Practice Test
- Directions: Each question or incomplete statement below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. In each case, HIGHLIGHT the statement that best answers the question or completes the statement. Allot 3 hours of uninterrupted time to take the practice test.
-
The LPN/LVN is gathering data from a client who is receiving treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Which of the following is the most important question the LPN/LVN should ask this client? - “Do you find yourself forgetting simple things?”
- “Do you find it difficult to focus on a given task?”
- “Do you have trouble controlling upsetting thoughts?”
- “Do you experience feelings of panic in a closed area?”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client who states, “I just want to die.” The LPN/LVN should examine the client’s medical record for which of the following documents? - Advance directives.
- Power of attorney.
- “Do not resuscitate” order.
- Living will.
-
A newly admitted client with a history of seizures suddenly says to the LPN/LVN, “I hear drums.” Which of the following should the LPN/LVN do first? - Tell the client to ignore the drums.
- Place client in a darkened room away from nurses’ station.
- Continue to question the client about the drum sound.
- Insert an oral airway in the client.
-
A client diagnosed with multiple myeloma is admitted to the unit after developing pneumonia. When the LPN/LVN enters the client’s room wearing a mask, the client says, in an irritated tone of voice, “Why are you wearing that mask?” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “The chest x-ray taken this morning indicates you have pneumonia.”
- “What have you been told about the x-rays that were taken this morning?”
- “You have been placed on contact precautions due to your infection.”
- “I am trying to protect you from the germs in the hospital.”
-
A nursing team consists of an RN, an LPN/LVN, and a unlicensed assistive personel (UAP). The LPN/LVN should be assigned to which of the following clients? - A client with a diabetic ulcer that requires a dressing change.
- A client diagnosed with cancer who is reporting bone pain.
- A client with terminal cancer being transferred to hospice home care.
- A client with a fracture of the right leg who asks to use the urinal.
-
To determine the structural relationship of one hospital department with another, the LPN/LVN should consult which of the following? - Organizational chart.
- Job descriptions.
- Personnel policies.
- Procedures manual.
-
A client reports pain in the right lower extremity. The primary health care provider prescribes codeine 60 mg and aspirin grains X PO every 4 hours, as needed for pain. Each codeine tablet contains 15 mg of codeine. Each aspirin tablet contains 325 mg of aspirin. Which of the following should the LPN/LVN administer? - 2 codeine tablets and 4 aspirin tablets.
- 4 codeine tablets and 3 aspirin tablets.
- 4 codeine tablets and 2 aspirin tablets.
- 3 codeine tablets and 3 aspirin tablets.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client receiving paroxetine. It is most important for the LPN/LVN to report which of the following to the primary health care provider? - The client reports no appetite change.
- The client reports recently being started on digoxin.
- The client reports applying sunscreen to go outdoors.
- The client reports driving the car to work.
-
A client with a “do not resuscitate” order experiences a cardiac arrest. Which of the following is the first action the LPN/LVN should take? - Administer lifesaving medications.
- Assess the client for signs of death.
- Open the airway and give 2 breaths.
- Summon the emergency code team.
-
An LPN/LVN is working in the newborn nursery. Which of the following client-care assignments should the LPN/LVN question? - A 2-day-old client lying quietly alert with a heart rate of 185 beats/minute.
- A 1-day-old client who is crying and has a bulging anterior fontanel.
- A 12-hour-old client whose respirations are 45 breaths/minute and irregular while being held.
- A 5-hour-old client whose hands and feet appear blue bilaterally while sleeping.
-
The LPN/LVN is inserting a nasogastric (NG) tube. The LPN/LVN should use which of the following personal protective equipment during NG tube insertion? - Gloves, gown, goggles, and surgical cap.
- Sterile gloves, mask, and gown.
- Gloves, gown, mask, and goggles.
- Double gloves, goggles, mask, and surgical cap.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for clients in the outpatient clinic. Which of the following clients should the LPN/LVN see first? - A client with hepatitis A who states, “My arms and legs are itching.”
- A client with a cast on the right leg who states, “I have a funny feeling in my right leg.”
- A client with osteomyelitis of the spine who states, “I am so nauseous that I can’t eat.”
- A client with rheumatoid arthritis who states, “I am having trouble sleeping.”
-
Which of the following client assignments should an LPN/LVN question? - A client with a chest tube who is ambulating in the hallhway.
- A client with a colostomy who requires colostomy irrigation assistance.
- A client with a right-sided stroke who requires assistance with bathing.
- A client who is refusing medication to treat cancer of the colon.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with hepatitis B. The client is to be discharged the next day. The LPN/LVN would be most concerned if the client made which of the following statements? - “I must not share eating utensils with my family members.”
- “I must use my own bath towel.”
- “I’m glad I can have intimate relations with my partner.”
- “I must eat small, frequent meals.”
-
The LPN/LVN is carrying out the plan for care of a client with anemia who reports weakness. Which of the following tasks could be assigned to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)? - Auscultate the client’s breath sounds.
- Set up the client’s lunch tray.
- Obtain client's dietary history.
- Instruct client how to balance rest and activity.
-
The LPN/LVN on the surgical floor is receiving hand-off report from the RN. Which of the following clients should the LPN/LVN see first? - A client admitted 3 days ago with a gunshot wound; 1.5-cm area of dark drainage noted on the dressing.
- A client who had a mastectomy 2 days ago; 23 mL of serosanguinous fluid noted in the wound drain.
- A client with a collapsed lung due to an accident; no drainage noted in the previous 8 hours.
- A client who had an abdominal-perineal resection 3 days ago; client now reports chills.
-
A client scheduled for a cardiac catheterization says to the LPN/LVN, “I know you were in here when I signed the consent form for the test. I thought I understood everything, but now I’m not so sure.” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “Why didn’t you listen more closely to the explanation?”
- “You sound as if you would like to ask more questions.”
- “I’ll get you a pamphlet about cardiac catheterization.”
- “That often happens during explanation of this procedure.”
-
A 1-day-old client diagnosed with intrauterine growth retardation has a high-pitched shrill cry and appears restless and irritable. The LPN/LVN also observes fist-sucking behavior. Based on this data, which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take first? - Gently massage the client's back every 2 hours.
- Tightly swaddle the client in a flexed position.
- Schedule feeding times every 3 to 4 hours.
- Encourage eye contact with the client during feedings.
