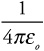 remember, is just the Coulomb’s law constant, k = 9.0 × 109 N-m2/C2!!!
remember, is just the Coulomb’s law constant, k = 9.0 × 109 N-m2/C2!!!The lists that follow are designed to help you study equations. Each prompt refers to a specific equation on the AP Equations Sheet (we’ve listed the prompts in the same order in which the equations appear on the Equations Sheet). So, for example, the prompt “Net force” refers to the equation, “Fnet = ma.”
There are several ways to use these prompts. First, you can use them as a self-test: for each prompt, write down the corresponding equation on a separate sheet of paper. Then check the equations you wrote down against the AP Equations Sheet to see if you got any wrong. You can also use these prompts when you study with a friend: have your friend read the prompts to you, and you respond by reciting the appropriate equation. Try to go through the list as fast as possible without making a mistake. Last, your physics teacher can use these prompts to lead your class through a Four-Minute Drill, which is an activity we describe in Chapter A.
Physics B
Newtonian Mechanics
1st kinematics equation
2nd kinematics equation
3rd kinematics equation
Net force
Force of friction
Centripetal acceleration
Torque
Momentum
Impulse
Kinetic energy
Potential energy due to gravity (near Earth)
Work
Power
Power—alternate expression
Force of a spring (The negative sign reminds you that the spring force is a restoring force, always acting toward the equilibrium point.)
Potential energy of a spring
Period of a mass on a spring
Period of a pendulum
Period in terms of frequency
Gravitational force between two massive objects
Gravitational potential energy between two massive objects. (Don’t use unless an object is far from a planet’s surface.)
Electricity and Magnetism
Electric force between two point charges— 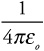 remember, is just the Coulomb’s law constant, k = 9.0 × 109 N-m2/C2!!!
remember, is just the Coulomb’s law constant, k = 9.0 × 109 N-m2/C2!!!
Electric force in terms of electric field
Potential energy in terms of potential, and then potential energy between two point charges (this line on the equation sheet really has two different equations. PE = qV is always valid, but PE = kqq/r is only valid between two point charges.)
Uniform electric field between two parallel plates
The potential at some point due to surrounding point charges
Definition of capacitance
Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
Energy stored on a capacitor
Definition of current
Resistance of a wire
Ohm’s law
Power in an electrical circuit
How to add parallel capacitors
How to add series capacitors
How to add series resistors
How to add parallel resistors
Magnetic force on a charge
Magnetic force on a wire
Magnetic field (not force) due to a long, straight wire
Induced EMF
Induced EMF in the special case of a rectangular wire with constant speed
Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Physics
Pressure in a static fluid column
Buoyant force—Archimedes’ principle
Continuity equation
Bernoulli’s equation
Thermal expansion
Rate of heat transfer
Definition of pressure
Ideal gas law
Average kinetic energy per molecule in an ideal gas
rms speed of the molecules of an ideal gas
Work done on a gas in an isobaric process (This reminds you that work done on a gas in any process can be found by the area under the PV graph.)
First law of thermodynamics
Definition of efficiency
Efficiency of an ideal heat engine
Waves and Optics
Velocity of a wave
Definition of the index of refraction
Snell’s law
How to find the critical angle for total internal reflection
Lensmaker’s equation / Mirror equation (They’re the same thing.)
Magnification
Focal length of a spherical mirror
Position of constructive interference points for light passing through slits
Position of constructive interference points for light passing through slits if the angle to the screen is small
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Energy of a photon—the second expression gives energy in terms of a photon’s momentum
Kinetic energy of an electron ejected from a metal surface, where W is the work function
De Broglie wavelength
Conversion between mass and energy
Physics C
Mechanics
1st kinematics equation
2nd kinematics equation
3rd kinematics equation
Net force
Force in terms of momentum
Impulse
Definition of momentum
Force of friction
Work
Kinetic energy
Power
Power—alternate expression
Gravitational potential energy near a planet
Centripetal acceleration
Torque
Newton’s second law for rotation
Definition of moment of inertia
Position of the center of mass
Conversion between linear and angular velocity
Angular momentum
Rotational kinetic energy
1st rotational kinematics equation
2nd rotational kinematics equation
Force of a spring (The negative sign reminds you that the spring force is a restoring force, always acting toward the equilibrium point.)
Potential energy of a spring
Period in terms of angular frequency and standard frequency
Period of a mass on a spring
Period of a pendulum
Gravitational force between two massive objects
Gravitational potential energy between two massive objects (Don’t use unless an object is far away from a planet’s surface.)
Electricity and Magnetism
Electric force between two point charges
Definition of electric field
Gauss’s law (Though you should never actually take an integral when using this.)
How to find electric field in terms of potential Potential energy in terms of potential, and then potential energy between two point charges (This line on the equation sheet really has two different equations. PE = qV is always valid, but PE = kqq/r is only valid between two point charges.)
The electric potential at some point due to surrounding point charges
Definition of capacitance
Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with a dielectric substance of constant k added
How to add parallel capacitors
How to add series capacitors
Definition of current
Energy stored on a capacitor
Resistance of a wire
Ohm’s law
How to add series resistors
How to add parallel resistors
Power in an electrical circuit
Magnetic force on a charge
Ampére’s law
Magnetic force on a wire
Magnetic field of a solenoid
Magnetic flux
Induced EMF
Voltage across an inductor
Energy stored in an inductor