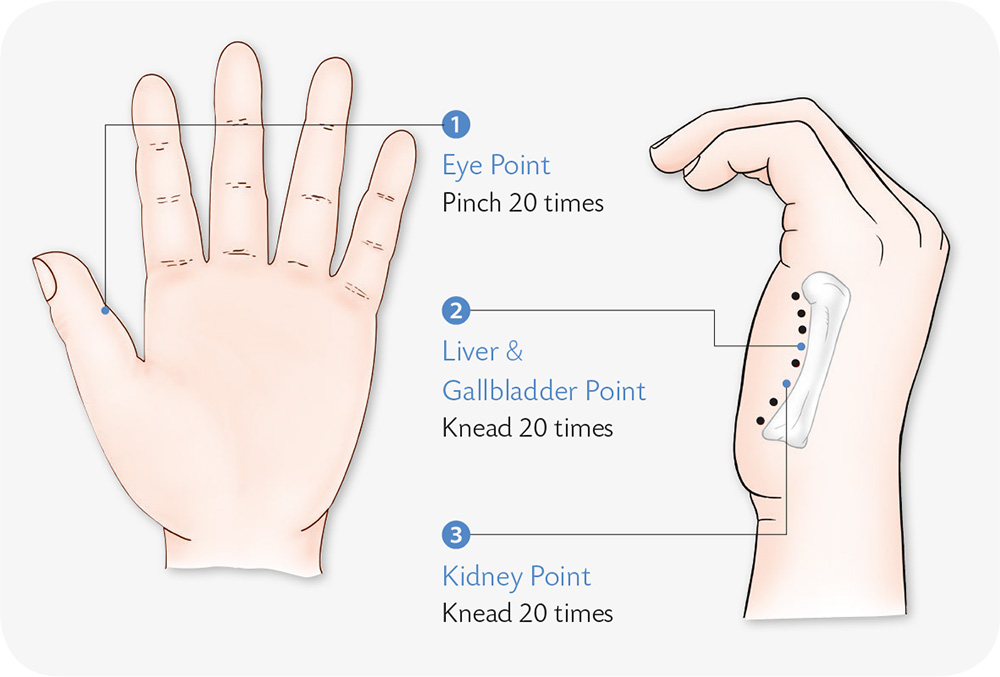
1. Align the four fingers side by side and hold them out against the center of the other palm (vertical). Swing left and right to jab the center of the palm.
2. Brush the center of the palm up and down with a toothbrush 30 times.
3. Spread out the five digits, and use a stick to jab the proximal and middle phalanges of the index finger in even dots.
Other Methods
People with glaucoma should maintain a healthy lifestyle.
First of all, make sure you sleep enough. Inadequate sleep and insomnia can result in rising eye pressure, inducing glaucoma. For the elderly, soak and wash your feet with warm water, and drink some milk before bed to ensure a good night’s sleep. For people who are already experiencing eye pressure, ample sleep is necessary.
Avoid working or playing in dim light. Research shows that people who work in front of a computer for nine hours or more double their risk of glaucoma. If you are already short-sighted, you are at an even higher risk, and should have regular and thorough eye examinations. Also, if you work mostly in front the computer, clean your screen often, and adjust the brightness and color to a comfortable level. Also make sure that your computer is in a comfortable location. Most importantly of all, examine your eyes regularly for early detection of glaucoma.
8. Cataract
A clouding of the eye’s natural lens, a cataract is caused by metabolic pathogens. The deterioration of the lens capsule can lead to impaired vision.
Congenital cataracts: Lens opacity at birth, often found in infants or young children. The cloudiness of the vitreous body is not total, and will not progress. The level of impact on the vision is determined by the location and the degree of the cloudiness.
Traumatic cataracts: This occurs after the lens capsular bag is either penetrated or burst. The former is penetration trauma, while the latter is blunt trauma.
