7.1 Introduction
In the global invasion literature published between 1980 and 2006, plants were the subject of 44% of studies and vertebrates 15%, while invertebrates were the subject of 36% of publications, despite their considerably greater diversity in terms of both native and introduced species. Moreover, the vast majority of all studies analysed are from North America, Europe and Australia, while Asia, and particularly Africa, were greatly underrepresented in the literature (Pyšek et al. 2008). Most earlier work on invertebrate invaders focused on agricultural pests, but even these studies were undertaken later than corresponding studies for plants (Pyšek et al. 2008; Kenis et al. 2009; Sutherst 2014).
Until recently, alien terrestrial invertebrates in South Africa received little research attention compared to either alien vertebrates or plants. However, monographic assessments of alien species within several of the better-known invertebrate groups have now been published, notably those for earthworms (Plisko 2010), molluscs (Herbert 2010), and especially for pests of cultivated crops (Annecke and Moran 1982; Visser 2009; Prinsloo and Uys 2015). Two recent publications have also attempted to compile listings of all known alien and invasive animals reported from South Africa (Picker and Griffiths 2011, 2017), while listings for all alien taxa, derived from these and other sources, have also been compiled (van Wilgen and Wilson 2018; van Wilgen et al. 2020, Chap. 1, Sect. 1.1). It is important to note that discrepancies between the numbers of species listed in these various sources are inevitable. This is not only because new introductions are constantly arriving or being reported, but also because of differing definitions of the term ‘alien species’; of the geographical area of coverage and, in the case of this review, the definition of ‘terrestrial’.
This chapter includes only species of terrestrial invertebrates that have been introduced to mainland South Africa and have established self-sustaining populations outside of captivity or cultivation. Our list therefore has considerably fewer species than reported in the recent national status report on biological invasions in South Africa (van Wilgen and Wilson 2018). This is because the status report lists many species that are not naturalised (status B1–C2 in their Table 4.3), and hence did not fit our criteria for inclusion. It also included some species which are invasive on the offshore Prince Edward Islands , but not to mainland South Africa. The data set used here is thus that of Picker and Griffiths (2011), updated to include those species recorded subsequent to that review. We define terrestrial invertebrates as including all those that have at least one life stage completed on land. The taxa considered thus include Collembola (springtails), Insecta (insects), Myriapoda (millipedes and centipedes), Arachnida (spiders, ticks and mites), Crustacea (woodlice and landhoppers), Nematoda (nematode worms), Oligochaeta (earthworms), Gastropoda (slugs and snails) and Plathyhelminthes (flatworms).
7.2 Composition of the Known Alien Terrestrial Invertebrate Fauna
Updated count of alien terrestrial vertebrates known in 2018, showing current number of species per group, the increase in number since 2011 and the number of biological control agents in each group
Group name | Number of species | Species added since 2011 | Number of biological control species |
|---|---|---|---|
Collembola | 13 | 0 | 0 |
Zygentoma | 3 | 0 | 0 |
Blattodea | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Dermaptera | 5 | 1 | 0 |
Phasmatodea | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Embioptera | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Psocoptera | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Hemiptera | 104 | 8 | 16 |