-
The LPN/LVN visits a neighbor who is at 20 weeks’ gestation. The neighbor reports nausea, headache, and blurred vision. The LPN/LVN notes that the neighbor has tremors and appears nervous and diaphoretic. It would be most important for the LPN/LVN to ask which of the following questions? - “Are you having menstrual-like cramps?”
- “When did you last eat or drink?”
- “Have you been diagnosed with diabetes?”
- “Have you been lying on the couch?”
-
The LPN/LVN notes that a client newly admitted to the pediatric unit is scratching the head almost constantly. It would be most important for the LPN/LVN to take which of the following actions? - Discuss basic hygiene with the parents.
- Instruct the child not to sleep with the dog.
- Advise parents to contact an exterminator.
- Observe the scalp for small white specks.
-
The client diagnosed with major depressive disorder who was admitted to the psychiatric unit for treatment and observation a week ago suddenly appears cheerful and motivated. The LPN/LVN should be aware of which of the following? - The client is likely sleeping well because of the medication.
- The client has made new friends and has a support group.
- The client may have finalized a suicide plan.
- The client is no longer depressed due to treatment.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client reports an off-white vaginal discharge with a curdlike appearance. The LPN/LVN observes the discharge and vulvular erythema. It would be most important for the LPN/LVN to ask which of the following questions? - “Do you routinely douche?”
- “Are you sexually active?”
- “What kind of birth control do you use?”
- “Have you taken any cough medicine?”
-
The primary health care provider orders application of an elastic wrap bandage for a client’s left leg from toes to mid-thigh. The LPN/LVN should do which of the following? - Increase friction between skin and bandage surfaces.
- Leave a small distal portion of the extremity exposed.
- Use multiple pins to secure the bandage.
- Position the left leg in abduction.
-
A client recovering from a laparoscopic laser cholecystectomy says to the LPN/LVN, “I hate the thought of eating a low-fat diet for the rest of my life.” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is most appropriate? - “I will ask the dietician to come speak with you.”
- “What do you think is so bad about following a low-fat diet?”
- “It may not be necessary for you to follow a low-fat diet for that long.”
- “At least you will be alive and not suffering that pain.”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for clients in a pediatric clinic. The mother of a 14-year-old male privately tells the LPN/LVN that she is worried about her son because she unexpectedly walked into his bedroom and discovered him masturbating. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is most appropriate? - “Tell your son he could go blind doing that.”
- “Masturbation is a normal part of sexual development.”
- “He’s really too young to be masturbating.”
- “Why don’t you give him more privacy?”
-
A client begins to breathe very rapidly. Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN would be the most appropriate? - Auscultate the client's apical pulse rate.
- Measure client's blood pressure and pulse.
- Notify the primary health care provider.
- Obtain the client's oxygen saturation level.
-
The LPN/LVN is planning morning care for a client hospitalized after a stroke resulting in left-sided paralysis and homonymous hemianopia. During morning care, the LPN/LVN should do which of the following? - Provide morning care from the right side of the client.
- Speak loudly and distinctly when talking with the client.
- Reduce the level of lighting in the client’s room to prevent glare.
- Provide the client’s care to reduce the client's energy expenditure.
-
A primigravid client at 32 weeks’ gestation comes to the clinic for her initial prenatal visit. The client reports periodic headaches and continually bumping into things. The LPN/LVN observes numerous bruises in various stages of healing around the client’s breasts and abdomen. Vital signs are: BP 120/80, pulse 72 beats/minute, respirations 18 breaths/minute, and fetal heart tones 142 beats/minute. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “Are you battered by your partner?”
- “How do you feel about being pregnant?”
- “Tell me about your headaches.”
- “You may be more clumsy due to your size.”
-
The LPN/LVN is providing care for a client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who is receiving oxygen through a nasal cannula. The LPN/LVN should expect which of the following to occur? - Arterial blood gases will be analyzed every 2 hours.
- The client’s oral intake will be restricted.
- The client will be maintained on bed rest.
- The oxygen flow rate will be set at 3 L/minute or less.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a pediatric client in a leg cast for treatment of a right ankle fracture. It is most important for the LPN/LVN to reinforce which of the following activities after discharge? - The client performs isometric exercises of the right leg.
- The parent massages the client's right foot with moisturizer.
- The parent cleans the leg cast with mild soap and water.
- The parent elevates the right leg on several pillows.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client who had a thyroidectomy 12 hours ago for treatment of Graves’ disease. The LPN/LVN would be most concerned if which of the following were observed? - The client’s vital signs include: blood pressure 138/82 mm Hg, pulse 84 beats/minute, and respirations 16 breaths/minute.
- The client supports the head and neck to turn head to right.
- The client spontaneously flexes the wrist when the blood pressure cuff is inflated during blood pressure measurement.
- The client becomes drowsy and reports a sore throat.
-
A client is admitted who reports severe pain in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take to assist the client with pain relief? - Encourage rhythmic, shallow breathing.
- Massage the right lower quadrant of the abdomen.
- Apply a warm heating pad to the client's abdomen.
- Position client for comfort using pillows.
-
Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN would be considered negligence? - Administering heparin subcutaneously into a client’s abdomen without first aspirating for blood.
- Crushing furosemide and adding to a teaspoon of applesauce for an elderly client.
- Lowering the bed side rails after administering meperidine and hydroxyzine to a client preoperatively.
- Placing a used syringe and needle in a sharps container in a client’s room.
-
The LPN/LVN is teaching an elderly client with right-sided weakness how to use a cane. Which of the following behaviors by the client indicates that the teaching was effective? - The client holds the cane with the right hand, moves the cane forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg.
- The client holds the cane with the right hand, moves the cane forward followed by the left leg, and then moves the right leg.
- The client holds the cane with the left hand, moves the cane forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg.
- The client holds the cane with the left hand, moves the cane forward followed by the left leg, and then moves the right leg.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for client whose vital signs have been within normal limits. Now vital signs include: tympanic temperature 103.6° F (39.7° C), pulse 82 beats/minute, regular and strong, respirations 14 breaths/minute, shallow and unlabored, and blood pressure 134/88 mm Hg. What should the LPN/LVN’s next action be?
- Notify primary health care provider immediately.
- Proceed with the client’s care.
- Record vital signs in medical record.
- Retake the temperature with different thermometer.
