Practice Test 2 Biology-E
The following Practice Test is designed to be just like the real SAT Biology-E test. It matches the actual test in content coverage and level of difficulty. The test is in two parts. Part A (Questions 1–60) is for everyone taking Biology-E or Biology-M. Part B (Questions 61–80) is ONLY for students taking Biology-E.
When you are finished with the test, determine your score and carefully read the answer explanations for the questions you answered incorrectly. Identify any weak areas by determining the areas in which you made the most errors. Review these chapters of the book first. Then, as time permits, go back and review your stronger areas.
Allow 1 hour to take the test. Time yourself and work uninterrupted. If you run out of time, take note of where you ended when time ran out. Remember that you lose ¼ of a point for each incorrect answer. Because of this penalty, do not guess on a question unless you can eliminate one or more of the answers. Your score is calculated using the following formula:
Number of correct answers − ¼ (Number of incorrect answer)
This Practice Test will be an accurate reflection of how you’ll do on test day if you treat it as the real examination. Here are some hints on how to take the test under conditions similar to those of the actual exam.
• Complete the test in one sitting.
• Time yourself.
• Tear out your Answer Sheet and fill in the ovals just as you would on the actual test day.
• Become familiar with the directions to the test and the reference information provided. You’ll save time on the actual test day by already being familiar with this information.
Answer Sheet

PART A
Time: 60 Minutes
Core Questions 1–60—for Both Biology-E and Biology-M
Directions: Determine the BEST answer for each question. Then fill in the corresponding oval on the Answer Sheet.
Questions 1–3
(A) Krebs cycle
(B) electron transport chain
(C) fermentation
(D) glycolysis
(E) Calvin cycle
1. Cellular respiration in the absence of oxygen
2. A biochemical pathway that utilizes pyruvate to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH2
3. A biochemical pathway that breaks down glucose into pyruvate
Questions 4–7
(A) primary consumers
(B) secondary consumers
(C) scavengers
(D) decomposers
(E) producers
4. Earthworms eat organic matter and return nutrients to the soil.
5. Cows eat grass.
6. Lions are hunters on the African plains.
7. Buzzards soar in the sky looking for dead animals.
Questions 8–12
(A) geographical isolation
(B) mechanical isolation
(C) temporal isolation
(D) hybrid sterility
(E) behavioral isolation
8. Groups are not attracted to each other for mating.
9. Structural differences prevent mating between individuals of different groups.
10. Groups are physically separated.
11. Groups reproduce at different times of the year.
12. Matings between groups do not produce fertile offspring.
Questions 13–15
(A) dominance
(B) reflex
(C) instinct
(D) imprinting
(E) habituation
13. Learned behavior that occurs only at a certain, critical time in an animal’s life
14. Automatic, unconscious reaction
15. Simple form of learned behavior
16. You are trying to identify a plant. If you look closely at the leaves, you see the veins are all parallel. What does this tell you about the plant?
(A) The plant is a dicot.
(B) The plant is a monocot.
(C) The plant is a gymnosperm.
(D) The plant is an angiosperm.
(E) The plant is a bryophyte.
17. Populations tend to grow because
(A) the large number of individuals reduces the number of predators
(B) the more individuals there are, the more likely they will survive
(C) random events or natural disturbances are rare
(D) there are always plentiful resources in every environment
(E) individuals tend to have multiple offspring over their lifetime
18.
I. jellyfish
II. mollusk
III. earthworm
Which of the above organisms lacks a complete digestive tract?
(A) I, II, and III
(B) I only
(C) II only
(D) III only
(E) I and III only
19. The internal need that causes an animal to act and is necessary for learning is called
(A) trail-and-error
(B) motivation
(C) habituation
(D) conditioning
(E) imprinting
20. The rigid shape of plant cells is due to the
(A) cell membrane
(B) cell wall
(C) cytoskeleton
(D) chloroplasts
(E) centrioles
21. An invertebrate that displays two distinct body forms, medusa and polyp, at different stages in its lifecycle belong to the phylum
(A) Porifera
(B) Cnidaria
(C) Nemotoda
(D) Mollusca
(E) Echinodermata
22. The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis is called
(A) nondisjunction
(B) translocation
(C) mutation
(D) crossing over
(E) disjunction
23. Which characteristic of fungi is used to classify them into different phyla?
(A) the type of food they grow on
(B) the type of hyphae they have
(C) the type of mushroom they produce
(D) the way they produce spores
(E) the material that makes up their cell wall
24. A rancher moved his herd of cattle to a different pasture. Which example below indicates that the carrying capacity of that pasture was exceeded?