Thysanoptera | 5 | 2 | 1 |
Phthiraptera | 13 | 0 | 0 |
Coleoptera | 87 | 6 | 45 |
Lepidoptera | 25 | 3 | 8 |
Diptera | 32 | 4 | 9 |
Siphonaptera | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Hymenoptera | 30 | 7 | 15 |
Myriapoda | 9 | 0 | 0 |
Arachnida | 41 | 2 | 1 |
Crustacea | 8 | 1 | 0 |
Nematoda | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Annelida | 38 | 0 | 0 |
Mollusca | 33 | 1 | 0 |
Platyhelminthes | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Total | 466 | 35 | 95 |
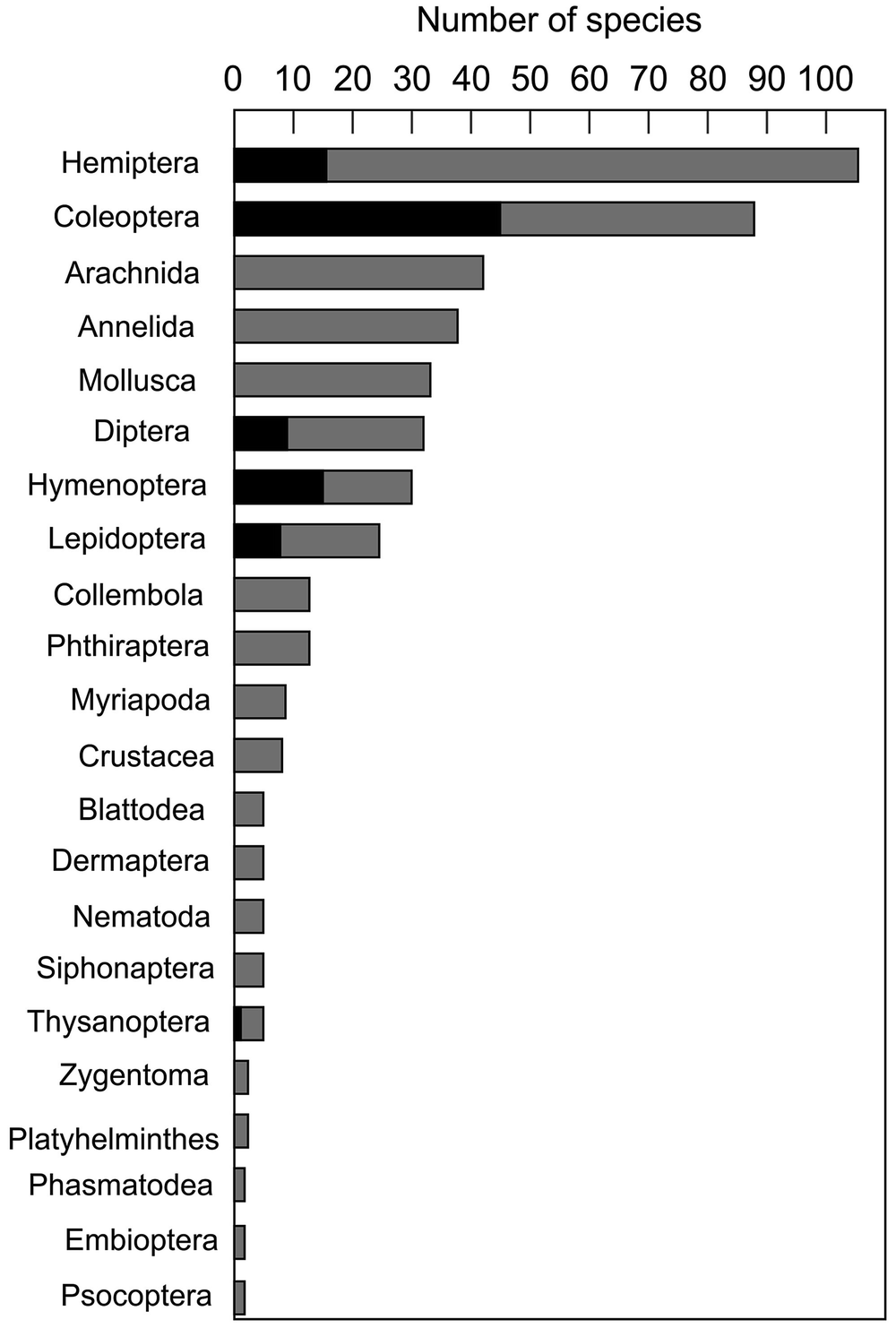
The total number of alien terrestrial invertebrate species per taxa in South Africa, with the number of biological control agents per taxa shown in black
Within the insects, the Hemiptera are the most species-rich group of alien terrestrial invertebrates, followed by the Coleoptera. The hemipterans are mostly from the suborder Sterrnorrhyncha (aphids and scale insects), which have piercing, sucking mouthparts, and thus often have severe economic impacts as plant pests. Half of all the alien Coleoptera in South Africa are biological control agents (45 species), most of these being from the families Chrysomelidae and Curculionidae. These groups are widely used as biological control agents of invasive alien plants, as many species are monophagous (specialised to eat only one plant species). Most of the invasive arachnids are mites (24 species), many of which are important agricultural pests, followed by spiders (16 species), which instead occur in and around human dwellings (Picker and Griffiths 2011). Amongst the terrestrial molluscs, invasive species from 10 families are present in South Africa (Herbert 2010), while the family Pyralidae (snout moths), which includes many economically important pests, are dominant amongst the terrestrial Lepidoptera (8 out of 25 species).
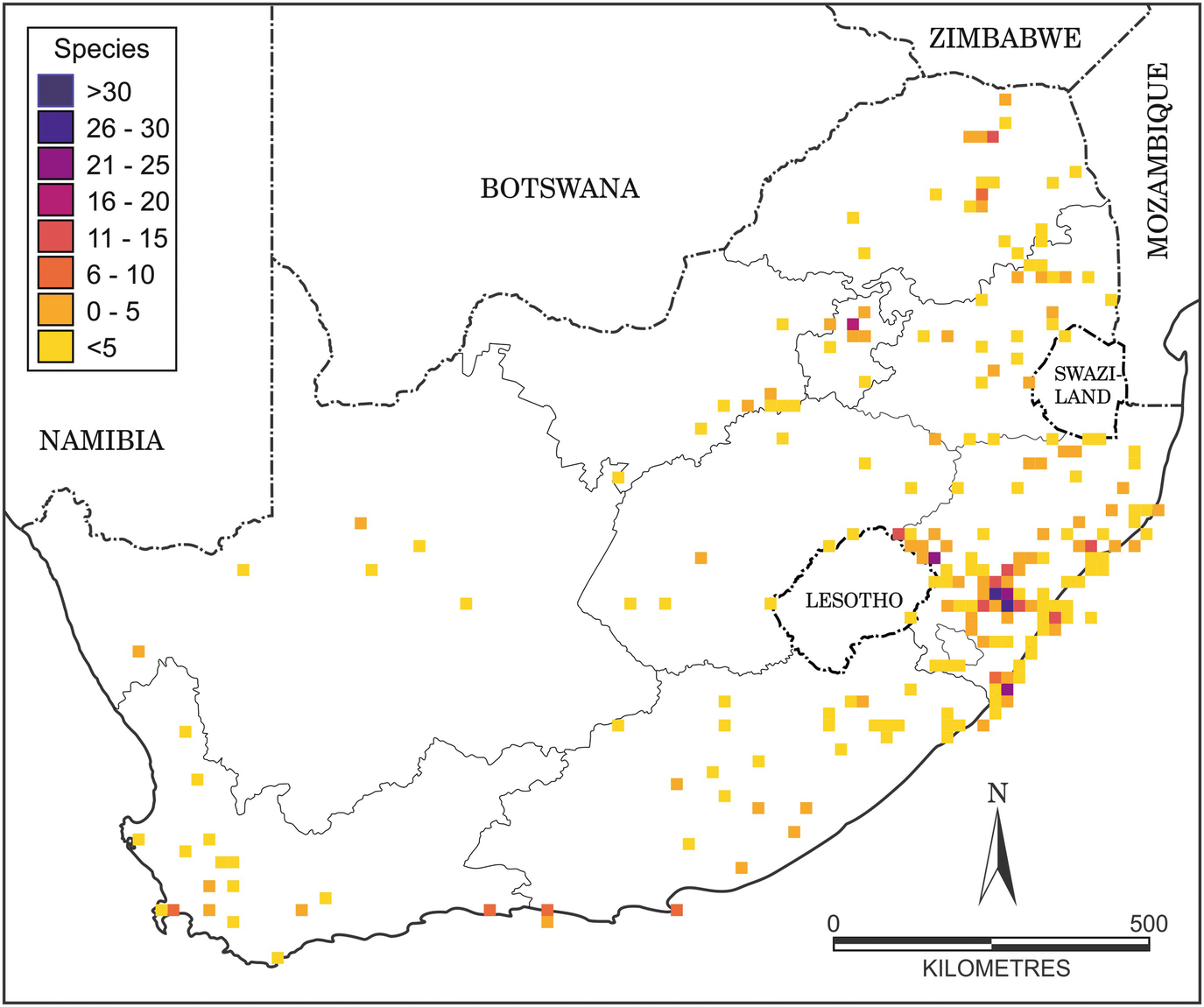
Distribution map of alien earthworms in South Africa (map produced by R. Leihy using data from Janion-Scheepers et al. 2016)
The total of 466 established alien terrestrial invertebrates recorded in South Africa is certainly an underestimate of the number already present. There are two primary reasons for this. Firstly, established alien species, some of which may have been present in the region for decades, are regularly being discovered, and more already-existing invasions will surely continue to be uncovered into the future. One notable example is the six recently-recorded Australian insects found associated with Eucalyptus trees by Bush et al. (2016). Many such suitable habitats (e.g. the numerous species of non-commercial, ornamental plants in urban gardens) still remain poorly explored, and are likely sites where existing alien terrestrial invertebrates remain undetected. Secondly, there are many groups for which regional taxonomic expertise is poor or entirely lacking, and these probably include many more alien or invasive species than are currently recognised, highlighting the need for improved foundational taxonomic knowledge in South Africa. This is especially the case for many groups of soil fauna, which are inconspicuous and understudied (Janion-Scheepers et al. 2016), but which can easily be introduced and distributed accidentally through eggs in soil and are thus almost certainly under-reported in the current lists.
7.3 Dates, Rates and Routes of Introduction
