
As a satellite such as the Moon orbits the Earth, it is pulled toward the Earth with a gravitational force that is acting as a centripetal force. As described in chapter 8, the inertia of the satellite would cause it to tend to follow a straight-line path, but the centripetal gravitational force pulls it toward the center of the orbit. Although we often approximate the orbits of satellites around the Earth (or Sun, in the case of the orbits of the planets) as circular, they are actually elliptical, with the Earth (or Sun) located at one focus of the ellipse.

This means that there are times when the satellite is closer to the Earth than other times. If the satellite is at point A in the figure above, the gravitational force acting on the satellite is greater than at point B, and the speed at A is greater than at B. This is consistent with the law of conservation of angular momentum discussed in chapter 8:
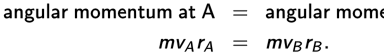
This equation shows that the closer the satellite gets to the planet (smaller r), the faster it goes (larger v). As the satellite orbits, potential energy and kinetic energy each change, but total energy (potential plus kinetic) remains constant.
Example: A satellite orbiting the Earth moves from point A to point B in an elliptical orbit as shown below.
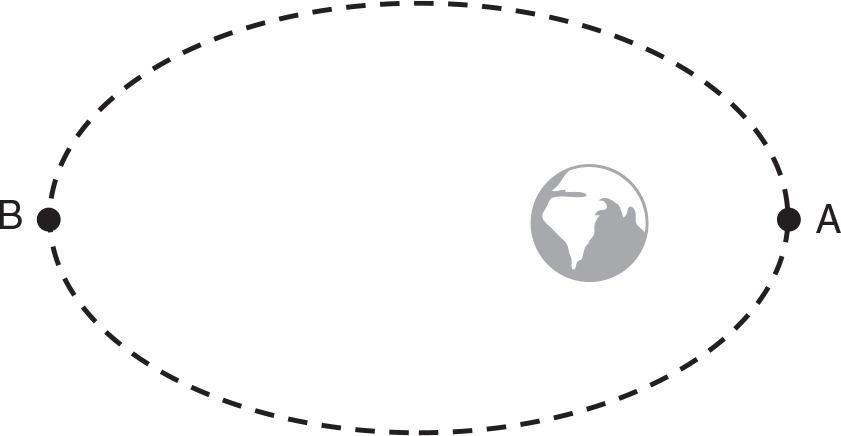
Fill in the table below with increases, decreases, or constant to describe the quantities related to the orbit as the satellite moves from point A to point B.
| Quantity | Increases, Decreases, Constant |
| Speed | |
| Angular momentum | |
| Kinetic energy | |
| Total energy | |
| Gravitational force |
Solution:
| Quantity | Increases, Decreases, Constant | Explanation |
| Speed | Decreases | The satellite is moving farther away from the planet and slowing down. |
| Angular momentum | Constant | Conservation of angular momentum |
| Kinetic energy | Decreases | Since the speed is decreasing, the kinetic energy must also be decreasing. |
| Total energy | Constant | Conservation of total energy |
| Gravitational force | Decreases | The satellite is getting farther away, thus the force is getting weaker due to the inverse square law. |