(A) The herd increased in size.
(B) The pasture became overgrazed and barren.
(C) The pasture had more grasses.
(D) The cows gained weight.
(E) The cows had more calves.
25. Some mutations are a source of genetic variation. Which type of cell is mostly likely to cause a genetic variation that could lead to evolution?
(A) skin cells
(B) body cells
(C) brain cells
(D) sex cells
(E) embryo cells
26. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of a dihybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals?
(A) 3:1
(B) 1:2:1
(C) 3:3:1
(D) 9:3:3:1
(E) 6:4:4:2
27. Which of the following nucleotide bases is found in RNA but not in DNA?
(A) uracil
(B) adenine
(C) cytosine
(D) thymine
(E) guanine
28. Some bacteria are able to reproduce with a simple form of sexual reproduction called
(A) binary fission
(B) fragmentation
(C) meiosis
(D) replication
(E) conjugation
29. Mendel’s law of segregation states that
(A) genes are separated on different chromosomes
(B) pairs of alleles separate during mitosis
(C) pairs of alleles separate during meiosis
(D) pairs of alleles exchange material during crossing over
(E) genes are passed from parents to offspring
Questions 30 and 31
This is a segment of DNA.
CGATGGCTA
30. Which represents the complimentary strand of DNA for the segment?
(A) CGATGGCTA
(B) GCTACCGAT
(C) UAGCCAUCG
(D) CGTAGGCAT
(E) ATCGGTAGC
31. What is the messenger RNA strand for the DNA segment?
(A) GCUACCGAU
(B) UCTACCGUA
(C) GUTAUUGAT
(D) CGATGGCTA
(E) ATCGGTAGC
32. The classification system set forth by Linneaus grouped organisms based on their
(A) similar coloring
(B) similar structures
(C) similar habitats
(D) genetic similarities
(E) evolutionary relationships
33. Which of the following best describes an ecosystem?
(A) a group of individuals of the same species that live together in the same area at the same time
(B) all populations of different species that live and interact in the same area
(C) all populations of different species that live and interact in the same area and the abiotic environment
(D) all the organisms that depend on the resources in a specific region
(E) the part of Earth where life exists
34. The diploid number of a human cell is 23. How many actual chromosomes are in a normal body cell?
(A) 22
(B) 23
(C) 44
(D) 46
(E) n
35. Which tissue transports carbohydrates and water through plants?
(A) epidermal tissue
(B) vascular tissue
(C) ground tissue
(D) epithelial tissue
(E) endodermal tissue
36. According to the cell theory, which of the following statements is correct?
(A) All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
(B) All organisms must be able to reproduce.
(C) Cells have organelles to carry on their functions.
(D) Cells evolved from a primordial soup on early Earth.
(E) Cells are able to regulate their external environment.
37. Which bird uses its beak to probe flowers for nectar?
(A) 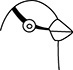
(B) 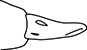
(C) 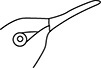
(D) 
(E) 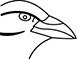
38. Which of the following best describes what will happen if cells are placed in distilled water?
(A) The cells remain unchanged.
(B) Water moves from inside of the cell to the outside.
(C) Water moves from outside of the cell to the inside.
(D) The cells shrink.
(E) The cells dissolve.
Questions 39 and 40
In an experiment in a laboratory, a population of bacteria in a petri dish is exposed to an antibiotic. The antibiotic kills most of the population. However, a few bacteria survive and soon repopulate the Petri dish with antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
39. According to modern evolutionary theory, which of the following explanations is correct for this experiment?
(A) Some of the bacteria tried and successfully adapted to the new conditions in the petri dish.
(B) Some members of the bacteria population developed a resistance to the antibiotic immediately after exposure.
(C) Some members of the bacteria population already had a resistance to the antibiotic so they were not killed.
