Practice Test 2
-
Part A
-
Directions
Each set of lettered choices below relates to the numbered questions immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best answers each question. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set.
-
Questions 1–3 relate to the following.
-
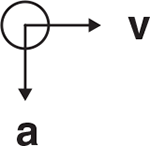
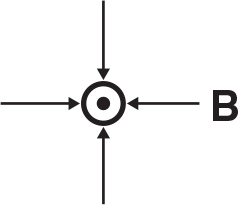
A ball of mass m on the end of a string is swung clockwise in a horizontal circle at a constant radius r. When the ball is a point P as shown below, some of the choices that follow represent the directions of the vectors associated with the motion of the ball.

-
-
What is the direction of the velocity of the ball at point P?
-
What is the direction of the acceleration of the ball at point P?
-
What is the direction of the net force acting on the ball at point P?
-
-
Questions 4–7 relate to the following series of images of a moving ball below.
-
Each image represents a time interval of one second, and the motion of the ball is not necessarily horizontal.
-
-
In which of the choices above is the ball increasing its speed?
-
In which of the choices above is the ball moving at a constant velocity?
-
Which of the choices above could represent the ball being thrown upward before it begins falling back down?
-
Which of the choices above could represent the ball being rolled up an incline and then allowed to roll back down again?
-
-
Questions 8–10 relate to the following diagram of two charges, +Q and –4 Q.
-

-
The net electric field is zero nearest which point?
-
At which point does the net electric field vector point to the left?
-
At which point would a small positive charge q feel the greatest force?
-
-
Questions 11–13 relate to the following graphs.
-
-
-
Which of the graphs above represents the energy of a photon vs. its frequency?
-
Which of the graphs above represents the maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted in the photoelectric effect vs. frequency of incoming light?
-
Which of the graphs above represents the mass of a relativistic particle vs. its speed?
-
-
Part B
-
Directions
Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five answer choices. Select the one that is best in each case.
-
Questions 14–15 refer to the following.
-
A red car and a blue car have the same mass and are moving on the highway. The red car is traveling at 60 miles per hour and the blue car is traveling at 30 miles per hour.
-
The ratio of the red car’s momentum to the blue car’s momentum is
- 4.
- 2.
- 1.
-
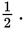
-

-
The ratio of the red car’s kinetic energy to the blue car’s kinetic energy is
- 4.
- 2.
- 1.
-

-

-
-
The waves on a lake cause a buoy to oscillate up and down 90 times per minute. The frequency of the waves in hertz is
- 90 Hz.
- 60 Hz.
- 1.5 Hz.
- 0.6 Hz.
- 0.67 Hz.
-

A ray of light passes through a piece of glass at the angle of incidence shown above. As the light passes through the glass and exits the glass into the air, the path of the ray is represented by which of the rays above?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
-
Questions 18–19 refer to the following.
-
A block falls onto a vertical spring from a height h and compresses the spring a distance y. Air resistance and friction may be neglected.

