Practice Test 1 Biology-E
The following Practice Test is designed to be just like the real SAT Biology-E test. It matches the actual test in content coverage and level of difficulty. The test is in two parts. Part A (Questions 1–60) is for everyone taking Biology-E or Biology-M. Part B (Questions 61–80) is ONLY for students taking Biology-E.
When you are finished with the test, determine your score and carefully read the answer explanations for the questions you answered incorrectly. Identify any weak areas by determining the areas in which you made the most errors. Review these chapters of the book first. Then, as time permits, go back and review your stronger areas.
Allow 1 hour to take the test. Time yourself and work uninterrupted. If you run out of time, take note of where you ended when time ran out. Remember that you lose ¼ of a point for each incorrect answer. Because of this penalty, do not guess on a question unless you can eliminate one or more of the answers. Your score is calculated using the following formula:
Number of correct answers − ¼ (Number of incorrect answer)
This Practice Test will be an accurate reflection of how you’ll do on test day if you treat it as the real examination. Here are some hints on how to take the test under conditions similar to those of the actual exam.
• Complete the test in one sitting.
• Time yourself.
• Tear out your Answer Sheet and fill in the ovals just as you would on the actual test day.
• Become familiar with the directions to the test and the reference information provided. You’ll save time on the actual test day by already being familiar with this information.
Answer Sheet

PART A
Time: 60 Minutes
Core Questions 1–60—for Both Biology-E and Biology-M
Directions: Determine the BEST answer for each question. Then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
Questions 1–4
(A) ribosome
(B) mitochondria
(C) chloroplast
(D) endoplasmic reticulum
(E) Golgi apparatus
1. Site where photosynthesis takes place
2. Extensive series of membranes throughout the cell
3. Powerhouse of the cell
4. Packaging and distribution system of a cell
Questions 5–7
(A) lipids
(B) proteins
(C) carbohydrates
(D) nucleic acids
5. long chains of amino acids
6. composed of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
7. also known as fats
Questions 8–11
(A) commensalism
(B) mutualism
(C) parasitism
(D) symbiosis
8. Two or more organisms in a close, long-term association
9. One organism benefits, while the other suffers from the relationship.
10. Both organisms benefit from the relationship.
11. One organism benefits and the other does not benefit nor is it harmed from the relationship.
Questions 12–15
(A) organ
(B) cell
(C) tissue
(D) organ system
12. Group of cells with a similar function
13. Smallest unit of organization in living things
14. Many different groups of cells working together
15. The highest level of organization that carries out important body functions
16. Protists are classified by their
(A) method of feeding
(B) method of moving
(C) method of reproducing
(D) size
(E) habitat
17. The part of the human brain that controls balance, posture, and coordination is the
(A) cerebrum
(B) cerebellum
(C) medulla oblongata
(D) thalamus
(E) hypothalamus
18. The characteristics that gymnosperms and angiosperms share are
(A) leaves, rhizomes, and spore
(B) leaves, stems, roots, and seeds
(C) flat leaves, trunks, and naked seeds
(D) lack of vascular tissue and small leaflets
(E) needle-like leaves, stems, roots, and fleshy fruits
19. All of the following are characteristics of living things EXCEPT for the ability to
(A) perform cellular respiration
(B) regulate their internal environment
(C) reproduce
(D) change their external environment
(E) pass traits to offspring
20. What happens to an enzyme during a biochemical reaction?
(A) It becomes part of the product.
(B) It is unchanged.
(C) It is broken down into amino acids.
(D) It reacts with fatty acids.
(E) It becomes a polypeptide.
21.
I. monera
II. plants
III. protists
Which kingdom(s) contain(s) chemotrophs as members?