(D) Some of the bacteria quickly evolve into a new species that resists the antibiotic.
(E) Some of the bacteria protected themselves from the antibiotic long enough to develop a resistance.
40. Which best describes what happened in the petri dish?
(A) macroevolution
(B) microevolution
(C) adaptive radiation
(D) divergent evolution
(E) speciation
41. All of the following are cycled though biogeochemical cycles EXCEPT
(A) water
(B) carbon
(C) energy
(D) phosphorus
(E) nitrogen
42. You cross a red flowered plant with a white flowered plant, and all of the offspring have pink flowers. What is the most probable explanation?
(A) Red is dominant.
(B) White is dominant.
(C) Pink is dominant.
(D) Red and white exhibit incomplete dominance.
(E) Red and white exhibit codominance.
43. If an organism has a haploid number of 24, how many chromosomes does it have?
(A) 6
(B) 12
(C) 24
(D) 36
(E) 48
44. Bats and insects both have wings. The wings of bats and insects are examples of
(A) homologous structures
(B) analogous characters
(C) vestigial structures
(D) adaptive structures
(E) derived traits
45.
I. vitamin synthesis
II. absorb water
III. absorb nutrients
In humans, what function does the small intestine serve?
(A) I and II only
(B) II and III only
(C) II only
(D) I only
(E) III only
46. A codon is
(A) a group of three nucleotide sequences
(B) the nucleotide units between the start and stop codes
(C) the nucleotide sequence that serves as the instructions for a protein
(D) a single nucleotide in an mRNA sequence
(E) the sequence of nucleotides that signals the start or stop of protein synthesis
47. Which of the following conditions is necessary for a virus to attack a host cell?
(A) The virus must have the DNA or RNA key sequence to enter the host cell.
(B) The virus must have the enzymes to cause the host cell to burst so that the host cell may be used as raw materials.
(C) The virus must have the proper enzyme to puncture the membrane of the host cell.
(D) The virus must have a particular shape that will match up with the proteins on the surface of the host cell.
(E) The viral DNA or RNA must have a sequence that is recognized by the ribosomes of the host cell.
48. Cytochrome–c is a protein that scientists often use to compare the evolutionary relationships among species. There is one difference in the cytochrome–c sequence between humans and rhesus monkeys. There are ten differences between humans and kangaroos. What can you infer about the relationship between these species?
(A) Humans and kangaroos have the same proteins coded in their genes.
(B) Humans and kangaroos share a more recent ancestor than humans and rhesus monkeys.
(C) Humans are not closely related to either kangaroos or rhesus monkeys.
(D) Humans and rhesus monkeys share a more recent ancestor than humans and kangaroos.
(E) Rhesus monkeys and kangaroos share a more recent ancestor than humans and rhesus monkeys.
49. A man with type A blood marries a woman with type B blood. Their child is blood type O. What are the genotypes of the parents?
(A) AO and BO
(B) OO and AB
(C) Aa and BO
(D) AO and Bb
(E) Aa and Bb
Questions 50 and 51
Each corn kernel in an ear of corn is ready to grow into a new plant.
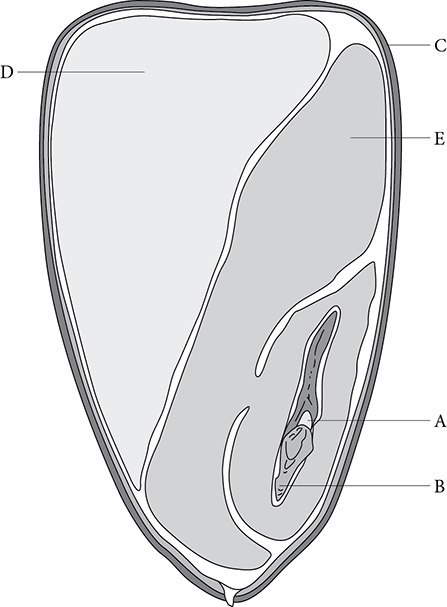
50. Which part of this seed makes up the plant embryo?
(A) A, B
(B) A, D
(C) B, C
(D) A, B, E
(E) B, C, D
51. Which part of the seed stores the energy for the plant embryo?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
(E) E
52. 