-
At the point of maximum compression, which of the following must be true?
- The speed of the block is maximum.
- The acceleration of the block is not zero.
- The potential energy of the block is zero.
- The kinetic energy of the block is maximum.
- The potential energy of the spring is zero.
-
The spring expands upward and throws the block vertically back into the air. Which of the following is true after the block leaves the spring?
- The block has no kinetic energy.
- The block has no potential energy.
- The block will rise to exactly half the height from which it was dropped.
- The block reaches its maximum acceleration just after leaving the spring.
- The block will rise to the height from which it was dropped.
-
-
Questions 20–21 relate to the following.
-
The velocity and acceleration vectors associated with the motion of three particles are shown below.
-
-
Which of the above could represent the velocity and acceleration vectors for an object in uniform circular motion?
- I only
- II only
- III only
- I and II only
- II and III only
-
Which of the above could represent the velocity and acceleration vectors for a projectile following a parabolic path?
- I only
- II only
- III only
- I and II only
- II and III only
-
-
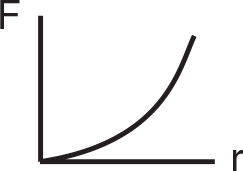
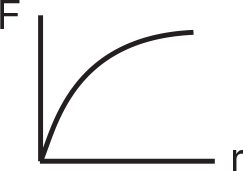
Two stars are separated by a distance r and are moving away from each other. Which of the graphs below best represents the gravitational force between the stars as a function of r, the distance between them?
-
-
Questions 23–24 refer to the following.
-
A 15 kg block rests on a surface of negligible friction and is pulled by a string that is passed over a pulley of negligible mass and connected to a hanging 5 kg block.
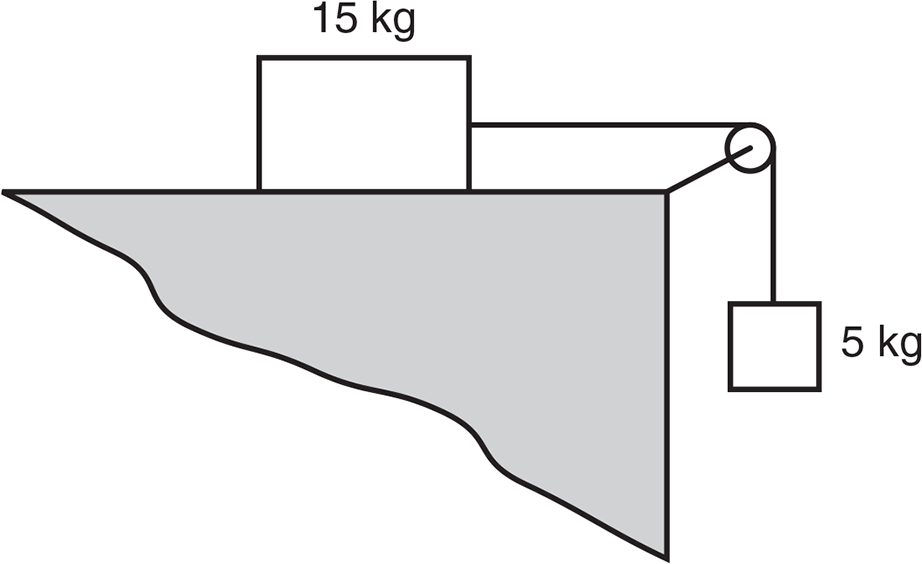
-
The net force acting on the 15 kg block is equal to
- the weight of the 5 kg block.
- the tension in the string.
- the difference between the weight of the 15 kg block and the 5 kg block.
- the sum of the weight of the 15 kg block and the 5 kg block.
- the weight of the 15 kg block.
-
In terms of the acceleration due to gravity g, the acceleration of the system is
-
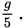
-

-

- g.
- 3 g.
-
-
-

The energy levels above ground state for a hypothetical atom are shown above. What is the energy of a photon emitted as a result of an electron in this atom making a transition from the third energy level to the second energy level?
- 10 eV
- 6 eV
- 4 eV
- 2 eV
- 1 eV
-
Consider the three statements below.
- The atom is mostly empty space.
- Electrons orbit the nucleus of the atom.
- The atom has a dense, positively charged nucleus.
Which of the above statements were conclusions drawn by Rutherford about the structure of the atom after studying the results of his alpha-scattering experiment?
- I only
- II only
- I and II only
- II and III only
- I, II, and III
-
Which of the following colors of light has the lowest frequency?
- violet
- blue
- green
- yellow
- orange
-
A heat pump warms a house by absorbing 90 J of heat and doing 60 J of work on the pump. The heat then delivered to the house is
- 5,400 J.
- 150 J.
- 30 J.
- 1.5 J.
- 0.67 J.
-
Questions 29–30 relate to the following.
-
A resistor in a closed circuit has 2 A of current flowing through it and 12 volts across it.
-
The value of the resistor is
- 6 Ω.
- 10 Ω.
- 14 Ω.
- 24 Ω.
- 144 Ω.
-
The power dissipated in the resistor is
- 6 watts.
- 10 watts.
- 14 watts.
- 24 watts.
- 144 watts.
-
-
Which of the following is NOT a unit for energy?
- joule
- kilowatt-hour
- calorie
- watt
- eV
-