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
22. Which bird has feet that are modified for grasping prey?
(A) 
(B) 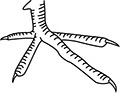
(C) 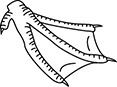
(D) 
(E) 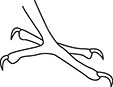
23. In RNA molecules, uracil is complementary to
(A) thymine
(B) guanine
(C) cytosine
(D) adenine
(E) uracil
24. Most mutations result from
(A) certain chemicals
(B) ionizing radiation
(C) infrared radiation
(D) ultraviolet radiation
(E) random events
25. The first vertebrates to evolve a three-chambered heart that ensured all cells in the body received the proper amount of oxygen are the
(A) fishes
(B) reptiles
(C) amphibians
(D) birds
(E) mammals
26. Which is the correct order of stages for an insect that undergoes complete metamorphosis?
(A) egg→larva→adult
(B) egg→nymph→adult
(C) egg→nymph→larva→adult
(D) egg→larva→pupa→adult
(E) egg→nymph→pupa→adult
27. Which process brings carbon into the living portion of its cycle?
(A) photosynthesis
(B) cellular respiration
(C) combustion
(D) decomposition
(E) fixation
28. Microspores of gymnosperms eventually develop into
(A) seeds
(B) cotyledons
(C) female gametophytes
(D) pollen grains
(E) archegonia
29. Bacteria are an important part of most food chains because they serve as
(A) primary consumers
(B) secondary consumers
(C) scavengers
(D) decomposers
(E) producers
30. Ground tissue provides all of the following functions in plants EXCEPT
(A) protection of other tissues
(B) supporting the plant
(C) storage of water and carbohydrates
(D) transport of materials
(E) photosynthesis
31. Which of the following scientific names is written in the correct form to identify a species?
(A) meleagris gallopavo
(B) Meleagris Gallopavo
(C) Meleagris Gallopavo
(D) Meleagris gallopavo
(E) Meleagris gallopavo
32. Which best describes the source of genes in an offspring resulting from sexual reproduction?
(A) The offspring gets a full set of genes from the mother and from the father.
(B) The offspring gets half the genes from the mother and half the genes from the father.
(C) The offspring gets all of its genes from the father.
(D) The offspring gets a random mixture of genes from the mother and father.
(E) The offspring gets all of its genes from the mother.
33. Which best describes how the following ecosystem will change over time?
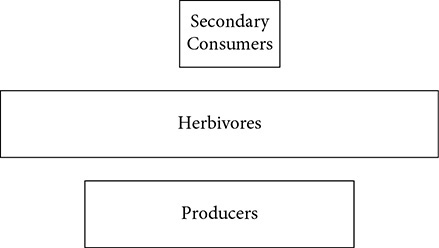
(A) The herbivores will decline because there is not enough food to support them.
(B) The herbivores will increase and the secondary consumers increase.
(C) The populations of producers, herbivores, and carnivores will remain the same.
(D) The secondary consumers will decline and the producers will increase.
(E) The producers will increase to support the herbivores.
34. If an organism has a haploid number of 28, how many chromosomes does it have?
(A) 7
(B) 14
(C) 28
(D) 42
(E) 56
35. A pea plant with a genotype of YY produces yellow seeds. A pea plant with a genotype of yy produces green seeds. If the pea plants are crossed, which describes the possible genotypes of the offspring?
(A) all are YY
(B) all are Yy
(C) all are yy
(D) half YY and half yy
(E) half YY and half Yy
36. Which set of offspring would result from a cross that was controlled by the law of independent assortment?
(A) Half the offspring are tall with white flowers and half are short with white flowers.
(B) All the offspring are tall or short and have white or purple flowers.
(C) All the offspring are short and have purple flowers.
(D) All the offspring are tall and have white flowers.
(E) All the offspring are tall and have purple flowers.
37. Which of the following statements about evolution is accurate?
(A) Populations evolve while individuals do not evolve.
(B) Populations do not evolve while individuals evolve.
(C) Populations evolve only when individuals evolve.
(D) Populations evolve only when isolated individuals evolve.
(E) Populations evolve only through mutations.
