Human Body Systems and Diseases
The Skeleton and Muscles
The skeleton and muscles are responsible for holding the body together as well as for movement. Without a skeleton you would be just an immobile mass of organs, veins, and skin. Some organisms, namely arthropods (including insects, spiders, and crustaceans), have exoskeletons, or external skeletons. However, vertebrate animals, including humans, have internal skeletons, or endoskeletons.
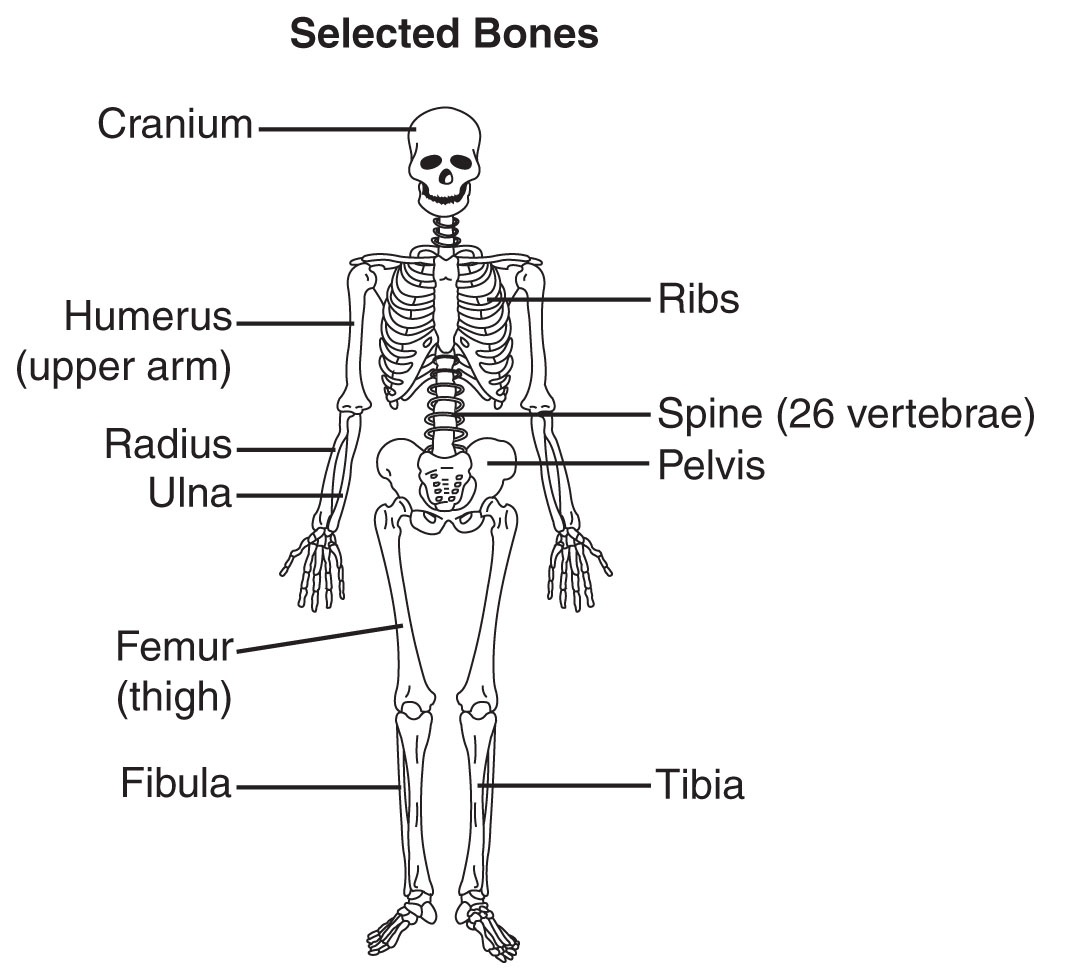
The human skeleton contains both bone and cartilage. Bones provide the primary support, while cartilage, which is more flexible, is found at the end of all bones, at the joints, in the nose, and in the ears. Bones not only provide structural support for the body and protect vital organs, but also produce blood cells and store minerals such as calcium. Tendons, tough fibrous cords of connective tissue, connect muscles to the skeleton. Ligaments, another type of connective tissue, connect bones to other bones at joints such as the elbow, knee, fingers, and vertebral column.