Age-related cataracts: Often manifested as progressive blurred vision of both eyes among people who are 45 or older. During an eye examination, some grey cloudiness is detected in the pupil.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
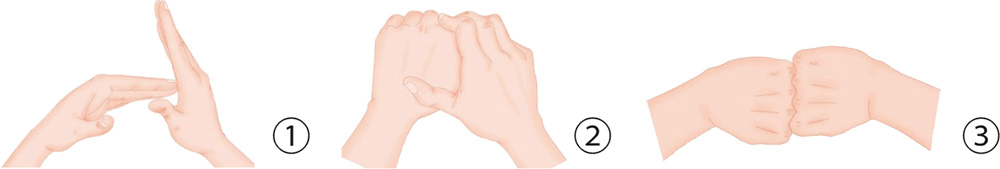
Hand Exercises
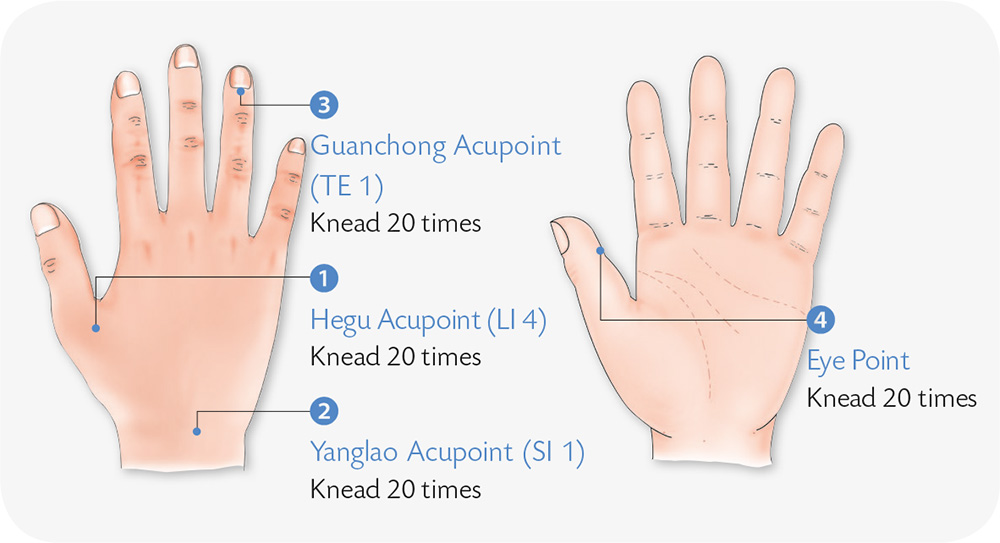
1. Align the four fingers side by side and hold them against the center of the other palm (vertical). Swing left and right to jab the center of the palm.
2. Form a tight fist with the left hand, and wrap the back of the fist with the right hand. Your right thumb presses and rubs the skin on the back of the left hand.
3. With the palms facing down, form fists with both hands. Interlock the knuckles, and press them into the depressions of the other fist with force.
Other Methods
Avoid intense UV light. Wear sunglasses with UV protection if you need to go out.
Limit your calorie intake. Research has found that an obese person has a 30 percent greater chance of cataracts than a person of normal weight.
If you have had cataract surgery, do not lift heavy objects or do intense exercise within one or two months; avoid spicy and irritating food, and do not smoke or drink alcohol. Have weekly follow-up consultations after surgery, and wear protective eye masks. If your eyes are red and swollen, and if you feel pain in the eyes or experience declining vision, go back to the clinic immediately for consultation. Your vision will usually stabilize within two to four weeks after the surgery.
9. Acute Conjunctivitis
Acute conjunctivitis is an infection of the conjunctiva caused by repeated contact with air irritants and other allergens. It is most common in spring and summer, and symptoms will subside in late fall when the weather cools down. It is generally believed that the onset is related to such allergens as pollen, hair, sunlight, and dust. Although not contagious, it may trigger other allergies.
Manifestations and Symptoms
1. Redness of the conjunctiva: The closer to the corneal vault, the more evident the redness is. Blood vessels are winding and irregular, shaped like a net.
2. Sticky or pus-like discharge from the eyes, crusting over the eyelashes and making it hard to open the eyes first thing in the morning.
3. If the condition is mild, you will feel an itch or a burning sensation in one or both eyes, as well as a gritty feeling; if more severe, you may be sensitive to light and experience runny eyes and heavy eyelids.
