Triumphal March from Egypt to the Promised Land (33:1–56)
Stages of the journey (33:1–49). The toponymic list of the stages of Israel’s departures and encampments from Ramesses in Egypt to the plains of Moab stands in the tradition of itineraries of ancient Near Eastern kings in their travels and conquests. Coats has demonstrated that the list in Numbers 33 is a genuine ancient Near Eastern itinerary.302 This compares with the Late Bronze Age itineraries of Thutmose III from Karnak, which were both military and economic expeditions that included topographical, geographical, and toponymic information.303 Later in the ninth and eighth centuries B.C., Assyrian kings such as Shalmaneser III and Tiglath-Pileser III listed cities and geographical features in their conquest annals.304
| Cycle 1—From Ramesses to the Red Sea | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Bible: Ex. 12–17; Num. 1–21; Deut. 1–4, 10 |
Variant readings: additional sites, location/identification |
|
|
Ramesses (Ex. 12:37) |
Pi-Ramesses: Heb. R-ʿ-m-s-s = Egyptian R-ʿ-m-s-s, identified as Khataana-Qantir (not = Tanis; Avaris loc. at Tel Daba).A-23 Built by and named after Ramesses II, est. size 4 x 2 miles.A-24 Israelites lived in District of Ramesses (Gen. 47:11). |
|
|
Sukkoth (5–6) |
Sukkoth (Ex. 12:37; 13:20) |
W. of Sea of Reeds and SE of Ramesses, Heb. Sukkoth (“Booths”), Egyptian Tjeku, recently identified with Tell el-Maskhutah in Wadi Tumilat, 40 miles SE of Pi-RamessesA-25 |
|
Desert of Etham (6–7) |
Etham (Ex. 13:20) |
Part of or near to the Shur Wilderness (Heb ??r = “wall” but not = an Egyptian khetem = “wall, fortress”). Perhaps ʾi(w)-(I)tm or similar word meaning “isle/mound of Atum” |
|
Pi-Hahiroth (7–8) |
Pi-Hahiroth (Ex. 14:2); between Migdol and Sea, opp. Baal Zephon, Yam Suph crossing (Ex. 14:21–31); Shur Wilderness (Ex. 15:22) |
MT—miphney-hahiroth—“from facing the gorge”—SP, Syriac, Vulgate, Sebourin = Pi-Hahiroth ~ “Mouth of the canals,” which empty into Sea of Reeds, near location of Sea crossingA-26 -Probably in Bitter Lakes or Lake Timsah area. |
|
Marah (8–9) |
Marah (Ex. 15:23), bitter waters made sweet |
Traditionally located at ʿAin Hawara (Bir el-Muwarah), just inland 8 miles E from city of Suez; alt. perhaps ʿUyun Musa. |
|
Elim (9–10); 12 springs and 70 palms |
Elim (Exod. 15:27); 12 springs, 70 palms, water |
Trad. JMA-27—Oasis in Wadi Gharandel, 75 miles SSE of Bitter Lakes. JSB—area of ʿUyun Musa or Wadi RiyanahA-28 |
|
Yam Suph (10–11) |
Yam Suph—Sea crossing site name (Ex. 14:21–31), but not same location. Here camp by Yam Suph shoreline, S of crossing. |
Sea of Reeds / Red Sea (see comment on Num. 21:4).A-29 JSB or JM—Somewhere along the E shoreline of Suez Gulf, SE of sea crossing (v. 7) but N of the Wadi Feiran. |
| Cycle II—The Deserts of Sinai: Sin, Sinai, and Paran | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Bible: Ex. 12–17; Num. 1–21; Deut. 1–4, 10 |
