Part 8: Mechanical Comprehension (MC)
19 Minutes 25 Questions-
Directions: In this section, you will be tested on your knowledge of mechanics and basic physics. Select the best answer for each question and mark the corresponding oval on your answer sheet.
-
The force of friction between two surfaces moving past each other DOES NOT depend on
- the normal force
- the nature of the surfaces in contact with each other
- the area of the surfaces in contact with each other
- the speed with which the surfaces are moving past each other
-
The formula for work is
- w = m × v
- w = m × g × h
- w = m × a
- w = F × d
-
A small pulley drives a large pulley with a belt. Which of the following statements about this arrangement are true?
- The pulleys turn in opposite directions.
- The smaller pulley turns faster.
- Speed output is greater than the input.
- The smaller pulley is above the larger pulley.
-
Any work that is done to accelerate an object at rest to speed v will be converted into the kinetic energy of that object. This principle is known as
- the work-energy theorem
- gravitational potential energy
- the principle of conservation of mechanical energy
- Newton’s second law
-
Performing work at the rate of 1 joule per second is the same as expending
- 100 foot-pounds
- 10 psi
- 1 meter per second
- 1 watt of power
-
All of the following statements about liquids are true EXCEPT
- liquids are practically incompressible
- liquids can be used to transmit force
- all liquids are good lubricants
- liquids conform to the shape of their container
-
A crate with a weight of 250 N is resting on a rough, horizontal surface with a coefficient of static friction of 0.8. What will happen if an applied horizontal force of 200 N acts on the crate?
- The crate will move and continually accelerate while the force acts.
- The crate will move at a constant speed.
- The crate will not move.
- The crate will move but then decelerate back to rest as friction increases.
-
If 100 pounds of force are applied over an area of 2 square inches, the pressure would be
- 5 psi
- 50 psi
- 100 psi
- 200 psi
-
The advantage gained by the use of a mechanism in transmitting force is known as
- pressure
- hydraulics
- torque multiplication
- mechanical advantage
-
The point that the lever pivots on is the
- gear
- torque
- fulcrum
- axle
-
A 30 N force is applied to 5 kg box. Assuming no friction, what is the acceleration gained by the box?
- 0.17

- 6
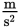
- 15
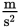
- 150

- 0.17
-
When a net force acts on an object,
- the object will slow to a stop
- the force will give the object a cumulative force
- the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force
- constant speed is impossible
-
If pulley X turns in a clockwise direction, in which direction will pulley Y turn?
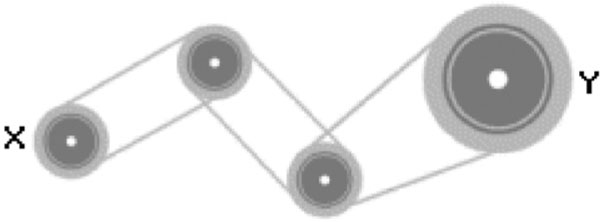
- clockwise only
- counterclockwise only
- either clockwise or counterclockwise
- the direction cannot be determined based on the information provided
-
The illustration below represents
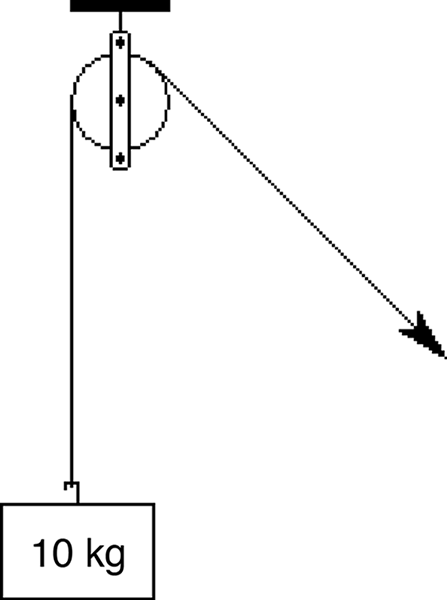
- a fixed pulley
- a moving pulley
- a rear axle
- a pendulum
-
In order for a piston with a total surface area of 10 square inches to support 100 pounds, how much pressure will have to be applied?