A pendulum is dropped from a height of 4 m as shown above. The speed of the pendulum at the lowest point in the swing is most nearly
- 6 m/s.
- 7 m/s.
- 8 m/s.
- 9 m/s.
- 10 m/s.
-

Consider the acceleration graph shown above and the following choices below.
- A stone is falling toward the Earth.
- A car is decreasing its speed.
- A bicycle is rolling up a hill.
Which of the choices above could be represented by the acceleration vs. time graph?
- I only
- II only
- II and III only
- I and III only
- I, II, and III
-

Two blocks of equal mass are connected by a string. Block 2 is pulled by a force of 40 N, which accelerates both blocks at 3 m/s2 along a surface of negligible friction. The tension in the string connecting the blocks is
- 120 N.
- 80 N.
- 40 N.
- 20 N.
- 13 N.
-
A ball dropped from a tower will strike the ground below in 3 s. If the ball is launched horizontally from the tower at a speed of 10 m/s, how far horizontally from the base of the tower will the ball land on the level ground?
- 100 m
- 45 m
- 30 m
- 10 m
- 3.3 m
-
A cluster of magnetically aligned atoms in a magnetic material is called a
- domain.
- molecule.
- pole.
- charge.
- electron cloud.
-
On the microscopic scale, friction is caused by which of the following fundamental forces?
- gravitational
- electrostatic
- strong nuclear
- weak nuclear
- proton and neutron
-
The time for one complete swing of a pendulum is called its period. The period of a pendulum for small swings near the Earth depends on its
- length and amplitude of swing only.
- amplitude of swing and mass only.
- length only.
- amplitude only.
- length, mass, and amplitude of swing.
-
Questions 39–41 refer to the circuit shown below.
-
A 50-volt battery supplies 100 w of power to each of the two identical light bulbs. The current passing through bulb 1 is 4 A.
-
The voltmeter across bulb 1 will read
- 100 V.
- 50 V.
- 25 V.
- 4 V.
- zero.
-
The current through bulb 2 is
- 2 A.
- 4 A.
- 8 A.
- 100 A.
- zero.
-
The resistance of each bulb is most nearly
- 25 Ω.
- 20 Ω.
- 6 Ω.
- 4 Ω.
- 2 Ω.
-
-
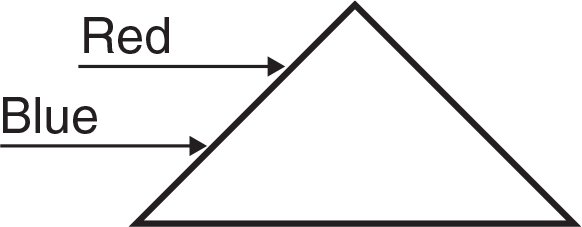
Two beams of light, red and blue, enter a prism as shown above. Which of the following statements is true concerning the light as it passes through the prism?
- The blue light will bend more than the red light, since the blue light has a longer wavelength.
- The red light will bend more than the blue light, since the red light has a longer wavelength.
- The blue light will bend more than the red light, since the blue light has a shorter wavelength.
- The red light will bend more than the blue light, since the red light has a shorter wavelength.
- The red and blue light will bend by the same amount, since all colors of light refract equally.
-
Green light is passed through two narrow slits and forms a pattern of bright and dark lines on a screen. The phenomena primarily responsible for this pattern is
- refraction.
- reflection.
- polarization.
- interference.
- intensity.
-
An ultraviolet photon has twice the frequency of a red photon. The ratio of the energy of the ultraviolet photon to the energy of the red photon is
- 4.
- 2.
- 1.
-
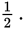
-

-
Questions 45–47 refer to the figure below, which represents a longitudinal wave moving through water in a glass tank of length 9 meters. The frequency of the wave is 500 Hz.
-

-
This wave could be which of the following types of waves?
- visible light
- radio wave
- microwave
- sound wave
- X-ray
-
What is the wavelength of the longitudinal wave?
- 1.5 m
- 3 m
- 4.5 m
- 9 m
- 18 m
-
The speed of the wave is most nearly
- 500 m/s.
- 750 m/s.
- 1,500 m/s.
- 3,000 m/s.
- 4,500 m/s.
-
-

