Answers and Explanations
Practice Test 1
- A
The slope of a displacement vs. time graph is velocity, and the slope is constant; thus the velocity is constant. - D
The object begins with a high velocity, then slows down until its velocity is zero, then begins speeding up again in the negative direction. - C
Both graphs imply that the velocity starts out as zero; then the slope of the s vs. t graph begins getting steeper and more negative, indicating that the velocity is increasing and negative. - D
Fission occurs when a large atom, such as uranium, splits into two smaller ones, such as xenon and strontium. - B
Radium is a radioactive element that emits an alpha particle (  ), leaving radon gas.
), leaving radon gas.
- C
A beta particle is an electron ( 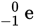 ) produced in this radioactive decay process where bismuth decays into polonium.
) produced in this radioactive decay process where bismuth decays into polonium.
- A
Fusion is the process in which two lighter atoms, such as two atoms of deuterium (  ), fuse to form a heavier atom, such as tritium (
), fuse to form a heavier atom, such as tritium (
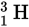 ).
).
- C
The ideal gas law relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. - B
The second law of thermodynamics, or the law of entropy, states that all natural systems tend toward a state of higher disorder. As the gas escapes from the bottle, it is becoming more disordered. - A
The first law of thermodynamics states that the heat lost by one liquid must be gained by the other liquid, as long as no work is done. - D
The heat of fusion or vaporization equation allows us to calculate the heat required to change the state of a substance from a solid to a liquid or a liquid to a gas. - B
The voltage across the resistor is equal to the voltage in the battery, since when the switch is first closed, the capacitor has no charge on it and therefore no voltage across it. - E
Immediately after the switch is closed, the capacitor has no charge on it and therefore provides no resistance to the current, and so the current is simply V/R by Ohm’s law. - A
A very long time after the switch is closed, the capacitor is full of charge and the voltage across the capacitor is equal and opposite to the voltage provided by the battery. Thus, the capacitor will not allow any current to flow through the circuit. - C
The velocity vs. time graph implies that the velocity is not changing. Graphs I and II both have a constant slope, which also implies a constant velocity, even though one graph begins at a different position than the other graph. - C
The plane must be at rest or moving at a constant velocity for the chain to hang vertically. A reference frame that has a constant velocity (including rest) is called an inertial reference frame. If the airplane were accelerating, the chain would angle forward or backward, depending on the direction of the acceleration. - D
The heat lost by the warmer water must be gained by the cooler water until all of the water reaches a final equilibrium temperature Tf.
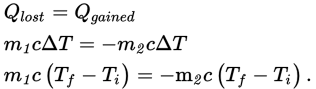
Since the specific heat is the same for water on both sides of the equation, we have

- A
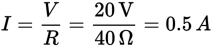
- B
If we draw the free-body force diagram for each block, we see that each block has a weight force of 50 N pulling downward that is balanced by the tension force pulling upward. Thus, the tension in the string must be 50 N.
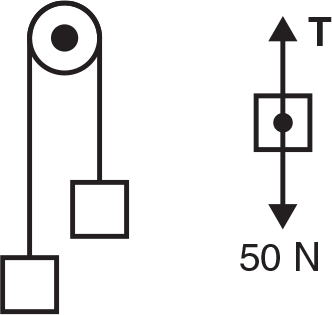
- C
Newton’s second law states that F = ma, so a = F/m. - D
The change in momentum of the block is equal to the impulse imparted to the block. The impulse is the product of the force and the time during which it acts, Ft. - A
The work-energy theorem states that the work (Fd) done on the block is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the block, since net work done on an object always changes the energy of the object. - C
If the charge is to feel no force, it must be closer to the smaller charge, –q, and farther away from the larger charge, –4 q. In other words, the charge must be at the “center of charge,” similar to the center of mass of two objects. If the charge were placed at points A, B, or E, it would be repelled and accelerate away from the two negative charges. The forces acting on the charge at point C balance each other out, since electric force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. - D
For a charge to experience a force in a magnetic field, its velocity must have a component that is perpendicular to the magnetic field lines, which implies that it is crossing the magnetic field lines. - C
For a current to be induced in a coil of wire by electromagnetic induction, there must be relative motion between the magnetic field of the coil. If the magnet stops, so does the current in the coil. - B
If the temperature is increased but the volume remains constant, the pressure inside the container will become greater since there will be more collisions between the molecules of the gas and the walls of the container. Since temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules, a higher temperature would imply a higher average kinetic energy of the molecules of the gas. - A
In the process of charging by induction, a positively charged rod is brought near the knob of the electroscope, and the electroscope is grounded so that more electrons that are attracted to the positively charged rod can come up from the ground and be deposited on the electroscope, giving it a net negative charge. - B
A transverse wave vibrates in a direction perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave, as this wave does. - D
The wavelength of the wave is 4 cm, being the length of one full vibration of the wave. The frequency of the wave is