Variant readings: additional sites, location, identification |
|
|
Sin Wilderness (11–12) |
Sin Wilderness (Ex. 16:1–15)—between Elim and Sinai on 15th day of 2nd month. Complaint of food, God gives manna and quail. |
Probably coastal area of NW Sinai along Gulf of SuezA-30 since quail generally do not migrate into the mountains. JM—Dibbet el-Rammleh JSB—SE of Bitter Lakes, E of city of Suez |
|
Dophkah (12–13) |
LXX—Raphaka. Trad. Serabit el-Khadim and Wadi el-‘E?? uncertainA-31—remains unknown. |
|
|
Alush (13–14) |
SP—Alish—Unknown location—in desert region between Suez Gulf and central mountain wadis. |
|
|
Rephidim (14–15); no water for people to drink |
Rephidim (Ex. 17:1)—No water; people quarrel; Massah and Meribah; Amalekite attack, Israel’s victory |
Trad. Wadi Refayid (30 miles NNW of S tip JSM—Prob. Wadi es-Sudr if Israel moved south; or Refidim if E, 35 miles E of Bitter Lakes (neg—in Shur Wilderness) (to JSB = 55 miles) |
|
Sinai Wilderness (15–16) |
Sinai Wilderness (Ex. 19:1–2—Moses w/ God, Mount Sinai) |
Trad. following Wadi Feiran to Jebel Musa and Central S. Sinai region, mt. 2,285m elev. JSB—Jebel Sin Bisher (618m elev.) vicinity and Wadi es-Sudr; other locations?A-32 |
|
Kibroth Hattaavah (16–17) |
Paran Desert (Num. 10:12); Kibroth Hattaavah (Num. 11:34) |
JM—between Jebel Musa and Ein Hudrah JSB—Suggest upper Wadi es-Sudr or upper Wadi Gheidara |
|
Hazeroth (17–18) |
Hazeroth (Num. 11:35) Paran Desert (Num. 12:16) |
JM—Wadi Hudeirat region and Ein Hudrah, 35 miles NE of Jebel Musa JSB—Region of Wadi Gheidara |
| Cycle III—Spies Sent from Paran Desert (13:3), Return to Kadesh in Paran Desert (13:26) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Bible: Ex. 12–17; Num. 1–21; Deut. 1–4, 10 |
Variant readings: additional sites, location, identification |
|
|
Rithmah (18–19) |
Location unknown. |
|
|
Rimmon-Perez (19–20) |
Location unknown. |
|
|
Libnah (20–21) |
SP (Gk)—Lebonah; Location unknown. |
|
|
Rissah (21–22) |
Location unknown. |
|
|
Kehelathah (22–23) |
LXX—Makellath (w/ v. 25), thus some scholars suggest that Kehelathah may be an alt form of Macheloth. Location unknown. |
|
|
Mount Shepher (23–24) |
Location unknown. |
|
|
Haradah (24–25) |
Location unknown. |
|
| Cycle IV—Kadesh to the Arabah | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Bible: Ex. 12–17; Num. 1–21; Deut. 1–4, 10 |
Variant readings: additional sites, location, identification |
|
|
Makheloth (25–26) |
Kadesh in Zin Wilderness (Meribah?) |
Location unknown. |
|
Tahath (26–27) |
LXX—Kataath. Location unknown. |
|
|
Terah (27–28) |
Location unknown. |
|
|
Mithkah (28–29) |
SP—Metikah. Location unknown. |
|
|
Hashmonah (29–30) |
LXX—Selmona. Location unknown. |
|
|
Moseroth (30–31) |
Moserah in Deut. 10:6 |
Location unknown. |
|
Bene Jaakan (31–32) |
Deut. 10:6 |
