(Click here to download a PDF of Practice Exam 2)
Three hours are allotted for this examination: 1 hour and 30 minutes for Section I, which consists of multiple-choice questions, and 1 hour and 35 minutes for Section II, which consists of problems and essay questions.
SECTION I
Time—1 hour and 30 minutes
Number of questions—75
Percent of total grade—50
This examination contains 75 multiple-choice questions. Therefore, for the examination questions, please be careful to fill in only the ovals that are preceded by numbers 1 through 75 on your answer sheet.
General Instructions
CALCULATORS MAY NOT BE USED IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION.
INDICATE ALL YOUR ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS IN SECTION I ON THE SEPARATE ANSWER SHEET.
No credit will be given for anything written in this examination booklet, but you may use the booklet for notes or scratchwork. After you have decided which of the suggested answers is best, COMPLETELY fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Give only one answer to each question. If you change an answer, be sure that the previous mark is erased completely.
Example:
Chicago is a
(A) state
(B) city
(C) country
(D) continent
(E) village
Sample Answer
![]()
Many candidates wonder whether or not to guess the answer to questions about which they are not certain. In this section of the examination, as a correction for haphazard guessing, one-fourth of the number of questions you answer incorrectly will be subtracted from the number of questions you answer correctly. It is improbable, therefore, that mere guessing will improve your score significantly; it may even lower your score, and it does take time. If, however, you are not sure of the correct answer but have some knowledge of the question and are able to eliminate one or more of the answer choices as wrong, your chance of getting the right answer is improved, and it may be to your advantage to answer such a question.
Use your time effectively, working as rapidly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not spend too much time on questions that are too difficult. Go on to other questions and come back to the difficult ones later if you have time. It is not expected that everyone will be able to answer all the multiple-choice questions.
CHEMISTRY
SECTION I
Time—1 hour and 30 minutes
Material in the following table may be useful in answering the questions in this section of the examination.

Note: For all questions involving solutions and/or chemical equations, assume that the system is in pure water and at room temperature unless otherwise stated.
Part A
Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered questions or statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best answers each question or best fits each statement and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set.
Questions 1–3 refer to the following elements.
(A) Ne
(B) Li
(C) Al
(D) Cl
(E) Ca
1. Which of the elements above is most commonly found as a negatively charged ion?
2. Which of the elements above has the same electron structure as Mg2+?
3. Which of the elements above is found as a diatomic gas in its uncombined state?
Questions 4–7 refer to the following substances.
(A) H2O
(B) NH3
(C) CH4
(D) HF
(E) CH3OH
4. This molecule is nonpolar.
5. This substance forms an aqueous solution with a pH that’s less than 7.
6. This molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape.
7. This substance does NOT exhibit hydrogen
bonding.
Questions 8–11 refer to the phase diagram shown below for a substance.

8. This point could be the boiling point for the substance.
9. If pressure is increased from the conditions represented by this point at constant temperature, deposition may occur.
10. At the conditions represented by this point, the substance can exist with liquid and solid phases in equilibrium.
11. If temperature is increased from the conditions represented by this point at constant pressure, no phase change will occur.
Questions 12–14 refer to an experiment in which five individual 1-liter aqueous solutions, each containing a 1-mole sample of one of the salts listed below, were subjected to various tests at room temperature.
(A) NaC2H3O2
(B) NaCl
(C) MgBr2
(D) HC2H3O2
(E) KBr
12. The solution containing this salt had the highest boiling point.
13. The solution containing this salt had the lowest conductivity.
14. The solution containing this salt had the highest pH.
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
15. Titanium metal is prepared by heating rutile, an oxide of titanium, along with carbon and chlorine gas. By mass, rutile is 40% oxygen and 60% titanium. What is the empirical formula of rutile?
(A) TiO
(B) Ti2O
(C) TiO2
(D) Ti2O3
(E) Ti3O2
16. What is the weight of NaNO3 (molecular weight 85.0) present in 100.0 ml of a 4.00-molar solution?
(A) 8.50 grams
(B) 17.0 grams
(C) 25.5 grams
(D) 34.0 grams
(E) 51.0 grams
17. A mixture of gases contains 5.0 moles of oxygen, 12 moles of nitrogen, and 4.0 moles of carbon dioxide. If the partial pressure due to carbon dioxide is 1.6 atmospheres, what is the partial pressure due to oxygen?