4. You may feel a swollen lymph node in front of your ear or under your jawbone.
Hand Reflexology and Acupressure
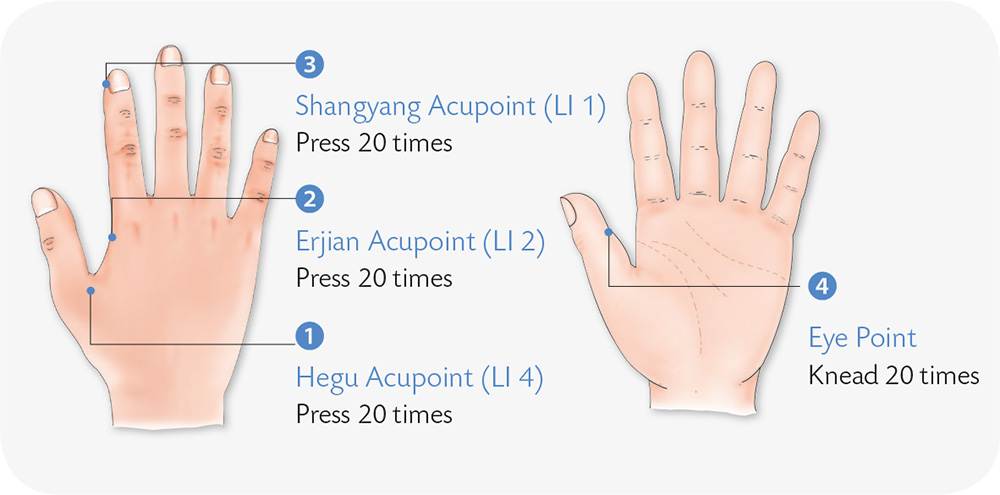
Hand Exercises
1. Form the finger-counting sign for “2,” then abruptly stretch out the ring finger 10 times.
2. Stretch your hand flat with the palm facing away from you; quickly withdraw your thumb, middle finger, ring finger, and little finger, leaving only the index finger raised.
3. Press the left little finger with both thumbs while your left index finger moves toward the middle finger and touches it; your right index finger holds onto the left middle finger. Keep it this way for 18 minutes.
Other Methods
1. If you have acute conjunctivitis, wear goggles to avoid direct eye contact with the water when swimming, as the pool water contains chlorine. The higher the chlorine content, the more irritating the water is to the eyes. Such irritation may lead to non-contagious conjunctivitis. If the water has a lower chlorine content, there is likely to be more bacteria, which may result in contagious conjunctivitis.
2. After swimming, wash your hands before taking off your goggles; then apply anti-inflammatory eye drops. If the eyes are red, runny, dry, sensitive to light, or gritty, see a doctor as soon as you can.
3. Pay attention to the hygiene of the eyes to avoid contracting the disease: Wash your hands often; if someone in your family has pinkeye, do not share potentially infected items such as towels and soap. Finally, stop visiting the swimming pool until the epidemic subsides.
10. Toothache
The primary causes of toothache include acute periodontitis, acute pulpitis, gum or periodontal abscess, acute gingivitis, dry socket syndrome, pain due to food lodged in the teeth, sensitive teeth, jaw tumors, and trigeminal neuralgia.
Manifestations and Symptoms
Toothache due to periapical periodontitis: Constant voluntary aching, radiating toward the head and the temple on the same side; the tooth feels as if it is growing longer; pain when chewing; evident pain when the teeth knock against each other lightly; swollen lymph nodes under the jaw; pain increases when pressed.
Toothache due to pulpitis: Spontaneous intermittent pain, which may radiate to the head and face on the same side, becoming severe during the night. It is hard to locate the affected tooth as the onset occurs; cold and hot stimuli may exacerbate the pain; light tapping of the tooth causes pain.
Toothache due to periodontitis: Red and swollen gum, oozing pus, bleeding; loose and weak teeth.
Toothache due to trigeminal neuralgia: Intermittent electrifying, stabbing, or prickling pain that lasts between ten seconds and one minute.
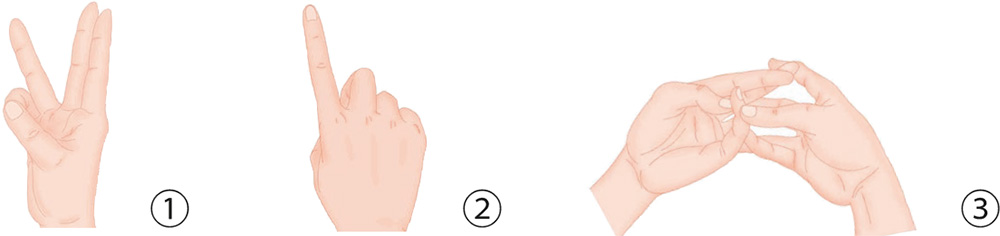
Hand Exercises
1. With five pairs of fingers facing each other, press the tips against each other to form the largest possible angle.
2. Bend the fingers of your right hand slightly, forming a hollow fist. Pinch the tips of your thumb and ring finger together.
3. Bend the five digits of your left hand slightly, forming a hollow fist. Pinch the tips of your thumb and the middle finger against each other.
Other Methods
Pay attention to oral hygiene in daily life, e.g., brush your teeth in the morning and at night, rinse your mouth after meals; avoid eating anything sweet before going to bed; avoid eating spicy and irritating food.