-
A client admitted to the hospital with right femur fracture is placed in balanced suspension traction with a Thomas splint and Pearson attachment. During the first 48 hours, the LPN/LVN should gather data related to which of the following complications? - Pulmonary embolism.
- Fat embolism.
- Avascular necrosis.
- Bone malunion.
-
The LPN/LVN is helping an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) provide a bed bath to a comatose client who is incontinent. The LPN/LVN should intervene if which of the following actions is noted? - The UAP answers the phone while wearing gloves.
- The UAP log-rolls the client to provide back care.
- The UAP places an incontinence pad under the client.
- The UAP positions client on the left side, head elevated.
-
A client is brought to the emergency department for treatment after being found on the floor by a family member. When comparing the legs, the LPN/LVN would most likely make which of the following observations? - The client’s left leg is longer than the right leg and externally rotated.
- The client’s left leg is shorter than the right leg and internally rotated.
- The client’s left leg is shorter than the right leg and adducted.
- The client’s left leg is longer than the right leg and is abducted.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with a cast on the left leg. The LPN/LVN would be most concerned if which of the following is observed? - Capillary refill time is less than 3 seconds.
- Client reports discomfort and itching.
- Client reports tightness and pain.
- Client’s foot is elevated on a pillow.
-
The LPN/LVN is assisting with discharging a client from an inpatient alcohol treatment unit. Which of the following statements by the client’s wife indicates that the family is coping adaptively? - “My husband will do well as long as I keep him engaged in activities that he likes.”
- “My focus is learning how to live my life.”
- “I am so glad that our problems are behind us.”
- “I’ll make sure that the children don’t give my husband any problems.”
-
An LPN/LVN is caring for clients in the mental health clinic. A client reporting insomnia and anorexia tearfully tells the LPN/LVN about a personal job loss after 15 years of employment with the company. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is most appropriate? - “Did you receive a severance package?”
- “Focus on your healthy, happy family.”
- “Explain what happened with your job.”
- “Job loss is very common these days.”
-
A client with a history of alcohol use disorder is transferred to the unit in an agitated state. The client is vomiting and diaphoretic, and states that it has been 5 hours since the last drink. The LPN/LVN would expect to administer which of the following medications? - Chlordiazepoxide.
- Disulfiram.
- Methadone.
- Naloxone.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client diagnosed with end-stage colon cancer. The spouse of the client says, “We have been married for so long. I am not sure how I can go on now.” What is the most appropriate response by the LPN/LVN? - “It sounds like your children will be there to help during your time of grieving.”
- “I know this is difficult. Tell me more about what you are feeling now.”
- “Think about the pain and suffering your spouse has endured lately.”
- “I will call the hospice nurse to discuss to your spouse's condition with you.”
-
The LPN/LVN is reinforcing teaching with an elderly client about how to use a standard aluminum walker. Which of the following behaviors by the client indicates that the reinforcement of teaching was effective? - The client slowly pushes the walker forward 12 inches (30 cm), then takes small steps forward while leaning on the walker.
- The client lifts the walker, moves it forward 10 inches (25 cm), and then takes several small steps forward.
- The client supports weight on the walker while advancing it forward, then takes small steps while balancing on the walker.
- The client slides the walker 18 inches (46 cm) forward, then takes small steps while holding onto the walker for balance.
-
An LPN/LVN is providing care for a group of elderly clients in a long-term care facility. The LPN/LVN knows that the elderly are at greater risk of developing sensory deprivation for which of the following reasons? - Increased sensitivity to the side effects of medications.
- Decreased visual, auditory, and gustatory abilities.
- Isolation from their families and familiar surroundings.
- Decreased musculoskeletal function and mobility.
-
The LPN/LVN would expect which of the following clients to be able to sign a consent form for nonemergent medical treatment? - A school-age child with a right tibia and fibula fracture.
- A client requiring surgery for acute appendicitis.
- A client who is confused after a motor vehicle accident.
- A client who has been legally declared incompetent.
-
An LPN/LVN is assisting with the discharge of a client with a diagnosis of hepatitis of unknown etiology. The LPN/LVN knows that teaching has been successful if the client makes which of the following statements? - “I am so sad that I am not able to hold my baby.”
- “I will eat my meal after my family finishes eating.”
- “I will make sure that my children don’t use my eating utensils.”
- “I’m glad that I don’t have to get help taking care of my children.”
-
The LPN/LVN checks the IV flow rate for a postoperative client. The client is to receive 3,000 mL of lactated Ringer’s lactate solution IV infused over 24 hours. The IV administration set has a drop factor of 10 drops per milliliter. The LPN/LVN would expect the client’s IV to infusing at how many drops per minute? - 18.
- 21.
- 35.
- 40.
-
A client diagnosed with emphysema becomes restless and confused. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take next? - Encourage pursed-lip breathing.
- Measure the client’s temperature.
- Assess the client’s potassium level.
- Increase oxygen flow rate to 5 L/minute.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client following cataract surgery on the right eye. The client reports severe eye pain in the right eye. Which of the following activities should the LPN/LVN do first? - Administer an analgesic to the client.
- Recheck the client's condition in 30 minutes.
- Document finding in client's medical record.
- Report the finding to the supervising RN.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client 4 hours after intracranial surgery. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take immediately? - Instruct the client to deep breathe, cough, and expectorate into a tissue.
- Position the client in a left lateral position with neck flexed.
- Perform passive range-of-motion exercises every two hours.
- Use a turning sheet under the client's head to midthigh to reposition in bed.
-
A pediatric client with a congenital heart disorder is admitted with heart failure. Digoxin 0.12 mg by mouth daily is prescribed for the client. The bottle contains 0.05 mg of digoxin in 1 mL of solution. Which of the following amounts should the LPN/LVN administer to the client after validating the dose with the RN? - 1.2 mL.
- 2.4 mL.
- 3.5 mL.
- 4.2 mL.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hospitalized for treatment of hemolytic anemia. The LPN/LVN should expect to implement which of the following actions? - Encourage activities with other clients in the day room.
- Isolate the client from visitors and clients to avoid infection.
- Provide a diet that contains foods that are high in vitamin C.
- Maintain a quiet environment to promote adequate rest.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with cervical cancer. The LPN/LVN notes that the radium implant has become dislodged. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take first? - Grasp the implant with a sterile hemostat and carefully reinsert it into the client.
- Wrap the implant in a blanket and place it behind a lead shield until reimplantation.