(A) 2.0 atm
(B) 4.8 atm
(C) 6.0 atm
(D) 6.8 atm
(E) 8.4 atm
18. Which of the diagrams below represents the enthalpy change for an endothermic reaction?
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 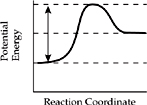
(D) 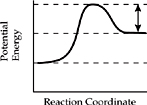
(E) 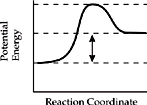
19. 2 NO(g) + Br2(g) → 2 NOBr(g)
For the reaction above, the experimental rate law is given as follows:
Rate = k[NO]2[Br2]
Which of the statements below is true regarding this reaction?
(A) The reaction is first-order overall.
(B) The reaction is first-order with respect to Br2.
(C) The reaction is first-order with respect to NO.
(D) The reaction is second-order overall.
(E) The reaction is second-order with respect to Br2.
20. Which of the following is the most likely electron configuration of a sulfur atom in its ground state?
(A) 1s2 2s2 2p6
(B) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
(C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
(D) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
(E) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 4s1
21. How many grams of carbon are present in 270 grams of glucose, C6H12O6?
(A) 12.0 grams
(B) 18.0 grams
(C) 67.5 grams
(D) 72.0 grams
(E) 108 grams
22. Calcium carbonate dissolves in acidic solutions as shown in the equation below.
CaCO3(s) + 2 H+(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
If excess CaCO3 is added to 0.250 liters of a 2.00-molar HNO3 solution, what is the maximum volume of CO2 gas that could be produced at standard temperature and pressure?
(A) 5.60 liters
(B) 11.2 liters
(C) 16.8 liters
(D) 33.6 liters
(E) 39.2 liters
23. A monoprotic acid was titrated with a solution of NaOH. For 55.0 milliliters of the acid, 37.0 milliliters of a 0.450-molar solution of NaOH was required to reach the equivalence point. Which of the following expressions is equal to the initial concentration of the monoprotic acid?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
24. Zn(s) + NO3–(aq) + 10 H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + NH4+(aq) + 3 H2O(l)
Which of the following statements regarding the reaction shown above is correct?
(A) The oxidation number of hydrogen changes from +1 to 0.
(B) The oxidation number of hydrogen changes from +1 to –1.
(C) The oxidation number of nitrogen changes from +5 to –3.
(D) The oxidation number of nitrogen changes from +5 to +3.
(E) The oxidation number of nitrogen changes from +6 to +4.
25. HC2H3O2(aq) + ClO–(aq)HClO(aq) + C2H3O2–(aq)
The standard free energy change for this reaction has a negative value. Based on this information, which of the following statements is true?
(A) Ka for HC2H3O2(aq) is less than Ka for HClO(aq).
(B) Kb for C2H3O2–(aq) is less than Kb for
ClO–(aq).
(C) Keq for the reaction is less than 1.
(D) The reaction occurs in the presence of a catalyst.
(E) HC2H3O2(aq) and HClO(aq) are conjugates.
26. A student added 0.20 mol of NaI and 0.40 mol of KI to 3 liters of water to create an aqueous solution. What is the minimum number of moles of Pb(C2H3O2)2 that the student must add to the solution to precipitate out all of the
I– ions as
PbI2?
(A) 2.40
(B) 1.20
(C) 0.60
(D) 0.30
(E) 0.15
27.
A molecule with the formula XY2 whose atoms are arranged linearly could have a central atom with which of the following hybridizations?
I. sp
II. sp3
III. dsp3
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and II only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
28. Which of the following statements regarding fluorine and nitrogen is NOT true?
(A) Fluorine has greater electronegativity.
(B) Fluorine has a greater first ionization energy.
(C) Fluorine has more valence electrons.
(D) Fluorine has a greater atomic weight.
(E) Fluorine has a greater atomic radius.
29. Which of the groups below is (are) listed in order from lowest to highest melting point?
I. KI, LiF, BeO
II. F2, Cl2, Br2
III. K, Na, Li
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
30. Which of the statements below regarding elemental nitrogen is NOT true?
(A) It contains one sigma bond.
(B) It contains two pi bonds.
(C) It has a bond order of 3.
(D) It has a large dipole moment.
(E) It exists as a diatomic gas.
31. The reaction of elemental chlorine with ozone in the atmosphere occurs by the two-step process shown below.
I. Cl + O3 → ClO +O2
II. ClO + O → Cl + O2
Which of the statements below is true regarding this process?
