For each question, circle the letter of your answer choice.
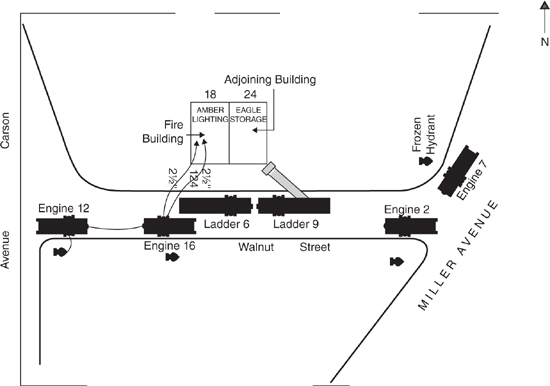
Directions: Study the fireground situation below for 3 minutes. At the end of that allotted time, cover the picture. Then answer questions 1 to 16.

1. What is the name of the building on fire?
(A) Eagle Storage
(B) Amber Lighting
(C) Carson Electric
(D) Miller Plumbing
2. What is the name of the building adjoining the fire building?
(A) Carson Electric
(B) Amber Lighting
(C) Miller Plumbing
(D) Eagle Storage
3. What is the designation of the apparatus raising a ladder?
(A) Engine 7
(B) Ladder 9
(C) Ladder 6
(D) Engine 16
4. What apparatus below is situated directly in front of the fire building?
(A) Ladder 9
(B) Ladder 6
(C) Engine 12
(D) Engine 2
5. From what apparatus are hose lines stretched into the building on fire?
(A) Engine 16
(B) Engine 12
(C) Engine 2
(D) Engine 7
6. What size diameter hose is being used to extinguish the fire?
(A) 1 inch
(B) 1½ inch
(C) 2 inch
(D) 2½ inch
7. What is the address of the building on fire?
(A) 24 Walnut Street
(B) 18 Carson Avenue
(C) 18 Walnut Street
(D) 24 Miller Avenue
8. How many fire hydrants are there in the picture?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
9. How many fire hydrants are frozen?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
10. What is the designation of the apparatus connected to a hydrant?
(A) Engine 7
(B) Engine 2
(C) Engine 16
(D) Engine 12
11. What activity listed below is Engine 12 performing?
(A) Raising a ladder to the building adjoining the fire building
(B) Supplying water to Engine 16
(C) Supplying water to the fire department connection at the fire building
(D) Supplying water to Ladder 6
12. What apparatus is adjacent to a frozen hydrant?
(A) Engine 7
(B) Engine 16
(C) Ladder 9
(D) Engine 12
13. How many fire hydrants are located on the south side of Walnut Street?
(A) 4
(B) 3
(C) 2
(D) 1
14. How many fire apparatus are there in the picture?
(A) 9
(B) 8
(C) 7
(D) 6
15. What is the ratio of Engines to Ladders found in the picture?
(A) 3:1
(B) 1:3
(C) 2:1
(D) 1:2
16. What is the best way for Engine 2 to obtain water?
(A) Connect to the hydrant at the SE corner of Walnut St. and Miller Ave.
(B) Connect to the hydrant at the NE corner of Walnut St. and Miller Ave.
(C) Receive water from Ladder 9
(D) Receive water from Engine 12
Directions: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions.
17. What is 40 increased by 40%? (Use Part = % · Whole ÷ 100.)
(A) 84
(B) 72
(C) 68
(D) 56
18. What is 70 decreased by 20%? (Use Part = % · Whole ÷ 100.)
(A) 53
(B) 56
(C) 58
(D) 59
19. The fraction 3/5 equals what percent?
(A) 60%
(B) 54%
(C) 48%
(D) 46%
20. 28% equals what fraction (in lowest terms)?
(A) 1/3
(B) 2/5
(C) 7/25
(D) 3/10
21. What is the missing number in the arithmetic sequence below?
4, 9, __, 19, 24, 29, 34, 39 . . .
