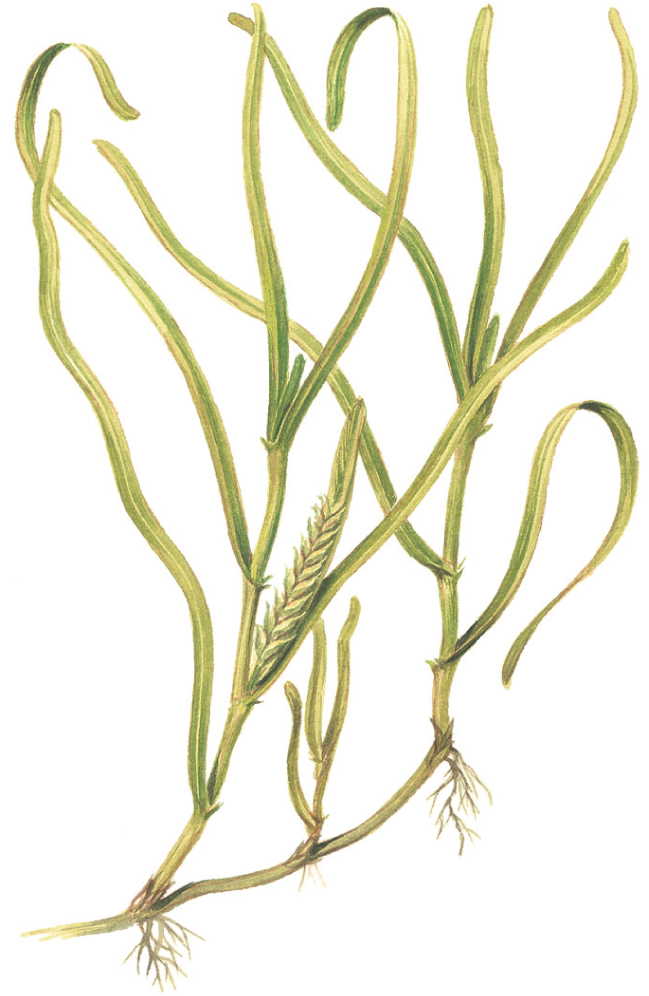
Eelgrass
Zostera spp.

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Length to 1m. Grass-like flowering plant that has become totally marine. Eelgrasses have leaves typical of grasses and their relatives – long and thin, with a series of parallel veins. There are separate male and female plants, each producing different flowers.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Two species of eelgrass (Z. angustifolia and Z. noltii) occur mainly in sheltered waters of estuaries from the middle shore down to shallow water. A third species (Z. marina) grows on muddy and sandy beaches from the lowest tide levels down to about 4m, and is thus rarely seen. All species of eelgrass flower from mid to late summer.
DISTRIBUTION
Found throughout Europe.
Sea Purslane
Halimione portulacoides

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 80cm. Small flowering evergreen shrub with greyish mealy leaves. Flowers are individually insignificant, but yellowish-green spikes are noticeable en masse in June–September.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Occurs commonly around the tops of salt marshes and along creeks, often forming a distinct zone. Well known as a hiding place for crabs, hence its alternate name of Crabgrass.
DISTRIBUTION
Common and frequently abundant in suitable sheltered sites across Europe.
Common Cord-grass
Spartina anglica
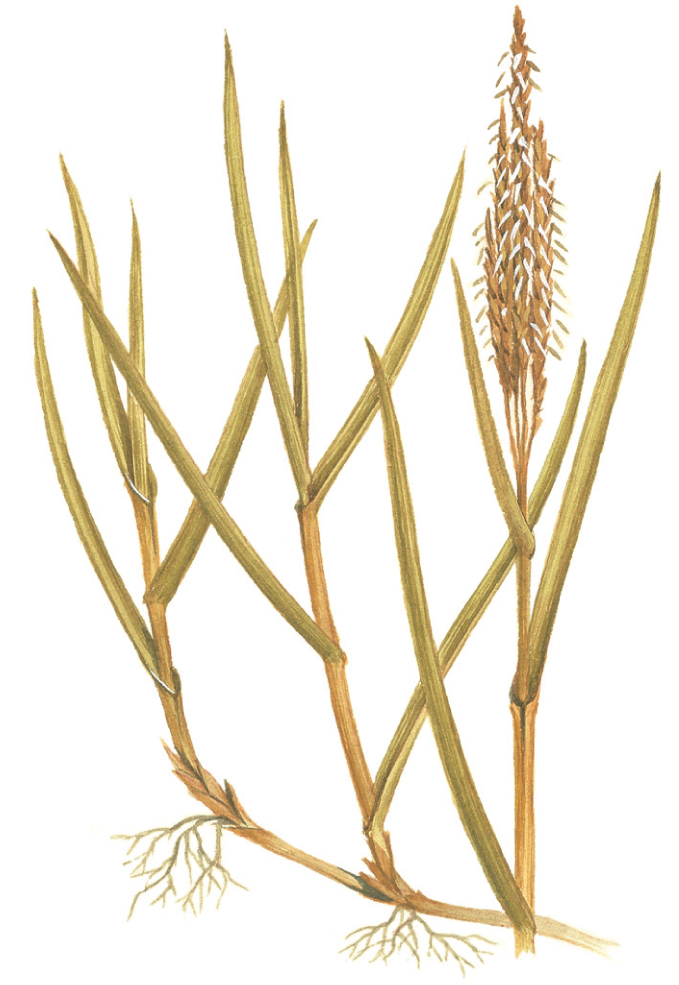