(A) Cl is a catalyst.
(B) O3 is a catalyst.
(C) ClO is a catalyst.
(D) O2 is an intermediate.
(E) O is an intermediate.
32. A student examined the line spectrum of a hydrogen atom and was able to conclude that when the electron in the hydrogen atom made the transition from the n = 3 to the n = 1 state, the frequency of the ultraviolet radiation emitted was 2.92 × 1015 Hz. When the same transition occurred in a He+ ion, the frequency emitted was 1.17 × 1016 Hz. Which of the following best accounts for the difference?
(A) More energy is released by the He+ transition because of the greater molar mass of the He+ ion.
(B) More energy is released by the He+ transition because of the greater nuclear charge of the He+ ion.
(C) More energy is released by the He+ transition because the ionic radius of He+ is greater than the atomic radius of H.
(D) Less energy is released by the He+ transition because the ionic radius of He+ is smaller than the atomic radius of H.
(E) Less energy is released by the He+ transition because of the greater nuclear charge of the He+ ion.
33. CH3CH2OH(g) +…O2(g) → …CO2(g) +…H2O(g)
The reaction above represents the oxidation of ethanol. How many moles of O2 are required to oxidize 1 mole of CH3CH2OH?
(A) ![]() moles
moles
(B) ![]() moles
moles
(C) 3 moles
(D) ![]() moles
moles
(E) 4 moles
34. How many milliliters of water must be added to 10 milliliters of an HCl solution with a pH of 1 to produce a solution with a pH of 2?
(A) 10 ml
(B) 90 ml
(C) 100 ml
(D) 990 ml
(E) 1,000 ml
35. Elemental iodine (I2) is more soluble in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) than it is in water (H2O). Which of the following statements is the best explanation for this?
(A) I2 is closer in molecular weight to CCl4 than it is to H2O.
(B) The freezing point of I2 is closer to that of CCl4 than it is to that of H2O.
(C) I2 and CCl4 are nonpolar molecules, while H2O is a polar molecule.
(D) The heat of formation of I2 is closer to that of CCl4 than it is to that of H2O.
(E) CCl4 has a greater molecular weight than does H2O.
36. A sample of water was electrolyzed to produce hydrogen and oxygen gas, as shown in the reaction below.
2 H2O(l) → 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
If 33.6 liters of gas were produced at STP, how many grams of water were consumed in the reaction?
(A) 11.1 grams
(B) 18.0 grams
(C) 24.0 grams
(D) 36.0 grams
(E) 44.8 grams
37. The following data were gathered in an experiment to determine the density of a sample of an unknown substance.
Mass of the sample = 7.50 grams
Volume of the sample = 2.5 milliliters
The density of the sample should be reported as
(A) 3.00 grams per ml.
(B) 3.0 grams per ml.
(C) 3 grams per ml.
(D) 0.3 grams per ml.
(E) 0.33 grams per ml.
38. 2 H2O2(g) + S(s) → SO2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Based on the information given in the table below, what is the enthalpy change in the reaction represented above?
| Substance | ∆H°f (kJ/mol) |
| H2O2(g) | –150 |
| SO2(g) | –300 |
| H2O(g) | –250 |
| S(s) | 0 |
(A) –500 kJ
(B) –200 kJ
(C) 200 kJ
(D) 400 kJ
(E) 600 kJ
39.
A chemist creates a buffer solution by mixing equal volumes of a 0.2-molar HOCl solution and a 0.2-molar KOCl solution. Which of the following will occur when a small amount of KOH is added to the solution?
I. The concentration of undissociated HOCl will increase.
II. The concentration of OCl– ions will increase.
III. The concentration of H+ ions will increase.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) II and III only
40. A 15-gram sample of neon is placed in a sealed container with a constant volume of 8.5 liters. If the temperature of the container is 27°C, which of the following expressions gives the correct pressure of the gas? The ideal gas constant, R, is 0.08 (L-atm)/(mole-K).
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
41. C(s) + CO2(g) + energy2 CO(g)
The system above is currently at equilibrium in a closed container. Which of the following changes to the system would serve to increase the number of moles of CO present at equilibrium?
I. Raising the temperature
II. Increasing the volume of the container
III. Adding more C(s) to the container
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and II only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
42. In a titration experiment, a 0.10-molar H2C2O4 solution was completely neutralized by the addition of a 0.10-molar NaOH solution. Which of the diagrams below illustrates the change in pH that accompanied this process?