A ball is moving downward with a velocity v as shown in the figure above, with a force F directed to the right acting on the ball. Which of the statements is true?
- The ball is moving with a constant velocity.
- The ball is moving with a constant speed.
- The force F is doing work on the ball.
- The force F is changing the kinetic energy of the ball.
- The velocity and the acceleration of the ball are in the same direction.
-

The bar of negligible mass shown above is marked in eight equal parts. The bar has a 2 kg mass attached to one end and a 6 kg mass attached to the other end. The center of mass of the two masses is most nearly at which point?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
-
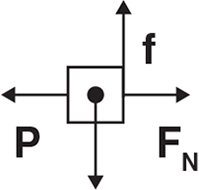
Questions 50–51 refer to the diagram below.
-
A block of mass m is pushed against a rough, fixed wall by a force P. The frictional force between the block and the surface is f, and the normal force is FN.

-
Which of the following diagrams correctly shows all of the forces acting on the block?
-
-
If the block is not moving, the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the block is equal to the magnitude of the force
- P.
- mg.
- FN.
- FN + P.
- FN – P.
-
-
Which of the following is NOT a vector quantity?
- kinetic energy
- force
- displacement
- velocity
- momentum
-
The molecules of an ideal gas are increasing their collisions per unit time with the walls of a sealed container of constant volume. Which of the three choices below must also be increasing?
- pressure
- temperature
- number of moles of gas
- I only
- II only
- I and II only
- II and III only
- I and III only
-
Questions 54–55 relate to the diagram below.
-
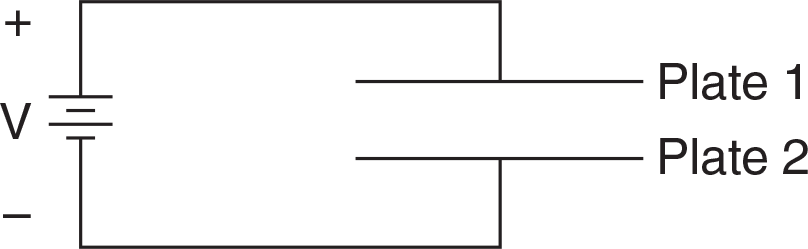
A battery of voltage V is connected to two parallel conducting plates, 1 and 2.
-
The device connected to the battery is generally called a
- generator.
- capacitor.
- motor.
- charger.
- resistor.
-
An electron is placed in the center of the space between the plates. The subsequent motion of the electron is described by which of the following?
- The electron accelerates toward plate 1.
- The electron accelerates toward plate 2.
- The electron moves with constant velocity toward plate 1.
- The electron moves with constant velocity toward plate 2.
- The electron remains at rest halfway between the plates.
-
-
The current in a wire is directed out of the page and perpendicular to the page. Which of the following best represents the magnetic field produced by the current in the wire?
-
-
Questions 57–58 refer to a candle burning inside the metal container shown below.
-

Three types of heat transfer are listed below.
- radiation
- conduction
- convection
-
Heat can be transferred to the inside surface of the walls of the container by which of the above?
- I only
- I and II only
- I and III only
- II only
- I, II, and III only
-
If you touch the outside surface of the metal container, your hand will become warmer directly by which of the above choices?
- I only
- I and II only
- I and III only
- II only
- III only
-
-
Let g be the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Earth. What would be the acceleration due to gravity at a distance of four Earth radii from the center of the Earth?
- 16 g
- 4 g
- 2 g
-

-
-

The graph above shows the number of kilograms of sand that falls into a truck per hour as a function of time in hours. The shaded area under the curve has units of
- volume.
- mass.
- mass per hour.
- volume per hour.
- inverse hours.
-
Questions 61–62 relate to the following.
-
An object starts with a speed of 10 m/s and accelerates at –2 m/s2.
-
How much time will pass until it comes to rest?
- 2 s
- 4 s
- 5 s
- 12 s
- 20 s
-
How far does the object travel before coming to rest?
- 10 m
- 25 m
- 50 m
- 75 m
- 100 m
-
-
Questions 63–65 relate to the graph of the net force F exerted on a 2 kg block as a function of time in seconds, shown here.
-