Here’s how an expert test taker would approach an ASVAB question about the skeletal system.
| Question | Analysis |
|---|---|
| What type of tissue would connect the humerus to the ulna? (A) bone (B) muscle (C) tendon (D) ligament |
Step 1: The question asks what type of tissue connects two bones to each other. Step 2: There is nothing to simplify. Step 3: Make a prediction: ligaments are connected to bone. Step 4: (D) is the correct answer. |
The Respiratory System
Respiration—the process by which blood cells absorb oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide and water vapor—is performed by the respiratory system.
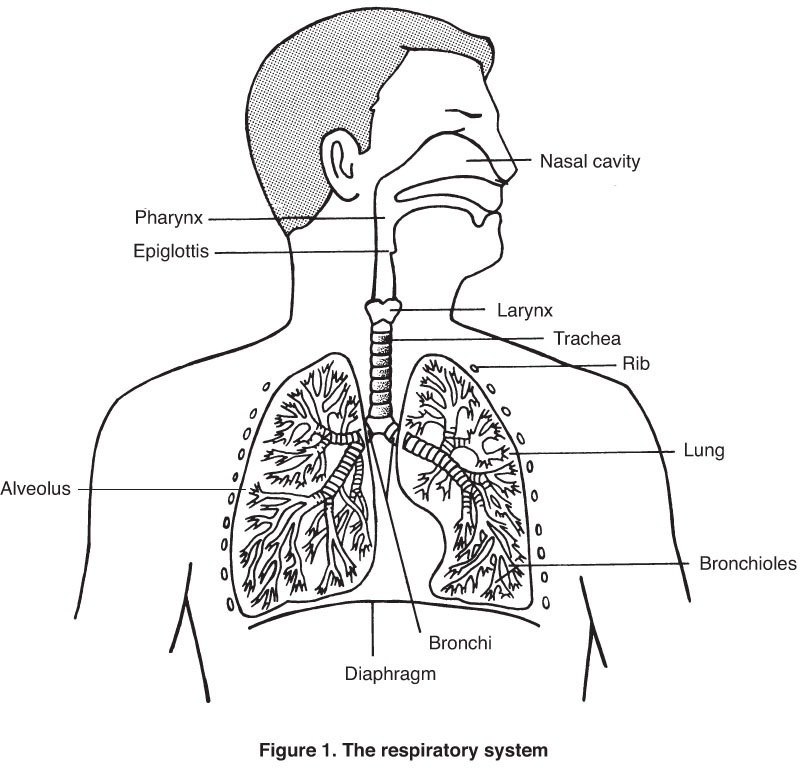
When air enters through the nose, it passes through the nasal cavity, which filters, moistens, and warms air, and then through the pharynx, which further filters the air and aids in protection against infection. The air then passes through the open epiglottis, which closes when swallowing to prevent food from going down the airway, and into the trachea, which further cleanses the air. The trachea branches into the left and right bronchi, which are two tubes that lead to the lungs. There the bronchi further subdivide into smaller tubes called bronchioles. Each bronchiole ends in a small sac called an alveolus. It is in the alveolus that oxygen from the air enters into the bloodstream via tiny blood vessels called capillaries. The diaphragm is a system of muscles that allows breathing. When the diaphragm causes the lungs to expand, air rushes in to fill the space, in a process called inhalation. When the diaphragm causes the lungs to contract, air is pushed out in an exhalation.