- A
The amplitude is the maximum displacement from the base line to the crest of the wave (or, equivalently, to the trough of the wave), which is 1 cm in this case. - A
The amount of current will be the same, since the coil is turned at the same constant rate, but since it is rotated in the opposite direction, the current is induced in the opposite direction. - D
The magnetic force acting on a charge in the magnetic field is a centripetal force causing the charge to turn its path downward in the magnetic field and point to the center of the circle, which is toward the bottom of the page from point A. - A
Since the charge is positive, we can use the right-hand rule to find the direction of the magnetic field. At point A, if you point your thumb in the direction of the velocity of the charge (to the right), and your palm faces the direction of the force on the charge at A (toward the bottom of the page), then your fingers point out of the page in the direction of the magnetic field. - E
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and ray E is reflected at an angle most similar to the incident angle. - A
Since the ray is passing from a less dense medium (air) to a more dense medium (glass), the refracted ray must bend toward the normal, causing the refracted angle to be smaller than the incident angle. - E
Since both the electric and gravitational forces are inverse-square laws, the farther apart the charged masses are, the smaller the forces between them. - C
The gravitational force is proportional to the product of the masses, so the gravitational force will be doubled. But the electric force is not related to the masses and so it will not change. - A
If they remain the same distance apart, then the gravitational force (attractive) is equal and opposite to the electric force, which must be repulsive in this case. Thus, the only answer choice that will produce a repulsive electric force is A, both charges are positive. - D
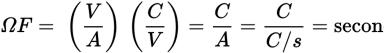
which is a unit of time.
- A
The weight vector always points straight down, the normal force is perpendicular to the plane, and the frictional force is acting up the plane to keep the block from sliding down the plane. - D
The 100 g sample of iodine is cut in half three times (50 g, 25 g, 12.5 g), which took 24 days. Thus, the time for the iodine sample to be cut in half one time is 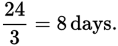
- B
The amount of iodine starts off at 100 g, and is reduced exponentially over time. - D
When the two waves meet, the crest of one wave is superposed onto the trough of the other, creating destructive interference, and the waves cancel each other out for the instant they occupy the same space at the same time. - A
After the waves completely pass each other, they behave exactly as they did before they met. They’ve just switched places. - A
As a ray of light passes through a lens, it is refracted and changes its direction. - B
Sound waves vibrate in a direction that is parallel to the direction of motion of the wave, and are thus longitudinal. - D
Momentum is mass times velocity, so 
- D
When the two spheres are touched, they exchange charge until they both have the same charge. Since the total charge is –6 μC, they will each retain –3 μC when they are again separated. - B
The bullet collides with and sticks to the block in an inelastic collision. Momentum is conserved in an inelastic collision, but kinetic energy is not conserved, since some of the energy is lost to heat and deformation of the wood and bullet. - B
After the bullet embeds itself in the block, the bullet and block have a new kinetic energy (since the collision is not elastic), which is converted into potential energy at the height h. - A
The two spheres will strike the floor at the same time since they have the same initial vertical velocity (zero) and the same vertical acceleration (10 m/s2). - A
Once again, the spheres will strike the floor at the same time, since mass has no effect on the acceleration of a falling object. - C
The force applied at C is the only force whose line of action does not pass through the point of rotation A, and thus it is the only force that can cause a torque and a rotation about point A. - C
When a wave passes from one medium to another, it is refracted, changing its speed and wavelength. The frequency does not depend on the medium, and therefore it is not changed when the wave is refracted. - C
Frequency (cycles/second) is the reciprocal of period (seconds/cycle). - A
The speed is the product of frequency and wavelength. - A
As the train approaches the stationary woman on the platform, she hears a higher pitch (frequency) than the pitch associated with 450 Hz since the waves appear to be reaching her more often due to the Doppler effect. The pitch she hears will be constant, since the train is not accelerating. - C
Since the parallel rays diverge as they exit the lens, this lens is a diverging (concave) lens, which is thinner in the center and thicker on the edges. - B
The speed of the object is increasing by 2 m/s for each second it moves. - B
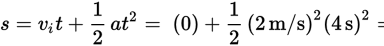
- D
The distance traveled at a constant speed between 4 s and 7 s is d = vt = (8 m/s)(3 s) = 24 m. - B
The torque on the left must equal the torque on the right for the board to be balanced.

- C
W = Fs cosθ = (40 N)(10 m)cos30° = 350 J.
- C
The normal force is equal to the difference between the weight of the block and the vertical component of the applied force.
FN = W – F sinθ = 50 N – (40 N)sin30° = 30 N. - B
Electric field lines are always drawn in the direction a small positive test charge would experience a force, which is radially outward anywhere around a positive source charge. - C
Ammeter 2 will read twice as much current as ammeter 1, since ammeter 2 is in series with a resistor with only half the ohms as the resistor on the parallel branch with ammeter 1. - B
An atom with extra electrons is a negative ion, and an atom with a deficiency of electrons is a positive ion. - A
Photons above the threshold frequency “dig out” electrons from the metal, which in turn are emitted by the metal. - D
An alpha particle is equivalent to a helium nucleus, and is composed of two protons and two neutrons. - E
The x vs. t graph and the v vs. t graph both imply that the object is initially moving at a constant positive velocity, then remains at rest for a time, then accelerates positively. - C
The net force acting on the falling stone is 10 N – 2 N = 8 N. The stone’s acceleration, then, is
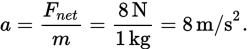
- D
The ideal gas law states that if temperature is held constant, pressure and volume are inversely proportional to each other. Thus, if volume is decreased, this will cause an increase in pressure. This relationship is sometimes referred to as Boyle’s law. - B
Conservation of angular momentum states that speed and orbital distance are inversely proportional to each other. Thus, the satellite moves faster as its orbital distance gets smaller (closer to the Earth). - A
A ray directed at an angle greater than the critical angle as measured from the normal line will not exit the medium, but will be reflected internally. - D
By the first right-hand rule, place your thumb in the direction of the current, and your fingers will curl around the wire in the direction of the magnetic field the current produces, which is out of the page at point A.