Solutions to Review Problems
- D
One mole of aldehyde reacts with one mole of alcohol via a nucleophilic addition reaction to form a product called a hemiacetal. In a hemiacetal, an –OH group, an –OR group, a H atom, and a –R group are attached to the same carbon atom.

- C
The reaction between one molecule of a ketone and one molecule of an alcohol produces a compound analogous to a hemiacetal called a hemiketal. This has an –OH group, an –OR group, and two –R groups attached to the same carbon atom. Of the given choices, only choice (C) represents a hemiketal. Choice (A) has two –OR groups and two –R groups attached to the same carbon atom; this compound is called a ketal. Choice (B) is a hemiacetal since it has an –OH group, an –OR group, a H atom, and a –R group attached to the same carbon atom. Choice (D) is a ketone. The correct choice, therefore, is (C). Note that a hemiketal is a very unstable compound; it reacts rapidly with a second molecule of alcohol to form a ketal.
- A
Aldehydes and ketones react with ammonia and primary amines to form imines (also called Schiff bases), compounds with a double bond between a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom.
(CH3)2C═O + H2N − C2H5→ (CH3)2C═NCH2CH3 + H2OThe correct choice is (A).
- D
The reactivity of the carbonyl bond in propanone, and in aldehydes and ketones in general, is due to the difference in electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atom has higher electronegativity and is therefore electron-withdrawing. Thus, the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic and the carbonyl oxygen is nucleophilic. Choices (A) and (B) are true statements and therefore are incorrect answer choices (remember, this is an EXCEPT question; three of the answers are true and one is false). The resonance structure of propanone places a positive charge on the carbon atom, so choice (C) is also a true statement and therefore incorrect. The π electrons of the carbonyl bond are pulled toward the more electronegative element, which is oxygen, not carbon; thus, choice (D) is a false statement and the correct answer choice.
- B

Esterification, choice (A), is the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols. Tautomerization, choice (B), is the interconversion of keto and enol forms of a compound. An elimination reaction, choice (C), is a reaction in which a substituent is lost and a double bond is introduced. A dehydration reaction, choice (D), is one in which a molecule of water is eliminated. The above reaction involves an interconversion of keto and enol forms of ethanal. The correct choice is therefore (B). Note that equilibrium lies to the left in the above reaction since the keto form is more stable.
- D
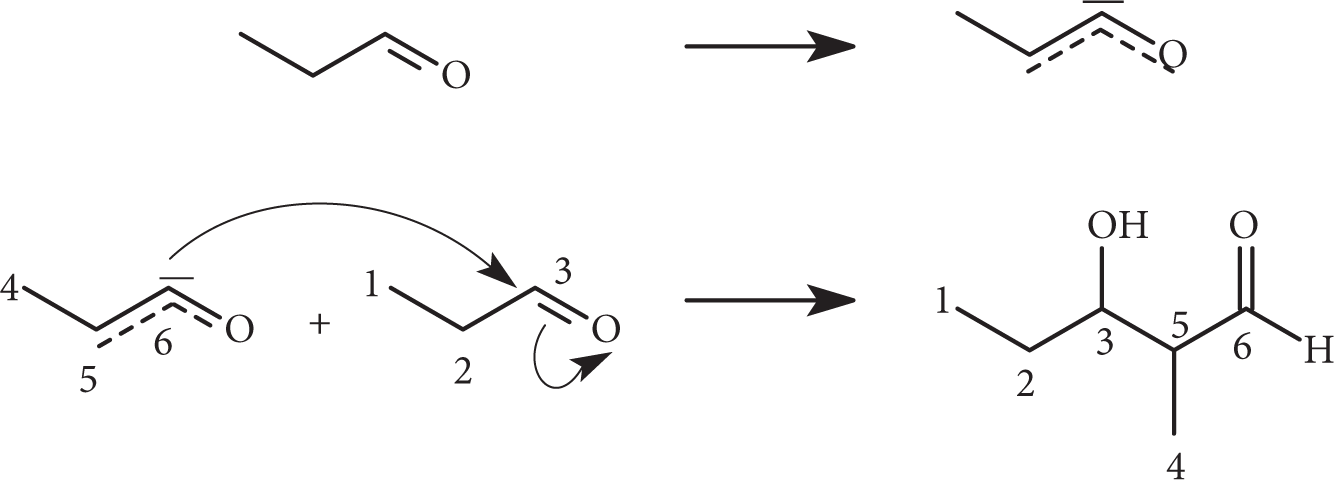
The above reaction is an example of aldol condensation. In the presence of a base, the alpha H is removed from an aldehyde, forming an enolate ion, CH3CH−CHO. The enolate ion then attacks the carbonyl group of another aldehyde molecule, CH3CH2CHO, forming the above aldol. The correct choice is (D).
- B
Aldehydes are easily oxidized to the corresponding carboxylic acids by KMnO4. The –CHO group is converted to –COOH. In this reaction, therefore, C2H5CHO is oxidized to C2H5COOH, which is choice (B). In choice (A), the aldehyde has been reduced to an alcohol. In choice (C), a –CH2 group has been added. Thus, choices (A) and (C) are incorrect. In choice (D), the –CHO group has been oxidized to –COOH, but a –CH2 group has been deleted, so choice (D) is incorrect.
- B
Heating an aldehyde or a ketone with amalgamated Zn/HCl converts it to the corresponding alkane; this reaction is called the Clemmensen reduction. Note that aldehydes and ketones can also be converted to alkanes under basic conditions by reaction with hydrazine (the Wolff-Kishner reduction).
- B
The hydrogen alpha to the carbonyl group is the most acidic, since its resultant carbanion is resonance-stabilized:
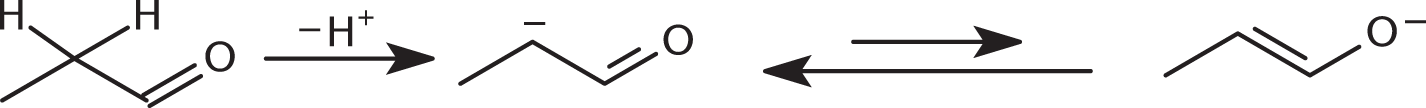
- B
LiAlH4 reduces carboxylic acids, esters, and aldehydes to primary alcohols, and ketones to secondary alcohols. In this reaction, therefore, the ketone is converted to a secondary alcohol. Thus, the correct answer is choice (B), C6H5CH(CH3)CHOHCH2CH3, a secondary alcohol.
-
- D
This product of this reaction is an acetal: two ethoxy groups bonded to the same carbon, represented by choice (D). This question states that an excess of ethanol is present, so benzaldehyde will first be converted to a hemiacetal, having an ethoxy and a hydroxy group bonded to the same carbon. Then the hemiacetal will be converted to the acetal by another equivalent of ethanol. Choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because they show the presence of two benzene rings in the final product. Choice (C) is incorrect since this is the hemiacetal that is formed initially, which then goes on to react with excess ethanol to produce the acetal.