Although the dates of introduction of most regional alien terrestrial invertebrates remain unknown, many are known to have been introduced more than 100 years ago (Picker and Griffiths 2011). Some of the earliest reported invasive invertebrates in South Africa were two species of flea, first recorded during the 1700s (the Human Flea Pulex irritans and the Chigoe Flea Tunga penetrans; Picker and Griffiths 2011). Other early invasive invertebrates recorded include the European Garden Snail (Cornu aspersum), first detected in 1855, the Sand Earwig (Labidura riparia) in 1863; the Australian Bug (Icerya purchasi) in 1873 and the Codling Moth (Cydia pomonella) in 1892. Subsequently, increased trade and importation of plants caused a progressive increase in the number of alien terrestrial invertebrates introduced into South Africa (Picker and Griffiths 2017). This has been particularly driven by the proliferation and broadening of international trade since the early twentieth century (Faulkner et al. 2020, Chap. 12, Sect. 12.2.2) and more recently by increasing rates of deliberate introduction of agents for the biological control of plant and animal pest species (Annecke and Moran 1982; Hill et al. 2020, Chap. 19).
The routes of introduction of alien species are discussed in more detail elsewhere in this volume (Faulkner et al. 2020, Chap. 12), but in contrast to many vertebrate or plant introductions, the majority of invertebrates introductions appear to have been accidental, as contaminants or stowaways (Faulkner et al. 2016), although 92 species are known to have been deliberately introduced as biological control agents. However, the exact pathways of introduction for less than 50% of invertebrates are properly known (Faulkner et al. 2015). This is partly due to their small size, which has resulted in many species having been imported undetected along with commercial goods, but is also because the identification of some introduced taxa remains problematic. This is especially concerning for phytophagous species, which may cause considerable damage to crops, resulting in economic losses and threats to food security (Giliomee 2011).
Both dates and routes of introduction are linked to geographical patterns of importation and trade, and how these have changed over time. For example, seed insects are usually introduced along with seeds and herbivorous invertebrates with plants, both of which may be introduced either as crops, or as food. In early colonial days, these products were mostly imported from Europe, whereas in more recent times other major trade routes have opened up, notably those to Asia, which has now become the source of some 25% of all terrestrial invasions (Picker and Griffiths 2017).
Changes in technology may also have impacts, for example, air freight of fresh produce may now allow the importation of short-lived, delicate species that would not have survived earlier, longer-duration passages by sea. Another example of changing vector patterns is an increase in the use of wooden crates in general trade, which has resulted in an increase in the number of woodborer beetles introduced into the USA (Herms and McCullough 2014).
7.4 Biological Control Agents
Twenty percent of the terrestrial invertebrates listed here (Table 7.1) were deliberately introduced biological control agents. These are highly selective natural enemies (herbivores, predators, parasites or pathogens ) used to control populations of invasive species, usually plants, but also some insect pests. Over the past century, the use of such biological control agents has become widespread and now takes place in about 130 countries, with over 550 biological control agents released globally (Zachariades et al. 2017). The use of biological control agents has many advantages over traditional manual or chemical control techniques, primarily economic ones, in that they are relatively cheap to apply and then usually self-sustaining, so that their benefits continue to accrue indefinitely. There are some costs involved, however, in the initial safe introduction of biological control agents, as candidate species have to be rigorously tested to assess the risk of them having any adverse impacts on native flora and fauna.
