The tar (Section 39.2) command isn't just for tape archives. It can copy files from disk to disk, too. And even if your computer has cp -r (Section 10.12), there are advantages to using tar.
The obvious way to copy directories with tar is to write them onto a tape archive with relative pathnames — then read back the tape and write it somewhere else on the disk. But tar can also write to a Unix pipe — and read from a pipe. This looks like:
%reading-tar|writing-tar
with one trick: the writing-tar
process has a
different current directory (Section 24.3, Section
24.4) (the place where you want the copy made) than the
reading-tar
. To do that, run the
writing-tar in a subshell (Section
43.7), or if your tar supports it, use
the -C
option.
The argument(s) to the reading-tar can be
directories or files. Just be sure to use relative
pathnames (Section
31.2) that don't start with a slash — otherwise, the
writing-tar may write the copies in the same
place from where the originals came!
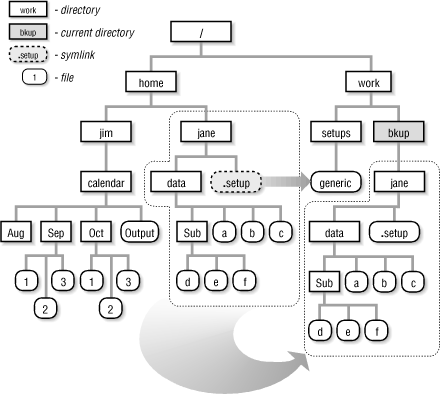
"How about an example," you ask? Figure 10-1 has one. It copies from the directory /home/jane, with all its files and subdirectories. The copy is made in the directory /work/bkup/jane:
%mkdir /work/bkup/jane%cd /home/jane%tar cf - . | (cd /work/bkup/jane && tar xvf -)
Or, if you want to use -C:
% tar cf - . | tar xvf - -C /work/bkup/janeIn the subshell version, the
&& operator (Section 35.14) tells the shell to start
tar xvf - only if the previous command
(the cd) succeeded. That prevents tar writing files into the same directory from
which it's reading — if the destination directory isn't accessible or you flub
its pathname. Also, don't use the v
(verbose) option in both
tars unless you want to see doubled
output; one or the other is plenty. I usually put it in the
writing-tar to see write progress, as that's more
interesting to me than how far ahead the system has cached the read for
me.
Warning
At least one tar version has a
v (verbose) option that writes the verbose text to
standard output instead of standard error! If your tar does that, definitely don't use v on the
reading-tar (the tar that feeds the pipe) — use v on the
writing-tar only.
You can use other options that your tar
might have — such as excluding files or directories — on the
reading-tar, too. Some gotchas:
Be aware that symbolic links (Section 10.4) will be copied exactly. If they point to relative pathnames, the copied links might point to locations that don't exist (Section 10.6). You can search for these symbolic links with find -type l.
If your system has rsh ( Section 1.21) or ssh, you can run either the
reading-taror thewriting-taron a remote system. For example, to copy a directory to the computer named kumquat:%
ssh kumquat mkdir /work/bkup/jane%tar cf - . | ssh kumquat 'cd /work/bkup/jane && tar xvf -'
—JP and DJPH