- Ensure the implant is picked up with long-handled forceps and placed in a lead container.
- Obtain a dosimeter reading on the client and report it to the primary health care provider.
-
The LPN/LVN comes to the home of a client with cellulitis of the left leg to perform a daily dressing change. The client tells the LPN/LVN that the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) changed the dressing earlier that morning. Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN is best? - Tell client that the new dressing looks fine.
- Notify the RN supervisor of the situation.
- Ask the client to describe the dressing change.
- Report the UAP to the home care agency.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with pernicious anemia. The LPN/LVN reinforces teaching about the plan of care. The LPN/LVN should report which of the following statements to the RN? - “In order to get better, I will take iron pills.”
- “I will attend smoking cessation classes.”
- “I will learn how to perform IM injections.”
- “I will make sure to eat a well-balanced diet.”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for clients on a general medical/surgical unit of an acute care facility. Four clients have been admitted in the last 20 minutes. Which of the admissions should the LPN/LVN see first? - A client reporting vomiting and diarrhea.
- A client with third-degree burns to face.
- A client with a fractured left hip.
- A client reporting epigastric pain.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with a diagnosis of chronic bronchitis. The client has audible wheezing, and an oxygen saturation of 85%. Four hours ago, the oxygen saturation was 88%. It is most important for the LPN/LVN to take which of the following actions? - Give beclomethasone, 2 puffs via metered-dose inhaler.
- Auscultate the client's bilateral breath sounds.
- Increase oxygen flow rate to 4 L/minute via mask.
- Administer albuterol, 2 puffs via metered-dose inhaler.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client hospitalized for observation following a fall. The client states, “My friend fell last year, and no one thought anything was wrong. She died 2 days later!” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “This happens to quite a few people.”
- “We are monitoring you, so you’ll be okay.”
- “Don’t you think I’m taking good care of you?”
- “You’re concerned that it might happen to you?”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for clients on the pediatric unit. A client with second- and third-degree burns on the right thigh is being admitted. The LPN/LVN should expect the new client to be placed with which one of the following roommates? - A client with chickenpox.
- A client with asthma.
- A client who developed acute diarrhea after antibiotic.
- A client with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
-
To evaluate the effectiveness of a client’s heparin therapy, the LPN/LVN should monitor which of the following laboratory values? - Platelet count.
- Clotting time.
- Bleeding time.
- Prothrombin time.
-
The LPN/LVN is reinforcing teaching with a client who is scheduled for a paracentesis. Which of the following statements by the client indicates that teaching has been successful? - “I will be in surgery for less than an hour.”
- “I must not void prior to the procedure.”
- “Two to 3 liters of fluid will be removed.”
- “I will lie on my back and breathe slowly.”
-
The LPN/LVN is performing chest physiotherapy on a client with chronic airflow limitations (CAL). Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? - Perform chest physiotherapy prior to meals.
- Auscultate breath sounds before the procedure.
- Administer bronchodilators after the procedure.
- Percuss each lobe prior to asking client to cough.
-
In which of the following situations would it be most appropriate for the LPN/LVN to wear a gown and gloves? - Administering oral medications to client with human immunodeficiency virus disease.
- Assisting in the care of a motor vehicle accident victim who continues to bleed.
- Bathing a client with an abdominal wound infection.
- Changing the linen of a client with sickle-cell anemia.
-
A client is receiving 1,000 mL of 5% dextrose in half normal saline solution IV to infuse over 8 hours. The IV administration set tubing delivers 15 drops per milliliter. The LPN/LVN should expect the flow rate to be how many drops per minute? - 15.
- 31.
- 45.
- 60.
-
A client is admitted to the hospital reporting seizures and a high fever. A positron emission tomography (PET) brain scan is ordered. Before the PET brain scan, the client asks the LPN/LVN what position his necessary for the test. Which of the following statements by the LPN/LVN is most accurate? - “You will be in a side-lying position, with the foot of the bed elevated.”
- “You will be in a semi-upright sitting position, with your knees flexed.”
- “You will be lying on your back with a small pillow under your head.”
- “You will be flat on your back, with your feet higher than your head.”
-
A client with a diagnosis of delirium is admitted to the hospital. Blood samples are sent to the laboratory to help determine the underlying cause. Laboratory test results include sodium 156 mEq/L (156 mmol/L), chloride 100 mEq/L (100 mmol/L), potassium 4 mEq/L (4 mmol/L), bicarbonate 21 mEq/L (21 mmol/L), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 86 mg/dL (30.7 mmol/L), glucose 100 mg/dL (5.5 mmol/L). Based on these laboratory results, the LPN/LVN would expect to see which of the following nursing diagnoses in the client's care plan? - Alteration in patterns of urinary elimination.
- Fluid volume deficit.
- Nutritional deficit: less than body requirements.
- Self-care deficit: feeding.
-
A client is to receive 3,000 mL of normal saline solution IV to infuse over 24 hours. The IV administration set delivers 15 drops per milliliter. The LPN/LVN would expect the flow rate to be how many drops of fluid per minute? - 21.
- 28.
- 31.
- 42.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client diagnosed with asthma. The primary health care provider prescribes neostigmine IM. Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN is most appropriate? - Administer medication, as prescribed.
- Obtain the client's blood pressure and pulse.
- Ask pharmacist if medication can be given orally.
- Notify the primary health care provider.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with a history of Addison’s disease who has received steroid therapy for several years. The LPN/LVN would expect the client to exhibit which of the following changes in appearance? - Buffalo hump, girdle-obesity, gaunt facial appearance.
- Skin tanning, mucous membrane discoloration, weight loss.
- Emaciation, nervousness, breast engorgement, hirsutism.
- Truncal obesity, purple striations on the skin, moon face.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with a history of pancreatic cancer who appears jaundiced. The LPN/LVN should give the highest priority to which of the following needs? - Nutrition.
- Self-image.
- Skin integrity.
- Urinary elimination.
-
An pediatric is seen in a clinic for treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Medication has been prescribed for the client along with family counseling. The LPN/LVN reinforces the teaching plan about the medication and discusses parenting strategies with the parents. Which of the following statements by the parents indicates that further teaching is necessary? - “We will give the medication at night so it doesn’t decrease appetite.”
- “We will provide a regular routine for sleeping, eating, working, and playing.”
- “We will establish firm but reasonable limits on behavior.”
- “We will reduce distractions and external stimuli to help concentration.”