South Africa first utilised this technique over a century ago, when Dactylopius ceylonicus (Cochineal Insect) was released in 1913 to control Opuntia monacantha (Drooping Prickly Pear), which was then highly invasive along the coast between the Western Cape and Durban (Moran et al. 2013). Despite the lack of precautionary testing, this introduction was a resounding success and resulted in rapid and permanent control of the host. Since that time, South Africa has become a global leader on the field of biological control and is now considered one of the top five countries in the world with regards to research in this field (Zachariades et al. 2017).
In the early years, the target plants were mostly invasive Cactaceae and the biological control agents introduced were ones whose effectiveness had already been proven in other countries. Later projects have targeted new hosts, for which the experimental testing had to be conducted in South Africa, and by 2018 a total of 93 species of insect, mites or plant pathogens had been released against 59 host plants species, with 25 additional plant species under investigation (Zachariades et al. 2017).
A few invasive invertebrates have also been targeted for biological control, the most common control agents in these cases being wasp parasitoids. For example, Megalyra fasciipennis is a pupal parasitoid that has been introduced to control invasive Eucalyptus Longhorn Borer Beetles (Phorocantha species) (Gess 1964), while Cotesia plutella is a parasitoid introduced to control Plutella xylostella (Diamondback Moth), a major pest of cabbages and other plant species in the family Brassicaceae (Nofemela and Kfir 2005). The solitary regional example of a nematode biological control agent, Beddingia siricidicola, was also introduced from Europe to control Sirex noctilio (Sirex Woodwasp) (Hurley et al. 2007).
Biological control agents that control invasive invertebrates have sometimes arrived accidentally. Thus, Psyllaephagus bliteus (a eucalypt gall wasp parasitiod), which is a classical biological control agent in many countries for the control of the Redgum Lerp Psyllid, Glycaspis brimblecombei, seems to have arrived in South Africa (and indeed other regions globally) without intervention, presumably as larvae within imported host populations (Bush et al. 2016). Conversely, the populations of some invasive invertebrates can also sometimes be brought under control by host-switching in native predators and/or parasitoids. For example, populations of the invasive Pieris brassicae (Large Cabbage White Butterfly), fluctuate dramatically between years and appear to be effectively controlled by an unidentified, but probably native, braconid wasp (Apantles species), which attacks the caterpillars, as well as by a native pteromalid wasp, Pteromalus puparum, which attacks the pupae (Picker and Griffiths 2011; Prinsloo and Uys 2015). Similarly, Nofemela and Kfir (2005) report eight species of native parasitic Hymenoptera attacking various life history stages of the invasive Plutella xylostella (Diamondback Moth), with parasitism rates reaching 100% in some samples (see Le Roux et al. 2020, Chap. 14, Sect. 14.2.4).
South African biological control programmes have contributed significantly to the control of 34 invasive plant species, 14 of which are considered to be under complete control (Klein 2011), with the most prominent successes being against Australian Acacia species (Box 7.1), cacti and several floating aquatic plants.
Recent assessments of the economic benefits derived from the biological control of invasive alien plants indicate that existing programmes have already reduced management costs by ZAR 1.38 billion, and have the potential to double these savings (Zachariades et al. 2017). The introduction of invertebrate biological control agents has thus already contributed substantially to the management of invasive alien plants and animals and further investment in the development of new agents can only increase this contribution in the future.
The Varroa Mite (Varroa destructor) is an external parasite, and is one of the world’s most devastating pests of honeybees. Female mites enter bee brood cells and lay their eggs on developing larvae. Young mites hatch at about the same time as the bees and leave the cells with the host, spreading to other bees and larvae. Adult mites suck the haemolymph of honeybees, leaving wounds and transmitting viral diseases. Infected colonies typically collapse after 1–2 years.