38. On the human skeletal system, which type of joint allows rotational movement?
(A) slightly moveable joint
(B) ball-and-socket joint
(C) pivot joint
(D) plane joint
(E) saddle joint
39. Which of the following best describes what will happen if cells are placed in a very salty solution?
(A) The cells remain unchanged.
(B) Water moves from inside of the cell to the outside.
(C) Water moves from outside of the cell to the inside.
(D) The cells burst.
(E) The cells dissolve.
40. The color red and the color white are codominant in horses. What would you expect if you crossed a homozygous red horse with a homozygous white horse?
(A) The offspring is white.
(B) The offspring is red.
(C) The offspring has both red and white hairs.
(D) The offspring is brown.
(E) The offspring is black.
41. The DNA of two closely related species would likely be
(A) completely different
(B) somewhat different
(C) very different
(D) very similar
(E) identical
42. All of the following are mechanisms of reproductive isolation EXCEPT
(A) geographical isolation
(B) ecological isolation
(C) temporal isolation
(D) reproductive failure
(E) niche overlap
43. The process of photosynthesis produces many products. Which of these products are used for starting cellular respiration?
(A) oxygen and ATP
(B) water and carbon dioxide
(C) NADP and hydrogen
(D) glucose and oxygen
(E) carbohydrates and NADP
Questions 44 and 45
This diagram is a cross section through the primary stem of a woody plant.
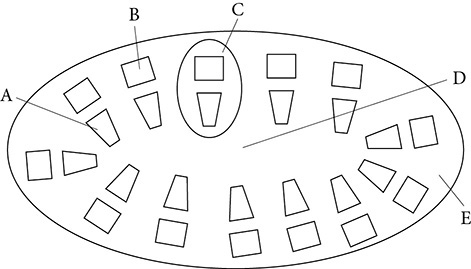
44. Which part of this stem is the vascular tissue?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
(E) E
45. Which part of this stem will develop into the bark of the woody plant?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
(E) E
46. Sequences of DNA that are easily and naturally copied from one location in the genome and inserted elsewhere are called
(A) duplication genes
(B) jumping genes
(C) crossing over genes
(D) recessive genes
(E) deletion genes
47. A bat wing and a human’s arm are examples of
(A) homologous structures
(B) analogous characters
(C) vestigial structures
(D) adaptive structures
(E) derived traits
48. A type of mutation that occurs when part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches to its sister chromatid resulting in the duplication of a gene on a chromosome is called
(A) deleting
(B) inserting
(C) separating
(D) substituting
(E) inverting
49. Cellular respiration in the absence of oxygen is called fermentation. What is the product of fermentation in animal cells?
(A) Acetyl-CoA
(B) alcohol
(C) carbon dioxide
(D) pyruvic acid
(E) lactic acid
50. Natural selection is an evolutionary force that can affect an entire population. One species can evolve into two species when only the extreme forms of a trait are favored and intermediate forms are selected against. This is known as
