Data model relationships must result in a single, unambiguous filter path across the tables of the model. In other words, a filter applied to one table must follow a single path to filter another table—the filter context cannot branch off into multiple intermediate tables prior to filtering a final table. In the following screenshot from the Relationships View, only one of the two relationships to the Auto Accidents fact table is allowed to be active (solid line):
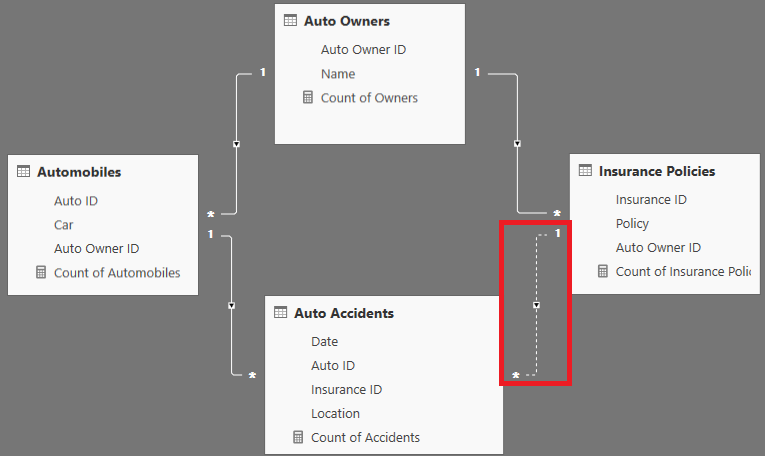
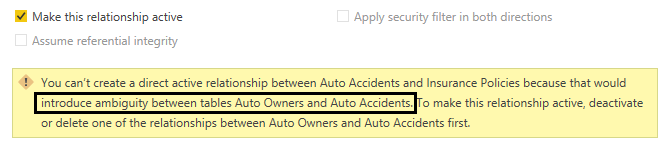
When a filter is applied to the Auto Owners table, the inactive relationship between Insurance Polices and Auto Accidents provides a single, unambiguous filter path from Auto Owners to Auto Accidents via relationships with the Automobiles table. If the model author tries to set both relationships to the Auto Accidents table as active, Power BI will reject this relationship and advise of the ambiguity it would create, as shown in the following screenshot:
Given the active relationship between the Automobiles and Auto Accidents tables, if the relationship between Insurance Policies and Auto Accidents was active, the Auto Owners table would have two separate paths to filter the Auto Accidents table (via Insurance Policies or via Automobiles).