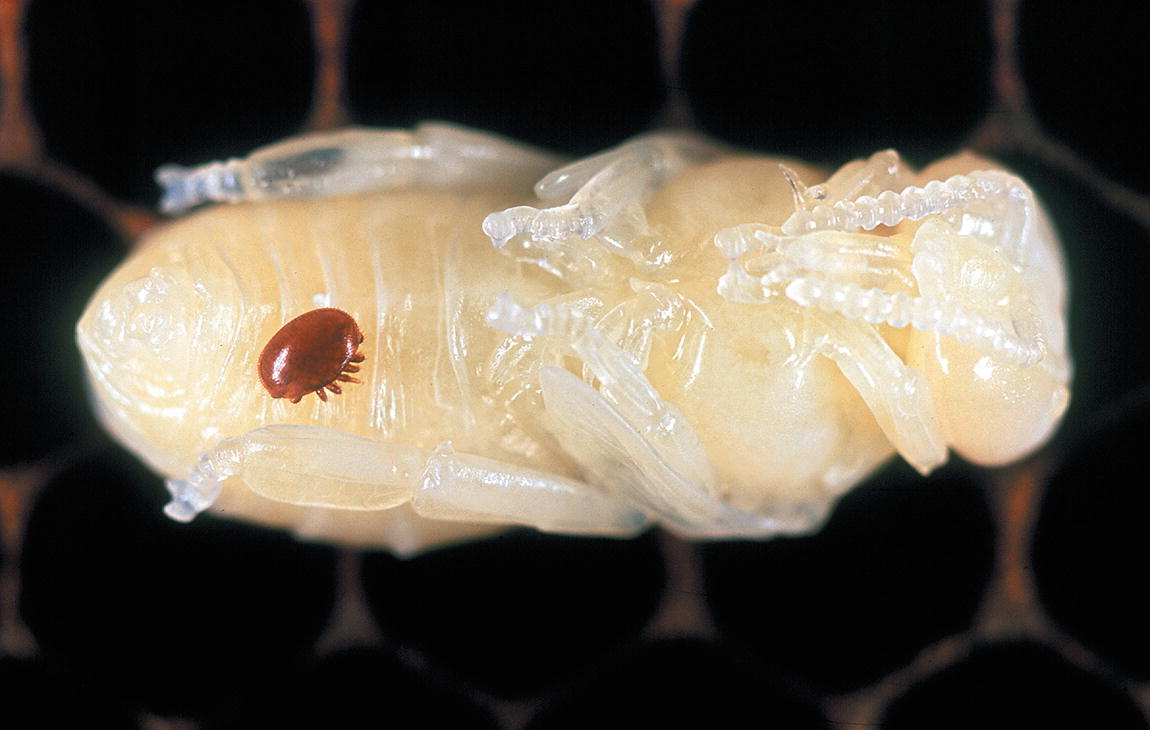
The Varroa Mite (Varroa destructor) on Apis mellifera (Honey Bee) larva (Photograph courtesy of CSIRO )
7.5 Impact of Invasive Invertebrates
The most severe and obvious impact of alien terrestrial invertebrates are as direct pest species on crops, domestic animals and stored products, and this may result in severe economic losses across a wide range of products (Prinsloo and Uys 2015). Some of the most devastating of the many invasive pests that attack crop plants are Aonidiella aurantii (Red Scale), Cydia pomonella (Codling Moth) and Phthorimaea operculella (Potato Tuber Moth). Economically important pests of domesticated animals include cattle ticks and Varroa destructor (Varroa Mite), which is an important pest of honeybees (Box 7.2); while those that attack stored goods include a variety of grain borer beetles and of meal and grain moths. The control of some alien invertebrate species is discussed in more detail elsewhere in this volume (Davies et al. 2020, Chap. 22). Of more concern is the prediction that crop losses due to insect pests are expected to increase globally with climate change , and that this may severely threaten food security (Bebber et al. 2013).
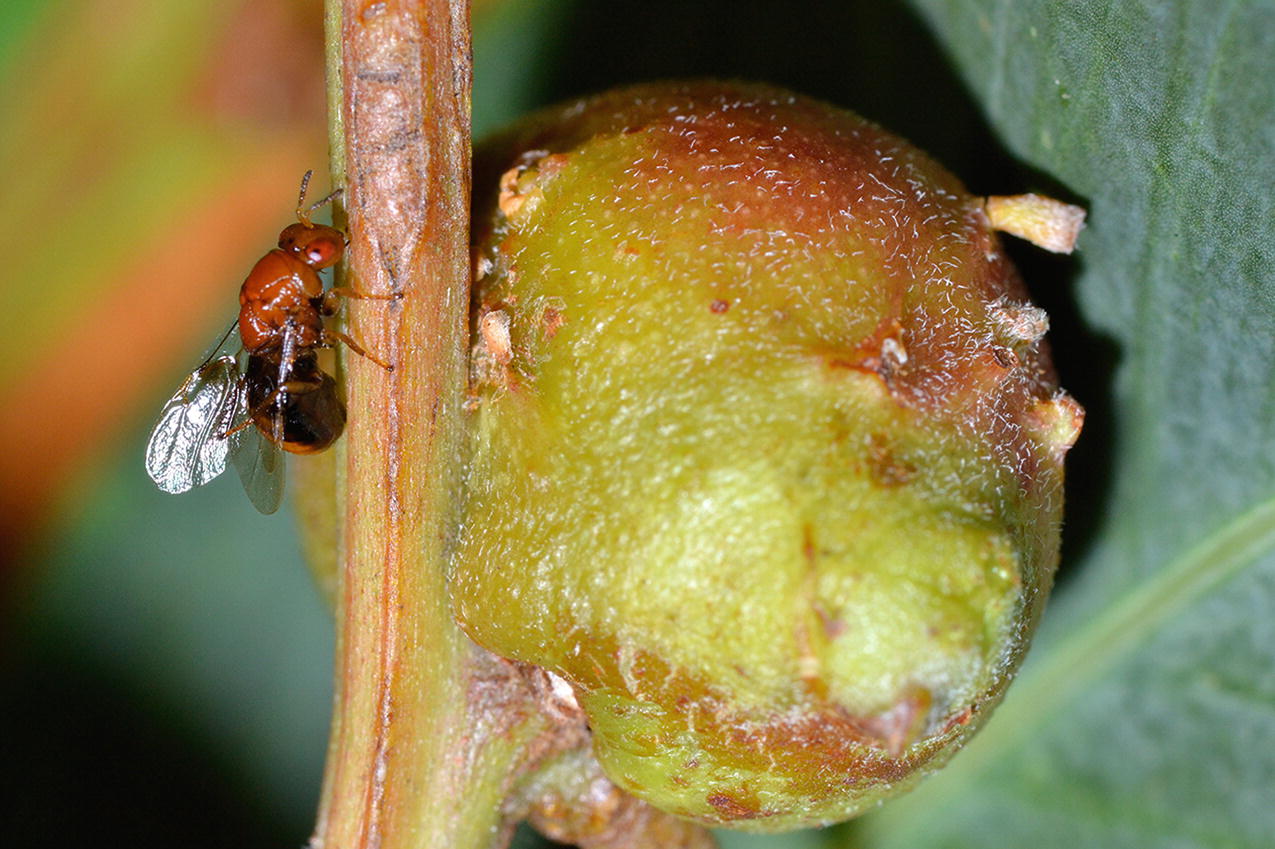

The Acacia Gall Wasp (Trichilogaster acaciaelongifoliae) and its gall (Photograph courtesy of Charles Griffiths)
Most alien terrestrial invertebrate species establish in agricultural habitats dominated by alien plants, or in disturbed and urbanised areas, especially in human habitations, although a proportion have managed to establish in native vegetation (also see Boxes 7.1–7.5). These species usually have non-specialist diets. For example, alien earthworms have been found in pristine forests in KwaZulu-Natal (Nxele 2012). Some examples of the detrimental effects of alien earthworms elsewhere include decreases in abundance and diversity of other soil invertebrates, which could subsequently affect ecosystem services provided by these organisms (Ferlian et al. 2018). Similar patterns may also be expected following the introduction of other invasive soil fauna, such as gastropods (Herbert 2010), which can be pests in the agricultural sector, but can also prey on other invertebrates. Generally, the functional impact of invasive soil biota on native communities and ecosystem function have not been well investigated in South Africa (Janion-Scheepers et al. 2016).