This graph shows the activation energy required for a certain biochemical reaction to take place. Which graph shows the effect of an enzyme on the same biochemical reaction?
(A) 
(B) 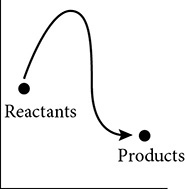
(C) 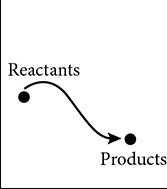
(D) 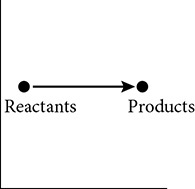
(E) 
53. Which is the correct order of stages for an insect that undergoes incomplete metamorphosis?
(A) egg→larva→adult
(B) egg→nymph→adult
(C) egg→nymph→larva→adult
(D) egg→larva→pupa→adult
(E) egg→nymph→pupa→adult
54. The number of trophic levels that are maintained in an ecosystem is limited by
(A) the number of species
(B) the population size
(C) the loss of potential energy
(D) the number of individuals
(E) the hours of sunshine
55. The law of independent assortment applies to
(A) two genes on different chromosomes
(B) two genes on the same chromosome
(C) two alleles on different chromosomes
(D) two alleles on the same chromosome
(E) two chromosome strands
56. Which is the correct order for the cell cycle beginning with the phase that most cells spend the majority of their time?
I. G2 Phase—growth and preparation for mitosis
II. Mitosis
III. G1 Phase—cell growth
IV. S Phase—DNA copied
V. Cytokinesis
(A) III, IV, I, II, V
(B) III, I, IV, V, II
(C) II, III, I, IV, V
(D) IV, III, I, II, V
(E) V, III, IV, I, II
57. For natural selection to occur, which of the following must be true?
(A) Individuals must evolve.
(B) The environment must be constant.
(C) Variation among organisms must exist.
(D) Traits must be acquired.
(E) Many species must be present.
58. What is the phenotypic ratio for a cross between a pea plant with purple flowers (PP) and a pea plant with white flowers (pp)?
(A) all white
(B) all purple
(C) half purple, half white
(D) 1PP, 2Pp, 1pp
(E) all Pp
59. Natural selection is a part of evolution of a species. Which of the following best describes the driving force that leads to evolution within a species?
(A) Individuals within a population change their behavior to accommodate changes in the environment and pass these to offspring.
(B) Individuals within a population develop new adaptations as selective pressures force change.
(C) Individuals within a population find new ways to adapt to environmental pressures.
(D) Individuals within a population use different parts of their body as conditions change and pass those changes to offspring.
(E) Individuals within a population have variations that give those individuals a better chance of survival.
60. Which of the following organisms is INCORRECTLY paired with its trophic level?
(A) tree–producer
(B) hawk–primary consumer
(C) fungi–detritivore
(D) fox–secondary consumer
(E) grasshopper–primary consumer
PART B
Biology-E Questions 61–80
61. All of the following could cause a large number of density-dependent deaths in a population EXCEPT
(A) winter storms
(B) disease-carrying insects
(C) predators
(D) limited resources
(E) small forest fire
62. Which of the following seeds depends on wind for dispersal?
(A) 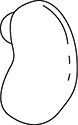
(B) 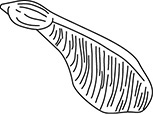
(C) 
(D) 
(E) 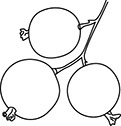
63. Which group of animals was the first to have internal fertilization?
(A) fishes
(B) amphibians
(C) reptiles
(D) birds
(E) mammals
64. Where would you most likely find nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
(A) on the stems of some plants
(B) in the leaves of trees
(C) on the roots of some plants
(D) on atmospheric dust particles
(E) in blue-green algae
65. Earthworms are hermaphroditic, meaning that they
(A) reproduce asexually
(B) only come up to the surface at night
(C) reproduce both sexually and asexually
(D) have specialized segments for specialized tasks
(E) have both male and female sex organs
66. According to the Hardy–Weinberg principle, allele frequencies change when evolutionary forces act on a population. All of these are possible evolutionary forces EXCEPT
(A) mutations
(B) gene flow
(C) genetic drift
(D) random mating
(E) natural selection
Questions 67–69
This is a typical food web in a pond.