Deut. 10:6 has order as Bene Jaakan, Moserah, Gudgodah, Jotbathah. Location unknown. |
| Cycle V—Desert Journeys to Edom and the Death of Aaron | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Bible: Ex. 12–17; Num. 1–21; Deut. 1–4, 10 |
Variant readings: additional sites, location, identification |
|
|
Hor Haggidgad (32–33) |
Gudgodah in Deut. 10:7 |
Few MSS, LXX, Vulg—Har-Haggidgad SP—Haggidgadah |
|
Jotbathah (33–34) |
Deut. 10:7 |
JM—ʿAin Tabah and et-Tabah, 6 miles S of Elat (etymologically weak) Modern Yotvata in southern Arabah? |
|
Abronah (34–35) |
Lacking |
Suggestion: ʿAin Defiyeh? |
|
Ezion Geber (35–36) |
Lacking, but “Way of Red Sea” mentioned in Num. 21:4 |
Probably Jezirat Faroun island in northern Gulf of Aqaba, S of ElatA-33 vs. trad. Tell el-Kheleifeh, just NE of modern Elat, probably not Ezion Geber.A-34 |
|
Kadesh (36–37) in Zin Wilderness |
Kadesh (Num. 20:1)—Miriam dies; Waters of Meribah |
Trad. ʿAin Qudeirat |
|
Mount Hor (37–41) |
Mount Hor (Num. 20:22) near border of Edom; Aaron dies at age 123, 40 yrs. after Exodus |
Others: Hormah (and Arad) Deut. 10:6—Aaron dies at Moserah. On the border of Edom. Trad.—J. Madeirah, S of Petra, too far East. Possible mountain in north-central Nahal Zin region such as Hor Hahar |
|
Lacking |
Unknown elsewhere in OT. Perhaps in region of Wadi Salmana, E of ‘Ein Hatzevah |
|
| Cycle VI—Punon to the Plains of Moab | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Bible: Ex. 12–17; Num. 1–21; Deut. 1–4, 10 |
Variant readings: additional sites, location, identification |
|
|
Punon (42–43) |
Lacking |
Trad. Feinan, 31 miles S of Dead Sea on E side of Arabah (ancient copper mining center).A-35 Roman—Phaenon |
|
Oboth (43–44) |
Oboth (Num. 21:10) |
Suggestions: ʿAin el-Weibeh (Simons) on W edge of the Arabah, 18 miles W of Feinan. Alt. site N of Kh. Feinan toward Kh. AyA-36 |
|
Ijeabarim (44) Iyim (45) |
Iye Abarim—E of Moab, then to Zered, Mattanah, Nahaliel, Bamoth, Pisgah (Num. 21:11) |
Add’l sites: Wadi Zered, Mattanah, Nahaliel, Bamoth, Pisgah cited in Num. 21:13–20. Iye Abarim = “ruins of Abarim (Mts.)” Thutmose III cites “Iyyin”—Possibly Muhai, 11 miles SE of Mazar nr. E edge of Moab; or Medeiyineh on N edge of W. Zered canyon.A-37 |
|
Dibon Gad (45–46) |
Dibon in Num. 21:30 proverb |
Add’l sites: Jahaz, Heshbon, Jazer, Edrei (Num. 21:23–35). Egyptian t-b-n-i; modern Dhiban—3 miles N of Arnon River gorge.A-38 Ramesses II—“Qarho (Dibon).” |
|
Almon Diblathaim (46–47) |
= Beth-diblathaim? (Jer. 48:22 w/ Dibon and Nebo), Mesha Stele, line 30.A-39 Near Baal-meon and Madaba. Deleilat el-Gharbiyeh.A-40 |
|
|
Mounts Abarim (47–48) before Nebo |
cf. Iye Abarim above (Num 21:11); Mount Nebo in Abarim Mts. in Deut. 32:49 |
Abarim = ridge of mountains separating Transjordan plateau from Jordan Valley, W of Madaba and Heshbon. Mount Nebo traditionally identified w/ mountain of 802 meters elev., 5 miles NW of Madaba. |
