Reading in program parameters from the command line at the startup of a program is easy in Rust, just use the method std::env::args(). We can use the function collect() to these parameters into a vector of String, like this:
// code from Chapter 4/code/arguments.rs:
use std::env;
fn main() {
let args: Vec<String> = env::args().collect();
println!("The program's name is: {}", args[0]);
for arg in args.iter() {
println!("Next argument is: {}", arg)
}
println!("Total arguments supplied: {}", args.len() - 1);
for n in 1..args.len() {
println!("The {}th argument is {}", n, args[n]);
}
}
Call the program like this:
- arguments arg1 arg2 on Windows
- ./arguments arg1 arg2 on Linux and OS X
Here is the output from a real call:
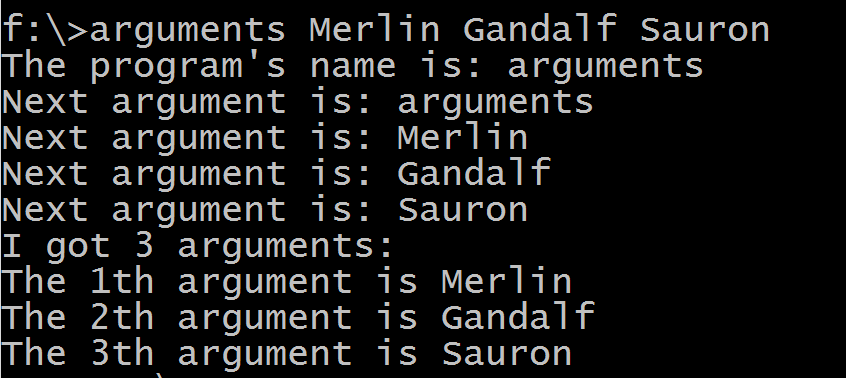
The argument args[0] is the program's name, the next arguments are the command-line parameters. We can iterate through the arguments or access them by index. The argument args.len()- 1 ;gives us the number of parameters.
For more complex parsing with options and flags use the getopts or the docopt crate. To get started there is an example at http://rustbyexample.com/arg/getopts.html.
In the same way env::vars() returns the operating system environment variables:
let osvars = env::vars();
for (key, value) in osvars {
println!("{}: {}", key, value);
}
This starts with printing out on Windows for example:
HOMEDRIVE: C:
USERNAME: CVO
LOGONSERVER: \\MicrosoftAccount