Mechanical Comprehension Practice Set 1
-
Select the best answer for each question. This question set has 16 practice questions, which is the number of Mechanical Comprehension questions you will see if you take the CAT-ASVAB.
-
The work required to lift an object is the same as - the change in potential energy of the object
- the weight of the object divided by gravity
- the force required to overcome friction
- half of the work required to put the object down
-
A constant force of 2 N is applied to a mass of 6 kg that is initially at rest for 3 seconds. Assuming there is no friction or any other force applied to the mass, what is the velocity of the mass after 3 seconds? - 0.5 m/s
- 1.0 m/s
- 6.0 m/s
- 12.0 m/s
-
Approximately how much force is needed to lift the weight below? 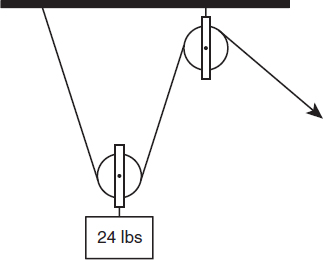
- 6 lbs
- 12 lbs
- 24 lbs
- 48 lbs
-
If a ball is dropped from a height of 5 m, what will be its approximate speed when it hits the ground? - cannot be determined because the mass is unknown.
- cannot be determined because the time it takes to reach the ground is unknown.
- 5 m/s
- 10 m/s
-
Adam’s car is stuck in the mud, so he recruits some friends to help push it out. If they apply 2,000 N of force to push the car 5 m, how much work did they accomplish? - 400 J
- 1,000 J
- 2,000 J
- 10,000 J
-
A machine in an assembly plant lifts parts weighing 10 N each from the floor to a height of 2 m. If this machine must lift batches of 20 parts at a time in 2 seconds, what amount of power is required? - 20 watts
- 100 watts
- 200 watts
- 400 watts
-
A man who weighs 900 N wants to compress some loose soil in his garden, so he puts a thick plate that is 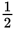 m wide and
m wide and
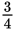 m long on the ground and stands on the plate. Assuming that the plate distributes
his weight evenly, how much pressure is applied to the soil?
m long on the ground and stands on the plate. Assuming that the plate distributes
his weight evenly, how much pressure is applied to the soil?
- 900
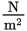
- 1600
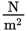
- 1800
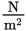
- 2400

- 900
-
Gear A has 15 teeth and gear B has 10. If gear A makes 14 revolutions, how many will gear B make? 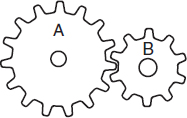
- 7
- 14
- 21
- 28
-
Two wheels are secured to a common axle. If the larger wheel has a radius of  m and the smaller wheel has a diameter of
m and the smaller wheel has a diameter of
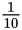 m, what is the mechanical advantage for a force applied to the larger wheel?
m, what is the mechanical advantage for a force applied to the larger wheel?
- 5 to 1
- 10 to 1
- 20 to 1
- 40 to 1
-
A basic kitchen knife, like the one below, is based on which of the following simple machines? 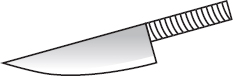
- wedge
- first-class lever
- pulley
- second-class lever
-
In order for Person X pulling a rope to lift an object with a block and tackle at the same rate of speed as Person Y pulling a rope to lift an identical object with a simple pulley, Person X will have to pull the rope as Person Y. - at the same rate
- faster
- slower
- at a rate based on the ratio of the diameters of the pulleys
-
How much force is needed to apply 50 ft-lb of torque to a bolt using a 2 ft long wrench? - 100 pounds
- 50 pounds
- 40 pounds
- 25 pounds
-
If a 10 N force applied to an object produces an acceleration of 10 m/s2, assuming friction is NOT negligible, what could the mass of the object have been? - less than 1 kg
- equal to 1 kg
- between 10 kg and 1 kg
- greater than 10 kg
-
The force of friction between two surfaces moving past each other DOES NOT depend on - the normal force
- the nature of the surfaces in contact with each other
- the area of the surfaces in contact with each other
- the speed at which the surfaces are moving past each other
-
The gravitational acceleration on Earth, g, is 9.8 m/s2. The gravitational acceleration on a neighboring planet, Xendor, is 3 times as much. What is the approximate weight of a 100 kg person on Xendor? (Hint: you can approximate the gravitational acceleration on Earth as 10 m/s2 to make calculations easier.) - 100 N
- 300 N
- 1,000 N
- 3,000 N
-
Assuming no friction, if 80 J of work was done to move an object 2 m, what was the net force that was applied? - 4 N
- 16 N
- 40 N
- 160 N