|
Plains of Moab (48–49) by Jordan from Beth Jeshimoth up to Abel Shittim |
Plains of Moab (22:1); Balaam encounters |
Beth Jeshimoth = Tel ‘Azeimah, 12 miles SE of Jericho near Dead Sea.A-41 Abel-shittim = Tell Kefrein, 5 miles E of Jordan and 7 miles N of Dead Sea (Josephus)A-42—or Tel Hammam Thutmoses III, Ramesses II—“Abel” |

Thutmose III on Seventh Pylon with a list of enemies defeated
Frederick J. Mabie
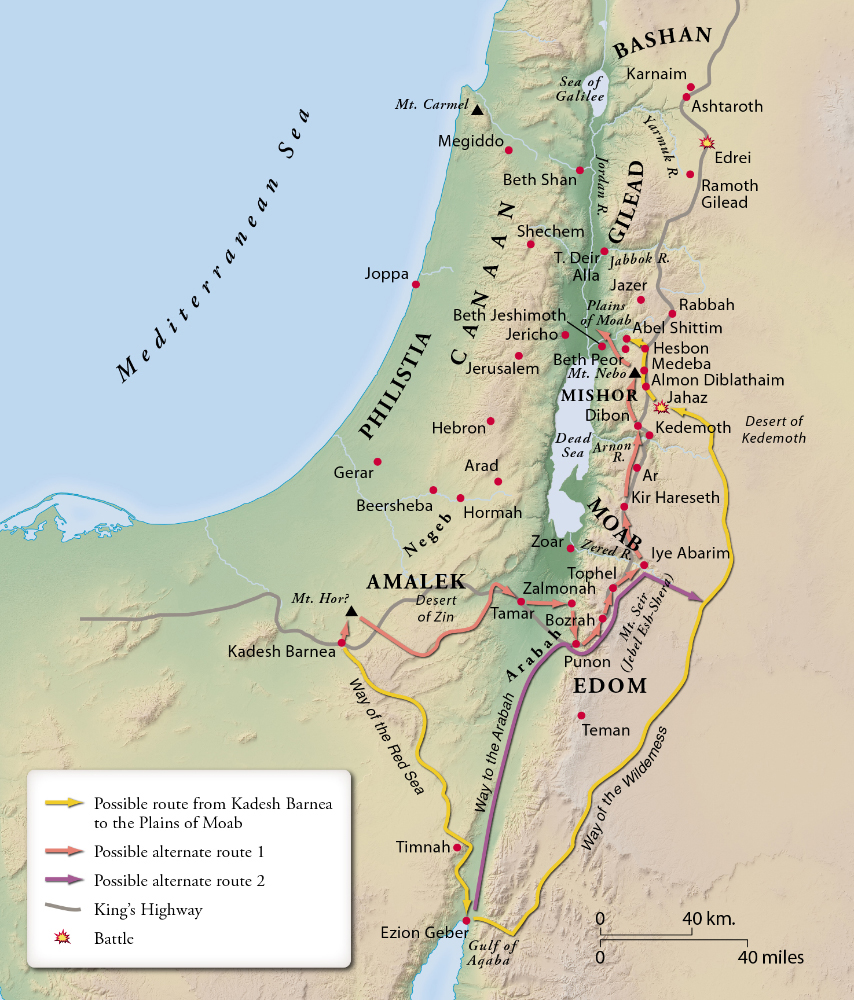
Israelite Itinerary in the Wilderness
Sinai (33:16). One of the key issues for locating sites in the second through fifth cycles is the location of Mount Sinai (see comments in introduction; also at 11:35). If the request of Moses before Pharaoh to journey three days into the desert to celebrate a festival to the Lord (Ex. 8:3) is to be applied to the quest for the mountain’s locale, then the sacred summit must be closer to the Egyptian border fortresses than most of the suggested mountains except Jebel Sin Bisher. The most explicit passage bearing on this question is the statement in Deuteronomy 1:2 that the distance from Horeb (= Sinai) to Kadesh Barnea via Ezion Geber is a distance of eleven days or about 140 to 150 miles.305
Rithmah (33:19). The sites recorded in cycles III and IV of the desert itinerary largely belong to the wilderness wandering period. Most of the sites are unknown to the rest of Scripture, later history, and modern historical geographers.
Carved images (33:52). Those images of deity carved from wood (e.g., Asherim)306 or sculpted from stone or ivory (e.g., the stylistic stele of Baal Hadad found at Bethsaida) are included.307 This kind of iconography represents a form of mimesis whereby a representation of the given deity functions as a record of the perception of reality conceived by the worshiper in relationship to the deity.308
Cast idols (33:52). Molten cast images (massēkôt) of deities are those in which clay or molten metal, such as copper or bronze, was poured into a pottery mold forming the shape of the deity.309 Numerous deity forms and their molds have been uncovered in excavations throughout Israel/Palestine.310

Initially referred to as the Baal Hadad Stele, this is now considered by many to represent the moon god.
Israel Museum, Jerusalem; © PBT & Dr. James C. Martin
High places (33:52). The phrase “high places” translates the Hebrew bāmôt, which may or may not refer to an elevated site or structure. With the variety of usage in the Old Testament, a generic phrase such as “sacred site” or “cultic installation” may better render this kind of worship center.311 Such a site may include (1) an altar on which animal, grain, vegetable, incense, or other product is rendered unto the deity; (2) cultic symbols and/or figurines, (3) standing stones (maṣṣēbôt), or (4) other cultic instruments.312

Hittite god
© The Trustees of the British Museum