Microsoft Dynamics NAV is used in many different vertical industries. Vertical industries often require specific features. Rather than trying to implement all these features in the standard product, Microsoft Dynamics NAV supports the framework and allows developers to design and create vertical features.
For these features, the 80/20 rule applies; Microsoft delivers 80 percent of the framework, which costs 20 percent of our time to implement. The missing 20 percent of the functionality is developed costing 80 percent of the budgeted time.
In this chapter, we will discuss how Microsoft Dynamics NAV is used for production in five different vertical industries. For each industry, we will discuss two specific vertical features and how they could be solved.
The general challenge in the fashion industry is sizes and colors. Each item can be produced and sold from XXS to XXXL and from pink to orange to green while remaining the same item.
This calls for the creative use of variants, which are heavily used by the available vertical solutions on the market.
To use manufacturing with variants, the bill of material structure should be changed since this exists by default on the item level. However, each size uses different quantities of fabric and the different colors of fabric are often represented by another item number in the raw materials.
A solution for this might be to move the bill of materials from Item level to Stock Keeping Unit level. An SKU supports variants for costing and the inventory.
Fashion companies produce items for a collection. Customers have the possibility to reserve on a collection in order for the production manager to determine how many to produce. Based on these numbers and an extra safety inventory, the production orders are created. Once the production orders are finished, the company needs to decide who gets the first items. This can be best described as a reversed make-to-order mechanism.
To enable this in Microsoft Dynamics NAV, we could create a worksheet that will create lines for each combination of production orders and sales orders. For each sales order that will be shipped, we could create a Warehouse Pick and Shipment from the Shipping Worksheet.
We will discuss stock keeping units, warehouse picks, and shipments in Chapter 6, Trade.
In the automotive industry, Microsoft Dynamics NAV is mostly used by car manufacturing suppliers, the companies that make prefabricated parts out of raw materials.
In these companies, the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is very important as well as the tooling amortization since the initial investments in tooling before the production process starts is high.
To support this, extra functionality needs to be developed for the tooling and BOM process. For example, the table Routing Tool (table 99000802) can be connected to a Fixed Asset (table 5600).
When something is wrong with a component of a car, it is important to be able to see what other cars have, the same components built by the same factory and tools using the same base materials.
In Microsoft Dynamics NAV, it is possible to use a single Lot no. for a component or an end product and to trace this back. It is not possible to simply move the Lot no. of the component to the end product or copy information from the component's Lot no. such as a container no. or a quality code to the end product.
To support this, we need to change the item tracking process. A good place to start would be the item journal where the reservation entry is moved to the item ledger entry.
When used by companies that manufacture medicines, using the expiration date for Lot numbers correctly is highly important.
In Microsoft Dynamics NAV, expiration dates are defined in the Item Ledger Entries and the Warehouse Entries.
It is not possible to define a single expiration date for a Lot. This can be changed by adding this field to the Lot No. Information table (6505). This table allows companies to predefine Lot numbers to be used in the production process.
By default, the expiration date is calculated based on the document date multiplied with the Expiration Calculation field in the Item table (27).
The Lot No. Information table can be used to save additional information about the specific production batch.
Quality control is important in most production processes but maybe extra important when dealing with medicines. Usually a small part of a Lot is taken for quality control.
In Microsoft Dynamics NAV, we can define quality measures in the Prod. Order Rtng Qlty Meas. Table (5413). However, these values are only saved as information for the production order.
To enhance quality control, we could add a document structure where a quality check document is created from a production order. The information should be saved in the Lot No. Information table.
When a Lot does not have the required quality, a workflow should be started. This workflow will lead the user through a process where decisions can be made. Sometimes, the quality can be improved and the items can still be used. Sometimes the item number even depends on the quality of the product.
Quality control is in between the Consumption Journal and the Output Journal. During the final quality check, the BOM items are used, but the final item is not yet available.
In the food industry, everything is about expiration dates and fresh products. Inventory is never very high and the rate of circulation is very high.
For this reason, it should be possible for fresh food companies to zero the inventory of certain Lot numbers once the expiration date is closing or has expired.
This could normally be done using the Physical Inventory Journal. Doing this manually with Lot numbers can be quite a job for someone to do this every day so for this vertical solution, we could create a function to do this. This function would create an Item Journal Line (83) with the field Phys. Inventory (56) activated and also create the Reservation entry for tracking and post the line automatically.
Fresh food companies use daily production processes that start on scheduled times. Each day, the factory starts the production process but the production numbers can be different based on the orders.
This can be done using the Make-To-Order policy but we need to make sure that there will be no new sales orders when the calculation process starts.
This can be achieved by creating an order schedule policy. New sales lines can be created for each item until a certain time. When the time has elapsed, the salespeople will get an error message. This allows the production planner to start the calculation process at a fixed time each day, knowing the sales orders quantities can be trusted.
The furniture industry is a large and very old industry that existed long before the industrial revolution and the introduction of computers.
We can roughly split the furniture industry into two parts. The first part has moved production to be standardized using size and color matrixes, which we can compare to the fashion industry. When buying a table or kitchen, the customer can choose from different sizes and colors. Depending on the number of choices, the products are either Made-To-Stock (IKEA) or Made-To-Order.
The second part is furniture manufacturers who still produce custom-made items. A desk or kitchen at these manufacturers can have any size or color. For these companies, it is next to impossible to create a bill of material for each custom item so they use predefined calculations with item categories.
For the examples in this book, we will discuss the second category.
Companies building custom-made furniture need the possibility to calculate the use of materials and resources, both at the item category and real item level. For this, we can create a calculation module with this data and posting model.
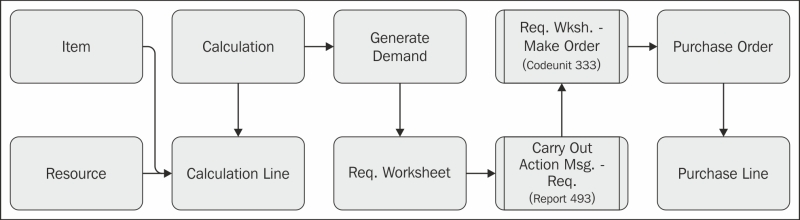
The basic structure of this calculation module is explained in Chapter 8, Consulting, where we have combined this into the jobs functionality of Microsoft Dynamics NAV.
Our furniture company uses a combination of product-specific items that are one of a kind and inventory items that are used in most of the products.
These items are combined into the end product and should be consumed when the product is finished. When the calculation module is integrated with jobs, for example, it would be possible to flush the components when the job is completed. This functionality can be compared to the posting of the Consumption Journal when a production order is finished.
The inventory items can be updated weekly using the Physical Inventory Journal and inventory counting. This enables us to use the requisition worksheet and reordering policy we will discuss in Chapter 6, Trade.