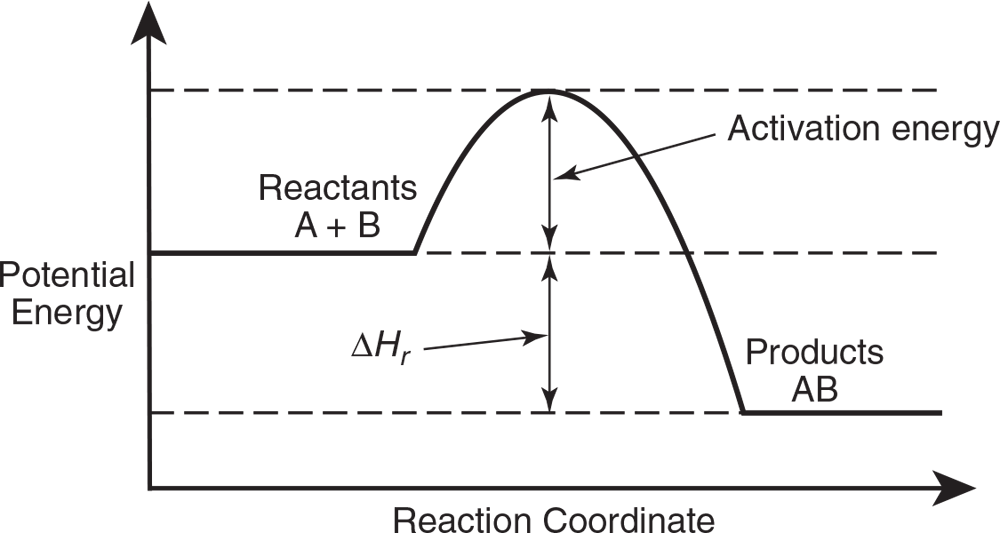
Often a reaction rate may be increased or decreased by affecting the activation energy, that is, the energy necessary to cause a reaction to occur. This is shown graphically in Figure 9.1 for the forward reaction.

Activation energy is the energy necessary to cause a reaction to occur.
A catalyst, as explained in the preceding section, is a substance that is introduced into a reaction to speed up the reaction by changing the amount of activation energy needed. The effect of a catalyst used to speed up a reaction can be shown as follows in Figure 9.2:
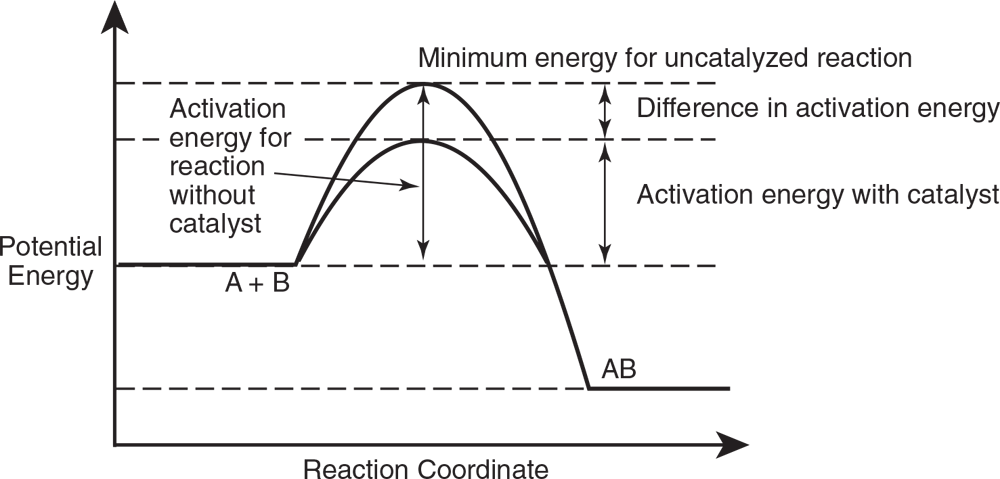
A catalyst speeds up the reaction but is not consumed itself.