V
Ventricular Standstill (Asystole)
 BASICS
BASICS
DEFINITION
Absence of ventricular complexes on the ECG or absence of ventricular activity (electrical-mechanical dissociation).
ECG Features
- Ventricular asystole can result from severe sinoatrial block or arrest or by third-degree AV block without a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm; ECG features include:
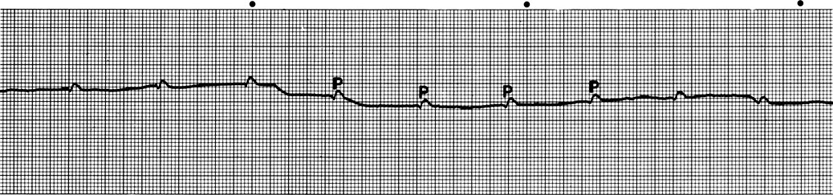
- P waves present if patient has complete AV block (Figure 1)
- P waves absent during asystole if patient has severe sinoatrial block or arrest
- No QRS complexes
- Electrical-mechanical dissociation—a recorded ECG cardiac rhythm (P-QRS-T) and no effective cardiac output or palpable femoral pulse.
Figure 1 Ventricular asystole in a dog with severe complete AV block. Only P wages (atrial activity) are present; there is no ventricular activity. (Lead II, 50 mm/second, 1 cm = 1 mV.) (From: Tilley LP. Essentials of Canine and Feline Electrocardiography, 3rd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1992, with permission.)
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Ventricular asystole represents cardiac arrest; if the ventricular rhythm is not restored in 3–4 minutes, irreversible brain injury can occur.
SYSTEMS AFFECTED
- Cardiovascular
- All organ systems affected by loss of perfusion
GENETICS
N/A
INCIDENCE/PREVALENCE
Unknown
GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION
None
SIGNALMENT
Species
Dogs and cats
Breed Predilections
None
Mean Age and Range
Unknown
SIGNS
Historical Findings
- Severe systemic illness or cardiac disease in many patients
- Other cardiac arrhythmias in some
- Syncope
Physical Examination Findings
- No ventricular pulse can be palpated
- Cardiac arrest
- Collapse
- Death
CAUSES
- Complete AV block with absence of ventricular or junctional escape rhythm.
- Severe sinus arrest or block.
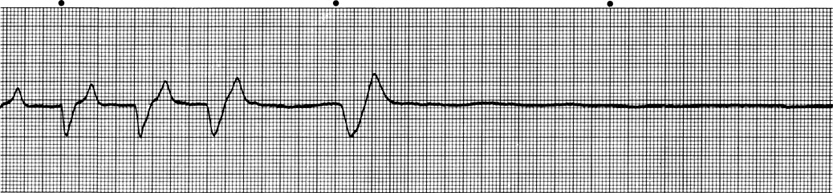
- Hyperkalemia (Figure 2).
RISK FACTORS
- Any severe systemic illness (e.g., severe acidosis and hyperkalemia) or heart disease.
- Hypoadrenocorticism causing hyperkalemia.
- Urinary tract rupture or obstruction, resulting in hyperkalemia.
 DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSIS
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Rule-out ECG artifact; reapply ECG clips and make sure skin contact is good and adequate alcohol is applied to leads.
CBC/BIOCHEMISTRY/URINALYSIS
Severe hyperkalemia possible cause
OTHER LABORATORY TESTS
N/A
IMAGING
N/A
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
Systemic blood pressure—readable pressure absent
PATHOLOGIC FINDINGS
N/A
 TREATMENT
TREATMENT
APPROPRIATE HEALTH CARE
- Asystole is a frequently fatal rhythm requiring immediate aggressive treatment.
- Artificial pacing with a transvenous pacemaker may succeed if myocardium is mechanically responsive.
- DC electrical conversion is not effective unless the rhythm can first be converted to ventricular fibrillation with medications.
NURSING CARE
Treat any treatable problems such as hypothermia, hyperkalemia, and acid-base disorders.
ACTIVITY
N/A
DIET
N/A
CLIENT EDUCATION
None
SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
None
 MEDICATIONS
MEDICATIONS
DRUG(S) OF CHOICE
- Institute cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Epinephrine 0.2 mg/kg IV, IT, or IL (double the dose for IT administration and deliver with equal volume of saline).
- Atropine 0.05 mg/kg IV, IT, or IL (double the dose for IT administration and deliver with equal volume of saline).
- Sodium bicarbonate 1 mEq/kg IV for each 10 minutes of cardiac arrest.
- Dexamethasone and dopamine may be helpful in patients with electrical-mechanical dissociation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Drugs that depress sinus node or AV node conduction in patients with sinus arrest or heart block (e.g., beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin).
PRECAUTIONS
None
Figure 2 Ventricular asystole in a cat with severe hyperkalemia (11 mEq/L) from urethral obstruction. No P waves or QRS complexes are seen after four wide and bizarre QRS complexes (atrial standstill with delayed ventricular conduction). (Lead II, 50 mm/sec, 1 cm = 1 mV.) (From: Tilley LP. Essentials of Canine and Feline Electrocardiography, 3rd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1992, with permission.)
POSSIBLE INTERACTIONS
None
ALTERNATIVE DRUG(S)
Calcium gluconate—patients with ventricular standstill and hyperkalemia.
 FOLLOW-UP
FOLLOW-UP
PATIENT MONITORING
- If animal is resuscitated—evaluate CBC, biochemical analysis, and urinalysis.
- If animal survives and primary cardiac disease is suspected—an echocardiogram and thoracic radiographs.
- ECG—closely and frequently.
PREVENTION/AVOIDANCE
Careful monitoring of critically ill patients to prevent and correct acid-base disturbances, hypotension, and hypoxemia.
POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS
- Death
- DIC and multiorgan failure
EXPECTED COURSE AND PROGNOSIS
Usually die. If sinus rhythm reestablished, prognosis still usually guarded to poor as not uncommon to arrest again.
 MISCELLANEOUS
MISCELLANEOUS
ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS
None
AGE-RELATED FACTORS
None
ZOONOTIC POTENTIAL
None
PREGNANCY/FERTILITY/BREEDING
None
SYNONYMS
Ventricular asystole
SEE ALSO
- Atrioventricular Block, Complete (Third Degree)
- Cardiopulmonary Arrest
- Sinus Arrest and Sinoatrial Block
ABBREVIATIONS
- AV = antrioventricular
- DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation
- ECG = electrocardiogram
- IL = intralingual
- IT = intratracheal
Suggested Reading
Kraus MS, Gelzer ARM, Moise S. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction disturbances. In: Tilley LP, Smith FWK, Oyama MA, Sleeper MM, eds., Manual of Canine and Feline Cardiology, 4th ed. St. Louis Saunders Elsevier, 2008, pp. 315–332.
Tilley LP, Smith FWK, Jr. Electrocardiography. In: Tilley LP, Smith FWK, Oyama MA, Sleeper MM, eds., Manual of Canine and Feline Cardiology, 4th ed. St. Louis Saunders Elsevier, 2008, pp. 49–77.
Author Francis W.K. Smith Jr.
Consulting Editor Larry P. Tilley and Francis W.K. Smith Jr.