(A) artificial selection
(B) directional selection
(C) targeted selection
(D) disruptive selection
(E) stabilizing selection
51. An example of a density-dependent factor is
(A) weather
(B) climate
(C) air
(D) food
(E) drought
52. Which best describes the advantage of crossing over during meiosis?
(A) makes for healthy offspring
(B) provides a source of genetic variation
(C) creates a random mix of chromosomes
(D) allows gametes to have half the number of chromosomes
(E) increases the number of gametes
53. A segment of a DNA molecule that carries instructions for a specific trait is called a
(A) gene
(B) chromosome
(C) nucleotide
(D) codon
(E) chromatid
54. Small, round bacteria that grow in a chain are called
(A) streptococci
(B) staphylobacilli
(C) spirillium
(D) diplococci
(E) bacillus
55. According to Darwin, organisms best suited to their environment
(A) are most likely to evolve
(B) are more likely to survive and reproduce
(C) are most likely to live the longest
(D) are the fastest organisms
(E) have the same chance of survival as other organisms
56. When lions and hyenas fight over a dead zebra, their interaction is called
(A) mutualism
(B) competition
(C) commensalism
(D) parasitism
(E) predation
57. Which is the best method for preserving the bio-diversity of an ecosystem?
(A) creating a preserve in an urban area
(B) building botanical gardens based on the ecosystem
(C) preserving a few very large areas on an ecosystem
(D) preserving many small areas of an ecosystem
(E) creating greenbelts along creeks and roadways in urban areas
58. Gregor Mendel found that the inheritance of one trait had no affect on the inheritance of different trait. He described this observation as the
(A) law of dominance
(B) law of universal inheritance
(C) law of segregation
(D) law of independent assortment
(E) law of separate chromosomes
59. Meiosis is the process of making sex cells or gametes. In humans, how many mature egg cells result from meiosis?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(E) 6
60. Which of the following are considered prokaryotes?
(A) animals
(B) plants
(C) fungi
(D) protists
(E) bacteria
PART B
Biology-E Questions 61–80
61. Which represents the correct order from simplest to most complex?
(A) organ system, organ, tissue, cell
(B) cell, tissue, organ, organ system
(C) tissue, cell, organ, organ system
(D) cell, organ, tissue, organ system
(E) cell, organ, organ system, tissue
62. Which property of a population may be described as even, clumped, or random?
(A) habitat
(B) dispersion
(C) size
(D) density
(E) growth rate
63. The process of evolution where an ancestral species evolves into an array of species that occupy different niches is called
(A) gradualism
(B) convergent evolution
(C) adaptive radiation
(D) punctuated equilibrium
(E) divergent evolution
64. Natural selection is often described as survival of the fittest. Which of the following species would likely be best able to survive in rapidly changing environmental conditions?
(A) a tree that takes 20 years to reach maturity and produces thousands of seeds
(B) a weed that only lives one year and produces hundreds of seeds
(C) a mouse that reproduces six to eight times a year with a litter of six mice
(D) a bird that reproduces once a year but lays four to six eggs
(E) a tree that lives for more than 500 years and produces many slow growing seeds
65. Bryophytes are nonvascular plants. In which of the following habitats would you most likely find bryophytes growing?
(A) in a desert
(B) on the top of a high tree
(C) in a cave
(D) under the soil
(E) at the mouth of a spring
66.
I. temperature
II. humidity
III. vegetation
Which of the above are abiotic factors?
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II only
(E) I, II, and III
67. When energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, about 90% of the energy is lost. If plants produce 1,000 kcal of energy, how much of the energy is passed to the next trophic level?
(A) 10,000 kcal
(B) 1,000 kcal
(C) 100 kcal
(D) 10 kcal
(E) 1 kcal
68. Which main factor(s) determine(s) which biome exists in a certain area?
(A) temperature
(B) elevation
(C) precipitation
(D) temperature and moisture
(E) temperature and elevation
Questions 69–74
Some Land (Terrestrial) Biomes:

69. A biome that is characterized by warm temperatures throughout the year and seasonal heavy rainfall is found in the
(A) temperate deciduous forest
(B) taiga
(C) tundra
(D) tropical rain forest
(E) savannah
70. Which pair of biomes would most likely be found adjacent to each other?
(A) temperate deciduous forest–taiga
(B) taiga–tundra
(C) tundra–swamp
(D) tropical rain forest–deciduous forest
(E) chaparral–tundra
71. Which describes the change you most likely see when moving from the equator toward the North Pole?
(A) tropical rain forests→deserts→taiga
(B) tundra→deserts→grasslands
(C) grasslands→ tundra→rainforests
(D) temperate deciduous forests→taiga→rain forests
(E) tropical rainforest→taiga→grasslands→tundra
72. Which biome produces much of our wheat crop?
(A) taiga
(B) grassland
(C) chaparral
(D) tropical rain forest
(E) temperate deciduous forest
73. Which two biomes are most similar in annual rainfall?
(A) taiga and tundra
(B) taiga and grassland
(C) grassland and tropical rain forest
(D) taiga and temperate deciduous forest
(E) tundra and grassland
74. The biome that has the highest biodiversity is the
(A) temperate deciduous forest
(B) taiga
(C) tundra
(D) savannah
(E) tropical rain forest
Questions 75–77
This chart shows the number of genera of brachiopods, a type of mollusk, throughout geologic time. Brachiopods were once numerous but today they are rare. They resemble clams but they are very different in form and structure. Most of the brachiopods living today are found in very cold waters or in the deep ocean. Brachiopods are very important to paleontologists because they give information about both time sequence and past environmental conditions.
