Discrete Practice Questions
-
Which of the following does NOT show optical activity?
- (R)-2-butanol
- (S)-2-butanol
- A solution containing 1 M (R)-2-butanol and 2 M (S)-2-butanol
- A solution containing 2 M (R)-2-butanol and 2 M (S)-2-butanol
-
How many stereoisomers exist for the following aldehyde?
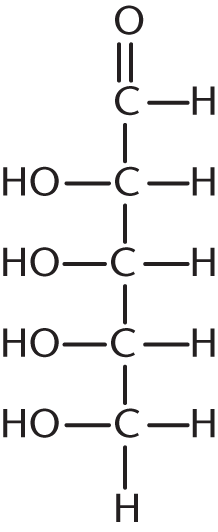
- 2
- 8
- 9
- 16
-
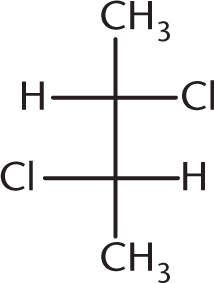
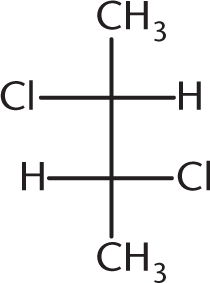
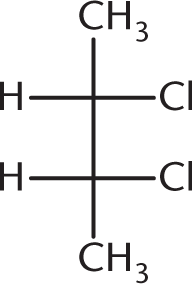
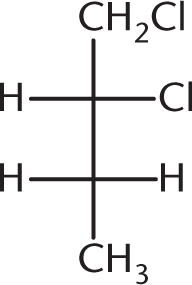
Which of the following compounds is optically inactive?
-
-
Cholesterol, shown below, contains how many chiral centers?

- 5
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
Which isomer of the following compound is the most stable?
-

-
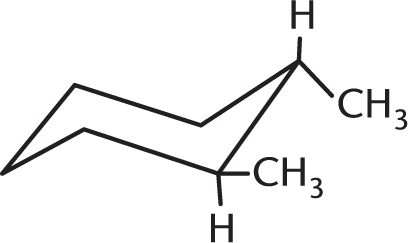
-
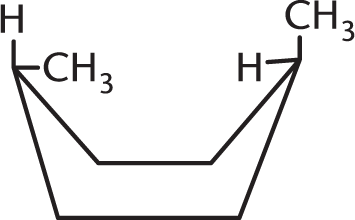
- They are all equally stable.
-
-
The following reaction results in:
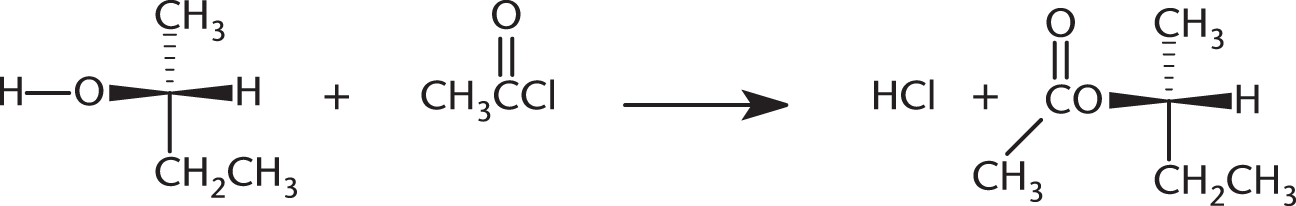
- retention of relative configuration and a change in the absolute configuration.
- a change in the relative and absolute configurations.
- retention of the relative and absolute configurations.
- retention of the absolute configuration and a change in the relative configuration.
-
The following molecules are considered to be:

- enantiomers.
- diastereomers.
- meso compounds.
- structural isomers.
-
(+)-Glyceraldehyde and (–)-glyceraldehyde refer to the (R) and (S) forms of 2,3-dihydroxypropanal, respectively. These molecules are considered:
- enantiomers.
- diastereomers.
- meso compounds.
- structural isomers.
-
Consider (E)-2-butene and (Z)-2-butene. This is a pair of what type(s) of isomers?
- Cis–trans isomers
- Diastereomers
- Enantiomers
- I only
- II only
- I and II only
- I and III only
-
3-methylpentane and hexane are related in that they are:
- enantiomers.
- diastereomers.
- constitutional isomers.
- conformational isomers.
-
(R)-2-chloro-(S)-3-bromobutane and (S)-2-chloro-(S)-3-bromobutane are:
- enantiomers.
- diastereomers.
- meso compounds.
- the same molecule.
-
A scientist takes a 0.5
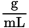 solution of an unknown pure dextrorotatory organic molecule and places it in a test tube with a diameter of 1 cm. He observes that a plane of polarized light is rotated 12° under these conditions. What is the specific rotation of this molecule?
solution of an unknown pure dextrorotatory organic molecule and places it in a test tube with a diameter of 1 cm. He observes that a plane of polarized light is rotated 12° under these conditions. What is the specific rotation of this molecule?- –240°
- –24°
- +24°
- +240°
-
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor commonly used in gastroesophageal reflux disease. When omeprazole, a racemic mixture, went off-patent, pharmaceutical companies began to manufacture esomeprazole, the (S)-enantiomer of omeprazole, by itself. Given 1 M solutions of omeprazole and esomeprazole, which solution(s) would likely exhibit optical activity?
- Omeprazole only
- Esomeprazole only
- Both omeprazole and esomeprazole
- Neither omeprazole nor esomeprazole
-
(2R,3S)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid and (2S,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid are:
- meso compounds.
- the same molecule.
- enantiomers.
- I only
- III only
- I and II only
- I and III only
-
If the methyl groups of butane are 120° apart, as seen in a Newman projection, this molecule is in its:
- highest-energy gauche form.
- lowest-energy staggered form.
- middle-energy eclipsed form.
- highest-energy eclipsed form.