Appendix C
Common Medical Abbreviations
- ABC – airway, breathing, circulation
- abd. – abdomen
- ABG – arterial blood gas
- ABO – system of classifying blood groups
- ac – before meals
- ACE – angiotensin-converting enzyme
- ACS – acute compartment syndrome
- ACTH – adrenocorticotrophic hormone
- ad lib – freely, as desired
- ADH – antidiuretic hormone
- ADL – activities of daily living
- AFP – alpha-fetoprotein
- AIDS – acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- AKA – above-the-knee amputation
- ALL – acute lymphocytic leukemia
- ALP – alkaline phosphatase
- ALS – amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- ALT – alkaline phosphatase (formerly SGPT)
- AMI – antibody-mediated immunity
- AML – acute myelogenous leukemia
- amt. – amount
- ANA – antinuclear antibody
- ANS – autonomic nervous system
- AP – anteroposterior
- A&P – anterior and posterior
- APC – atrial premature contraction
- aq. – water
- ARDS – adult respiratory distress syndrome
- ASD – atrial septal defect
- ASHD – atherosclerotic heart disease
- AST – aspartate aminotransferase (formerly SGOT)
- ATP – adenosine triphosphate
- AV – atrioventricular
- BCG – Bacille Calmette-Guerin
- bid – two times a day
- BKA – below-the-knee amputation
- BLS – basic life support
- BMR – basal metabolic rate
- BP – blood pressure
- BPH – benign prostatic hypertrophy
- bpm – beats per minute
- BPR – bathroom privileges
- BSA – body surface area
- BUN – blood urea nitrogen
- C – centigrade, Celsius
-
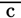 – with
– with
- Ca – calcium
- CA – cancer
- CABG – coronary artery bypass graft
- CAD – coronary artery disease
- CAL – chronic airflow limitations
- CAPD – continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- caps – capsules
- CBC – complete blood count
- CC – chief complaint
- cc – cubic centimeter
- CCU – coronary care unit, critical care unit
- CDC – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- CHF – congestive heart failure
- CK – creatine kinase
- Cl – chloride
- CLL – chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- cm – centimeter
- CMV – cytomegalovirus
- CNS – central nervous system
- CO – carbon monoxide, cardiac output
- CO2 – carbon dioxide
- comp – compound
- cont – continuous
- COPD – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CP – cerebral palsy
- CPAP – continuous positive airway pressure
- CPK – creatine phosphokinase
- CPR – cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- CRP – C-reactive protein
- C&S – culture and sensitivity
- CSF – cerebrospinal fluid
- CT – computerized tomography
- CTD – connective tissue disease
- CTS – carpal tunnel syndrome
- cu – cubic
- CVA – cerebrovascular accident or costovertebral angle
- CVC – central venous catheter
- CVP – central venous pressure
- D&C – dilation and curettage
- DC – discontinue
- DCBE – double-contrast barium enema
- DIC – disseminated intravascular coagulation
- DIFF – differential blood count
- dil. – dilute
- DJD – degenerative joint disease
- DKA – diabetic ketoacidosis
- dL, dl – deciliter (100 mL)
- DM – diabetes mellitus
- DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid
- DNR – do not resuscitate
- DO – doctor of osteopathy
- DOE – dyspnea on exertion
- DPT – vaccine for diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus
- Dr. – doctor
- DRE – digital rectal exam
- DVT – deep vein thrombosis
- D/W – dextrose in water
- Dx – diagnosis
- ECF – extracellular fluid
- ECG, EKG – electrocardiogram
- ECT – electroconvulsive therapy
- ED – emergency department
- EEG – electroencephalogram
- EMD – electromechanical dissociation
- EMG – electromyography
- ENT – ear, nose, and throat
- ERCP – endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- ESRD – end-stage renal disease
- ET – endotracheal tube
- F – Fahrenheit
- FBD – fibrocystic breast disease
- FBS – fasting blood sugar
- FDA – U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- FFP – fresh frozen plasma
- FHR – fetal heart rate
- FHT – fetal heart tone
- fl – fluid
- FOBT – fecal occult blood test
- 4 × 4 – piece of gauze 4 inches by 4 inches; used for dressings
- FSH – follicle-stimulating hormone
- ft. – foot, feet (unit of measure)
- FUO – fever of undetermined origin
- g – gram
- GB – gallbladder
- GCS – Glasgow coma scale
- GFR – glomerular filtration rate
- GH – growth hormone
- GI – gastrointestinal
- gr – grain
- gtt – drops