75. During which of the following times did a mass extinction occur?
(A) Cambrian–Ordovician
(B) Silurian–Devonian
(C) Permian–Triassic
(D) Jurassic–Cretaceous
(E) Tertiary–Quaternary
76. During which period of time was there a population explosion of species?
(A) Cambrian–Ordovician
(B) Silurian–Devonian
(C) Permian–Triassic
(D) Jurassic–Cretaceous
(E) Tertiary–Quaternary

77. A paleontologist finds a rock unit with Strophomenida, Spiriferida, and Pentamerida brachiopods. Which of the following times is the rock unit most likely from?
(A) Cambrian
(B) Silurian
(C) Triassic
(D) Cretaceous
(E) Tertiary
Questions 78–80
The diagram represents the events of the cell cycle:

78.
I. mitosis
II. G1 phase
III. S phase
Which phase of the cell cycle involves DNA replication?
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
79. During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes uncoil at opposite ends of the cell followed by the formation of the nuclear membrane?
(A) interphase
(B) prophase
(C) metaphase
(D) anaphase
(E) telophase
80. During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes begin condensing and become visible?
(A) interphase
(B) prophase
(C) metaphase
(D) anaphase
(E) telophase
-------------------------------------------STOP-------------------------------------------
If you finish before time runs out, go back and check your work.
Answer Key
Part A
1. C
2. D
3. B
4. E
5. B
6. C
7. A
8. D
9. C
10. B
11. A
12. C
13. B
14. A
15. D
16. B
17. B
18. B
19. D
20. B
21. A
22. A
23. D
24. E
25. C
26. D
27. A
28. D
29. D
30. A
31. E
32. B
33. A
34. E
35. B
36. B
37. A
38. B
39. B
40. C
41. D
42. E
43. D
44. C
45. B
46. B
47. A
48. B
49. E
50. D
51. D
52. B
53. A
54. A
55. B
56. B
57. C
58. D
59. A
60. E
Part B
61. B
62. B
63. C
64. B
65. E
66. D
67. C
68. D
69. D
70. B
71. A
72. B
73. D
74. E
75. C
76. A
77. B
78. C
79. E
80. B
Score Sheet
Answers and Explanations
Part A
1. (C) Chloroplasts are the organelles that contain chlorophyll and other photopigments used during photosynthesis.
2. (D) The endoplasmic reticulum is an extensive network of membranes that are in the cytoplasm. The endoplasmic reticulum is a transportation network to move molecules around the cell.
3. (B) The mitochondria are the site where ATP is produced, providing energy for cellular functions.
4. (E) The Golgi apparatus consists of flattened sacs that collect and distribute molecules produced by cellular functions.
5. (B) Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together. Proteins serve many different functions in cells.
6. (C) Carbohydrates are used by the body for energy. Carbohydrates range from such simple sugars as glucose to complex polysaccharides such as starch.
7. (A) Lipids are a diverse class of organic compounds that include olive oil, vegetable oil, and even beeswax. Lipids do not dissolve in water.
8. (D) Symbiosis is two or more organisms that live together in a long-term association. Symbiosis has different forms depending on whether organisms benefit from the relationship or not.
9. (C) Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits at the expense of the other organism. Tapeworms are an example. Tapeworms get food from the digestive system of their host.
10. (B) Mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit from the relationship. Some ants and aphids are an example. The ants care for and protect the aphids. In return, the aphids provide the ants with a sweet liquid.