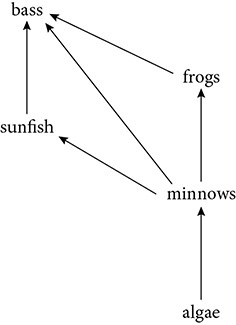
67. Which two organisms in this food web are in direct competition?
(A) bass and minnows
(B) minnows and sunfish
(C) frogs and sunfish
(D) bass and algae
(E) frogs and algae
68. Which shows one possible direct pathway for energy flow to the bass?
(A) algae→minnows→frogs→bass
(B) algae→bass
(C) algae→frogs→sunfish→bass
(D) minnows→frogs→bass
(E) bass→frogs→minnows→algae
69. Based on this food web, what would happen if the bass disappeared due to over fishing?
(A) The algae population would increase.
(B) The frogs and sunfish would disappear.
(C) The minnow population would increase and the sunfish population would decrease.
(D) The frog and sunfish populations would increase.
(E) The minnow population and algae would increase.
Questions 70–72
This chart shows the relative abundance of different groups of echinoderms throughout geologic time. The width of the band indicates the number of species for each group.

70. Which of the following time periods shows a mass extinction of animals?
(A) end of the Ordovician
(B) end of the Silurian
(C) end of the Devonian
(D) end of the Permian
(E) end of the Triassic
71. Which of the following time periods showed a boom in all echinoderm groups?
(A) Ordovician
(B) Silurian
(C) Mississippian
(D) Permian
(E) Jurassic
72. All of the following statements are correct EXCEPT
(A) The Blastoids are extinct.
(B) The Echinodermata will become extinct in the near future.
(C) The Echinoids are a successful group.
(D) The Blastoids were not able to adapt to the same changes as the Crinoids.
(E) The Crinoids have been living in a stable environment since the Triassic.
Questions 73–77
Vegetation follows established patterns of regrowth and change after disturbances by farming, timber harvesting, hurricanes, or fire. This process of patterned regrowth and change is called plant succession. The rate of succession and the species present at various stages depend on the type and degrees of disturbance, the environment of the particular sites, and the species available to occupy the site. In the Piedmont of North Carolina, land subjected to disturbances will grow back in a century or two to become mixed hardwood forest.
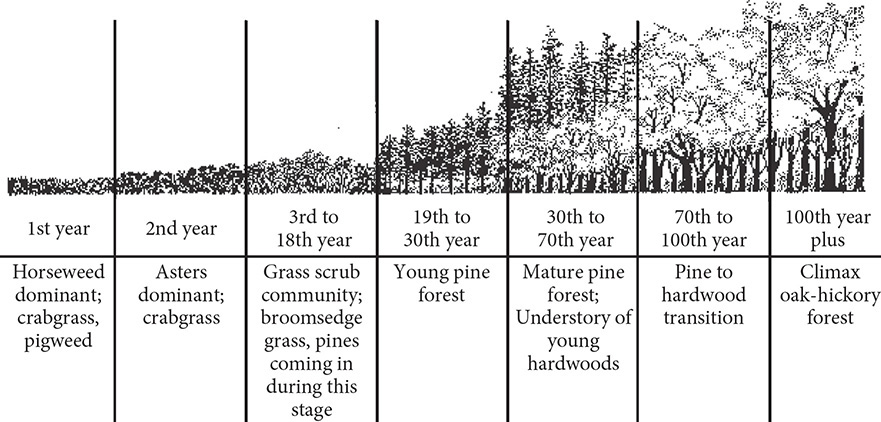
73. Based on this diagram, after 80 years, which will make up the majority of trees?
(A) young pines
(B) mature pines
(C) oak trees
(D) oak and hickory trees
(E) pine, oak, and hickory trees
74. Which best describes the change that takes place when pines become the dominant vegetation?
(A) The pine trees increase the amount of nutrients available in the soil.
(B) The pine trees increase the soil moisture.
(C) The pine trees decrease the amount of sunlight reaching the forest floor.
(D) The pine trees change the character of the soil from loam to sandy loam.
