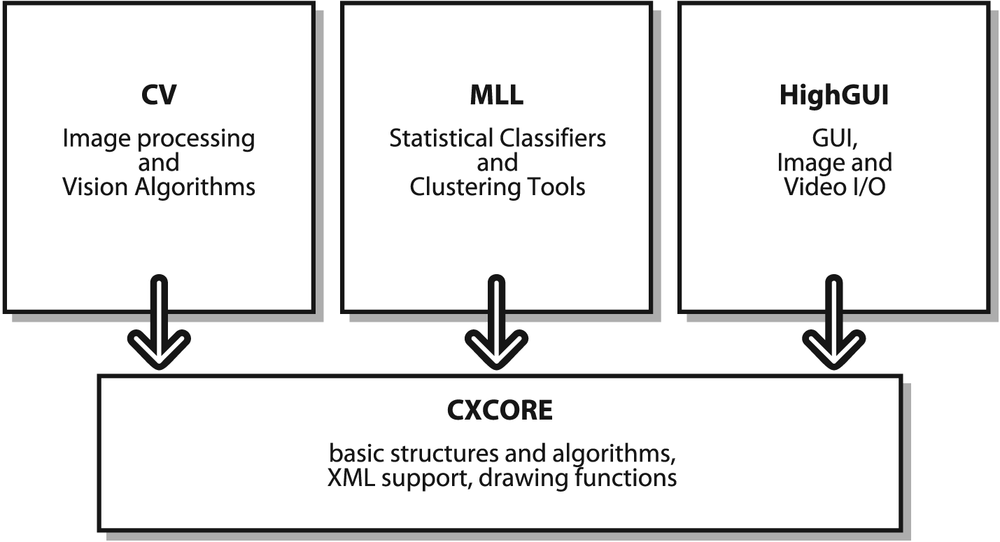
OpenCV is broadly structured into five main components, four of which are shown in Figure 1-5. The CV component contains the basic image processing and higher-level computer vision algorithms; ML is the machine learning library, which includes many statistical classifiers and clustering tools. HighGUI contains I/O routines and functions for storing and loading video and images, and CXCore contains the basic data structures and content.
Figure 1-5 does not include CvAux, which contains both defunct areas (embedded HMM face recognition) and experimental algorithms (background/foreground segmentation). CvAux is not particularly well documented in the Wiki and is not documented at all in the …/opencv/docs subdirectory. CvAux covers:
Eigen objects, a computationally efficient recognition technique that is, in essence, a template matching procedure
1D and 2D hidden Markov models, a statistical recognition technique solved by dynamic programming
Embedded HMMs (the observations of a parent HMM are themselves HMMs)
Extensions to Delaunay triangulation, sequences, and so forth
Stereo vision
Shape matching with region contours
3D tracking
Finding skeletons (central lines) of objects in a scene
Warping intermediate views between two camera views
Video surveillance (see Wiki FAQ for more documentation)
Camera calibration C++ classes (the C functions and engine are in CV)
Some of these features may migrate to CV in the future; others probably never will.