What is the formula for acceleration?
acceleration = change in velocity ÷ change in time:
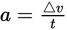
Mass is the amount of matter an object has, while weight is the amount of force exerted on the object’s mass by gravity.
newton (N); the force required to accelerate one kg by one meter per second per second: kg . m/s2
Newton’s first law of motion
acceleration = change in velocity ÷ change in time:
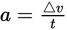
joule (J); Newtons times meters (or kg . m2/s2)
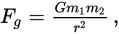 where Fg is the force of gravity, G is a constant equal to 6.67 × 10−11, and r is the distance between the two objects
where Fg is the force of gravity, G is a constant equal to 6.67 × 10−11, and r is the distance between the two objects
Energy
the rate at which work is performed; watts (or sometimes horsepower)
net force
Inertia is the tendency of objects to resist changes in their motion.
9.8
w = fd
work = force × displacement
p = mv, where p = momentum, m = mass, and v = velocity
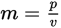
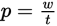
Power = work divided by time
Kinetic
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
meters per second per second, or
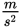
second law of motion
Potential
change in a quantity
one joule per second, or one ampere times one volt
either the Newton-meter or the foot-pound
In a third-class lever, the fulcrum is positioned near one end of the lever, and an upward force is applied to the middle of the lever in order to lift an object positioned on the other end of the lever.
the joule (J), which represents

directly
hydraulic
PE = mgh, where m represents the mass of the object in kg, g is acceleration due to gravity (roughly 9.8 m/s2), and h is the height of the object in meters
Ff = μ Fn, where Ff represents the force of friction, µ represents the coefficient of friction (static or kinetic), and Fn represents the normal force (the force a surface exerts when an object presses against it)
the pressure in any part of an enclosed fluid is the same and points in all directions.
 where P represents pressure expressed in pounds of force per square inch, F represents force in pounds, and A represents area in square inches
where P represents pressure expressed in pounds of force per square inch, F represents force in pounds, and A represents area in square inches
the number of pulleys
Drag
The work-energy theorem states that any work done to move an object from a resting position to a certain velocity will be converted into the kinetic energy of that object.
by increasing the ratio of the diameter of the large wheel to that of the small wheel
kinetic
τ = rF, where τ (the Greek letter tau) represents torque, r represents the length of the lever arm of the object being turned, and F represents a force being applied perpendicularly to that lever arm
Mechanical advantage is defined as the advantage gained by using a mechanism to help transmit force.
larger; smaller
block and tackle
kinetic energy and potential energy
increases
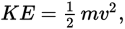 where m is mass in kg and v is speed in meters per second
where m is mass in kg and v is speed in meters per second
Static
In a first-class lever, the fulcrum is positioned in the middle portion of the lever. Force is applied to one end of the lever to lift an object on the other end.
550 foot-pounds per second, or 746 watts
direction
static; kinetic
The efficiency of a machine is an expression of how much of the force inputted into the machine is turned into movement or force.
wedge
Potential energy derives from an object’s position or shape, and it has the potential to be converted into kinetic energy (that is, energy of movement).
Torque
Tension
The principle of the conservation of mechanical energy states that the total mechanical energy (PE + KE) of an object remains constant as long as no other force is applied.
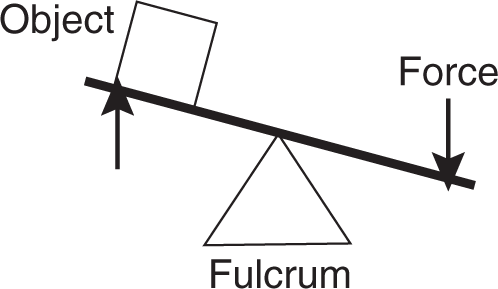
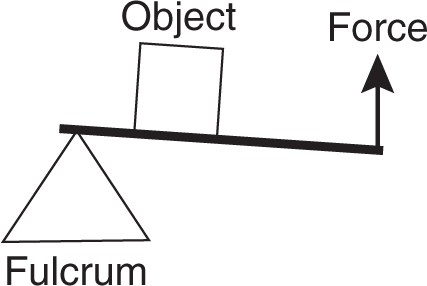
In a second-class lever, the fulcrum is positioned near one end of the lever underneath it, and the force is applied upward to the other end in order to move an object resting on the lever between the force and the fulcrum.
sizes
by moving the object to be lifted closer to the fulcrum, perhaps by making the lever longer
by increasing the ratio of the distance between the force and the fulcrum to the distance between the fulcrum and the object to be lifted
slower; torque (or rotational force)
inclined plane