Review Questions
-
When charge is transferred from one object to another, which of the following are actually transferred?
- electrons
- protons
- neutrons
- quarks
- photons
-
Two conducting spheres of equal size have a charge of −3 C and +1 C, respectively. A conducting wire is connected from the first sphere to the second. What is the new charge on each sphere?
- −4 C
- +4 C
- −1 C
- +1 C
- zero
-
If the electric force between two charges is attractive, which of the following must be true?
- One charge is positive and the other charge is negative.
- Both charges are positive.
- Both charges are negative.
- The two charges must be equal in magnitude.
- The force must be directed toward the larger charge.
-
Two charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance r and apply a force F to each other. If both charges are doubled, and the distance between them is halved, the new force between them is
-

-

- 4F.
- 8F.
- 16F.
-
-
Two uncharged spheres A and B are near each other. A negatively charged rod is brought near one of the spheres.

The far right side of sphere B is
- uncharged.
- neutral.
- positive.
- negative.
- equally positive and negative.
-
Two charges A and B are near each other, producing the electric field lines shown.
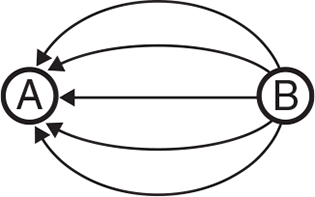
What are the two charges A and B, respectively?
- positive, positive
- negative, negative
- positive, negative
- negative, positive
- neutral, neutral
-
A force of 40 N acts on a charge of 0.25 C in a region of space. The electric field at the point of the charge is
- 10 N/C.
- 100 N/C.
- 160 N/C.
- 40 N/C.
- 0.00625 N/C.
-
Electric potential
- is a vector quantity.
- is proportional to the work done in an electric field.
- is always equal to the electric field.
- is zero when a charge is in an electric field.
- is measured in N/C.
-
Two conducting plates are separated by a distance of 0.001 m. A 9 V battery is connected across the plates. The electric field between the plates is
- 9,000 V/m.
- 900 V/m.
- 9 V/m.
- 0.009 V/m.
- 0.00011 V/m.
-
Questions 10–11 refer to the following.
-
Two charged parallel plates are oriented as shown.
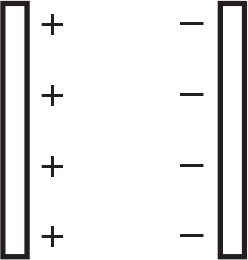
The following particles are placed between the plates, one at a time:
- electron
- proton
- neutron
-
Which of the particles would move to the right between the plates?
- I and II only
- I and III only
- II and III only
- II only
- I only
-
Which of the particles would not experience a force while between the plates?
- I and II only
- II and III only
- I only
- III only
- I, II, and III
-