(E) The pine trees increase the amount of soil erosion.
75. Which of the following factors would be LEAST likely to restart succession?
(A) forest fire
(B) volcanic eruption
(C) clear-cut logging
(D) glaciation
(E) drought
76. Pine beetles are a type of insect that burrow into the bark of mature and over-mature pine trees. The pine trees die as a result of the infestations. If pine beetles attacked a mature pine forest, which of the following events would most likely occur?
(A) Succession would start over.
(B) The rate of transition to a hardwood forest would be increased.
(C) The succession will stall at being a young pine forest.
(D) The succession will stall at being a mature pine forest while young pines mature.
(E) The pine beetles will not affect the rate of succession in the forest.
77. Which of the following statements about succession is true?
(A) Succession is a natural progression that takes place at a constant rate.
(B) Succession only takes place on freshly cleared or new land such as islands.
(C) The rate of succession can be changed by factors such as fire, clear cutting, and lava flows.
(D) Succession is a natural progression of plant types that cannot be reversed.
(E) Succession always occurs over a short period of time.
Questions 78–80
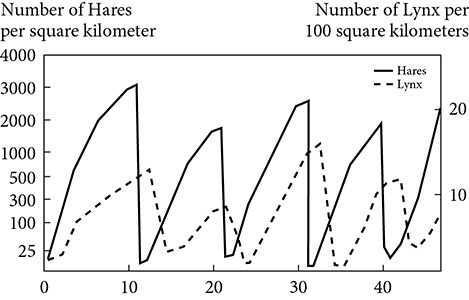
78. If lynxes depend mainly on hares for food, which best describes the relationship between hares and lynxes?
(A) As the hare population decreases, the lynx population increases.
(B) As the hare population decreases, the lynx population stays the same.
(C) As the hare population increases, the lynx population increases.
(D) As the hare population increases, the lynx population stays the same.
(E) There is no relationship between the populations of lynxes and hares.
79. Based on this chart, which of the following statements is true?
(A) Lynxes and hares depend on each other for survival.
(B) Hares become better at hiding from lynxes over time.
(C) Hares are capable of reproducing quickly.
(D) Lynxes only prey on hares in certain seasons.
(E) Lynxes migrate into and out of areas on a regular basis.
80. What would happen to the hare population if the lynxes were removed from the habitat?
(A) The hare population would continue on a boom and bust cycle.
(B) The hare population would dwindle.
(C) The hare population would grow exponentially and not stop.
(D) The hare population would quickly reach the carrying capacity and stabilize.
(E) The hare population would slowly increase over time.
-------------------------------------------STOP-------------------------------------------
If you finish before time runs out, go back and check your work.
Answer Key
Part A
1. C
2. A
3. D
4. D
5. A
6. B
7. C
8. E
9. B
10. A
11. C
12. D
13. D
14. B
15. E
16. B
17. E
18. B
19. B
20. B
21. B
22. A
23. D
24. B
25. D
26. D
27. A
28. E
29. C
30. B
31. A
32. B
33. C
34. D
35. B
36. A
37. C
38. C
39. C
40. B
41. C
42. D
43. E
44. B
45. E
46. A
47. D
48. D
49. A
50. D
51. D
52. B
53. B
54. C
55. C
56. A
57. C
58. B
59. E
60. B
Part B
61. A
62. B
63. C
64. C
65. E
66. D
67. C
68. A
69. D
70. D
71. C
72. B
73. E
74. C
75. E
76. B
77. C
78. C
79. C
80. D
Score Sheet

Answers and Explanations
Part A
1. (C) Fermentation is the cellular respiration process that takes place in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation converts glucose to either lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.
2. (A) The Krebs cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway of respiration. It takes in pyruvate and produces ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
3. (D) Glycolysis is the biochemical pathway that breaks down glucose to pyruvate. Glycolysis produces a net gain of 2 ATP molecules.
4. (D) Earthworms are decomposers because they break down organic matter and return nutrients to the soil. The returned nutrients are ready for use by plants.
5. (A) Cows are primary consumers because they eat plants, which are producers. Primary consumers are on the next trophic level above producers.
6. (B) Lions are secondary consumers because they eat animals, other consumers.