Blood and the Circulatory System
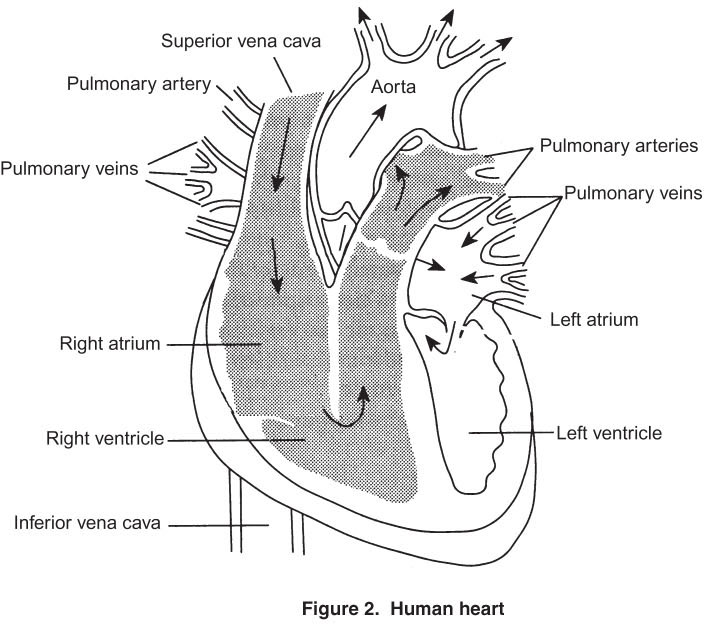
In conjunction with the respiratory system, the circulatory system functions to transport oxygen throughout the body while removing carbon dioxide. Additionally, the circulatory system transports nutrients provided by the digestive system and clears away waste by transporting it to the excretory system. The organ that drives the circulatory system is the heart. The human heart is a four-chambered pump, with two collecting chambers called atria (singular: atrium), and two pumping chambers called ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the venae cavae (plural of vena cava), the two largest veins in the body, and passes it to the right ventricle, which pumps the blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Blood picks up oxygen in the lungs and returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein. From there it passes to the left ventricle and is pumped through the aorta, the body’s largest artery, into several smaller branching arteries that take it through the rest of the body. The heart’s valves are essential to efficient pumping of the heart. When blood is pumped out of the ventricles, valves close to prevent the blood from flowing backward into the heart after the contraction of the ventricles is complete.
The right side of the heart is associated with deoxygenated blood (because the blood hasn’t gotten to the lungs yet), whereas blood coming into the left side of the heart is oxygenated because it’s sent there from the lungs.
Heart disease (also known as cardiovascular disease) is the most common cause of death in the United States. High cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and lack of exercise can all contribute to the development of heart disease, which can lead to heart attack or heart failure.
The Human Heart
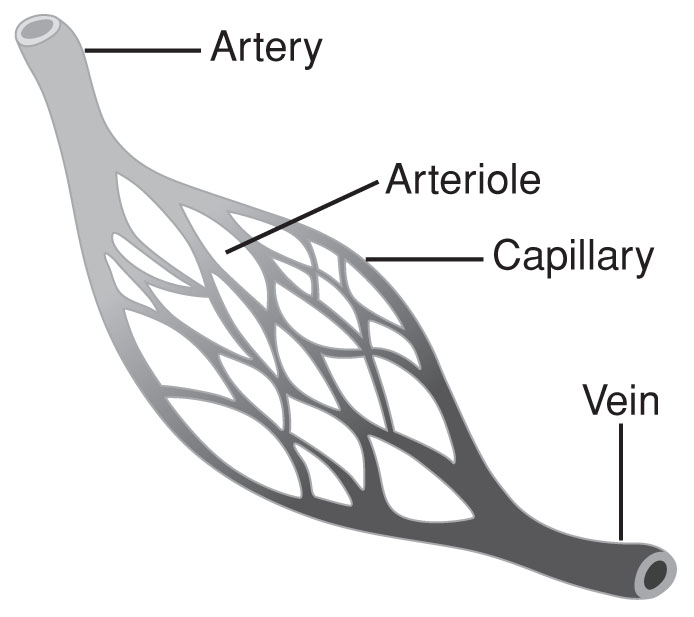
The arteries carry blood from the heart to the tissues of the body. They repeatedly branch into smaller arteries (arterioles), which supply blood to bodily tissues via the capillaries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and thus must be thick-walled because they carry oxygenated blood at high blood pressure. Only the pulmonary artery, which carries blood from the heart into the lungs, does not contain oxygenated blood.