(A) 17
(B) 15
(C) 14
(D) 11
22. A Boy Scout troop is composed of 18 boys and 3 men. What is the ratio of boys to men?
(A) 3:1
(B) 4:1
(C) 5:1
(D) 6:1
23. A box of candy contains 60 mints, of which 12 are filled with chocolate. What is the probability of selecting a mint with chocolate at random from the box on your initial try? (Use: Probability = event/possible outcomes.)
(A) 1/6
(B) 1/5
(C) 5/1
(D) 6/1
24. A dresser drawer contains 7 different colored shirts, 2 pants (jeans and dress), and 5 dissimilar patterned ties. How many different shirt/pant/tie combinations can be worn from the clothes in the drawer?
(A) 70
(B) 60
(C) 55
(D) 40
25. 93 =
(A) 27
(B) 81
(C) 243
(D) 729
26. 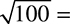
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 20
(D) 50
27. 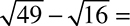
(A) 65
(B) 33
(C) 8
(D) 3
28. A painter is paid $12 an hour. If in a week she worked 4 eight-hour days and 1 half-day (four hours), how much money did the painter earn for the week?
(A) $384
(B) $418
(C) $432
(D) $476
29. A part-time bartender earns $71.98 in tips on Friday night and $63.21 on Saturday night. How much more cash did the bartender earn on Friday night than on Saturday night?
(A) $8.77
(B) $8.97
(C) $135.19
(D) $137.85
30. A sharpshooter taking target practice is able to squeeze off 8 shots in a 15-second time frame. If the shooter continues for two minutes, how many shots will be fired?
(A) 30
(B) 32
(C) 54
(D) 64
31. The price of a pizza is $12.00. If three people share the cost of the pie equally, how much money would each person have to pay?
(A) $4.50
(B) $4.00
(C) $3.50
(D) $3.00
32. 35°C equals what temperature on the Fahrenheit scale? (Use: F = 9/5C + 32.)
(A) 120.6°F
(B) 102°F
(C) 95°F
(D) 91°F
33. 68°F equals what temperature on the Celsius scale? (Use C = 5/9(F − 32).)
(A) 5.4
(B) 8
(C) 18
(D) 20
Directions: Read the passage below to answer questions 34 to 43.
Rescue operations carried out by firefighters inside locations that are below ground and restricted from natural ventilation are known as confined space incidents. Examples of confined spaces are water tunnels, utility trenches, ship holds, and storage tanks. The safety of the rescue workers is the most important factor in these situations. Recognizing the inherent hazards of the confined space prior to entry is paramount to a safe and successful operation.
Atmospheric condition hazards that must be addressed by rescue workers include oxygen deficiency, combustible and flammable gas vapors, and toxic gases. Physical hazards may also be present inside the confined space. Limited access and egress, unstable structural conditions, liquids in depth, and open gas lines or live electric lines are just a few of the physical hazards encountered.
No firefighter should enter a confined space location alone. The wearing of all personal protective equipment (PPE) and the use of positive pressure breathing apparatus (SCBA) is mandatory for firefighters working inside confined spaces. Long air supply hoses may be utilized and attached to the SCBA to allow firefighters to work for longer periods of time inside the space. Each firefighter entering the confined space must be attached to a lifeline (rope) and constantly monitored by a safety officer. The safety officer must keep a log of all members inside the confined space, how long each member has been operating, and how much oxygen each rescuer has remaining to ensure a safe return. A standby team must be assembled by the safety officer equal in number to the rescuers working inside the confined space. This reserve team must have the tools and equipment necessary to safely enter, medically treat, transport, and remove any and all rescue workers inside the confined space should the need arise.
A communications system must be established between the rescue workers and the safety officer. Portable radios may not be the method of choice if rescue workers are inside a combustible or flammable atmosphere for fear of an explosion as a result of radio transmissions. One way of communicating is via the OATH method. Each letter represents a single tug from the lifeline. One pull (O) on the rope by both exterior and interior members in reply stands for the verification that the members inside the confined space are OK and not in any danger. Two tugs (A) from each group represent the advancement of air supply line. Conversely, three pulls (T) from each end of the rope calls for the taking up of air supply line. Four tugs (H) is a distress signal and a call for help from the members inside the confined space with confirmation (four tugs) from members outside the confined space that help is on the way.
