Cell theory states that (1) all living things are composed of cells, (2) cells are the basic units and structure of living things, and (3) new cells are produced from existing cells.
Cells are classified into two categories based on the absence or presence of a nucleus: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are characterized by not having a nucleus; bacteria are one example.
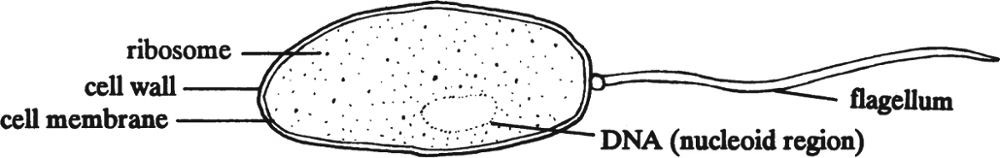
Structure of a Prokaryotic Cell

Plants, animals, fungi, and protists are made up of eukaryotic cells and characterized by having a nucleus and a more complex structure than a prokaryotic cell. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell contains the genetic material of the cell. Outside the nucleus lies the cytoplasm, a substance which surrounds the other cell structures. The cytoplasm contains many other organelles (cell parts with specific functions). These include:
Structure of a Eukaryotic Cell

Plant cells also have a somewhat rigid cell wall surrounding the membrane. The cell wall provides structure and support for cells.
Some plant cells produce their own energy through the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water react to make sugar and oxygen. It serves as a source of energy for the cells and takes place in plant cells.
Animal cells are surrounded by a semipermeable membrane which allows for the diffusion of water and oxygen from inside the cell to the outside of the cell and vice versa. These cells cannot produce their own energy and rely on consuming outside sources to provide them with the tools to make energy through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which the mitochondria process sugar and oxygen to produce energy, water and carbon dioxide. Cellular respiration serves as the energy source for animal cells. If no oxygen is present, cellular respiration will result in fermentation, where either lactic acid or alcohol is produced instead of sugar.
Cell division is the process where genetic material is replicated in the nucleus. Cell division begins in interphase, where DNA replication occurs. This results in the replication of the chromosomes in the nucleus. Chromosomes are tightly coiled threads of DNA composed of twin strands called chromatids. Interphase is the longest part of cell division and is divided into periods of cell growth and DNA replication. The cell grows in size to accommodate the increase in chromosomes. Following interphase is prophase. During prophase, chromatids begin to pair up with their sister chromatids. This leads into metaphase, where the sister chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. During the next phase, anaphase, the chromatids begin to pull apart into two separate poles. The cell becomes elongated during this phase, which makes it very easy to identify. During telophase, the two new nuclei become completely separated. The final phase in cell division is cytokinesis, where the cytoplasm and cell membranes complete their separation and two daughter cells are formed.
Normally, cell reproduction is closely regulated by genetic signals in the cell that tell it when to stop reproducing; cancer occurs when the signals are mutated and cells can grow without limit. Factors such as smoking, sun exposure, and genetic mutations can cause damage to cells and may lead to cancer. The most common type of cancer is skin cancer, caused by exposure to UV rays in sunlight.
Study the example below to see how an expert test taker would approach an ASVAB question about cellular functions.
| Question | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Cellular fermentation takes place when | Step 1: The question is asking the circumstances during which cellular fermentation takes place. |
| Step 2: There is notthing to simplify here. | |
| Step 3: Cellular fermentation occurs when no oxygen is present. When oxygen is not present, the cell is in anaerobic respiration and produces either alcohol or lactic acid instead of ATP. | |
| (A) no oxygen is present during cellular respiration (B) oxygen is present during cellular respiration (C) lactic acid is present during cellular respiration (D) yeast is present during cellular respiration |
Step 4: Based on the prediction above, select answer choice (A). |
Answer choice (C) is correct. The nucleus contains all genetic material. DNA replication takes place in the nucleus during interphase. Interphase is the longest phase of mitosis.