- 1,000 psi
- 50 psi
- 10 psi
- 5 psi
-
Given the following forces acting on a block, what are the net or resultant forces? (Assume that “left” means your left.)
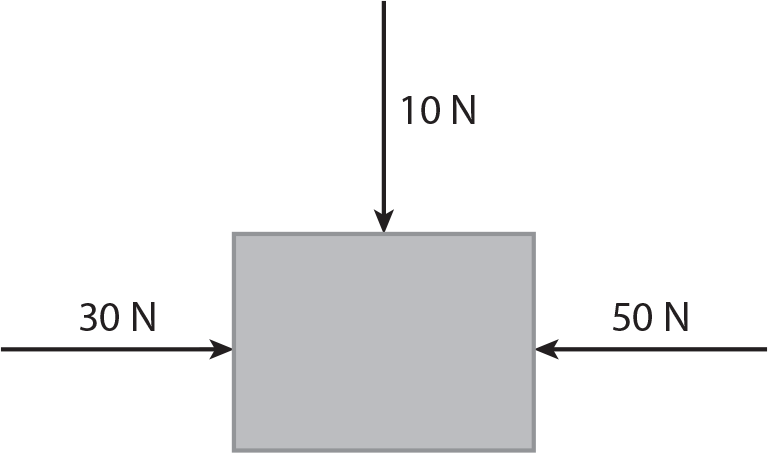
- 80 N to the right and 10 N down
- 80 N to the left and 10 N down
- 20 N to the left and 10 N down
- 20 N to the right and 10 N down
-
Given a block and tackle with four ropes to lift a load one foot, barring friction, what is the mechanical advantage gained?
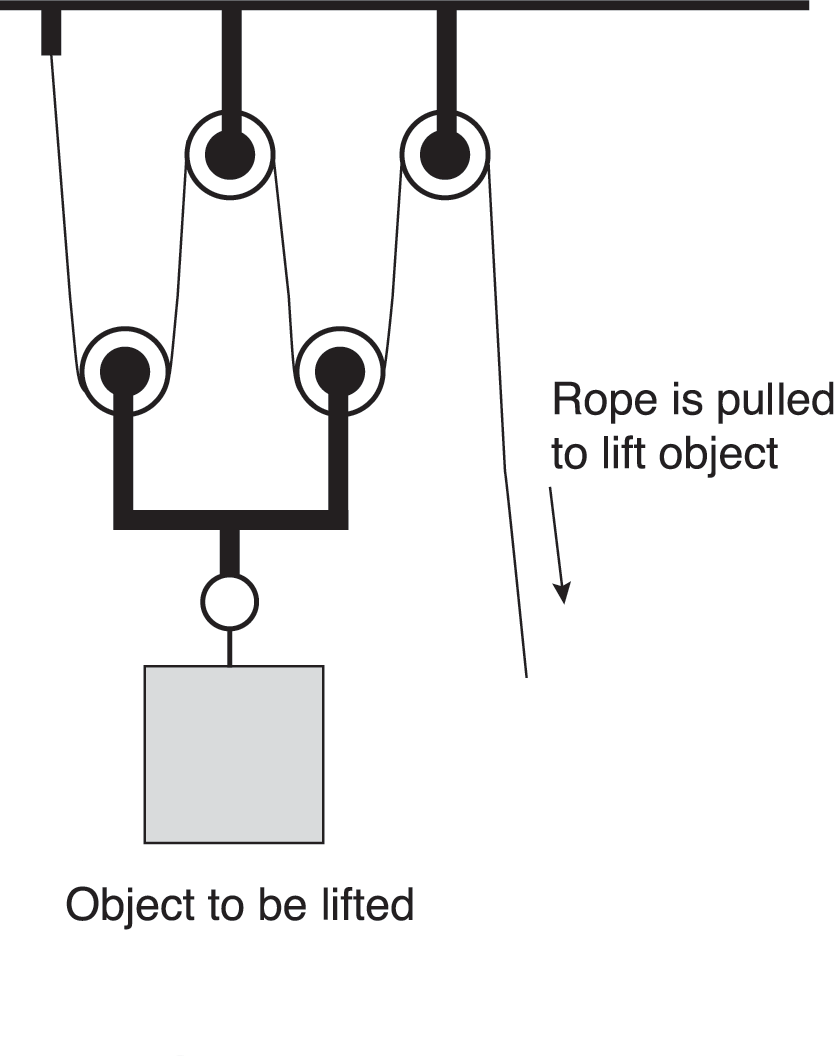
- 24:1
- 10:1
- 8:1
- 4:1
-
A child’s teeter-totter, of the sort shown below, is an example of which kind of lever?