-
The client diagnosed with anorexia nervosa is admitted to the hospital. Which of the following statements by the client requires immediate follow-up by the LPN/LVN? - “My gums bled this morning.”
- “I’m getting fatter every day.”
- “Nobody likes me, I’m so ugly.”
- “I feel dizzy and weak today.”
-
A client is admitted to the hospital for treatment of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia and Kaposi’s sarcoma. The client informs the LPN/LVN about a personal decision to become an organ donor. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “What does your family think about your decision?”
- “You will help many people by donating your organs.”
- “Would you like to speak to an organ donor coordinator?”
- “Your illness prevents you from becoming an organ donor.”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client 2 days after a pancreatectomy for cancer of the pancreas. The LPN/LVN observes minimal drainage from the nasogastric (NG) tube. It is most important for the LPN/LVN to take which of the following actions? - Notify primary health care provider.
- Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes.
- Check the NG tube for kinking.
- Replace the NG tube immediately.
-
The LPN/LVN is planning to administer furosemide 20 mg PO to a client diagnosed with chronic kidney disease. The client asks the LPN/LVN the reason for receiving this medication. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “To increase the blood flow to your kidney.”
- “To decrease your circulating blood volume.”
- “To increase excretion of sodium and water.”
- “To decrease the workload on your heart.”
-
The LPN/LVN is reinforcing discharge teaching for a client with Parkinson’s disease. To maintain safety, the LPN/LVN should make which of the following suggestions to the family? - Install a raised toilet seat.
- Obtain a hospital bed.
- Instruct client to hold arms dependently during ambulation.
- Participate in an exercise program during the late afternoon.
-
The LPN/LVN is reinforcing discharge teaching for a client with chronic pancreatitis. Which of the following statements by the client indicates that further teaching is necessary? - “I do not have to restrict physical activity.”
- “I should take pancrelipase before meals.”
- “I will eat three large meals every day.”
- “I need to avoid alcoholic beverages.”
-
Following a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the client reports abdominal pain and bloating. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best? - “Increase intake of fresh fruits and vegetables.”
- “I’ll give you the prescribed pain medication.”
- “Why don’t you take a walk down the hallway?”
- “You may need an indwelling urinary catheter.”
-
The nursing team consists of an RN, an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP), and an LPN/LVN. The LPN/LVN would expect to be assigned to which of the following clients? - A client scheduled for MRI of the brain.
- An unconscious client who requires a bed bath.
- A client in balanced suspension traction.
- A client with diabetes who needs help bathing.
-
The primary health care provider prescribes 1 L dextrose 5% in half normal saline solution IV to infuse over 8 hours. The drip factor stated on the IV administration set tubing is 15 gtt/mL. How many milliliters should the LPN/LVN expect to be infused every hour?
mL
-
A client underwent vagotomy with antrectomy for treatment of a duodenal ulcer. Postoperatively, the client develops dumping syndrome. Which of the following statements by the client indicates to the LPN/LVN that further dietary teaching is necessary? - “I should eat bread with each meal.”
- “I should eat smaller meals more frequently.”
- “I should lie down right after eating.”
- “I should avoid drinking fluids with my meals.”
-
The LPN/LVN reinforces discharge teaching with a client with emphysema. Which of the following statements by the client indicates that teaching was successful? - “Cold weather should help my breathing problems.”
- “I'll eat three balanced meals daily but limit my fluid intake.”
- “I'll limit outside activity when polution levels are high.”
- “Intensive exercise should help me regain strength.”
-
A client has been taking aluminum hydroxide daily for 3 weeks. The LPN/LVN should be alert for which of the following side effects? - Nausea.
- Hypercalcemia.
- Constipation.
- Anorexia.
-
The LPN/LVN is hearing a client call for help. The LPN/LVN enters the room and finds a client in bilateral wrist restraints with a cool, pale right hand and no palpable radial pulse. Which of the following would be the most appropriate action for the LPN/LVN to take first? - Leave to find the client’s nurse.
- Massage the client’s wrist and hand.
- Remove the right wrist restraint.
- Reposition the client to reduce pressure.
-
The LPN/LVN is reinforcing discharge teaching for a client with a new colostomy. The LPN/LVN knows teaching was successful when the client chooses which of the following menu options? - Sausage, sauerkraut, baked potato, and fresh fruit.
- Cheese omelet with bran muffin and fresh pineapple.
- Pork chop, mashed potatoes, turnips, and salad.
- Baked chicken, boiled potato, cooked carrots, and yogurt.
-
A client is admitted to the unit with suspected acute kidney injury. The LPN/LVN would be most concerned if the client made which of the following statements? - “My urine often appears pink-tinged.”
- “It is hard for me to start the flow of urine.”
- “It is quite painful for me to urinate.”
- “I urinate in the morning and again before dinner.”
-
The LPN/LVN is implementing the protocol for teaching a new mother how to breastfeed her newborn. The LPN/LVN knows that teaching has been successful if the client makes which of the following statements? - “My baby’s weight should equal the birthweight in 5 to 7 days.”
- “My baby should have at least 6 to 8 wet diapers per day.”
- “My baby will sleep at least 6 hours between feedings.”
- “My baby will feed for about 10 minutes per feeding.”
-
A client is admitted to the telemetry unit for evaluation of reported chest pain. Eight hours after admission, the client's cardiac monitor shows ventricular fibrillation. The primary health care provider defibrillates the client. The LPN/LVN understands that the purpose of defibrillation is to do which of the following? - Increase cardiac contractility, preload, and cardiac output.
- Depolarize cells allowing SA node to recapture pacing node
- Reduce the degree of cardiac ischemia and acidosis.
- Provide electrical energy for depleted myocardial cells.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client who suddenly reports chest pain. The LPN/LVN knows that which of the following symptoms would be most characteristic of an acute myocardial infarction (MI)? - Intermittent, localized epigastric pain.
- Sharp, localized, unilateral chest pain.
- Severe substernal pain radiating down the left arm.
- Sharp, burning chest pain moving from place to place.
-
The primary health care provider prescribes packing for a nonhealing open surgical wound. Which of the following is the first action by the LPN/LVN? - Identify wound size, shape, and depth.
- Observe for wound drainage or discharge.
- Plan to set up for clean technique.
- Select the proper dressing material.