7. (C) Buzzards are scavengers because they find and eat already dead animals rather than killing them.
8. (E) Behavioral isolation occurs when two groups diverge and have different courtship rituals.
9. (B) Mechanical isolation occurs when two groups evolve differences in their genitalia.
10. (A) Geographical isolation occurs when groups are physically separated, such as by a mountain range or large body of water.
11. (C) Temporal isolation occurs when two groups diverge and have different mating seasons.
12. (D) Hybrid sterility occurs when nonfertile offspring are produced. This is a dead end as far as passing genes on is concerned.
13. (D) Imprinting is a learned behavior that occurs at a certain time of an animals life, such as just after birth.
14. (B) A reflex is an automatic and uncontrollable response. This is a direct stimulus–response scenario.
15. (E) Habituation is learned behavior that occurs as a result of doing some repeatedly.
16. (B) All monocots have parallel veins in their leaves.
17. (E) Populations grow as a result of multiple births through the lifespan of an organism. If each organism in a population only reproduced once, the population would not grow.
18. (B) Jellyfish are primitive, multicellular organisms. An opening to the digestive tract serves as both the mouth and anus for jellyfish.
19. (B) Motivation is needed for learning. If an animal lacks motivation, there will be no learning.
20. (B) Plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose. The cellulose is rigid and gives the plant cell a defined shape.
21. (B) Cnidarians have two distinct body plans during their lives. A jellyfish is an example of a medusa, and a sea anemone is an example of a polyp.
22. (A) Sometimes during meiosis, a pair of chromosomes fails to separate. This causes an extra chromosome in one daughter cell and a missing chromosome in the other.
23. (D) Fungi have many different forms, but the shape of their spores classifies them all.
24. (B) When a pasture exceeds the carrying capacity, it lacks the food to support that number of animals. A pasture in this condition will have all its available food eaten and will appear barren.
25. (D) The only mutation that can be passed to offspring is one that occurs in the sex cells. These are the only cells that undergo meiosis and take part in reproduction.
26. (D) A dihybrid cross has two factors in the cross. This results in a total of four potential phenotypes with a ratio of 9:3:3:1.
27. (A) Uracil does not occur in DNA but is in RNA. In RNA, uracil replaces thymine and attaches to adenine.
28. (E) Bacteria usually reproduce through binary fission but they sometimes get together, exchange genetic information, and reproduce by a process known a conjugation.
29. (C) During meiosis, the chromosome pairs separate and go to different daughter cells. This means that each daughter cells acquires one allele for a specific trait.
30. (B) The complementary strand of DNA will have the opposite nucleotide bases as the original strand.
31. (A) The mRNA strand will have the opposite nucleotides as the DNA with uracil substituted for thymine.
32. (B) When Linneaus proposed a method for classifying organisms, he based his system on structural similarities. This system has worked fairly well but many refinements are now done using genetic analysis.
33. (C) An ecosystem is all interactions among the organisms in the environment as well as the abiotic features.
34. (D) The diploid number refers to the number of pairs of chromosomes. In humans, the normal diploid number is 23 so that means that a cell has 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes.
35. (B) Plants are made up of many different types of tissues. The tissues that are part of the transport system for plants are vascular tissues such as xylem and phloem.
36. (A) This is the most basic statement of the cell theory.
37. (C) A bird that probes flowers for nectar would need a long, thin beak to reach inside the flower. A hummingbird is an example of a bird that feeds on nectar from flowers.
38. (C) Distilled water is hypotonic compared to a cell. As a result, water moves from an area of higher concentration (outside the cell) to the area of lower concentration (inside the cell).
39. (C) Because of genetic variations, some of the bacteria were able to survive the antibiotics. They passed this genetic advantage to their offspring and soon repopulated the petri dish with antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
40. (B) This scenario is an example of microevolution. Microevolution is a small change in a population but not enough to create a new species.
41. (C) Biogeochemical cycles are cycles where minerals move between the biotic and abiotic part of the environment. Energy is not a mineral.
42. (D) Incomplete dominance occurs when neither of two traits is dominant. When both alleles appear, the phenotype is expressed as a blend.
43. (E) The haploid number for chromosomes is the actual number of chromosomes in a gamete. The total number of chromosomes in an organism would be double the haploid number.