Veins, on the other hand, carry blood back to the heart from other parts of the body. Veins are relatively thin-walled, conduct blood at low pressure, and contain many valves to prevent backflow. Veins have no pulse and carry dark red, deoxygenated blood. The lone exception is the pulmonary vein, which carries freshly oxygenated blood from the lungs back into the heart.
Finally, capillaries are thin-walled vessels that are very small in diameter. Capillaries, rather than arteries or veins, permit exchange of materials such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and waste between the blood and the body’s cells through diffusion.
The Capillary System
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, can cause damage to blood vessels as well as other parts of the body like the kidneys. Limiting salt intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and exercising can help prevent or manage hypertension.
Blood consists of cells suspended in plasma, the liquid component of blood. There are three types of cells found in blood: red blood cells, which are the oxygen-carrying cells; white blood cells, which fight infection by destroying foreign organisms; and platelets, which are cell fragments that allow blood to clot. All blood cells are created in the bone marrow, which is located in the center of bones.
Each of these blood cell types can be measured in the blood as an indicator of overall health. When white blood cell levels are higher than normal, that indicates that the body is fighting off some sort of infection by either bacteria or a virus.
It is also important to note that blood comes in four different types: A, B, AB, and O, which can be further designated as either “negative” or “positive.” One combination may be written as “A+” or “A positive,” for example. The letter designation is determined by the type of molecules (antigens) found on the outside of the red blood cells. The positive or negative designation is assigned based on whether or not cells have a third type of antigen called the Rh factor. A person who has blood that is Rh-factor negative cannot receive blood with a positive type; however, a person with positive type blood can receive donor blood that is Rh-negative. Type O negative is the universal donor, which means that type O negative blood can be given to anybody. Type AB positive is the universal recipient, which means that someone with this type of blood can receive any other type of blood.
Here’s how an expert test taker would think through an ASVAB question about the circulatory system.
| Question | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Which of the following does not contain oxygen-rich blood? |
Step 1: The question asks which listed item does not contain oxygen-rich blood. Step 2: Possible answer choices will contain three choices that do contain oxygen-rich blood and one (the correct answer) that does not. Step 3: A vague question like this can be hard to predict, because it doesn’t tell you if you are looking for a blood vessel or a part of the heart. Either way, you should start thinking about what you know about blood flow in the heart and to the body. |
| (A) aorta (B) left ventricle (C) pulmonary vein (D) right atrium |
Step 4: The aorta (A) carries oxygenated blood away from the left ventricle (B) of the heart, so neither of those is correct. The pulmonary vein (C) carries oxygenated blood to the left side of the heart from the lungs, so that leaves choice (D), right atrium, as the correct answer. |
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down foods into material the body can use for energy and building body tissues. The digestive tract is essentially a long and winding tube that begins at the mouth and ends at the anus.
The process of digestion progresses as follows:
- In the mouth, the teeth and the tongue aid in mechanical digestion (chewing), while the enzyme salivary amylase, contained in the saliva, begins to break down starch.
- From the mouth, the chewed food moves into the esophagus. Contractions push the food down through the esophagus and into the stomach.
- In the stomach, food is mixed with gastric acids and pepsin, which help break down protein.
- Most digestion takes place in the small intestine. The small intestine is very long, about 23 feet on average. Food is broken down completely by enzymes produced in the walls of the small intestine, in the pancreas, and in the liver. The acids produced by the pancreas contain lipase, which converts fat to glycerol and fatty acids; pancreatic amylase, which breaks down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars; and trypsin, which converts polypeptides (the molecules that compose proteins) into amino acids. Bile, which is produced by the liver, aids in digestion by emulsifying fat (physically separating it into individual molecules). All these digested substances, except for the fatty acids and glycerol, are then absorbed in the small intestine through capillaries that carry the blood into the liver and then throughout the rest of the body.
- In the large intestine, also known as the colon, water and minerals remaining in the waste matter are absorbed back into the body.
- Chemical waste, such as urea, excess salts, minerals, and water, are filtered from the blood by the kidneys and secreted into the urine. Urine is transported to the bladder from the kidneys through the ureters.