-
A client returns to the clinic 2 weeks after hospital discharge. The client is taking wafarin sodium 2 mg PO daily. Which of the following statements by the client to the LPN/LVN indicates that further teaching is necessary? - “I take an antihistamine before bedtime.”
- “I take aspirin whenever I have a headache.”
- “I put on sunscreen whenever I go outside.”
- “I take an antacid if my stomach gets upset.”
-
To enhance the percutaneous absorption of nitroglycerin ointment, it would be most important for the LPN/LVN to select a site that is which of the following? - Muscular.
- Near the heart.
- Non-hairy.
- Bony prominence.
-
When assisting the RN in planning care for a postoperative client, which of the following should be the first choice of the LPN/LVN to reduce the client’s risk for pooled airway secretions and decreased chest wall expansion? - Chest percussion.
- Incentive spirometry.
- Position changes.
- Postural drainage.
-
Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN would be most helpful in preventing injury to elderly clients in a health care facility? - Closely monitor the temperature of hot oral fluids.
- Keep unnecessary furniture out of the way.
- Maintain the safe function of all electrical equipment.
- Use safety protection caps on all medications.
-
Which of the following statements by a client during a group therapy session requires immediate follow-up by the LPN/LVN? - “I know I’m a chronically compulsive liar, but I can’t help it.”
- “I don’t ever want to go home; I feel safer here.”
- “I don’t really care if I ever see my girlfriend again.”
- “I’ll make sure that doctor is sorry for what he said.”
-
A client newly diagnosed with major neurocognitive disorder (NCD) due to Alzheimer’s disease is admitted to the unit. Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN is best? - Place the client in a semi-private room away from the nurses’ station.
- Ask family members to wait in the waiting room during the admission process.
- Assign a different nurse daily to care for the client.
- Ask the client to state the current date.
-
A female client visits the clinic reporting right calf tenderness and pain. It would be most important for the LPN/LVN to ask which of the following questions? - “Do you exercise excessively?”
- “Have you had any recent fractures?”
- “What type of birth control do you use?”
- “Are you under a lot of stress?”
-
Which of the following should be the LPN/LVN’s first priority in providing care for a client who has end-stage ovarian cancer and has been weakened by chemotherapy? - Collect data to see if client has pain.
- Determine if the client is hungry or thirsty.
- Explore client’s feelings about dying.
- Observe the client’s self-care abilities.
-
The LPN/LVN in the postpartum unit is caring for a client who delivered her first child the previous day. The LPN/LVN notes multiple varicosities on the client’s lower extremities. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN perform? - Teach the client to rest in bed when the baby sleeps.
- Encourage early and frequent ambulation.
- Apply warm soaks for 20 minutes every 4 hours.
- Perform passive range-of-motion exercises 3 times daily.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client who sustained a left femur fracture in a bicycle accident. A cast is applied. The nurse knows that which of the following exercises would be most beneficial for this client? - Passive exercise of the affected limb.
- Quadriceps setting of the affected limb.
- Active range-of-motion exercises of unaffected limb.
- Passive exercise of the upper extremities.
-
In preparation for a dressing change, the LPN/LVN puts on sterile gloves. Where should the LPN/LVN initially grip the first sterile glove? 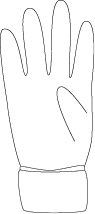
-
A client is being discharged from the hospital following a right total hip arthroplasty. The LPN/LVN reinforces discharge teaching. Which of the following statements by the client indicates that teaching was successful?
- “I can bend over to pick up something on the floor.”
- “I should not cross my ankles when sitting in a chair.”
- “I need to lie on my stomach when sleeping in bed.”
- “I should spread my knees apart to put on my shoes.”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client with continuous bladder irrigation. At 7 a.m., the LPN/LVN notes 4,200 mL of normal saline solution left in the irrigation bags. During the next shift (7 a.m. to 3 p.m.), the LPN/LVN hangs another 3,000 mL and empties a total of 5,625 mL from the urine drainage bag. At 3 p.m., there are 2,300 mL of irrigant left hanging. What is the actual urine output for the client from 7 a.m. to 3 p.m.?
mL
-
The LPN/LVN is observing activities on a medical/surgical unit. The LPN/LVN should intervene if which of the following is observed?
- A client’s family member disposes of the client's used tissue in the bedside container before opening the roommate’s milk carton.
- An UAP removes gloves and washes hands for 15 seconds after emptying an indwelling urinary catheter.
- An LPN/LVN puts on a gown, gloves, mask, and goggles prior to inserting a nasogastric tube.
- A visitor talks with a client diagnosed with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) wound infection while eating lunch.
-
A client with a history of type 1 diabetes mellitus is admitted to the unit reporting nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The client reduced the insulin dose four days ago when influenza symptoms prevented eating The LPN/LVN observes poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and fruity breath odor. The LPN/LVN should be alert for which of the following problems?
- Rebound hypoglycemia.
- Viral gastrointestingal illness.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic coma.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a group of clients. The nurse knows that it is most important for which of the following clients to receive scheduled medications on time?
- A client diagnosed with myasthenia gravis receiving pyridostigmine bromide.
- A client diagnosed with bipolar disorder receiving lithium carbonate.
- A client diagnosed with tuberculosis receiving isonicotinic acid hydrazide.
- A client diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease receiving levodopa.
-
An school-age client is admitted to the hospital for evaluation for a kidney transplant. The LPN/LVN learns that the client received hemodialysis for 3 years due to stage 5 kidney disease. The LPN/LVN knows that the illness can interfere with this client’s achievement of which of the following?
- Intimacy.
- Trust.
- Industry.
- Identity.
-
The LPN/LVN notes that a client has an unsteady gait. The LPN/LVN should do which of the following? Select all that apply.
- Apply a chest or vest restraint at night.
- Help the client put on nonskid shoes for walking.
- Keep the call light within the client’s reach.
- Lower the bed and raise all 4 side rails.
- Provide adequate lighting in room and bathroom.
- Remove obstacles and room clutter.
-
Haloperidol 5 mg PO tid is prescribed for a client with schizophrenia. Two days later, the client reports “tight jaws and a stiff neck.” The LPN/LVN should recognize that these complaints are which of the following?
- Common side effects of therapy that will diminish over time.
- Early symptoms of extrapyramidal reactions to the medication.
- Psychosomatic symptons resulting from a delusional system.
- Permanent side effects associated with haloperidol therapy.
