Cutting Tools
Manual (Hand) Saws
Cutting a material like wood requires the use of a saw. Saws are used in many different trades, but are typically utilized by carpenters.
The crosscut saw is designed to do what its name suggests: cut across the grain of the wood. Crosscut saw teeth are unique in that they cut like a knife. This is in contrast to a rip saw, which is made to cut with the grain of the wood and whose teeth are shaped like chisels. A rip saw’s teeth are also set (bent) alternately from side to side to cut a relatively wide kerf (slot). This style of teeth allows the rip saw to cut a straight line even if the grain of the wood is curved.
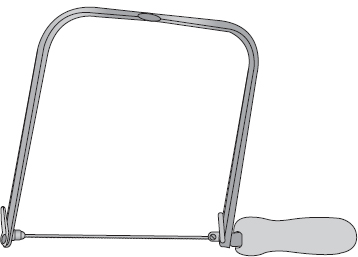
A coping saw is used to make fine, curving cuts. This saw uses a thin, flexible blade that is held tight on a wide frame. The blade can be rotated in the frame for further flexibility, making it easier to make difficult cuts on larger pieces of material.
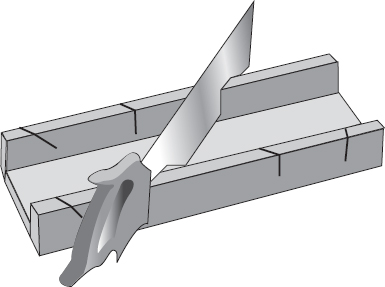
The back saw is also made from thin material, but has a rigid strip of steel on its top edge for reinforcement. A back saw is normally used for making fine cuts, so it has 14 to 16 teeth per inch. Back saws can be used with a miter box for making even cuts at specific angles.
The one saw that can be found in a mechanic’s toolbox is a hacksaw. Hacksaws are used for cutting metals such as steel, aluminum, or copper. The blades in a hacksaw are replaceable, and it is important to choose the right blade for the material that is going to be cut.
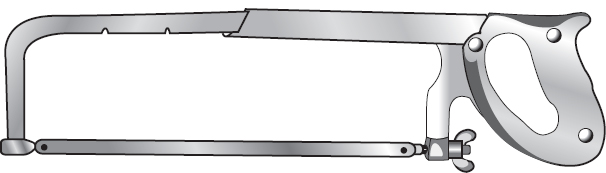
When selecting a hacksaw blade, keep in mind that larger numbers of teeth per inch help when cutting thinner materials. Also, remember that when installing a new blade, the blade must be oriented so that the teeth point away from the handle. This makes the hacksaw cut on the forward stroke, so let up on the downward pressure when pulling the hacksaw back to prevent breaking the blade.
Powered Saws
For jobs that require faster cuts or that involve especially strong materials, powered saws may be used in lieu of hand saws. A common type of powered saw is a circular saw which, as the name suggests, has a circular blade that rotates quickly to make a cut. There are two very common types of circular saw. A miter saw is a self-contained tool that sits atop a tool bench and is useful for making crosscuts in lumber, especially when the cut needs to be at a specific angle. Don’t get this confused with a table saw which also has a circular blade; a table saw has the blade actually embedded into the table or bench itself. Another key difference lies in how the saws are used. To use a miter saw, clamp or otherwise brace the material to be cut in order to keep it steady, and then lower the rotating circular saw to make the cut. To use a table saw, carefully slide the material to be cut toward the rotating blade.

Another common type of power saw is a band saw, which is so called because its blade is one continuous band of metal that revolves very quickly on two spinning wheels to make a continuous cut in a piece of wood or metal. Band saws are used for creating lumber out of timber and can also be useful for cutting straight or curved lines in a material. When using a saw like this for cutting metal, it is vital to use a coolant wash to keep the material cool and debris-free.
Drilling and Boring Tools
Making small holes in wood or metal is done by drilling the material. Large holes can be made in wood or soft metals using a process known as boring. The two processes are essentially the same, but they use different tools to get the job done.
Drill bits are used for drilling holes. A carpenter would use drill bits up to
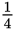 " in diameter, but a mechanic would commonly use drill bits as large as
" in diameter, but a mechanic would commonly use drill bits as large as
 ". If holes larger than this must be made, special tools would be used to bore the hole.
". If holes larger than this must be made, special tools would be used to bore the hole.
The vast majority of drill bits are made to cut while rotating in a clockwise direction. These are known as right-hand drill bits. Left-hand drill bits are made to cut in the opposite direction. The most common practical application for a left-hand drill bit is the removal of broken bolts from threaded holes.
Hole saws can also be used for boring large holes. Hole saws are not adjustable, so each one is only capable of drilling one size of a hole.
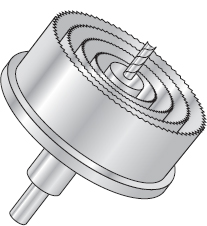
Today, it is rare for anyone to use hand-operated tools to drive drill bits and other boring tools. Instead, it is common practice to perform these operations using an electric drill. Electric drills can be identified by chuck size, reversibility, and whether they are designed to operate at a constant or variable speed.
The chuck of an electric drill is the part that holds the drill bit. A chuck is identified by the largest diameter bit that will fit in it. Common chuck sizes include
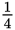 ",
",
 ", and
", and
 " Regular drill chucks can be tightened and loosened using a chuck key. Since it is easy to lose a chuck key, keyless chucks are becoming more popular. A keyless chuck makes it possible to tighten and loosen the chuck by hand.
" Regular drill chucks can be tightened and loosened using a chuck key. Since it is easy to lose a chuck key, keyless chucks are becoming more popular. A keyless chuck makes it possible to tighten and loosen the chuck by hand.
Some drills can operate in both the clockwise and counterclockwise directions. These are known as reversible drills. Variable speed drills are designed to operate over a range of speeds that can be determined by the position of the trigger.
As battery technology advances, it is getting more common for people to use cordless drills. Longer times between battery recharges and portability are just two of the reasons why these have become so popular. Many of these cordless drills come with a wide range of attachments (called drivers or bits) and can double as powered screwdrivers and socket wrenches as well.
The most important safety consideration when using a drill is to use a sharp bit. Dull bits require more time and more pressure placed on the drill to get the job done. With smaller bits, this could result in bit breakage and damage to the surface of the material being drilled. Drill bits can be sharpened on a bench grinder using a special attachment.
| Question | Analysis |
| You are attempting to cut a rounded shape from a square piece of wood. What is the best saw to choose? |
Step 1: This question asks which tool would be best for cutting a round shape from a square. Step 2: Not much info to simplify. Step 3: You can narrow your prediction by thinking about the type of saw that can cut a round, rather than straight, line. |
|
Step 4: Choice (A) matches that prediction. The remaining saws are designed for straight cuts. |
Now try your hand at a question about saws.
-
Which of these would a mechanic be most likely to use? - coping saw
- crosscut saw
- hacksaw
- rip saw
Explanation
Of these four choices, only choice (C), hacksaw, is commonly used to cut material other than wood, so that is the saw most likely to be in a mechanic’s toolbox.