The establishment of a command post and staging area is also critical at confined space operations. A command post is required for the incident commander (ranking chief officer) to coordinate manpower and equipment resources. From the command post, the incident commander will also meet with other agency leaders who will be needed for assistance that is essential to a successful operation. The staging area should also be formed in an adequate space far enough away from the incident as not to interfere but close enough for resources to arrive at the command post in a timely fashion. A staging area chief officer should be designated in charge to ensure resources are recorded and properly managed both to and from the incident. Confined space operations are inherently dangerous to both trapped victims and firefighters. No firefighter should enter a confined space without these safety procedures being implemented. It is the responsibility of all supervisors to ensure that these rules are adhered to by all firefighters under their command. The special precautions listed in this article will not guarantee a successful operation but will enhance the safety of all firefighters.
34. Which of the following is NOT a true statement about the OATH method used to communicate with firefighters inside a confined space?
(A) One pull at each end verifies that firefighters inside the space are OK.
(B) Two pulls at each end represents the stretching of a hose line.
(C) Three pulls at each end calls for taking up the air supply line.
(D) Four pulls is a distress signal.
35. Long air supply hoses attached to SCBA allow firefighters inside the confined space to
(A) contact the safety team
(B) contact the safety officer
(C) work longer
(D) keep a log of all members inside the confined space
36. Which of the following atmospheric hazards is NOT mentioned in the reading?
(A) Oxygen deficiency
(B) Oxygen-enriched atmosphere
(C) Toxic gases
(D) Flammable gas vapors
37. Which of the following is NOT considered a confined space?
(A) A ship’s hold
(B) A utility trench
(C) A water tunnel
(D) A high-rise office building
38. According to the passage, a command post is important to the incident commander of a confined space operation for all but which of the following reasons?
(A) It is used to record resources.
(B) It is a place to meet with other agency leaders.
(C) It helps to utilize manpower.
(D) It helps to utilize equipment.
39. When entering a confined space, firefighters should wear and use certain protective equipment and devices to ensure their safety. Which of the following is NOT an item of protective gear?
(A) Self-contained positive pressure breathing apparatus
(B) PPE
(C) Lifeline
(D) Nozzle
40. Recognizing the inherent hazards of a confined space is important to ensure
(A) a safe and successful operation
(B) advancement of hose lines
(C) camaraderie among the firefighters working inside the confined space
(D) none of the above
41. A staging area chief officer at a confined space incident should be designated in charge to perform which of the following duties?
(A) Ensure resources arrive promptly at the command post.
(B) Monitor the oxygen of each rescuer inside the confined space.
(C) Establish the command post close to the staging area.
(D) Inspect the lifeline prior to it being used inside the confined space.
42. Which of the following is NOT an example of a physical hazard inside a confined space?
(A) Toxic gases
(B) Combustible gases
(C) Personal protective equipment
(D) Liquids in depth
43. Which of the following is NOT a responsibility of the safety officer?
(A) Monitor firefighters inside the confined space
(B) Keep a log
(C) Carry and use rescue tools
(D) Assemble a standby rescue team
Directions: The following figures show the Rule of Nines used to estimate the area of the body burned in a fire. Use information from the figures to answer questions 44 to 50.