-
A client is receiving a continuous gastric tube feeding at 100 mL per hour. The LPN/LVN checks for gastric residual volume and finds 90 mL in the client’s stomach. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take?
- Discard the gastric residual volume and continue the tube feeding.
- Discard the gastric residual volume and stop the tube feeding.
- Return the gastric residual volume and continue the tube feeding.
- Return the gastric residual volume and stop the tube feeding.
-
The LPN/LVN is opening several sterile gauze dressings on the client’s over-the-bed table. The LPN/LVN knows that the sterile dressings will be contaminated if LPN/LVN does which of the following?
- Does not allow the dressings prolonged exposure to the air.
- Keeps sterile dressings inside border of the sterile packaging.
- Positions top of the over-the-bed table at or above waist level.
- Pours sterile saline onto the opened sterile dressing on table.
-
A client has adamantly refused hygiene measures over the past 3 days. Eventually the LPN/LVN was able to collaborate with the client to develop the hygiene goal: “self-administration of a complete bath daily while in the hospital.” To evaluate if this goal is achieved, the LPN/LVN should do which of the following?
- Ask the client whether self-bathing was accomplished.
- Bathe the client to be sure the hygiene goal is met.
- Observe the client performing portions of the daily bath.
- Remind the client to bathe and provide the needed supplies.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client in labor. The primary health care provider palpates a firm, round form in the uterine fundus, small parts on the client’s right side, and a long, smooth, curved section on the left side. Based on these findings, where should the LPN/LVN anticipate auscultating the fetal heart tones?
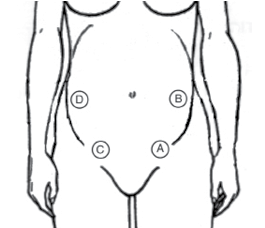
- A
- B
- C
- D
-
When completing data collection of an immobilized client, the LPN/LVN knows that edema is commonly observed in which of the following locations?
- Abdomen.
- Feet and ankles.
- Fingers and wrists.
- Sacrum.
-
A client is preparing to take her 1-day-old infant home from the hospital. The LPN/LVN discusses the test for phenylketonuria (PKU) with the client. The LPN/LVN’s reinforcement of teaching should be based on an understanding that the test is most reliable in which of the following circumstances?
- After source of protein has been ingested.
- After the meconium has been excreted.
- After the danger of hyperbilirubinemia has passed.
- After the effects of delivery have subsided.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for an Rh-negative client who has delivered an Rh-positive child. The client states, “The doctor told me about RhoGAM, but I’m still a little confused.” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is most appropriate?
- “RhoGAM is given to your child to prevent the development of antibodies.”
- “RhoGAM is given to your child to supply the necessary antibodies.”
- “RhoGAM is given to you to prevent the formation of antibodies.”
- “RhoGAM is given to you to encourage the production of antibodies.”
-
A client is hospitalized with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder. While in the activities room on the psychiatric unit, the client flirts with other clients disrupting unit activities. Which of the following approaches would be most appropriate for the LPN/LVN to take at this time?
- Set limits on the behavior and remind the client of the rules.
- Distract the client and escort the client back to the room.
- Instruct the other clients to ignore this client’s behavior.
- Inform client of negative behavior and return client to room.
-
A client is brought to the emergency department bleeding profusely from a stab wound in the left chest area. Vital signs include: blood pressure 80/50 mm Hg, pulse 110 beats/minute, and respiratory rate 28 breaths/minute. The LPN/LVN should expect which of the following potential problems?
- Hypovolemic shock.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Neurogenic shock.
- Septic shock.
-
A client is admitted to the hospital for surgical repair of a detached retina in the right eye. In implementing the plan of care for this client postoperatively, the LPN/LVN should encourage the client to do which of the following?
- Perform self-care activities.
- Maintain patches over both eyes.
- Limit movement of both eyes.
- Refrain from excessive talking.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client who receives a balanced complete formula through an enteral feeding tube The LPN/LVN knows that the most common complication of an enteral tube feeding is which of the following?
- Edema.
- Diarrhea.
- Hypokalemia.
- Vomiting.
-
An infant is brought to the hospital for treatment of pyloric stenosis. The following nursing diagnosis is on the infant’s care plan: “fluid volume deficit related to vomiting.” The LPN/LVN would expect to see which of the following findings to support this diagnosis?
- The infant eagerly accepts feedings.
- The infant vomited once since admission.
- The infant’s skin is warm and moist.
- The infant’s anterior fontanel is depressed.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a preschool-age client diagnosed with a fractured pelvis caused by a motor vehicle accident. The LPN/LVN prepares the child for the application of a hip spica cast. It is most important for the LPN/LVN to take which of the following actions?
- Obtain a doll for the client with a hip spica cast in place.
- Tell the client that the cast will feel cold when applied.
- Reassure the client that cast application is painless.
- Introduce the client to another client who has a hip spica cast.
-
A client comes to the clinic because for suspected pregnancy. Tests confirm pregnancy. The client’s last menstrual period began on September 8 and lasted for 6 days. The LPN/LVN calculates that her expected date of confinement (EDC) is which of the following?
- May 15.
- June 15.
- June 21.
- July 8.
-
An infant is brought to the pediatrician’s office for a well-baby visit. During the examination, congenital subluxation of the left hip is suspected. The LPN/LVN would expect to see which of the following symptoms?
- Lengthening of the limb on the affected side.
- Deformities of the foot and ankle.
- Asymmetry of the gluteal and thigh folds.
- Plantarflexion of the foot.
-
After completing data collection, the LPN/LVN observes that a client is exhibiting early symptoms of a dystonic reaction related to the use of an antipsychotic medication. Which of the following actions by the LPN/LVN would be most appropriate?
- Reality-test with the client and assure the client that physical symptoms are not real.
- Teach the client about common side effects of antipsychotic medications.
- Explain to the client that there is no treatment that will relieve these symptoms.
- Notify the primary health care provider to obtain a prescription for IM diphenhydramine.
-
The LPN/LVN is preparing to perform oral care for an unconscious client. Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take first?
- Assess for the presence of a gag reflex.
- Place the client into Sims’ position.
- Separate teeth with a padded tongue blade.
- Suction secretions from the oral cavity.
-
As a client nears death, the client’s family member says, “I wish I could do something her.” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is most appropriate?
- “It may be comforting if you talk to her calmly and clearly.”
- “She does not know that you are here, but you can sit here.”
