
Torque is the result of a force acting at a distance from a rotational axis, and it may cause a rotation about the axis only if there is a component of the force perpendicular to the radius. Torque is the product of the perpendicular component of the force (F⊥) and the distance (r) (as in radius) from the rotational axis:
The unit for torque is the newton-meter. To open a hinged door, you apply a force perpendicular to the door at the doorknob, which is mounted a certain distance from the hinges, and create a torque that causes the door to rotate around the hinges. When you use a wrench to tighten a bolt, you apply a force at the end of the wrench and perpendicular to it to get the most torque to turn the bolt. The distance from the rotational axis (r) is sometimes called the lever arm length; a lever is a rigid object used to apply a force around a rotational axis.

For a system in static equilibrium, the sum of the forces must equal zero, and the sum of the torques must also equal zero. This is illustrated in the next example.
Example: Two children sit on a seesaw that is 9 m long and pivots on an axis at its center. The first child has a mass m1 of 20 kg and sits at the left end of the seesaw, while the second child has a mass m2 of 40 kg and sits somewhere on the seesaw to the right of the axis. At what distance r2 from the axis should the second child sit to keep the seesaw horizontal?
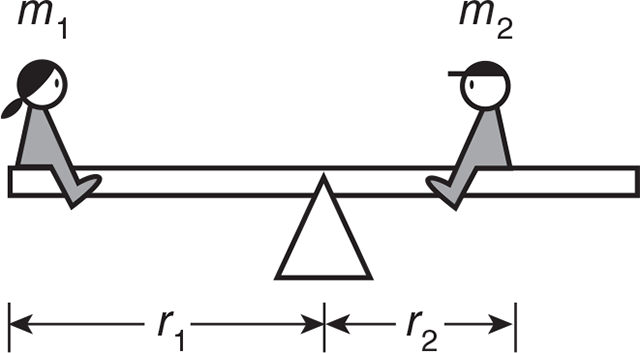
Solution: For the seesaw to remain horizontal, the torque on the left must equal and act in the opposite direction as the torque on the right. The forces acting on the seesaw on either side are just the weight (mg) of each child. So
where each force is applied perpendicular to the seesaw board,
Canceling the g’s and solving for r2 we get
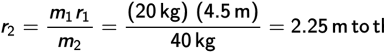
Could you have guessed this answer before we worked it out? Since the child on the right is twice as heavy as the child on the left, he should sit half as far from the axis on the right side to balance the torque the lighter child is producing on the left side.