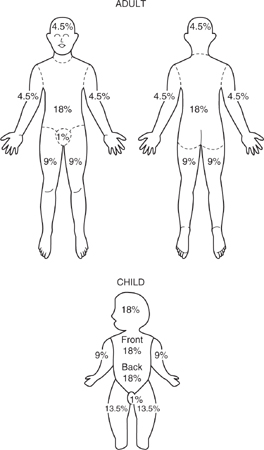
44. Which of the following parts of the adult body encompasses the most area?
(A) Right arm (anterior and posterior)
(B) Chest
(C) Left leg (anterior only)
(D) Groin
45. A burn injury to the head covers what percent of an adult’s total body?
(A) 18%
(B) 9%
(C) 4.5%
(D) 1%
46. A burn injury to both arms (anterior only) of an adult covers what percent of the total body?
(A) 9%
(B) 13.5%
(C) 15%
(D) 18%
47. A burn injury to both legs (anterior and posterior) of an adult covers what percentage of the total body?
(A) 36%
(B) 32%
(C) 18%
(D) 13.5%
48. A burn injury to the right leg (anterior and posterior) of a child covers what percentage of the total body?
(A) 1%
(B) 9%
(C) 13.5%
(D) 18%
49. The groin area of both an adult and a child counts for what percent of the total body?
(A) 18%
(B) 9%
(C) 1%
(D) 5%
50. The head area of a child counts for what percent of the total body?
(A) 1%
(B) 9%
(C) 13.5%
(D) 18%
Directions: Use the figure below to answer question 51.
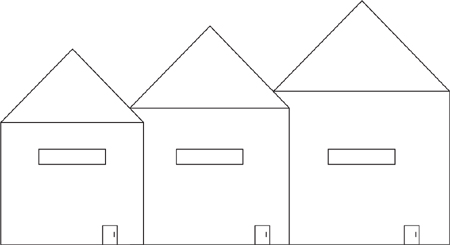
51. Which of the following shows how the buildings would appear from above?
(A) 
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 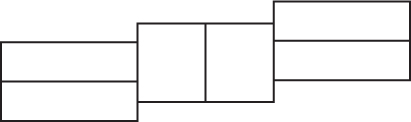
Directions: Use the figure below to answer question 52.
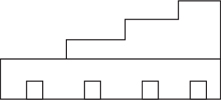
52. Which of the following shows how the building would appear from the rear?
(A) 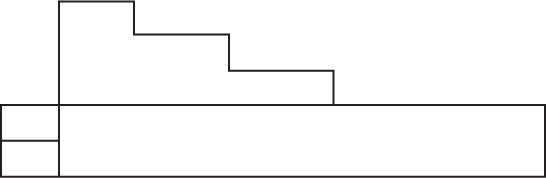
(B) 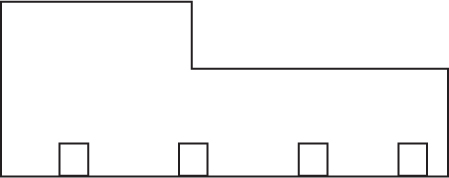
(C) 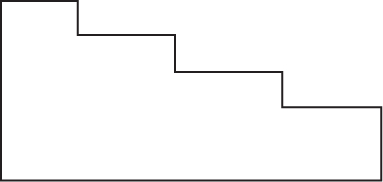
(D) 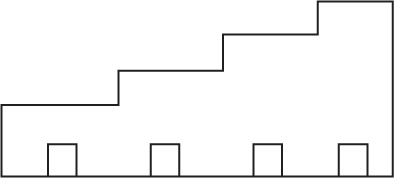
Directions: Use the figure below to answer question 53.
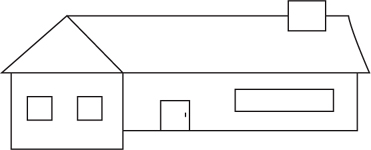
53. Which of the following shows how the home would appear from a tower ladder basket in position above it?
(A) 
(B) 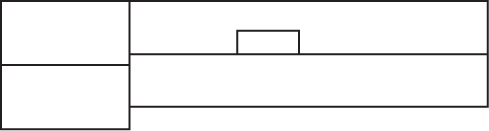
(C) 
(D) 
Directions: Use the figure below to answer question 54.