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height 1m or more. Stout erect grass that may cover vast areas in sheltered estuaries and bays. Tall wheat-like flowering spikes are produced in June– August. Species arose as a hybrid between two more slender and rarer Spartina species (S. maritima and S. alternifolia), but is now accepted as a species itself.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
More aggressive than its parents, and colonizes further into deeper water, often ousting more demanding salt-marsh species. Widely used as a mud binder to reclaim tidal land, which it raises by trapping silt.
DISTRIBUTION
Widespread and common in the majority of areas, and often introduced.
Marsh Samphire
Salicornia europaea
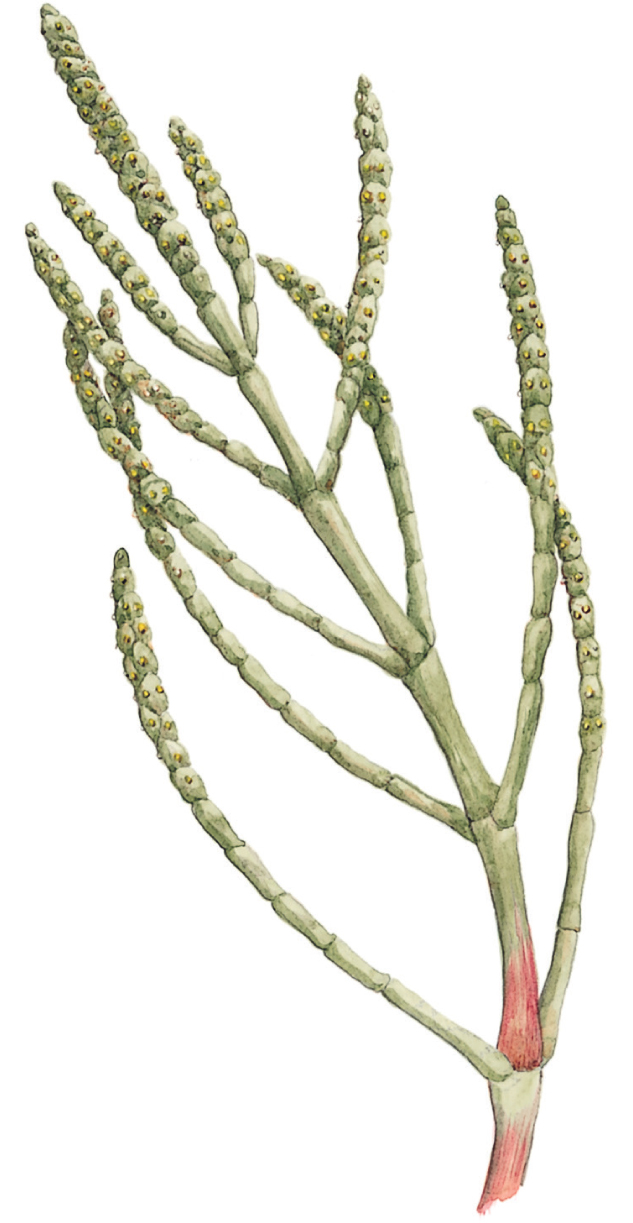