-
The acceleration of the block between 0 and 2 seconds is
- 1.5 m/s2.
- 3 m/s2.
- 4 m/s2.
- 6 m/s2.
- 9 m/s2.
-
The speed of the block is greatest at
- 2 s.
- 3 s.
- 4 s.
- 5 s.
- The speed is constant at all times.
-
If the block starts from rest, its momentum at 5 seconds is
- 1 kg m/s.
- 3 kg m/s.
- 6 kg m/s.
- 8 kg m/s.
- 10 kg m/s.
-
-
Questions 66–67 refer to a positive charge moving in a straight line through space.
-
A person who is at rest as the charge moves by him will measure
- a magnetic field and an electric field due to the moving charge.
- a magnetic field, but not an electric field due to the moving charge.
- an electric field, but not a magnetic field due to the moving charge.
- neither an electric field nor a magnetic field due to the moving charge.
- a decrease in the amount of charge.
-
A person who is moving parallel to the charge and at the same velocity as the charge will measure
- a magnetic field and an electric field due to the moving charge.
- a magnetic field, but not an electric field due to the moving charge.
- an electric field, but not a magnetic field due to the moving charge.
- neither an electric field nor a magnetic field due to the moving charge.
- a decrease in the amount of charge.
-
-
In 1887, Heinrich Hertz discovered the photoelectric effect. When ultraviolet light is shined on a zinc metal surface, he found that the metal
- emitted protons.
- emitted neutrons.
- became negatively charged.
- became positively charged.
- emitted photons.
-
Which of the following is NOT a postulate or result of Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom?
- Excited gases emit a bright-line emission spectrum.
- The electron in the hydrogen atom can be found at any radius around the nucleus of the atom.
- When the electron makes a transition to a higher energy level, it has absorbed energy.
- When the electron makes a transition to a lower energy level, it has emitted energy.
- The energy levels of the electron are quantized.
-
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that
- we can measure the position of an electron only if we know its momentum.
- we can measure the momentum of an electron only if we know its position.
- only one electron can exist in the lowest energy level of an atom.
- light can behave like a wave or a photon.
- there is a limit to the accuracy of the measurement of subatomic particles.
-
If electricity costs $0.12 per kilowatt-hour, how much does it cost for electricity to operate a 150-watt light bulb for 5 hours?
- $0.009
- $0.09
- $0.90
- $9.00
- $90.00
-
Questions 72–74 relate to the temperature vs. time graph below for 2 kg of a particular substance. Heat is being applied to the system for the entire time interval that is graphed. The substance is in the solid state at a temperature of 20°C.
-

-
The interval during which the substance is changing from the liquid phase to the gas phase is
- AB.
- AC.
- BC.
- CD.
- DE.
-
If 100 J of heat is needed to completely change the substance from a solid to a liquid state, what is the heat of fusion for the substance?
- 1,000 J/kg
- 100 J/kg
- 50 J/kg
- 20 J/kg
- 5 J/kg
-
If 200 J of heat is added during the time interval from B to C, the specific heat of the substance is
- 200 J/kg°C.
- 100 J/kg°C.
- 60 J/kg°C.
- 17 J/kg°C.
- 1.67 J/kg°C.
-
-
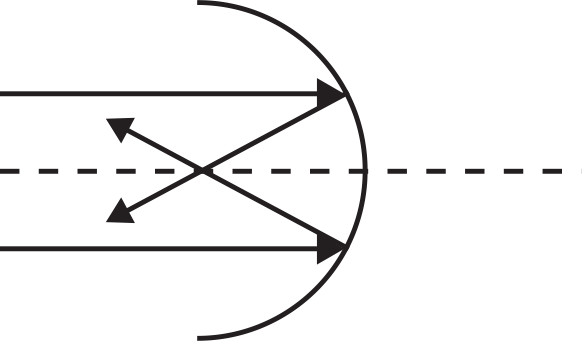
The diagram above best represents the ray diagram for a
- converging lens.
- diverging lens.
- converging mirror.
- diverging mirror.
- plane mirror.