54. Which of the following shows how the structure would appear from the rear?
(A) 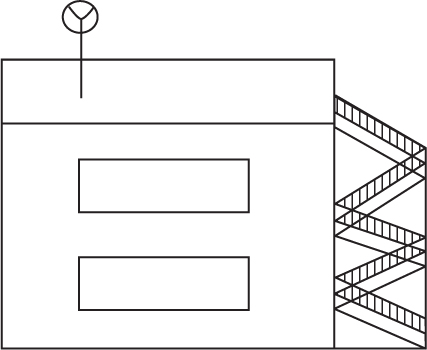
(B) 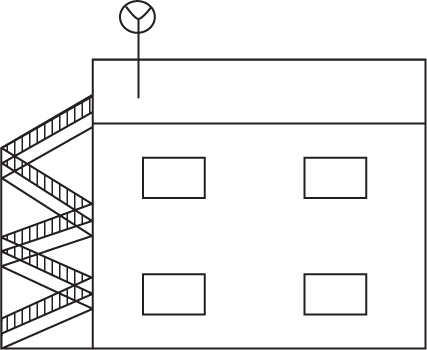
(C) 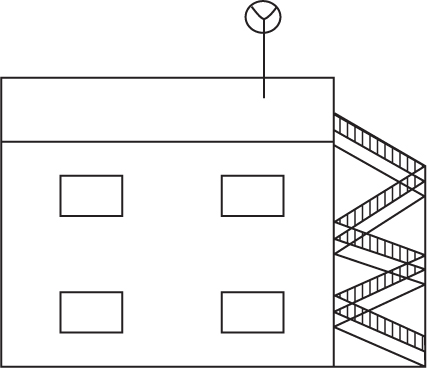
(D) 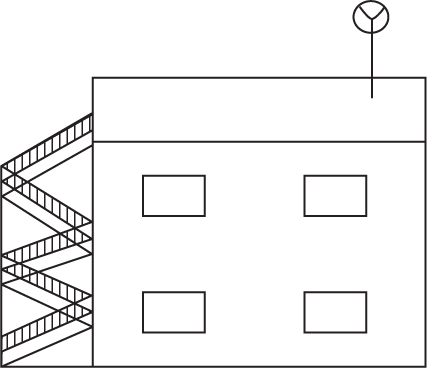
Directions: Use the figure below to answer question 55.
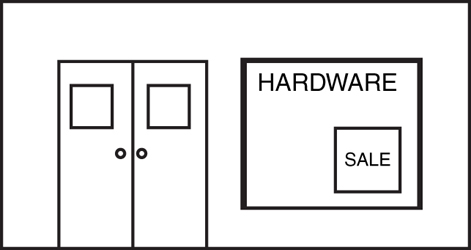
55. Which of the following shows how the front of the hardware store would appear from inside the store?
(A) 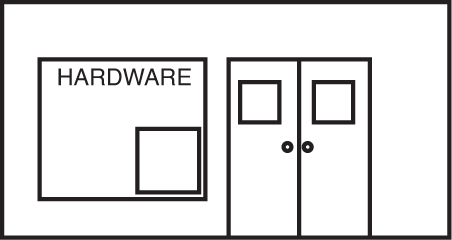
(B) 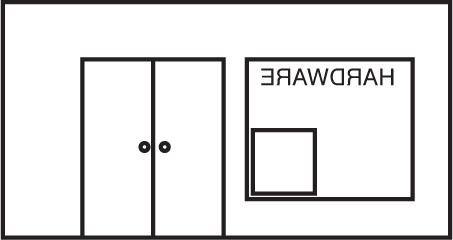
(C) 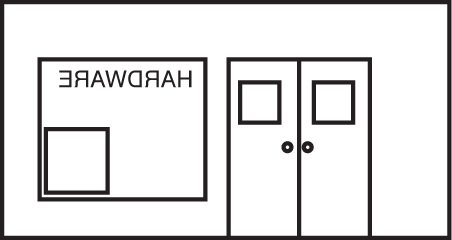
(D) 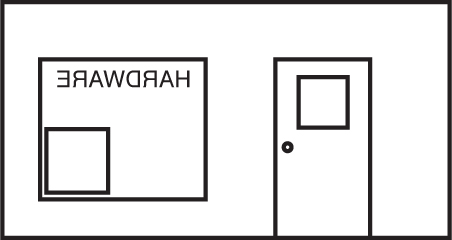
Directions: Use the figure below to answer question 56.