11. (A) Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits, while the other neither benefits nor is harmed. Barnacles growing on a whale is an example of commensalism. The barnacles are carried across the oceans while the whale is not affected.
12. (C) A tissue is a group of cells that are serve a similar function.
13. (B) A cell is the smallest unit of life capable of carrying out all functions.
14. (A) Organs are composed of a group of tissues. The tissues collectively work to perform different functions within the organ.
15. (D) Organ systems are groups of organs that work together to make up a system.
16. (B) Protists are classified by the way they move or method of locomotion. The methods are pseudopods, cilia, flagella, or nonmotile.
17. (B) The cerebellum is a small region at the back of the brain. The cerebellum controls smooth, coordinated movements, helps maintain muscle tone, posture, and balance.
18. (B) Gymnosperms and angiosperms are advanced plants. They have many similarities including their leaves, stems, roots, and reproduction with seeds.
19. (D) Most organisms do not have the ability to change their external environments.
20. (B) An enzyme acts as a catalyst for the biochemical reaction. Catalysts lower the activation energy required for a reaction but they are not changed in any way during the reaction.
21. (A) Chemotrophs are able to breakdown inorganic chemical molecules to obtain energy. This has only been found in the Kingdom Monera. Some members of this kingdom are able to break down hydrogen sulfide to obtain energy. Chemotrophs do not depend on sunlight for energy.
22. (A) Birds such as hawks and falcons have strong feet with long talons for grasping prey.
23. (D) In RNA, uracil replaces thymine and is complimentary to adenine.
24. (E) There are many causes of mutations in cells. The most common are the random processes that take place in cells.
25. (C) Amphibians were the first to have a three-chambered heart. This advancement allowed the circulatory system to include lungs.
26. (D) Complete metamorphosis occurs when an organism has a different body shape at different stages of its life cycle. For example, in butterflies, the larva state, called a caterpillar, is very different from the adult butterfly.
27. (A) Photosynthesis is the fixing of atmospheric carbon into molecules that can be used by organisms.
28. (D) Microspores result from meiosis that takes place in the pollen cone of a gymnosperm. The microspores develop into pollen grains, or more correctly, microgametophytes.
29. (D) Bacteria break down or decompose organic matter. Because of their actions, they are considered decomposers in an ecosystem.
30. (A) Ground tissues in plants serve many different functions. Ground tissues do not protect other tissues.
31. (E) The proper way of writing a species name is with the genus capitalized and the specific epithet lower case. The entire name is written in italics or, in older texts, underlined.
32. (B) When gametes are formed in parents; each gamete has half the genetic material of the parent. When the gametes unite, the resulting offspring will receive half the genetic material of each parent.
33. (A) An ecosystem only has so much energy available to pass up to each level of the trophic pyramid. Only about 10% of the energy is actually passed up to the next higher level. When one level of the pyramid is larger than the level below it, there must be a shift to reduce the energy demands.
34. (E) The haploid number of chromosomes is the number of pairs found in an organism. In this case a haploid number of 28 translates to 28 pairs or 56 chromosomes.
35. (B) In this type of cross, the offspring get one allele from each parent. The result is that all offspring will be Yy.
36. (B) The law of independent assortment only applies to traits that are on different chromosomes. The common traits in pea plants all happen to be on different chromosomes so this law applies.
37. (A) Evolution affects populations, not individuals. Individuals can have traits that give them an advantage, and they may pass the traits on, but they do not evolve.
38. (B) The ball-and-socket joint is the type of joint found in the shoulder. The joint allows rotational movement.
39. (B) When a cell is placed in a very salty solution, water moves from the area of higher concentration, inside the cell, to the area of lower concentration, outside the cell.
40. (C) Both codominant traits are always expressed. In horses, the offspring has both red and white hairs.
41. (D) Species that are very closely related have very similar DNA with only minor differences. They are related through a common ancestor.
42. (E) Niche overlap is a form of competition instead of reproductive isolation.
43. (D) Glucose and oxygen are products of photo-synthesis. They enter the cellular respiration pathway where they are used to release energy.