If you have no painkillers at hand, try the following methods to alleviate the pain:
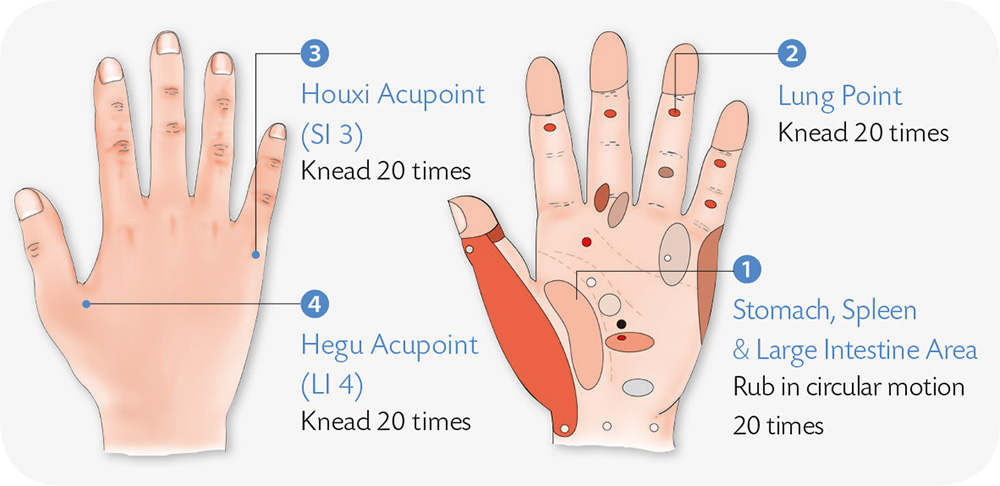
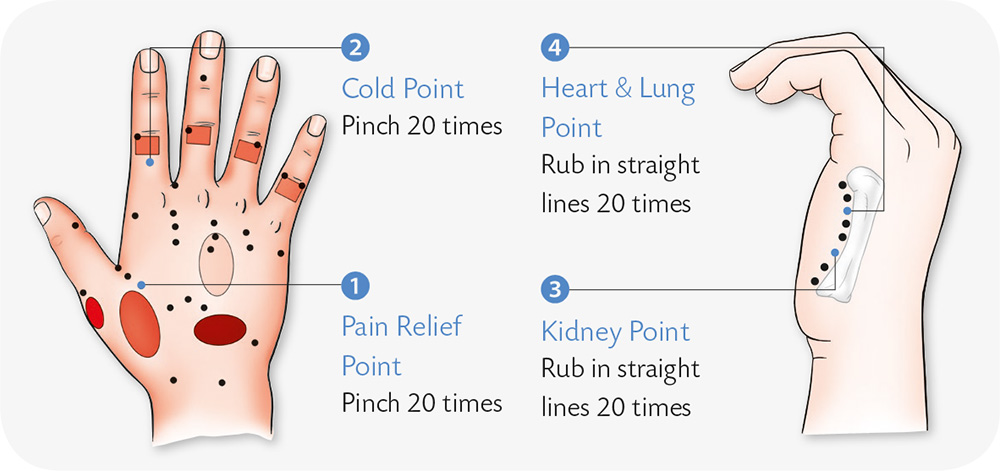
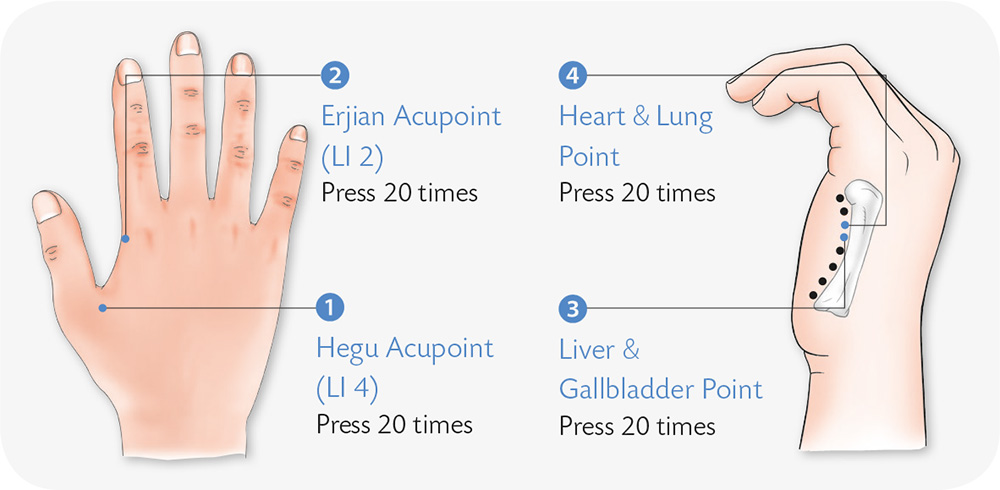
1. Rub the Hegu acupoint (see page 20) with cold water or press it with your fingers.
2. If the tooth is sensitive to anything hot, there may be a buildup of pus in it. In this case, put a cold compress on the cheek and the pain will be alleviated.