56. The figure shows a set of tools lying on a tabletop in front of you. Which of the following shows how the tools would look from behind the table?
(A) 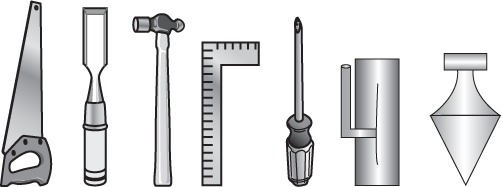
(B) 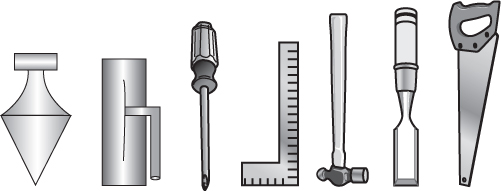
(C) 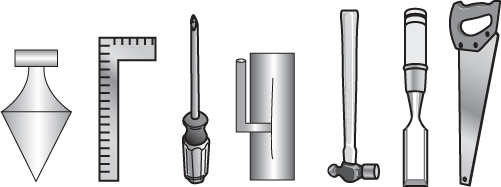
(D) 
Directions: For each item of wildland firefighting equipment listed in Column A, write the letter of the corresponding description in Column B in the space provided.
Column A |
Column B |
____ 57. Bambi bucket |
(A) Large square blade used for lifting fire debris |
____ 58. Drip torch |
(B) Long-handled combination rake and hoe |
____ 59. Pulaski tool |
(C) Designed for direct attack on fires in grass and leaves |
____ 60. McLeod tool |
(D) Last resort personal life safety device |
____ 61. Indian pump |
(E) Slung below a helicopter |
____ 62. Scoop shovel |
(F) Flexible square-shaped rubber flap |
____ 63. Fire rake |
(G) Has steel head with axe blade and adze |
____ 64. Fire swatter |
(H) Long-handled tool used to cut foliage and brush |
____ 65. Fire broom |
(I) Used to ignite foliage and brush |
____ 66. Fire shelter |
(J) Backpack-mounted water tank |
Directions: Study the road map shown above to answer questions 67 to 71. All responses by the fire apparatus must be performed in a legal manner as designated by road map directional signs.
67. The quickest way for the fire apparatus to arrive from quarters to a sprinkler water flow alarm at the hospital is to make a
(A) left turn out of quarters, right turn onto Avenue Q, left turn onto Apple Street
(B) right turn out of quarters, right turn onto Avenue N, right turn onto Cherry Street
(C) left turn out of quarters, left turn onto Avenue Q, left turn onto Apple Street
(D) right turn out of quarters, right turn onto Avenue P
68. An ambulance parked in front of the entrance to the museum and receiving an emergency call for the day care center should make a
(A) left turn on Apple Street, right turn onto Avenue N, left turn onto Cherry Street
(B) right turn on Mott Street, right turn onto Avenue N, left turn onto Cherry Street
(C) right turn on Blue Street, right turn onto Avenue N, left turn onto Cherry Street
(D) U-turn on Avenue P and a left turn onto Cherry Street
69. When firefighters are parked with the apparatus in front of City Hall, a pedestrian asks them the fastest way to get to the entrance of the health center. The firefighters should instruct the person to go
(A) east on Avenue O, south on Apple Street, and east on Avenue Q
(B) west on Avenue O, south on Greene Street, and east on Avenue Q
(C) west on Avenue O, south on Blue Street, and east on Avenue Q
(D) east on Avenue O, south on Cherry Street, and west on Avenue Q
70. A captain needing to mail an official document at the post office should direct the driver of the apparatus leaving the firehouse to go
(A) north on Mott Street, east on Avenue M, south on Blue Street
(B) north on Mott Street, east on Avenue N, north on Blue Street
(C) south on Mott Street, east on Avenue Q, north on Blue Street
(D) north on Mott Street, east on Avenue N, north on Apple Street, west onto Avenue M
71. The street intersection that touches on the most designated buildings (not counting unmarked boxes) is
(A) the intersection of Avenue N and Apple Street
(B) the intersection of Avenue P and Blue Street
(C) the intersection of Avenue O and Greene Street
(D) the intersection of Avenue Q and Cherry Street
Directions: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions.