- In the rectum, solid waste matter is stored. Liquid waste (urine) is stored in the bladder.
- Solid waste matter is periodically released through the anus, and urine is released through the urethra.
The Digestive System

Study the example below to see how an expert test taker might approach a question about the digestive system.
| Question | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Where does food go after the step where proteins begin to be digested? |
Step 1: The question is asking about the next step in digestion after digestion of proteins begins. Step 2: This is essentially two questions in one. First, identify where proteins are digested. Second, recall where food goes after that step. Step 3: Recall that protein digestion begins in the stomach with the help of stomach acid and pepsin. Predict where food goes after being in the stomach: the small intestine. |
| (A) esophagus (B) stomach (C) small intestine (D) large intestine |
Step 4: Choice (C) is correct. |
The Nervous System
The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and the network of billions of nerve cells called neurons, which behave like electrical wires that send and receive signals throughout the body. The nervous system controls the functions of the body and receives and processes stimuli from the environment.
The nervous system consists of the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains all the other neurons found throughout the body.
The main components of the central nervous system are as follows:
- The cerebrum is the major part of the brain. It is thought to be the center of intelligence, responsible for hearing, seeing, thinking, etc.
- The cerebellum is a big cluster of nerve tissue that forms the basis for the brain. It is most closely associated with balance, movement, and muscle coordination.
- The medulla, which is part of the brainstem, is the connection between the brain and the spinal cord. It controls involuntary actions such as breathing, swallowing, and the beating of the heart.
- The spinal cord is the major connecting center between the brain and the network of nerves. It carries impulses between all organs and the brain and is also the control center for many simple reflexes.
The Human Brain

The peripheral nervous system can be subdivided into:
- The somatic nervous system, which consists of nerve fibers that send sensory information to the central nervous system and control voluntary actions.
- The autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary activity in the heart, stomach, and intestines.
The example below walks you through the expert approach to an ASVAB question about the nervous system.
| Question | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Which of the following parts of the brain, if damaged, would likely cause a person to have poor balance? |
Step 1: The question asks for a part of the brain that would affect balance if it were damaged. Step 2: There’s nothing to simplify. Step 3: Make a prediction based on what you know about the brain: the cerebellum is closely related to balance. |
| (A) medulla (B) spinal cord (C) cerebellum (D) cerebrum |
Step 4: Choose (C). The medulla and spinal cord are associated with more basic, involuntary functions like breathing and reflexes, whereas the cerebrum handles higher functions like our intelligence, so none of these choices fit. |
The Reproductive System
Human reproduction occurs when a female’s egg is fertilized by a male’s sperm. During female ovulation, which occurs approximately every 28 days, an egg (ovum) is released from one of the ovaries and begins to travel through the oviduct (fallopian tube) and into the uterus. At the same time, the endometrial lining of the uterus becomes prepared for implantation.
Male and Female Reproductive Systems
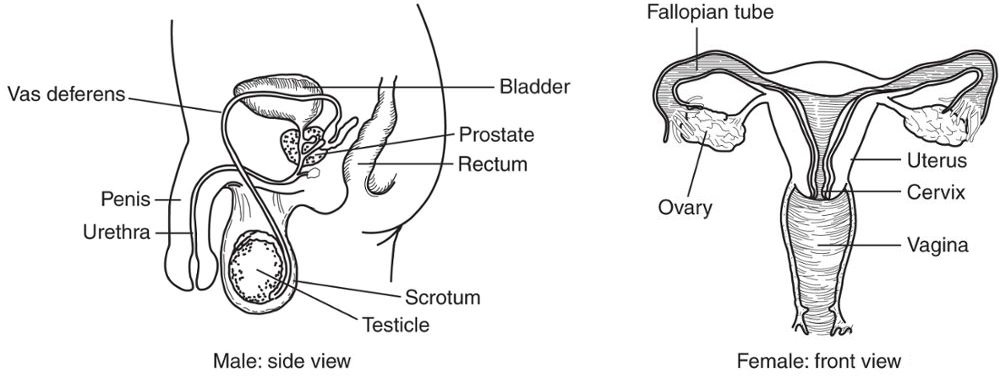
During intercourse, the penis ejaculates more than 250 million sperm, produced in the testes, into the vagina. Some of the sperm make their way to the uterus, where they may encounter an egg to fertilize. If the sperm unites with the ovum, a fertilized egg (zygote) is formed, which may implant in the uterus and eventually develop into a fetus. During pregnancy and after childbirth, prolactin, a hormone secreted by the pituitary, activates the production of breast milk (lactation).