(A) 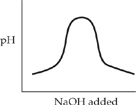
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
(E) 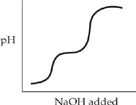
43. If 52 grams of Ba(NO3)2 (molar mass 260 grams) are completely dissolved in 500 milliliters of distilled water, what are the concentrations of the barium and nitrate ions?
(A) [Ba2+] = 0.10 M and [NO3–] = 0.10 M
(B) [Ba2+] = 0.20 M and [NO3–] = 0.40 M
(C) [Ba2+] = 0.40 M and [NO3–] = 0.40 M
(D) [Ba2+] = 0.40 M and [NO3–] = 0.80 M
(E) [Ba2+] = 0.80 M and [NO3–] = 0.80 M
44. An acid solution of unknown concentration is to be titrated with a standardized hydroxide solution that will be released from a buret. The buret should be rinsed with
(A) hot distilled water.
(B) distilled water at room temperature.
(C) a sample of the unknown acid solution.
(D) a sample of the hydroxide solution.
(E) a neutral salt solution.
45. All of the following statements concerning the alkali metals are true EXCEPT
(A) They are strong oxidizing agents.
(B) They form ions with a +1 oxidation state.
(C) As the atomic numbers of the alkali metals increase, the electronegativity decreases.
(D) As the atomic numbers of the alkali metals increase, their first ionization energy decreases.
(E) They form ions that are soluble in water.
46. As a beaker of water is heated over a flame, the temperature increases steadily until it reaches
373 K. At that point, the beaker is left on the open flame, but the temperature remains at 373 K as long as water remains in the beaker. This is because at 373 K, the energy supplied by the flame
(A) no longer acts to increase the kinetic energy of the water molecules.
(B) is completely absorbed by the glass beaker.
(C) is less than the energy lost by the water through electromagnetic radiation.
(D) is dissipated by the water as visible light.
(E) is used to overcome the heat of vaporization of the water.
47. For which of the following reactions will the equilibrium constants Kc and Kp have the same value?
(A) 2 N2O5(g) ![]() 2 NO2(g) + O2(g)
2 NO2(g) + O2(g)
(B) 2 CO2(g) ![]() 2 CO(g) + O2(g)
2 CO(g) + O2(g)
(C) H2O (g) + CO(g) ![]() H2(g) + CO2(g)
H2(g) + CO2(g)
(D) 3 O2(g) ![]() 2 O3(g)
2 O3(g)
(E) CO(g) + Cl2(g) ![]() COCl2(g)
COCl2(g)
48. A student added solid potassium iodide to 1 kilogram of distilled water. When the KI had completely dissolved, the freezing point of the solution was measured to be –3.72°C. What was the mass of the potassium iodide added? (The freezing point depression constant, kf , for water is 1.86 K-kg/mol.)
(A) 334 grams
(B) 167 grams
(C) 84 grams
(D) 42 grams
(E) 21 grams
49. Each of the following compounds was added to distilled water at 25°C. Which one produced a solution with a pH that was less than 7?
(A) N2
(B) O2
(C) NaI
(D) MgO
(E) SO2
50.…Be2C +…H2O →…Be(OH)2 +…CH4
When the equation for the reaction above is balanced with the lowest whole-number coefficients, the coefficient for H2O will be
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 5
51. A sample of an ideal gas is placed in a sealed container of constant volume. If the temperature of the gas is increased from 40°C to 70°C, which of the following values for the gas will NOT increase?
(A) The average speed of the molecules of the gas
(B) The average kinetic energy of the molecules of the gas
(C) The pressure exerted by the gas
(D) The density of the gas
(E) The frequency of collisions between molecules of the gas
52. A ![]() nuclide decays through the emission of two beta particles and two alpha particles. The resulting nuclide is
nuclide decays through the emission of two beta particles and two alpha particles. The resulting nuclide is
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
53. When 80.0 ml of a 0.40 M NaI solution is combined with 20.0 ml of a 0.30 M CaI2 solution, what will be the molar concentration of I– ions in the solution?
(A) 0.70 M
(B) 0.44 M
(C) 0.38 M
(D) 0.35 M
(E) 0.10 M
| Compound | Ksp at 25ºC |
| FeS | 6.33 × 10–18 |
| PbS | 8.03 × 10–28 |
| MnS | 1.03 × 10–13 |
A solution at 25°C contains Fe2+, Pb2+, and Mn2+ ions. Which of the following gives the order in which precipitates will form, from first to last, as Na2S is steadily added to the solution?