72. A pry bar used to lift out a nail as shown in the figure is acting as what class lever system?
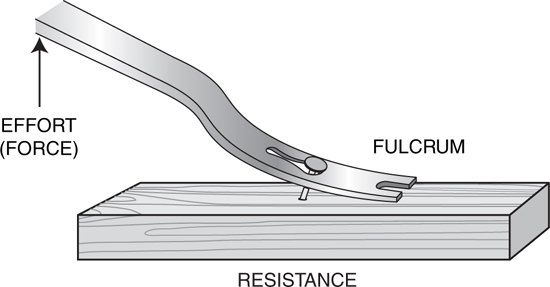
(A) First class
(B) Second class
(C) Third class
(D) Fourth class
73. It takes 100 N of force to raise a sail on a yacht. The load is also 100 N. What is the mechanical advantage?
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 4
74. Effort force is applied to gear A, which is interlocked with gear B. If gear A has 48 teeth, the resulting effect on gear B with 16 teeth is
(A) a speed advantage of 2
(B) a force advantage of 2
(C) a speed advantage of 3
(D) a force advantage of 3
75. The block and tackle pulley system shown has a mechanical advantage of
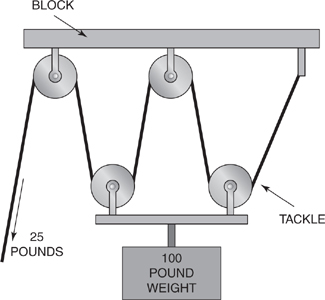
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
76. A simple machine invented to draw out water from a ship’s hold is called
(A) Archimedes’ screw
(B) Archimedes’ ramp
(C) Archimedes’ lever
(D) Achilles’ pulley
77. The simple machine listed below that converts rotational motion to linear motion is a(n)
(A) wedge
(B) class three lever
(C) screw
(D) inclined plane
78. A seesaw (teeter-totter) is an example of what type of simple machine?
(A) First-class lever
(B) Second-class lever
(C) Third-class lever
(D) Pulley
79. A warehouse worker rolls a wooden barrel weighing 80 pounds up an inclined plane. If the distance along the plane is 8 feet and the height of the far end of the plane is 2 feet, how much effort (force) was exerted by the worker?
(A) 80 pounds
(B) 60 pounds
(C) 40 pounds
(D) 20 pounds
80. Which of the following statements about pulley drive systems is INCORRECT?
(A) Pulleys work in a similar way to gears but are not directly joined.
(B) Pulleys can be used at a distance from each other.
(C) Pulleys rotate in opposite directions just as interlocking gears do.
(D) Pulleys can be used to reverse drive action by putting a twist into the belt.
81. In a belt drive system, the driver pulley wheel has a diameter of 200 mm while the driven pulley wheel has a diameter of 50 mm. If the driver pulley wheel rotates at 80 rpm, how fast is the driven pulley wheel revolving?
(A) 20 rpm
(B) 160 rpm
(C) 320 rpm
(D) 400 rpm
82. A knife, chisel, axe head, and nail are all examples of what type of simple machine?
(A) Screw
(B) Wedge
(C) Inclined plane
(D) Pulley
83. A modern use of the wheel and axle is in a
(A) log roller
(B) tongs
(C) doorknob
(D) log splitter
Directions: Study the apparatus accident situation below for 3 minutes. At the end of the time, cover the picture. Then answer questions 84 to 91.