44. (B) Analogous structures are those that serve a similar function but have structural differences and are not linked through evolution.
45. (E) The small intestine is lined with villi that increase the surface area and aid in the absorption of nutrients from digested food. The large intestine carries out the absorption of water, and the large intestines are also the site of some vitamin synthesis by bacteria living there symbiotically.
46. (A) The genetic code is based on sets of three nucleotides called codons.
47. (D) The shape of a virus allows it to attach to a host cell. Once this is accomplished, the virus can inject DNA or RNA into the host cell.
48. (D) Evolution results in changes to proteins. For cytochrome-c, the fewer the changes, the more closely related the organisms.
49. (A) A and B are dominant over O. O can only be expressed if paired with another O. The only way the offspring could have two O alleles is if the parents were AO and BO.
50. (D) The embryo of the corn plant is made up of the embryonic shoot (A), the embryonic root (B), and the cotyledon (E).
51. (D) The endosperm is energy stored for the plant embryo.
52. (B) An enzyme is a catalyst. Catalysts facilitate reactions by lowering the activation energy of the reaction pathway. They cannot change the initial or final energy level of the participating molecules.
53. (B) An insect with incomplete metamorphosis has a nymph stage that looks similar to the adult stage. Unlike complete metamorphosis, there is no pupa stage.
54. (C) Potential energy is the amount of energy for the next trophic level. Each trophic level only passes on about 10% of its total energy to the next higher level.
55. (C) The law of independent assortment states that traits are inherited independently of other traits. This only applies to alleles that are on separate chromosomes.
56. (A) Cells spend most of their time in the G1 phase. After that comes the S phase, the G2 phase, mitosis, and finally cytokinesis.
57. (C) Organisms must already have traits for variation before natural selection occurs. Under most conditions, the variation in traits does not provide any particular advantage, so there is no natural selection. The variation only becomes important for natural selection when there is pressure that gives one trait an advantage over another.
58. (B) All of the plants in the first generation will be heterozygous so they exhibit the dominant trait.
59. (E) Individuals have traits that make them more successful, which gives them a reproductive advantage.
60. (B) Hawks are secondary consumers because they eat other consumers.
Part B
61. (A) A winter storm will not cause density-dependent deaths. It can be a density-independent cause of deaths.
62. (B) A maple seed has wings that allow it to be carried by the wind to a more distant location.
63. (C) Reptiles were the first animals with internal fertilization. This ended the dependence on water to carry sperm to the egg.
64. (C) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are found in the ground. They often live in a symbiotic relationship with plants on their roots. Legumes or beans are a common example.
65. (E) Earthworms have both male and female reproductive organs.
66. (D) Random mating does not give any reproductive advantage to a trait. As a result, it does not change allele frequencies in a population.
67. (C) Frog and sunfish both rely on the same food source so they are in direct competition.
68. (A) Energy flows from the producer (algae) through consumers before it reaches the bass.
69. (D) The loss of the secondary consumer would remove pressure from primary consumers and allow their populations to grow until they reach the carrying capacity.
70. (D) It is necessary to read the chart from bottom to top. At the end of the Permian, Crinoids became reduced in diversity, and Blastoids became extinct.
71. (C) During the Mississippian, all the echinoderm groups increased in diversity.
72. (B) The Echinoids have been increasing in diversity. It is unlikely that they will have a collapse unless there is significant global change.
73. (E) At 80 years, the forest is in a transition with large numbers of pines, oaks, and hickories.
74. (C) The pines are the first plants that grow tall. They shade the soil and reduce the populations of plants that depend on full sunlight.
75. (E) A drought will not likely last long enough to kill off all the trees.
76. (B) If the mature pines are removed, the rate of transition to a climax oak–hickory forest will be increased.
77. (C) Succession is a process that does not follow a distinct timeline. Many factors can affect rate of succession or even restart it.
78. (C) The hares are a food source for lynxes. As the population of hares increases, more food is available for lynxes so their population increases, too.
79. (C) There is a short lag time between the boom and bust cycle on hares so they must have a quick reproduction time.
80. (D) Without the lynxes, the hare will quickly reproduce and reach the carrying capacity.