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 30cm. Erect flowering plant with shiny succulent jointed stems bearing numerous shorter side branches all around. Dark green at first, becoming yellowish-green and eventually reddish and woody when in fruit, dying back completely by late autumn. Also called Glasswort. A number of related species in Europe.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows in extensive masses on mudflats, and in salt marshes and estuaries.
DISTRIBUTION
Occurs in suitable coastal locations in much of Europe.
Sea-holly
Eryngium maritimum

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 60cm. Striking architectural perennial. Leaves are bluish-green, leathery and ovate, with sharp spines that give them a holly-like appearance. Basal leaves are stalked, while stem leaves are stalkless. Flowers are small and purple-blue, appearing in June– September. They are packed into rounded teasel-like heads borne with spiny bracts below, and attract bees and butterflies. Roots were once pulped, sugared and sold as sweets.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows in stable and undisturbed coastal sand and shingle.
DISTRIBUTION
Widespread in suitable areas on European coasts.
Lovage
Ligusticum scoticum

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 60cm. Perennial with thick stems and a substantial rhizome. Leaves are large and divided into three leaflets, which are again divided into three segments, with diamond-shaped lobes and toothed margins. White flowers are borne in dense compound umbels 4–6cm across in June–July.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows in shingle, sand dunes and rocky outcrops along the seashore and on sea cliffs.
DISTRIBUTION
Locally common along the coasts of Scotland, Northern Ireland and northern Europe as far as Norway.
Oysterplant
Mertensia maritima

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 60cm. Sprawling perennial with fleshy bluish-grey leaf stems. Leaves are up to 6cm long, spoon shaped or pointed. Lower leaves are stalked, upper leaves stalkless. Funnel-shaped flowers are 6mm across, borne in terminal clusters in June– August, and pink at first, becoming pale blue. Also called Sea Lungwort.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows on sand and shingle beaches around the high-tide mark.
DISTRIBUTION
Locally distributed on the Atlantic coasts of northern Britain and Ireland, and the coast of continental Europe from Jutland northwards.
Rock Samphire
Crithmum maritimum

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 50cm. Perennial that is woody at the base, and has fleshy hairless stems and leaves with straight fleshy lobes. Flowers are yellow and borne in thick-stalked, plate-like umbels. Fruits are 5–6mm in diameter, yellow or purple, with thick ridges.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows in coastal areas among rocks and stabilized shingle.
DISTRIBUTION
Occurs on the Atlantic coast of Britain from Scotland southwards, and from north-west France south, including the coasts of the Black Sea and Mediterranean.
Alexanders
Smyrnium olusatrum

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 1.5m. Biennial with celery-scented shiny dark green leaves divided into three, each segment being three lobed with a toothed margin. Flowers are yellow with up to 15 simple umbels forming a compound umbel. Fruits are up to 6mm in diameter, oval, hard and reddish-brown.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows in sandy soils, often near the sea.
DISTRIBUTION
Naturalized and common around the coasts of southern Britain and continental Europe, northwards to Denmark.
Sea Kale
Crambe maritima
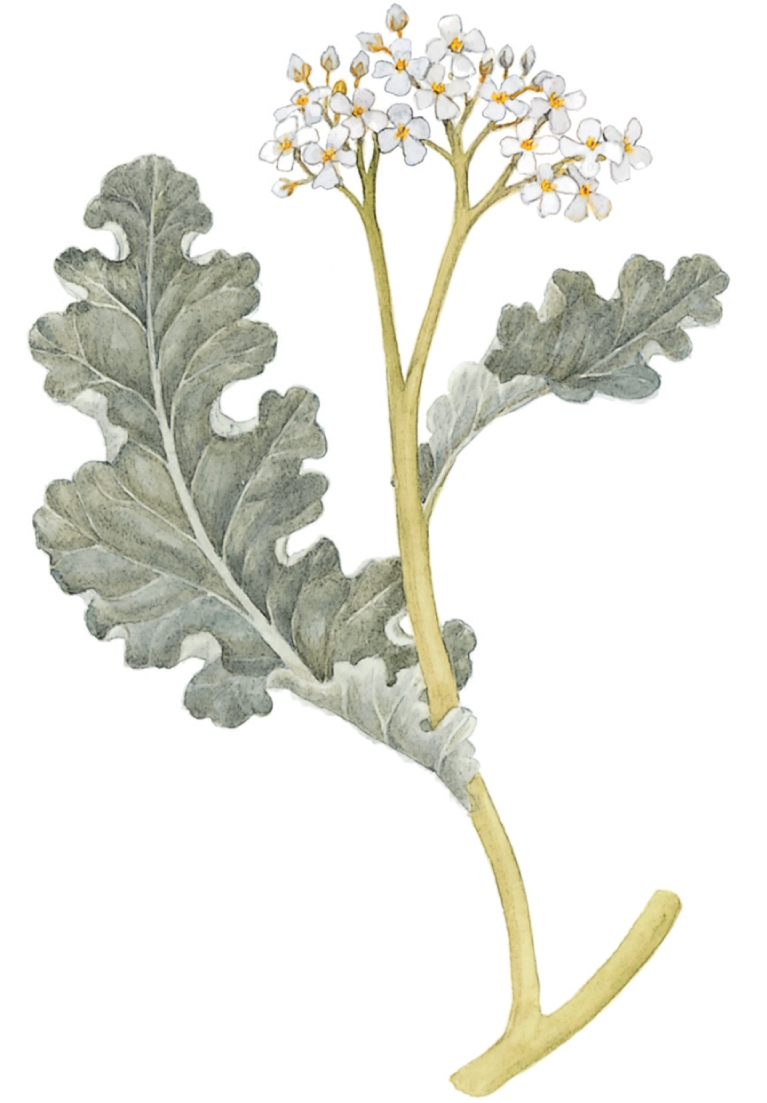