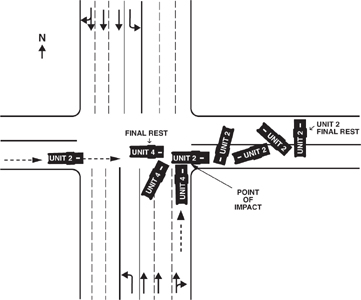
84. What type of accident has occurred?
(A) Rear-end collision
(B) Right-angle collision
(C) Front-end collision
(D) Sideswipe collision
85. In what direction was Unit 4 traveling prior to the collision?
(A) East
(B) South
(C) North
(D) West
86. In what direction was Unit 2 traveling prior to the collision?
(A) East
(B) South
(C) North
(D) West
87. How many northbound traffic lanes, including turning lanes, are south of the intersection?
(A) Two
(B) Three
(C) Four
(D) Five
88. How many northbound traffic lanes, including turning lanes, are north of the intersection?
(A) Two
(B) Three
(C) Four
(D) Seven
89. The final resting point of Unit 4 after the collision shows the apparatus facing
(A) east
(B) south
(C) north
(D) west
90. The final resting point of Unit 2 after the collision shows the apparatus facing
(A) east
(B) south
(C) north
(D) west
91. Which of the following accurately describes this apparatus accident?
(A) Unit 4 was struck by Unit 2 as Unit 4 entered the intersection.
(B) Unit 2 was struck on the driver side of the apparatus.
(C) Unit 2 struck Unit 4 in the front (cab) section of the apparatus.
(D) Unit 4 was in the right-hand lane.
Directions: Select the correct answer for the following questions.
92. A flammable gas generated at most structural fires is
(A) chlorine
(B) fluorine
(C) carbon monoxide
(D) helium
93. A boiler failure is an example of what type of explosion?
(A) Nuclear
(B) Endothermic
(C) Backdraft
(D) Mechanical
94. A component of the fire triangle listed below is
(A) fuel
(B) uninhibited chemical chain reaction
(C) foam
(D) water
95. What characteristic of most solid materials causes them to be more susceptible to ignition?
(A) High moisture content
(B) High surface area to mass ratio
(C) Low resistance to gravity
(D) Irregular shape
96. The ratio of the weight of a liquid to the weight of an equal volume of water is called the liquid’s
(A) flash point
(B) specific gravity
(C) ignition temperature
(D) boiling point
97. A flammable liquid has a boiling point of
(A) less than 100°F
(B) 100°F or greater
(C) 100°F to 200°F
(D) greater than 200°F
98. Liquids with low flash points tend to
(A) evaporate slowly
(B) flow evenly
(C) vaporize readily
(D) not burn
99. The property used to determine whether vapors/gases will hug the ground or rise up into the atmosphere is
(A) reactivity
(B) combustibility
(C) solubility
(D) vapor density
100. The lower and upper flammable limits of vapors/gases in air is used to determine
(A) if the vapor/gases will dissolve in water
(B) if the vapor/gases are lighter/heavier than air
(C) if the vapor/gases will ignite
(D) if the vapor/gases are toxic
For answer explanations to the questions on this exam, refer to this book’s companion website.
1. B
2. D
3. B
4. B
5. A
6. D
7. C
8. D
9. A
10. D
11. B
12. A
13. B
14. D
15. C
16. A
17. D
18. B
19. A
20. C
21. C
22. D
23. B
24. A
25. D
26. B
27. D
28. C
29. A
30. D
31. B
32. C
33. D
34. B
35. C
36. B
37. D
38. A
39. D
40. A
41. A
42. C
43. C
44. B
45. B
46. D
47. A
48. C
49. C
50. D
51. B
52. C
53. A
54. D
55. C
56. B
57. E
58. I
59. G
60. B
61. J
62. A
63. H
64. F
65. C
66. D
67. C
68. B
69. A
70. D
71. B
72. B
73. B
74. C
75. D
76. A
77. C
78. A
79. D
80. C
81. C
82. B
83. C
84. B
85. C
86. A
87. C
88. B
89. A
90. C
91. D
92. C
93. D
94. A
95. B
96. B
97. A
98. C
99. D
100. C