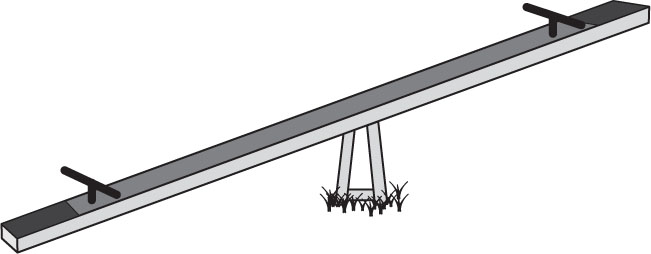
- first-class
- second-class
- third-class
- fourth-class
-
A hockey puck slides across frozen ice. The puck will eventually slow to a stop because of
- wind drag
- gravity
- sliding frictional force
- inertia
-
What is being applied to the bolt as it is being tightened?
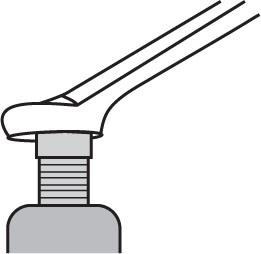
- torque
- friction
- kinetic energy
- gear ratio
-
When tightening a fastener, if one uses a wrench that is 1 foot long, and applies a force of 100 pounds to the end of the wrench, of torque is being applied.
- 10 foot-pounds
- 100 foot-pounds
- 1,000 foot-pounds
- 10,000 foot-pounds
-
Given the following pulley system, suppose a person is holding the other end of the rope, so that the box is stationary and the system is in equilibrium. What is the Tension force T that develops in the rope?
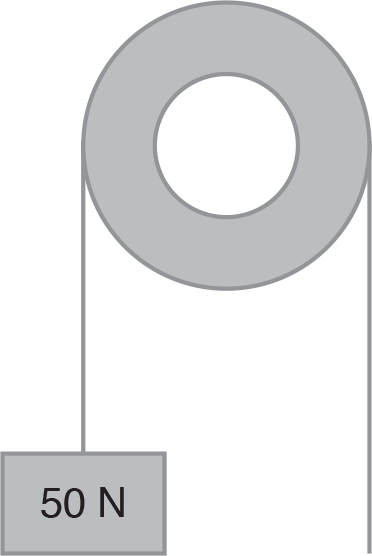
- 10 N
- 25 N
- 50 N
- 100 N
-
Neglecting friction, the mechanical advantage provided by a block and tackle is equal to
- the number of pulleys used in the block and tackle
- half of the number of pulleys used in the block and tackle
- twice the number of pulleys used in the block and tackle
- the diameter of the pulleys divided by the number of pulleys used in the block and tackle
-
The symbol g, according to Newtonian laws, refers to
- acceleration due to gravity
- mass, in grams
- the Earth’s surface
- the ground
-
The fulcrum is
- the location that the force is applied to a lever
- the location that the object is applied to a lever
- the pivot point of a lever
- the distance from the pivot point of a lever to the location the force is applied to the lever