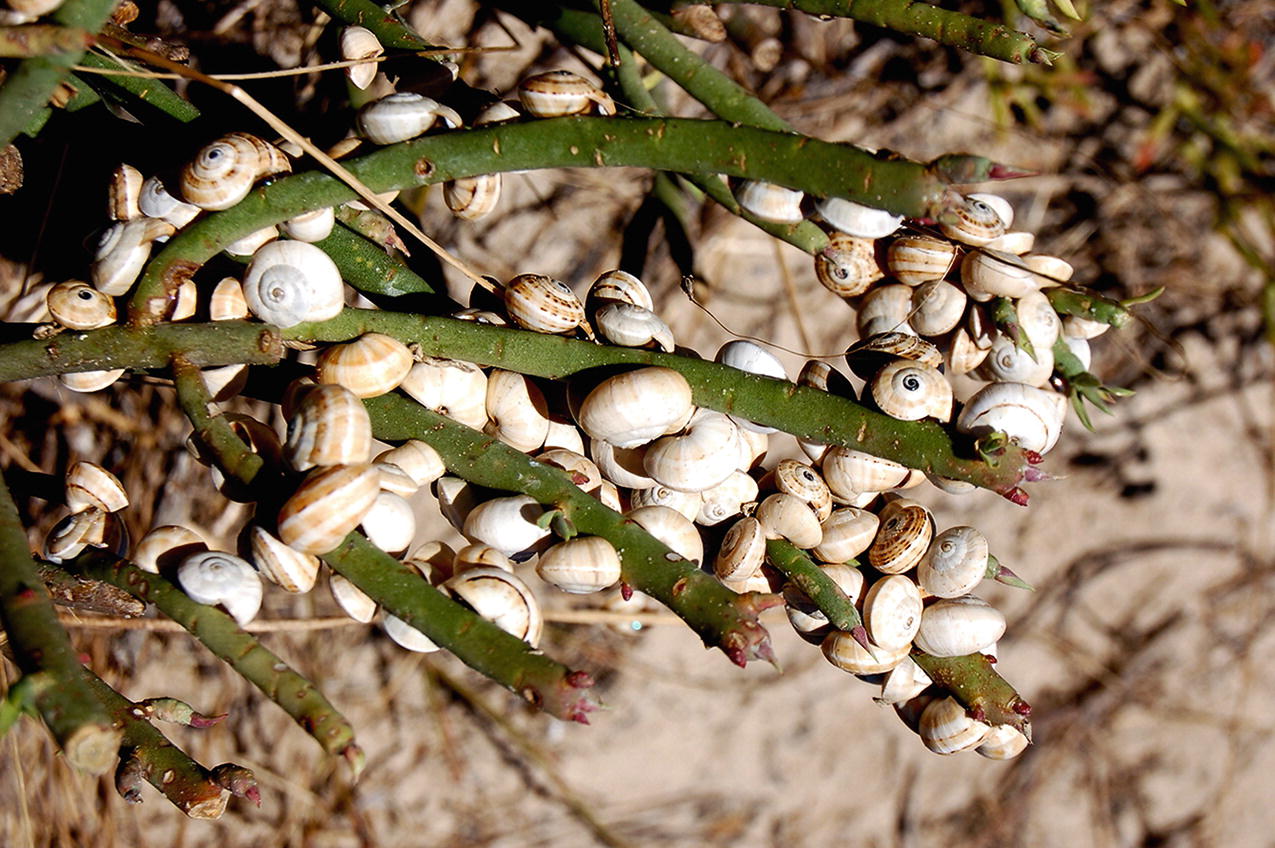

White Garden Snail (Theba pisana) in the West Coast National Park (Photograph courtesy of Charles Griffiths)
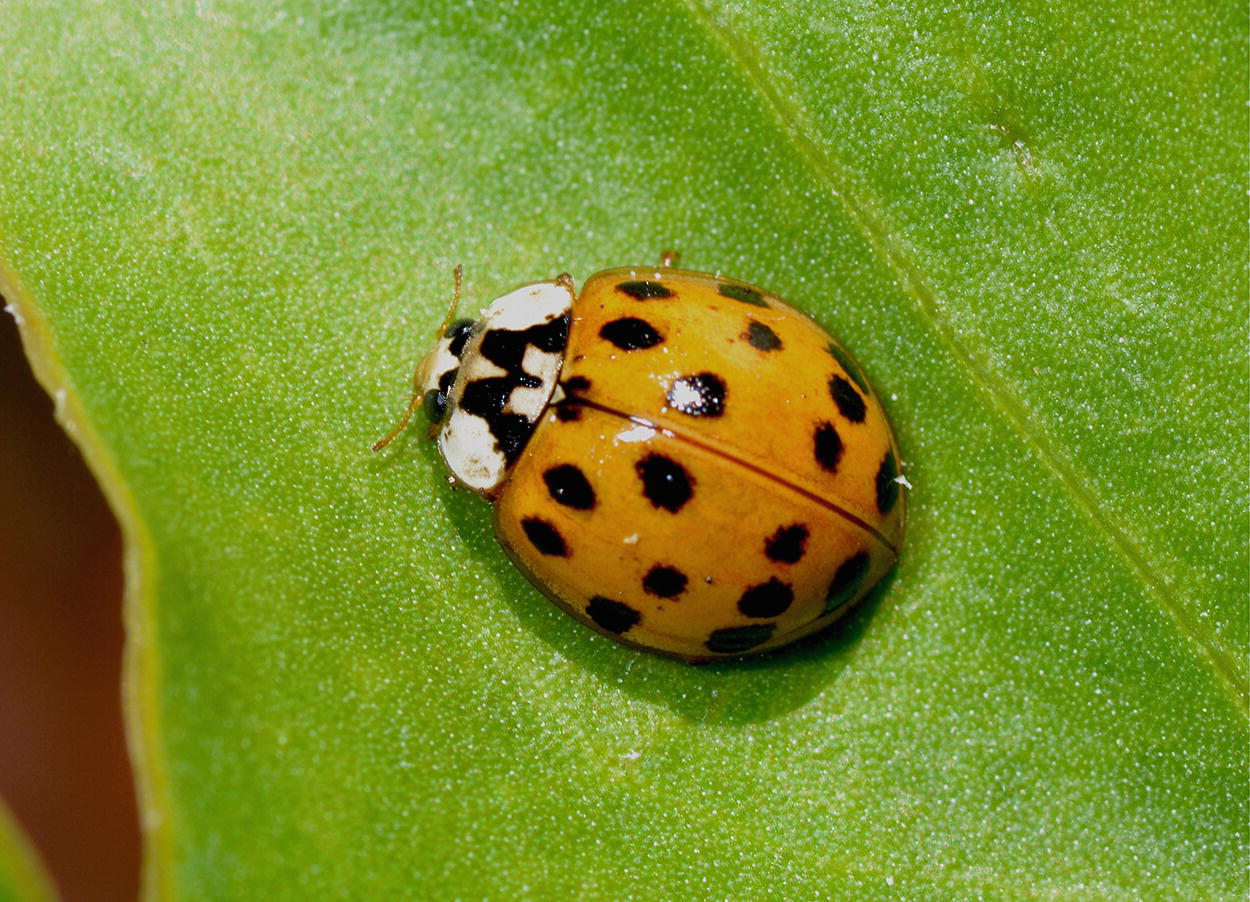

The Harlequin Lady Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Photograph courtesy of Charles Griffiths)

The European Wasp Vespula germanica (Photo: Charles Griffiths)
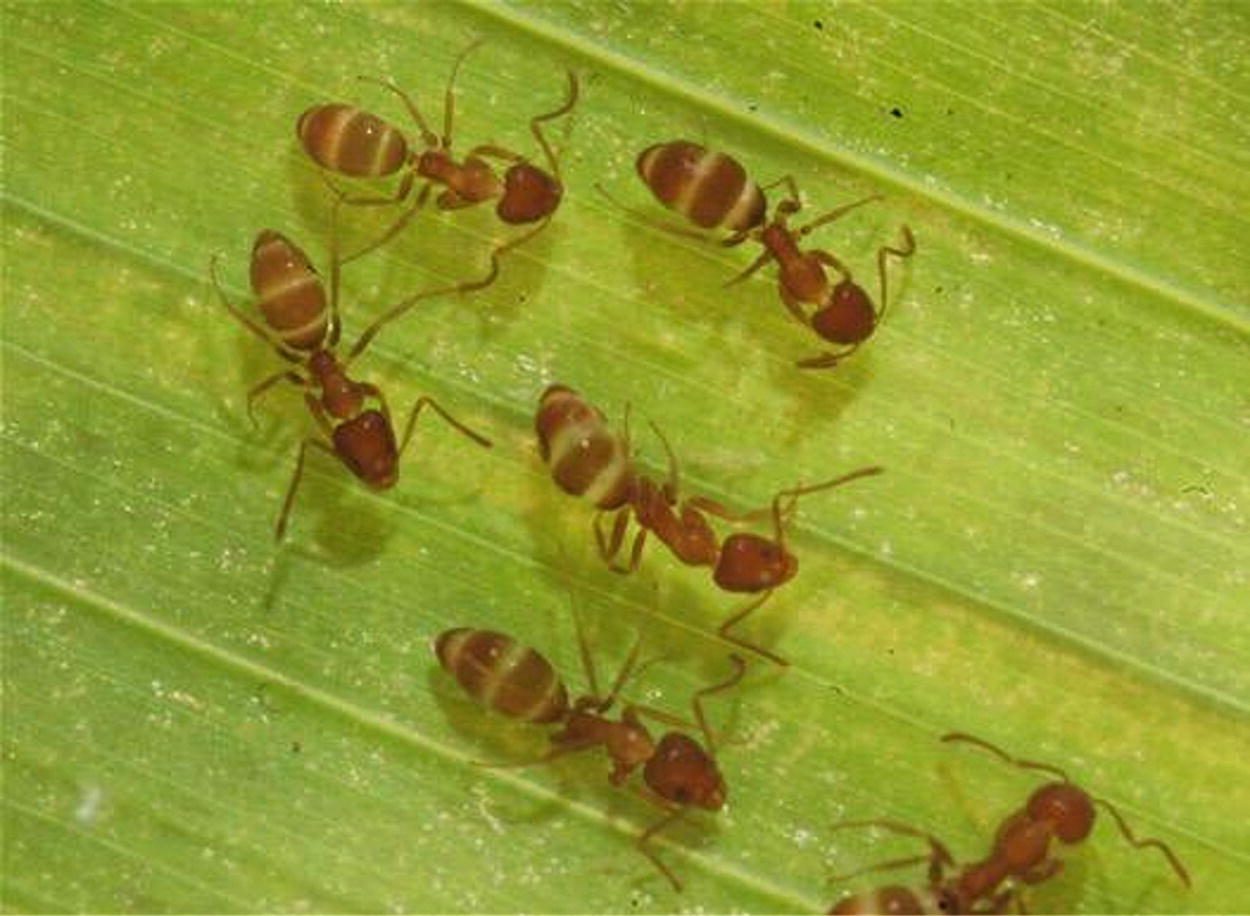

Argentine Ant Linepithema humile (Photograph courtesy of Charles Griffiths)
In most cases, the impacts of alien terrestrial invertebrates have only been investigated in respect of their immediate hosts, and their wider impacts on the structure and functioning of the ecosystems within which they have established, remain very poorly known. For example, introduced biological control agents on introduced Australian acacias, such as the parasitoids Trichilogaster acaciaelongifoliae, can create novel food webs in its introduced range, compared to its native range (Box 7.2, Veldtman et al. 2011). Such wider, and sometimes indirect, impacts can, however, take many forms and may ultimately be recognised as being the most significant impacts of many alien terrestrial invertebrates. Here we illustrate the diversity and complexity of ecosystem effects that can occur by profiling six important regional alien terrestrial invertebrates: the Varroa Mite (Box 7.1), the Acacia Gall Wasp (Box 7.2), the White Garden Snail (Box 7.3), the Harlequin Lady Beetle (Box 7.4), the European Wasp (Box 7.5) and the Argentine Ant (Box 7.6).
7.6 Risk Assessment