(A) FeS, PbS, MnS
(B) MnS, PbS, FeS
(C) FeS, MnS, PbS
(D) MnS, FeS, PbS
(E) PbS, FeS, MnS
55. Hydrogen sulfide is a toxic waste product of some industrial processes. It can be recognized by its distinctive rotten egg smell. One method for elimininating hydrogen sulfide is by reaction with dissolved oxygen, as shown below.
2 H2S + O2 → 2 S + 2H2O
If 102 grams of H2S are combined with 64 grams of O2, what is the maximum mass of elemental sulfur that could be produced by the reaction?
(A) 16 grams
(B) 32 grams
(C) 48 grams
(D) 64 grams
(E) 96 grams
56. Mn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
A voltaic cell based on the reaction above was constructed from manganese and zinc half-cells. The standard cell potential for this reaction was 1.52 volts, but the observed voltage at 25°C was 1.66 volts. Which of the following could explain this observation?
(A) The Mn2+ solution was more concentrated than the Cu2+ solution.
(B) The Cu2+ solution was more concentrated than the Mn2+ solution.
(C) The manganese electrode was larger than the copper electrode.
(D) The copper electrode was larger than the manganese electrode.
(E) The atomic weight of copper is greater than the atomic weight of manganese.
57. The rate of effusion of helium gas (atomic weight 4.0) at a given temperature and pressure is known to be x. What would be the expected rate of effusion for hydrogen gas (molecular weight 2.0) at the same temperature and pressure?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) x
(D) ![]()
(E) 2x
58. H2O(g) → H2O(l)
Which of the following is true of the values of ΔH, ΔS, and ΔG for the reaction shown above at 25°C?
| H | ΔS | ΔG | |
| (A) | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| (B) | Positive | Negative | Negative |
| (C) | Negative | Positive | Negative |
| (D) | Negative | Negative | Positive |
| (E) | Negative | Negative | Negative |
59. A student added 1 liter of a 1.0 M Na2SO4 solution to 1 liter of a 1.0 M Ag(C2H3O2) solution. A silver sulfate precipitate formed, and nearly all of the silver ions disappeared from the solution. Which of the following lists the ions remaining in the solution in order of decreasing concentration?
(A) [SO42–] > [C2H3O2–] > [Na+]
(B) [C2H3O2–] > [Na+] > [SO42–]
(C) [C2H3O2–] > [SO42–] > [Na+]
(D) [Na+] > [SO42–] > [C2H3O2–]
(E) [Na+] > [C2H3O2–] > [SO42–]
60. Iron ore is converted to pure iron by the following reaction, which occurs at extremely high temperatures:
Fe2O3 + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO2
A 1,600 gram sample of iron ore reacted completely to form 558 grams of pure iron. What was the percent of Fe2O3 (molecular weight 160) by mass in the original sample?
(A) 25%
(B) 33%
(C) 50%
(D) 67%
(E) 100%
61. Gold and silver have been used throughout history to make coins. Which of the following statements could account for the popularity of these metals for use in coins?
(A) Network bonds make these metals especially durable.
(B) Negative oxidation potentials for these metals make them especially unreactive with their surroundings.
(C) These metals are among the lightest of the elements.
(D) These metals are commonly found in nature.
(E) These metals form ions that are extremely soluble in water.
62. A student added a salt to an aqueous solution of sodium sulfate. After the salt was added, a sulfate compound was observed as a precipitate. Which of the following could have been the salt added in this experiment?
I. BaCl2
II. Pb(NO3)2
III. AgC2H3O2
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
63. 2 HI(g) → H2(g) + I2(g)
For the reaction given above, ΔHo is –50 kJ. Based on the information given in the table below, what is the average bond energy of the H–I bond?
| Bond | Average Bond Energy (kJ/mol) |
| H–H | 440 |
| I–I | 150 |
(A) 270 kJ/mol
(B) 540 kJ/mol
(C) 590 kJ/mol
(D) 640 kJ/mol
(E) 1,180 kJ/mol
64. A solid piece of barium hydroxide is immersed in water and allowed to come to equilibrium with its dissolved ions. The addition of which of the following substances to the solution would cause more solid barium hydroxide to dissolve into the solution?
(A) NaOH
(B) HCl
(C) NaCl
(D) BaCl2
(E) NH3
65. All of the elements listed below are gases at room temperature. Which gas would be expected to show the greatest deviation from ideal behavior?