If the ovum fails to become fertilized, the uterine lining sloughs off during menstruation. From puberty to menopause, this menstrual cycle repeats monthly except during pregnancy.
Human Pathogens
Some diseases, such as deficiency disorders, hypertension, and heart disease, are caused by diet and/or lifestyle factors. Another major cause of human disease are pathogens—disease-causing agents—such as bacteria and viruses. Bacteria, which are single-celled organisms, are responsible for diseases such as strep throat, staph infections, and pneumonia; these illnesses may be treated with antibiotic medications.
On the other hand, viruses are not technically living things because they are only able to replicate inside a host’s cells. Viral illnesses in humans include the common cold and flu, AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), and herpes. These illnesses cannot be treated with antibiotics, but may be treated with specially-designed antiviral drugs.
Both bacteria and viruses may be spread from person to person in several different ways. Some bacteria and viruses (including the cold and flu) may be passed through the air, wherein an infected person coughs or sneezes and another individual inhales the pathogen. Some viruses, like HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), can only be transmitted through contact with infected body fluids, as in sexual intercourse or intravenous drug use. Others, like herpes, can be spread by skin-to-skin contact. Every type of virus and bacteria has a unique profile when it comes to how it is transmitted and what type of cells it infects.
Luckily, many diseases caused by viruses (and a few caused by bacteria) can be prevented through vaccination. Vaccination, also called immunization, prevents many diseases that, not long ago, would have been very severe if not fatal, including smallpox, polio, and the measles. When a person receives a vaccine, a small amount of deactivated, weakened, or partial pathogen is injected into the body, causing the immune system to react; if the body is exposed to that pathogen in the future, the immune system will have a quick response to it, protecting the person from infection.
Here’s how to approach an ASVAB question about human health on Test Day.
| Question | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Which of the following illnesses could be treated with an antibiotic? |
Step 1: The question asks which illness can be treated with an antibiotic. Step 2: Antibiotics can only treat bacterial infections, so that’s what you’re looking for. Step 3: It’s hard to make a specific prediction, but you do know you’re looking for an illness that’s caused by bacteria. |
| (A) influenza (B) anemia (C) strep throat (D) herpes |
Step 4: Influenza and herpes are caused by a virus, while anemia is caused by iron deficiency. The correct answer is (C), strep throat, which is caused by bacteria. |
Now that you’ve gotten an overview of the human body systems and causes of disease, try your hand at a few questions:
-
1. Blood pressure is generally highest in which of the following? - veins
- capillaries
- arteries
- lungs
-
2. White blood cells are produced in - the heart
- the superior vena cava
- the lymph nodes
- the bones
-
3. Processing of signals from the heart and regulation of cardiac rhythm occurs in - the cerebrum
- the medulla, or brain stem
- the cerebellum
- the spinal cord
Explanations
1. (C) arteries Arteries pump blood away from the heart to the rest of the body, so the blood pressure is highest in those vessels. Some veins, (A), have such low blood pressure that they need valves to keep the blood from flowing the wrong way! Capillaries, (B), are tiny vessels located far from the heart, so their blood pressure is relatively low as well.
2. (D) the bones Reading the question stem carefully, home in on the key word, “produced.” Try to make a prediction before -looking at your answer choices, if possible. Although white blood cells are found in the blood, and thus pass through the vena cava and heart, they are produced in the center of bones, the marrow, so look for an answer like “marrow” or “bone.”
3. (B) the medulla, or brain stem Make a prediction. Regulation of the heart is an autonomic (involuntary) process. It occurs in the brain stem (medulla).