- GU – genitourinary
- GYN – gynecological
- h, hrs – hour, hours
- (H) – hypodermically
- Hb, Hgb – hemoglobin
- HCG – human chorionic gonadotropin
- HCO3 – bicarbonate
- Hct – hematocrit
- HD – hemodialysis
- HDL – high-density lipoprotein
- Hg – mercury
- HGH – human growth hormone
- HHNK – hyperglycemia hyperosmolar nonketotic coma
- HIV – human immunodeficiency virus
- HLA – human leukocyte antigen
- H2O – water
- HR – heart rate
- HSV – herpes simplex virus
- HTN – hypertension
- Hx – history
- Hz – hertz (cycles/second)
- IAPB – intra-aortic balloon pump
- IBBP – intermittent positive pressure breathing
- IBS – irritable bowel syndrome
- ICF – intracellular fluid
- ICP – intracranial pressure
- ICS – intercostal space
- ICU – intensive care unit
- I&D – incision and drainage
- IDDM – insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type 1)
- IgA – immunoglobulin A
- IM – intramuscular
- I&O – intake and output
- IOP – increased intraocular pressure
- IPG – impedance plethysmogram
- IPPB – intermittent positive-pressure breathing
- IUD – intrauterine device
- IV – intravenous
- IVC – intraventricular catheter
- IVP – intravenous pyelogram or intravenous pyelography
- JRA – juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- K+ – potassium
- kcal – kilocalorie (food calorie)
- kg – kilogram
- KO, KVO – keep vein open
- KS – Kaposi’s sarcoma
- KUB – kidneys, ureters, bladder
- L, l – liter
- lab – laboratory
- lb – pound
- LBBB – left bundle branch block
- LDH – lactate dehydrogenase
- LDL – low-density lipoprotein
- LE – lupus erythematosus
- LH – luteinizing hormone
- liq – liquid
- LLQ – left lower quadrant
- LOC – level of consciousness
- LP – lumbar puncture
- LPN – licensed practical nurse
- Lt, lt – left
- LTC – long-term care
- LUQ – left upper quadrant
- LV – left ventricle
- LVN – licensed vocational nurse
- m – minum, meter, micron
- MAO – monoamine oxidase inhibitor
- MAST – military antishock trousers
- mcg – microgram
- MCH – mean corpuscular hemoglobin
- MCV – mean corpuscular volume
- MD – muscular dystrophy, medical doctor
- MDI – metered dose inhaler
- mEq – milliequivalent
- mg – milligram
- Mg – magnesium
- MG – myasthenia gravis
- MI – myocardial infarction
- mL, ml – milliliter
- mm – millimeter
- MMR – vaccine for measles, mumps, rubella
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging
- MS – multiple sclerosis
- N – nitrogen, normal (strength of solution)
- NIDDM – non–insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (type 2)
- Na+ – sodium
- NaCl – sodium chloride
- NANDA – North American Nursing Diagnosis Association
- NG – nasogastric
- NGT – nasogastric tube
- NLN – National League for Nursing
- noc – at night
- NPO – nothing by mouth (nil per os)
- NS – normal saline
- NSAID – nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- NSNA – National Student Nurses’ Association
- NST – non-stress test
- O2 – oxygen
- OB-GYN – obstetrics and gynecology
- OCT – oxytocin challenge test
- OOB – out of bed
- OPC – outpatient clinic
- OR – operating room
-
 – by mouth
– by mouth
- OSHA – Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- OTC – over-the-counter (drug that can be obtained without a prescription)
- oz – ounce
-
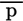 – with
– with
- P – pulse, pressure, phosphorus
- PA Chest – posterior-anterior chest x-ray
- PAC – premature atrial complexes
- PaCO2 – partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood
- PaO2 – partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood
- PAD – peripheral artery disease
- Pap – Papanicolaou smear
- pc – after meals
- PCA – patient-controlled analgesia
- pCO2 – partial pressure of carbon dioxide
- PCP – Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (formerly Pneumocystitis carinii pneumonia)
- PD – peritoneal dialysis
- PE – pulmonary embolism
- PEEP – positive end-expiratory pressure
- PERRLA – pupils equal, round, react to light and accommodation
- PET – postural emission tomography
- PFT – pulmonary function test
- pH – hydrogen ion concentration
- PICC – peripherally inserted central catheter
- PID – pelvic inflammatory disease
- PKD – polycystic disease
- PKU – phenylketonuria
- PMS – premenstrual syndrome
- PND – paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- PO, po – by mouth
- pO2 – partial pressure of oxygen
- PPD – positive purified protein derivative (of tuberculin)
