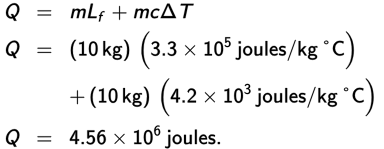
While heat is associated with the change of thermal energy, a system does not necessarily increase in temperature when heat is applied. Heat can also increase the potential (rather than kinetic) energy of the particles in a system; this occurs during a phase change. Heat is required to melt something (change its phase from a solid to a liquid), or to vaporize something (change its phase from a liquid to a gas), or to sublimate something (change its phase directly from a solid to a gas). In all these cases, the molecules are overcoming the attractive forces that hold them together. This is where the energy supplied by heating is being put to use. Conversely, heat is released as a substance freezes or condenses. During such phase changes, the temperature remains constant, and the heat involved in these processes can be expressed as
where m is the mass of the substance undergoing the phase change and L is the heat of transformation, the value of which depends on both the substance and the particular process we are talking about: vaporization, sublimation, or fusion (melting).
Example: The heat of fusion Lf of ice is 3.3 × 105 joules/kg°C, and the specific heat of water is 4.2 × 103 joules/kg°C. How much heat is required to completely melt 10 kg of ice (initially at 0°C) and then raise the temperature of the water from 0°C to 30°C?
Solution: The heat required to melt the ice and then raise the temperature of the water is
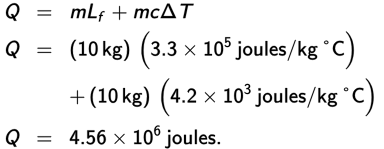
This is approximately 1 million calories.
If we were to continue to heat the water until it boiled and turned to steam at 100°C, and then continued to add heat to the steam to raise its temperature beyond 100°C, the temperature would not change during the phase changes from ice to water and water to steam. The heat added would go into changing the phase of the water, not its temperature.
A graph of temperature vs. heat added for this process is shown below.
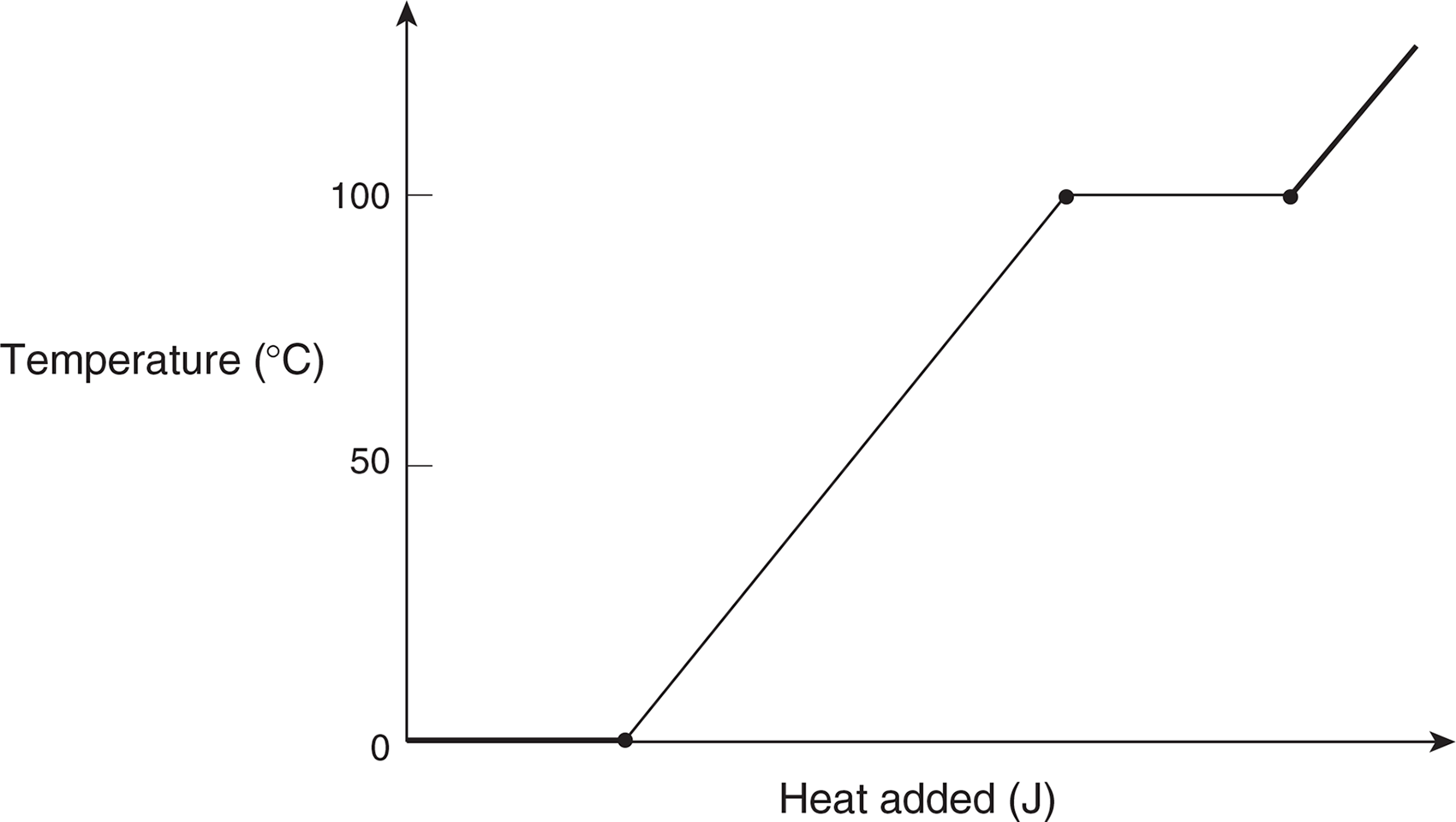
The flat portions of the graph imply that the temperature is not changing, and correspond to the processes of melting and boiling.