Review Questions
-
According to Hooke’s law for a mass vibrating on an ideal spring, doubling the stretch distance will
- double the velocity of the mass.
- double the force that the spring exerts on the mass.
- quadruple the force the spring exerts on the mass.
- double the period.
- double the frequency.
-
For an ideal spring, the slope of a force vs. displacement graph is equal to
- the work done by the spring.
- the amplitude.
- the period.
- the frequency.
- the spring constant.
-
Consider the force vs. displacement graph shown for an ideal spring.
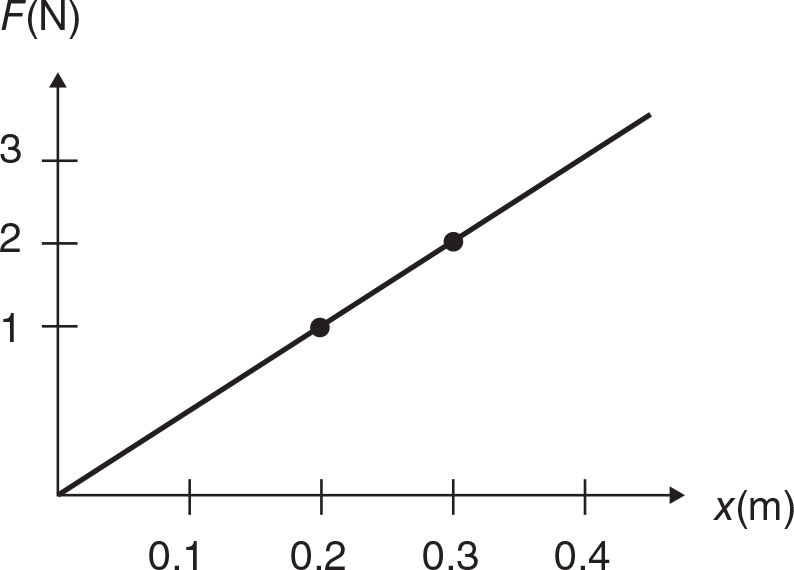
The work done in stretching the spring from 0.2 m to 0.3 m is
- 1 J.
- 10 J.
- 0.10 J.
- 0.15 J.
- 1.5 J.
-
A pendulum swings with an amplitude θ as shown.

If the amplitude is increased and the pendulum is released from a greater angle,
- the period will decrease.
- the period will increase.
- the period will not change.
- the frequency will increase.
- the frequency will decrease.
-
A mass on an ideal spring vibrates between points A and E as shown.
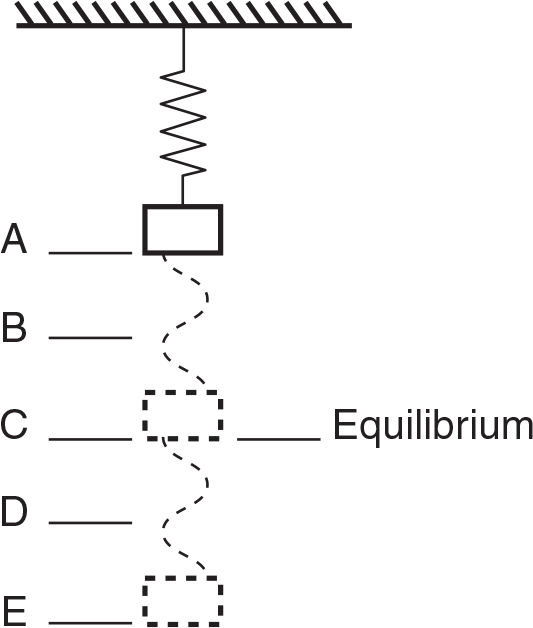
At which point is the acceleration of the mass the greatest?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- The acceleration is the same at all points.
-
A mass vibrates on an ideal spring as shown.

The total energy of the spring is 100 J. What is the kinetic energy of the mass at point B?
- 25 J
- 50 J
- 75 J
- 100 J
- 200 J