44. (C) The vascular tissue in plants moves water up the plant from the roots and moves sugars from the leave, throughout the plant, and down to the roots.
45. (B) The phloem becomes the bark in woody plants.
46. (B) Jumping genes are genes that easily jump or move from one location on a chromosome to another. Jumping genes are what cause some corn to have multicolored kernels.
47. (A) Homologous structures are structures that are similar in two different species. In this case, the bones in the human arm are similar to those in a bat. The finger bones in a human are similar to the thin bones in the bat wing.
48. (B) Inserting is a type of mutation. As the name implies, a repeat of a sequence is inserted into a different chromosome.
49. (E) In animal cells, when fermentation takes place, lactic acid is formed.
50. (D) Disruptive selection takes place when some environmental pressure works to make the extremes in variation the most successful organisms. These organisms are those that reproduce and pass their traits to their offspring.
51. (D) Density-dependent factors are ones that affect a population differently depending on its size and density.
52. (B) Crossing over is a process where genetic material is exchanged by two different chromosomes during meiosis. This is similar to shuffling a deck of cards and increasing variation in the genes.
53. (A) Genes are segments on DNA that on a chromosome that have a specific function.
54. (A) Streptococci means long chain of small round bacteria. Strepto refers to a chain and cocci refers to round.
55. (B) The concept of the survival of the fittest states that those best able to survive are the ones most likely to reproduce and pass on their genes.
56. (B) The ecological concept of competition is when two species try for a limited resource. The species best suited to exploit the resource gets the larger share of the resource.
57. (C) Preserves usually work better as larger areas. The same amount that is fragmented does not have the same healthy exchange of genetic material as one large area.
58. (D) Mendel explained that different traits are inherited independently if they are found on different chromosomes.
59. (A) During meiosis, three of the resulting cells are called polar bodies and are discarded. Only one of the cells becomes an egg.
60. (E) Bacteria are prokaryotes because they lack a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
Part B
61. (B) The cell is the smallest unit of life. When a group of similar cells works together, it is called a tissue. Groups of tissues are linked together to form organs. Organs that work together are called organ systems.
62. (B) The dispersion of a population is a way of describing how members of a population are spread out in their habitat.
63. (C) Adaptive radiation describes how a species moves into new, unfilled niches and becomes more specialized to fill each niche.
64. (B) Natural selection works best in a rapidly changing environment when an organism is capable of producing many offspring in a short amount of time.
65. (E) Bryophytes do best in an environment that is constantly wet. Of the ones listed, the mouth of a spring is the best habitat.
66. (D) Abiotic factors are things that are not living. Vegetation is living; therefore it is a biotic factor.
67. (C) Each trophic level only passes about 10% of its energy to the next higher level.
68. (D) Temperature and moisture are the two main controlling factors that determine biome type. Plants and animals have specific requirements on needs and these are the most basic.
69. (D) Tropical rain forests are found in warm regions near the equator.
70. (B) The taiga and tundra are both found in cold climates. The permafrost is much shallower in tundra so it cannot support large plants.
71. (A) Tropical rain forests are found at the equators. Deserts are found in the midlatitudes. Taiga is found at high latitudes.
72. (B) Grain crops are grasses so they grow best in a grassland biome.
73. (D) The taiga and temperate deciduous forest have similar rainfall amounts. The main difference is the temperature.
74. (E) The tropical rain forest has a warm temperature year round, which gives it a high biodiversity.
75. (C) The chart clearly shows a large drop in number of genera at the end of the Permian.
76. (A) At the end of the Silurian, there was a big increase in the number of genera of brachiopods.
77. (B) Of the times listed, the Silurian is the only one where all three brachiopod groups are present.
78. (C) DNA is replicated during the S, or synthesis phase of the cell cycle.
79. (E) Telophase takes place close to the end of mitosis. The cell is getting ready to split into two daughter cells.
80. (B) Prophase occurs at the beginning of mitosis. The chromosomes condensing is the first step in preparation for mitosis.