- PPE – personal protective equipment
- PPN – partial parenteral nutrition
- PRN, prn – as needed, whenever necessary
- pro time – prothrombin time
- PSA – prostate-specific antigen
- psi – pounds per square inch
- PSP – phenolsulfonphthalein
- PT – physical therapy, prothrombin time
- PTCA – percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
- PTH – parathyroid hormone
- PTSD – post-traumatic stress disorder
- PTT – partial thromboplastin time
- PUD – peptic ulcer disease
- PVC – premature ventricular contraction
- q – every
- QA – quality assurance
- qh – every hour
- q 2 h – every two hours
- q 4 h – every four hours
- qid – four times a day
- qs – quantity sufficient
- R – rectal temperature, respirations, roentgen
- RA – rheumatoid arthritis
- RAI – radioactive iodine
- RAIU – radioactive iodine uptake
- RAS – reticular activating system
- RBBB – right bundle branch block
- RBC – red blood cell or red blood count
- RCA – right coronary artery
- RDA – recommended dietary allowance
- resp – respirations
- RF – rheumatic fever, rheumatoid factor
- Rh – antigen on blood cell indicated by + or –
- RIND – reversible ischemic neurologic deficit
- RLQ – right lower quadrant
- RN – registered nurse
- RNA – ribonucleic acid
- R/O, r/o – rule out, to exclude
- ROM – range of motion (of joint)
- Rt, rt – right
- RUQ – right upper quadrant
- Rx – prescription
-
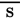 – without
– without
- S., Sig. – (Signa) to write on label
- SA – sinoatrial node
- SaO2 – systemic arterial oxygen saturation (%)
- sat sol – saturated solution
- SBE – subacute bacterial endocarditis
- SDA – same-day admission
- SDS – same-day surgery
- S/E – side effects
- sed rate – sedimentation rate
- SGOT – serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (see AST)
- SGPT – serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (see ALT)
- SI – International System of Units
- SIADH – syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
- SIDS – sudden infant death syndrome
- SL – sublingual
- SLE – systemic lupus erythematosus
- SMBG – self-monitoring blood glucose
- SMR – submucous resection
- SOB – shortness of breath
- sol – solution
- sp gr – specific gravity
- spec. – specimen
-
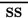 – one half
– one half
- SS – soapsuds
- S/S, s/s – signs and symptoms
- SSKI – saturated solution of potassium iodide
- stat – immediately
- STD – sexually transmitted disease
- subcut, SubQ – subcutaneous
- sx – symptoms
- Syr. – syrup
- T – temperature, thoracic (followed by the number designating specific thoracic vertebra)
- T&A – tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy
- tabs – tablets
- TB – tuberculosis
- T&C – type and crossmatch
- TED – antiembolitic stockings
- temp – temperature
- TENS – transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
- TIA – transient ischemic attack
- TIBC – total iron binding capacity
- tid – three times a day
- tinct, tr. – tincture
- TLC – total lymphocyte count
- TMJ – temporomandibular joint
- TPA, t-pa – tissue plasminogen activator
- TPN – total parenteral nutrition
- TPR – temperature, pulse, respiration
- TQM – total quality management
- TSE – testicular self-examination
- TSH – thyroid-stimulating hormone
- tsp. – teaspoon
- TSS – toxic shock syndrome
- TURP – transurethral prostatectomy
- UA – urinalysis
- um – unit of measurement
- ung – ointment
- URI – upper respiratory tract infection
- UTI – urinary tract infection
- VAD – venous access device
- VDRL – Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (test for syphilis)
- VF, Vfib – ventricular fibrillation
- VPC – ventricular premature complexes
- VS, vs – vital signs
- VSD – ventricular septal defect
- VT – ventricular tachycardia
- WBC – white blood cell or white blood count
- WHO – World Health Organization
- WNL – within normal limits
- wt – weight
- X PO – 10 grains per orem
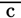 – with
– with
 – by mouth
– by mouth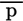 – with
– with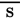 – without
– without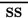 – one half
– one half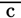 – with
– with
 – by mouth
– by mouth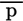 – with
– with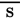 – without
– without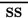 – one half
– one half