(A) He
(B) Ne
(C) Ar
(D) Kr
(E) Xe
Questions 66 and 67 refer to the information given below.
F2(g) + 2 ClO2(g) → 2 FClO2(g)
| Experiment | [F2] (M) | [ClO2] (M) | Initial rate of disappearance of F2 (M/ sec) |
| 1 | 0.10 | 0.010 | 1.2 × 10–3 |
| 2 | 0.20 | 0.010 | 2.4 × 10–3 |
| 3 | 0.40 | 0.020 | 9.6 × 10–3 |
66. Based on the data given in the table, which of the following expressions is equal to the rate law for the reaction given above?
(A) Rate = k[F2]
(B) Rate = k[ClO2]
(C) Rate = k[F2][ClO2]
(D) Rate = k[F2]2[ClO2]
(E) Rate = k[F2][ClO2]2
67. What is the initial rate of disappearance of ClO2 in experiment 2?
(A) 1.2 × 10–3 M/sec
(B) 2.4 × 10–3 M/sec
(C) 4.8 × 10–3 M/sec
(D) 7.0 × 10–3 M/sec
(E) 9.6 × 10–3 M/sec
68. Hypobromous acid, HBrO, is added to distilled water. If the acid dissociation constant for HBrO is equal to 2 × 10–9, what is the concentration of HBrO when the pH of the solution is equal to 5?
(A) 5-molar
(B) 1-molar
(C) 0.1-molar
(D) 0.05-molar
(E) 0.01-molar
69. N2(g) + 3 Cl2(g) → 2 NCl2(g) ΔH = 460 kJ
Which of the following statements is true regarding the reaction shown above?
(A) It is not spontaneous at any temperatures.
(B) It is spontaneous only at very high temperatures.
(C) It is spontaneous only at very low temperatures.
(D) It is spontaneous only at very high concentrations.
(E) It is spontaneous only at very low concentrations.
70. At 25°C, the vapor pressure of water is 24 mmHg. Which of the following expressions gives the vapor pressure of a solution created by adding 2.0 moles of sucrose to 55 moles of water?
(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
(E) ![]()
71. PCl5(g)PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
When PCl5 is placed in an evacuated container at 250°C, the above reaction takes place. The pressure in the container before the reaction takes place is 6 atm and is entirely due to the PCl5 gas. After the reaction comes to equilibrium, the partial pressure due to Cl2 is found to be 2 atm. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, Kp,
for this reaction?
(A) 0.5
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 5
(E) 10
72. Co2+ + 2 e– → Co Eo = –0.28 V
Cr3+ + e– → Cr2+ Eo = –0.41 V
According to the information shown above, which of the following statements is true regarding the reaction below?
2 Co + Cr3+ → 2 Co2+ + Cr2+
(A) Cr3+ acts as the reducing agent.
(B) The reaction would take place in a galvanic cell.
(C) Keq for the reaction is less than 1.
(D) Cobalt metal is reduced in the reaction.
(E) Chromium metal will plate out in the reaction.
73. What is the pH of a solution made by mixing 200 milliliters of a 0.20-molar solution of NH3 with 200 milliliters of a 0.20-molar of an NH4Cl solution? (The base dissociation constant, Kb, for NH3 is
1.8 × 10–5.)
(A) Between 3 and 4
(B) Between 4 and 5
(C) Between 5 and 6
(D) Between 8 and 9
(E) Between 9 and 10
74. POCl3(l) → POCl3(g)
For the reaction above, ∆H is 50 kilojoules per mole and ∆S is 100 joules per mole. What is the boiling point of POCl3? (Assume that ∆H and ∆S remain constant with changing temperature.)
(A) 0.5 K
(B) 2 K
(C) 50 K
(D) 200 K
(E) 500 K
75. When fluorine gas is bubbled through a concentrated aqueous solution of potassium chloride at room temperature, which of the following would be expected to occur?
(A) A reaction will occur, and chlorine gas will be produced.
(B) A reaction will occur, and potassium fluoride will precipitate.
(C) A reaction will occur, and solid chlorine will precipitate.
(D) A reaction will occur, and solid potassium will precipitate.
(E) No reaction will occur, and the fluorine gas will bubble through.
STOP
END OF SECTION I
IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, YOU MAY CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS SECTION.
DO NOT GO ON TO SECTION II UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.