Several traits associated with alien terrestrial invertebrates can be used to make informative decisions or risk assessments regarding preventing, detecting, controlling or managing invertebrate introductions (Kumschick et al. 2016). Important features include life-history traits, such as those related to reproduction (e.g. sexual or parthenogenetic, number of eggs produced), overwintering strategy, dispersal, and thermal tolerance. Several physiological studies using Collembola (springtails) as model organisms have indicated that invasive species are generally more tolerant of warmer, drier conditions than native species ( Chown et al. 2007; Slabber et al. 2007; Janion et al. 2010; Janion-Scheepers et al. 2018). Research on the importance of physiological traits on the invasiveness of invertebrates include studies on the phenotypic plasticity and local adaptation of Drosophila (Gibert et al. 2016) and Ceratitis flies (Nyamukondiwa et al. 2013; Weldon et al. 2018). Understanding these traits may shed some light on how to better manage or prevent the introduction of invasive species (Karsten et al. 2016), especially pest species, which are predicted to change in distribution with climate change (Bebber et al. 2013; Pecl et al. 2017). In the case of the dominant South African invasive invertebrate groups, such as the Hemiptera and Coleoptera, some of these traits may also be important, but data on ‘invasiveness ’ traits in these groups are lacking.
7.7 Conclusion and Research Gaps
The ecological impacts of most alien terrestrial invertebrates in South Africa are poorly known, even for those within taxonomically well-known groups. Indeed, a recent survey of all soil biota suggested that for most groups of soil invertebrates in South Africa, the impact of introduced species on the local biota and ecosystem functioning remain unknown (Janion-Scheepers et al. 2016). The negative effects of invasive earthworms on ecosystems elsewhere are clear (Hendrix et al. 2008; Ferlian et al. 2018), and their impact on soil biodiversity and health need to be better understood in South Africa. This group is taxonomically well known, and a useful key exists to distinguish between South African and introduced earthworm species (Plisko and Nxele 2015).
The rate of introduction of alien terrestrial invertebrates is clearly increasing over time (Giliomee 2011), as is also the case in both Europe and the USA (McCullough et al. 2006). The cryptic nature of many of these invertebrates makes early detection very difficult. In addition, the identification of terrestrial alien terrestrial invertebrates is often problematic in South Africa, where local taxonomic expertise is lacking for many groups, meaning that even native species cannot be reliably identified. The training of taxonomists is a key priority to facilitate the detection of newly introduced species and to aid in their eradication and control ( Convention on Biological Diversity 2014). In some cases, even if a trained taxonomist is available locally, or can be consulted abroad, the available specimens are often in immature forms, eggs or damaged (Briski et al. 2011). In these cases, the identification of the species can only be confirmed through molecular approaches, such as DNA barcoding (www.boldsystems.org), which has been successfully used globally as an early detection and management tool for invasive species (Armstrong and Ball 2005; Bergstrom et al. 2018). Lastly, ongoing survey work should be continued to increase detection of new invasive species, to better document their distribution patterns and spread and especially to investigate their impacts, not only directly on their host species, but throughout the wider biological communities within which they live.

Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.