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 75cm. Architectural perennial with a branched fleshy rhizome and a thick erect stem. Leaves are bluish and leathery, lobed with wavy margins. Mature leaves are very large, usually 30–50cm long. Flowers are white, up to 1.5cm in diameter and borne in striking dense terminal clusters in June–August. Plant forms a large and almost hemispherical thicket resting on the ground.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows on shingle beaches on coasts, in poor calcareous soils.
DISTRIBUTION
Widespread but sparsely distributed on the shores of Britain and continental northern Europe.
Common Scurvy-grass
Cochlearia officinalis

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 30cm. Biennial or perennial with a long taproot. Several smooth and fleshy stems spring from the rootstock and are either trailing or vertical. Basal leaves are heart shaped varying to kidney shaped or round, with long stalks. Stem leaves are stalkless, clasp the stem, and are lobed and toothed. Flowers are small with four white petals, and arranged in loose spikes.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows in salt marshes, on coastal cliffs, and inland near salt mines and saline springs.
DISTRIBUTION
Occurs throughout most European coastal areas. Common in much of Britain.
Sea Beet
Beta vulgaris maritima
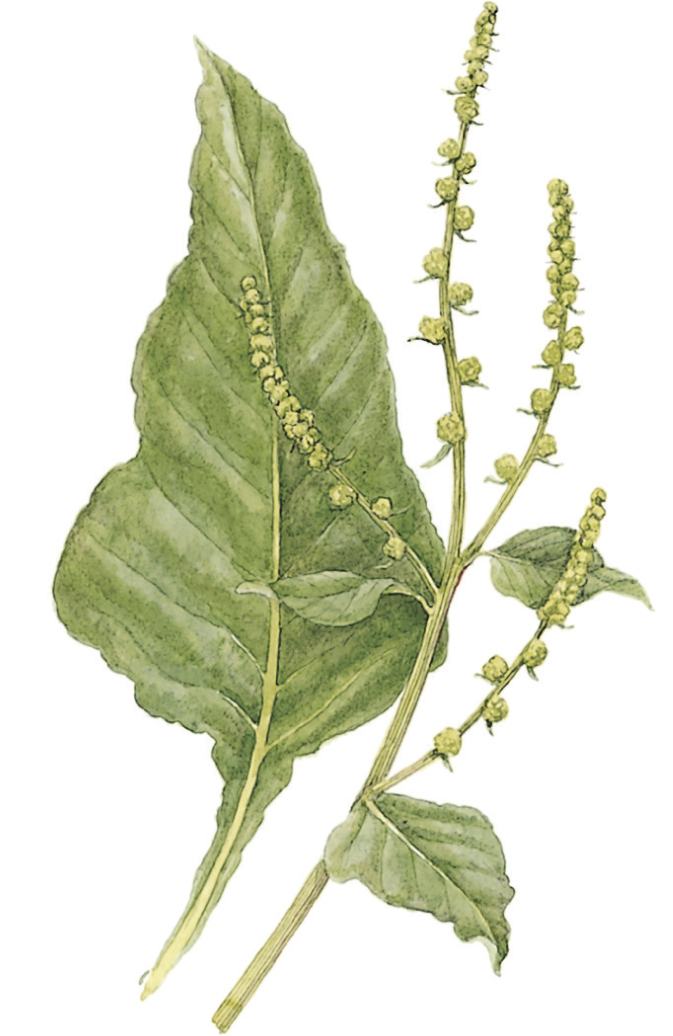