- “Unfortunately, there is little that you can do at this point.”
- “Why don’t you take a break? It is just a matter of time now.”
-
The LPN/LVN is providing care to clients in a long-term care facility. Four meal choices are available to the clients. The LPN/LVN should ensure that a client on a low-cholesterol diet receives which of the following meals?
- Egg custard and boiled liver.
- Fried chicken and potatoes.
- Hamburger and french fries.
- Grilled flounder and green beans.
-
The LPN/LVN is removing a client’s breakfast tray and notes that the client consumed 4 oz of pudding, 4 oz of gelatin, 6½ oz of tea, and 5 oz of apple juice. How many milliliters should the LPN/LVN record for the client’s breakfast intake?
mL
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client diagnosed with cholecystitis. The client says to the LPN/LVN, “I don’t understand why my right shoulder hurts when the gallbladder is not by my shoulder!” Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best?
- “Sometimes small pieces of the gallstones break off and travel to other parts of the body.”
- “There is an invisible connection between the gallbladder and the right shoulder.”
- “The gallbladder is on the right side of the body and so is that shoulder.”
- “Your shoulder became tense because you were guarding against the gallbladder pain.”
-
A client comes to the clinic at 32 weeks’ gestation. A diagnosis of pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is made. The LPN/LVN is reinforcing teaching performed by the RN. Which of the following statements by the client indicates that further teaching is required?
- “Lying in bed on my left side is likely to increase my urinary output.”
- “If the bed rest works, I may lose a pound or two in the next few days.”
- “I should be sure to maintain a diet that has a good amount of protein.”
- “I will have to keep my room darkened and not watch much television.”
-
The LPN/LVN is collecting data about a client’s fluid balance. Which of the following findings most accurately indicates to the LPN/LVN that the client has retained fluid during the previous 24 hours?
- Edema is found in both ankles.
- Fluid intake is equal to fluid output.
- Intake of fluid exceeds output by 200 mL.
- Weight gain of 4 lb (1.8 kg) is noted.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a group of residents in a dependent-living facility. The LPN/LVN determines which of the following clients is most at risk to develop pneumonia?
- A client female with left-sided hemiparesis after a stroke.
- A client who has a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
- A client with a history of depression who walks one mile daily.
- An client who smokes and has a history of lung cancer.
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Which of the following behaviors by the client indicates that a manic episode is subsiding?
- The client tells several jokes during a group meeting.
- The client sits and talks with other clients at mealtimes.
- The client begins to write a book about personal story.
- The client initiates a unit effort to start a radio station.
-
A parent brings a child to the pediatrician for treatment of chronic otitis media. The parent asks the LPN/LVN how to prevent the child from getting ear infections. The LPN/LVN’s response should be based on an understanding that the recurrence of otitis media can be decreased by which of the following?
- Covering the child’s ears while bathing.
- Treating upper respiratory infections quickly.
- Administering nose drops at bedtime.
- Isolating the child from other children.
-
A client is calling the suicide prevention hotline to report a personal suicide plan. Which of the following questions should the LPN/LVN ask first?
- “What happened to cause you to want to end your life?”
- “Tell me the details of the plan you developed to kill yourself?”
- “When did you start to feel as though you wanted to die?”
- “Do you want me to prevent you from killing yourself?”
-
Prior to the client undergoing a scheduled intravenous pyelogram (IVP), it would be most important for the LPN/LVN to ask which of the following questions?
- “Do you have any difficulty voiding?”
- “Do you have any allergies to shellfish or iodine?”
- “Do you have a history of constipation?”
- “Do you have a history of frequent headaches?”
-
The LPN/LVN is assigned to a newly admitted elderly client in the hospital setting that reports having no living relatives and only friends of similar age. One of the LPN/LVN’s most immediate considerations for this client will be to help the RN implement which of the following?
- A concept map.
- A critical pathway.
- A discharge plan.
- A utilization group.
-
A client observes the LPN/LVN in the delivery room place drops in her newborn’s eyes. The client asks the LPN/LVN why this was done. Which of the following responses by the LPN/LVN is best?
- “The drops constrict your baby’s pupils to prevent injury.”
- “The drops will remove mucus from your baby’s eyes.”
- “The drops will prevent infections that might cause blindness.”
- “The drops will prevent neonatal conjunctivitis.”
-
The LPN/LVN is caring for a client admitted for a possible herniated intervertebral disk. The primary health care provider prescribed ibuprofen, propoxyphene hydrochloride, and cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride to be given as needed for pain. Several hours after admission, the client reports . Which of the following actions should the LPN/LVN take first?
- Give the client ibuprofen to promptly manage the pain.
- Ask the primary health care provider which drug to give first.
- Gather more information from the client about the complaint.
- Allow the client some time to rest to see if the pain subsides.
-
The LPN/LVN is completing a client’s preoperative checklist prior to surgery. The nurse obtains the client’s vital signs: temperature 97.4° F (36° C), radial pulse rate 84 beats/minute, respiratory rate 16 breaths/minute, and blood pressure 132/74 mm Hg. Which action should the LPN/LVN take first?
- Notify the primary health care provider of client’s vital signs.
- Obtain orthostatic blood pressures lying and standing.
- Lower the side rails and place the bed in its lowest position.
- Record the data on the client’s preoperative checklist.
-
The LPN/LVN is expecting to see which of the following physiological changes in a client experiencing an episode of acute pain?
- Decreased blood pressure.
- Decreased heart rate.
- Decreased skin temperature.
- Decreased respirations.
-
A client is transferred to a long-term care facility after a stroke. The client has right-sided paralysis and dysphagia. The LPN/LVN observes an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) preparing the client to eat lunch. Which of the following situations would require an intervention by the LPN/LVN?
- The client remains in bed in the high Fowler’s position.
- The client’s head and neck are positioned slightly forward.
- The UAP places food in back of the mouth of unaffected side.
- The UAP adds tap water to the pudding to help client swallow.
-
The LPN/LVN’s is collecting data and a client’s blood pressure is 146/92 mm Hg with labored respirations at a rate of of 24 breaths/minute. Bloody drainage appears on the client’s IV dressing. The client reports pain in the left hip, depression, and hunger. The LPN/LVN identifies which of these as subjective data? Select all that apply.
- Blood pressure.
- Depression.
- Hip pain.
- Hunger.
- IV drainage.
- Respirations.