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 80cm. Annual, biennial or perennial, sometimes sprawling, but usually bushy. Leaves are shiny green, oval or wedge-shaped, and pointed. Flowers are small and greenish, arranged in clusters of up to three and borne on a branched spike. The wild ancestor of common vegetables such as beetroot, sugar beet and Swiss chard.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Grows on coasts on the edges of salt marshes and along coastal footpaths on calcareous soils.
DISTRIBUTION
Found in southern and western Europe, including southern Britain, but rarer further north.
Yellow Horned-poppy
Glaucium flavum
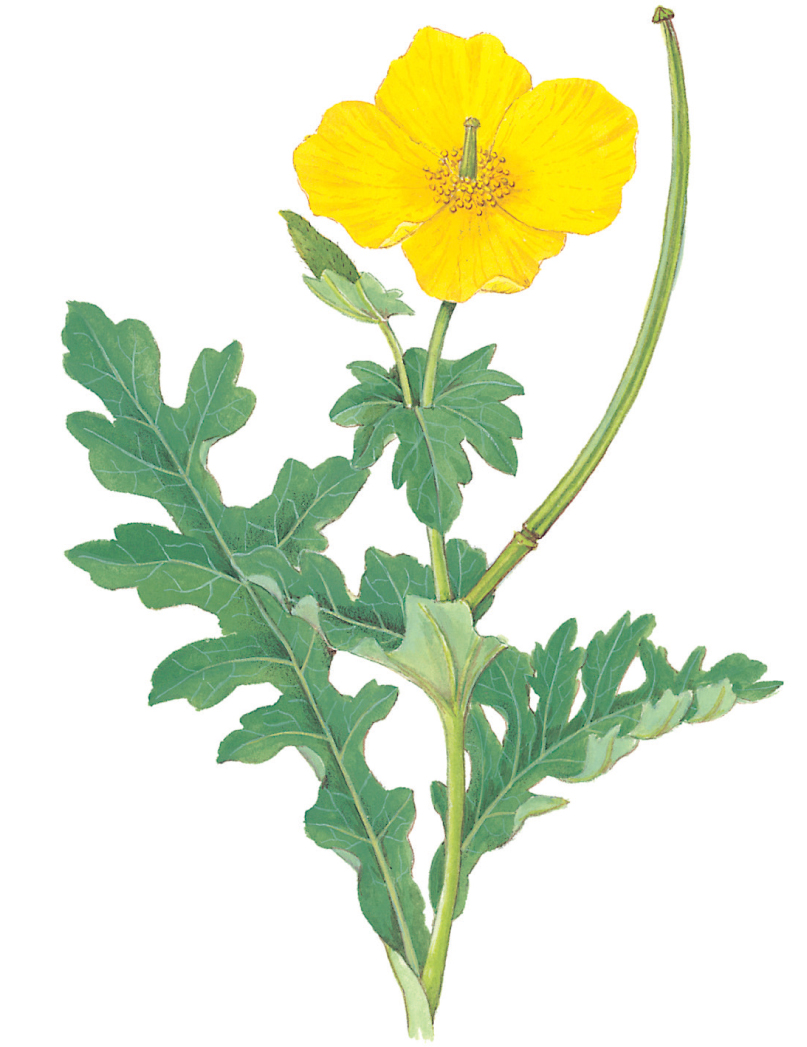

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Height to 90cm. Branching clump-forming biennial or perennial. Leaves are blue-green, the basal ones being deeply pinnately lobed and arranged in a rosette. Flowers are 6–8cm across and consist of two sepals and four papery bright yellow petals; they appear in April–September. Horn-like pods are up to 30cm long, slender and curved.
HABITAT AND ECOLOGY
Restricted principally to stable stretches of coastal shingle.
DISTRIBUTION
Occurs on most suitable coasts around Europe, but generally only locally common.