Practice Test 4
Answer Sheet
This practice test will help measure your current knowledge of chemistry and familiarize you with the structure of the SAT Chemistry test. To simulate exam conditions, use the answer sheet below to record your answers and the appendix tables at the back of this book to obtain necessary information.

PART A
Time: 60 Minutes
Note: Unless otherwise stated, for all statements involving chemical equations and/or solutions, assume that the system is in pure water.
Directions: Each of the following sets of lettered choices refers to the numbered formulas or statements immediately below it. For each numbered item, choose the one lettered choice that fits it best. Then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each choice in a set may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
Questions 1–4
(A) The point of equilibrium
(B) The triple point
(C) The freezing point
(D) The point where reactants first form products
(E) The boiling point
1. A specific temperature and pressure where solid, liquid, and gas phases exist simultaneously
2. Can be shifted by adding more reactants
3. Vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the pressure of the surroundings
4. The activated complex
Questions 5–8
(A) Red
(B) Purple
(C) Orange
(D) Green
(E) Blue
5. Copper(II) sulfate solution
6. Chlorine gas
7. KMnO4 solution
8. Bromine liquid
Questions 9–11
(A) Voltaic cell
(B) Electrolytic cell
(C) Geiger Counter
(D) pH meter
(E) Calorimeter
9. Requires an external current to make a redox reaction spontaneous
10. Requires a salt bridge
11. Detects radioactive particles
Questions 12–15
(A) Halogens
(B) Alkali metals
(C) Alkaline earth metals
(D) Noble gases
(E) Lanthanides
12. Valence electrons are located in the f orbitals
13. Need to lose one electron to form a stable octet
14. Will have the highest first ionization energies
15. Contain elements in the solid, liquid, and gas phases at STP
Questions 16–19
(A) 9.03 × 1023 molecules
(B) 44.8 liters
(C) 3.5 moles
(D) 6.0 grams
(E) 3.01 × 1023 atoms
16. 0.25 moles of O2 at STP
17. 3.0 moles of H2 at STP
18. 56 grams of N2 at STP
19. 96.0 grams of SO2 at STP
Questions 20–22
(A) Water
(B) Hydrogen bromide
(C) Iron
(D) Argon
(E) Sodium chloride
20. Hydrogen bonding
21. Highly polar
22. Dispersion forces
Questions 23–25
(A) Alpha particle
(B) Beta particle
(C) Gamma radiation
(D) Positron
(E) Deuteron
23. Po-218 → At-218 + X
24. Tc-99 → Tc-99 + X
25. Ne-19 → F-19 + X
PART B
Note to Students: THE QUESTIONS IN PART B ARE OUT OF SEQUENCE WITH THE QUESTIONS IN PARTS A AND C. PLEASE GO TO THE SPECIAL SECTION AT THE LOWER LEFT-HAND CORNER OF YOUR ANSWER SHEET LABELED “CHEMISTRY” AND ANSWER QUESTIONS 101–115 ACCORDING TO THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS.
Directions: Each question below consists of two statements. For each question, determine whether statement I in the leftmost column is true or false and whether statement II in the rightmost column is true or false. Fill in the corresponding T or F ovals on the answer sheet provided. Fill in the oval labeled “CE” only if statement II correctly explains statement I.


PART C
Directions: Each of the multiple-choice questions or incomplete sentences below is followed by five answers or completions. Select the one answer that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet provided.
26. As we move across period 3 from left to right, a periodic trend that generally occurs is in the graph below:
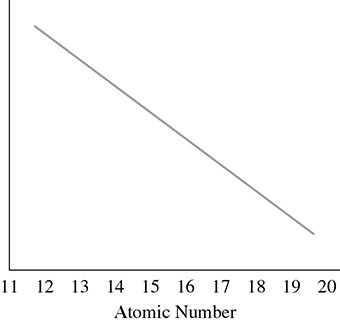
This periodic trend could be
I. metallic character
II. first ionization energy
III. atomic radius
(A) I only
(B) II and III only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II, and III
(E) II only
27. Which of the following are uses for radiation and radioactivity that are of benefit to us?
I. Nuclear waste
II. Radioisotopes
III. Excess exposure
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II only
(E) I and III only
28. Which of the following statements is not part of the kinetic molecular theory?
(A) The average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to temperature.
(B) Attractive and repulsive forces are present between gas molecules.
(C) Collisions between gas molecules are perfectly elastic.
(D) Gas molecules travel in a continuous, random motion.
(E) The volume that gas molecules occupy is minimal compared to the volume within which the gas is contained.
29. The following redox reaction occurs in an acidic solution: Ce4+ + Bi → Ce3+ + BiO1+. What is the coefficient before the Ce4+ when the equation is fully balanced?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 6
(E) 9
30. Which statement regarding significant figures is false?
(A) Zeros can be significant.
(B) When multiplying, the answer is determined by the number of significant figures.
(C) When adding, the answer is determined by the number of decimal places.
(D) When dividing, the answer is determined by the number of decimal places.
(E) The number 50,004 has five significant figures.
31. Which statement below best describes the molecule in question?
(A) Water has a bent molecular geometry and one lone pair of electrons.
(B) Ammonia has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry and two lone pairs of electrons.
(C) Methane has a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
(D) Carbon dioxide is linear because it has one single bond and one triple bond.
(E) The carbon atoms in ethane are sp3 hybridized.
32. A compound was analyzed and found to be 12.1% C, 71.7% Cl, and 16.2% O. What is the empirical formula for this compound?
(A) C2OCl
(B) COCl
(C) CO2Cl2
(D) C2O2Cl
(E) CCl2O
33. Which statement is true about the percent composition by mass in C6H12O6?
(A) Carbon is 6.7% by mass.
(B) Oxygen is 53.3% by mass.
(C) Hydrogen is 12% by mass.
(D) Carbon is 72% by mass.
(E) Carbon is 20% by mass.
34. Which process would have a positive value for the change in entropy?
I. The expansion of the universe
II. The condensation of a liquid
III. A food fight in a school cafeteria
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) II and III only
(E) I and III only
35. Of the gases below, which would react with rain water to produce acid rain?
I. CFCs
II. Methane
III. Carbon dioxide
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
36. A sample of gas is trapped in a manometer and the stopcock is opened. (See Figure 1.) The level of mercury moves to a new height as can be seen in the diagram. If the pressure of the gas inside the manometer is 815 torr, what is the atmospheric pressure in this case?

Figure 1
(A) 760 torr
(B) 740 torr
(C) 750 torr
(D) 815 torr
(E) 880 torr
37. Which aqueous solution is expected to have the highest boiling point?
(A) 1.5 m FeCl2
(B) 3.0 m CH3OH
(C) 2.5 m C6H12O6
(D) 2.5 m NaCl
(E) 1.0 m CaCl2
38. Which Ka value is that of a better electrolyte?
(A) 1.0 × 10−2
(B) 2.0 × 10−12
(C) 5.0 × 10−7
(D) 3.0 × 10−4
(E) 1.0 × 10−6
39. The following substances were all dissolved in 100 grams of water at 290 K to produce saturated solutions. If the solution is heated to 310 K, which substance will have a decrease in its solubility?
(A) NaCl
(B) KI
(C) CaCl2
(D) HCl
(E) KNO3
40. Methane undergoes a combustion reaction according to the reaction CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l). How many grams of methane gas were burned if 67.2 liters of carbon dioxide gas are produced in the reaction? (Assume STP.)
(A) 16 grams
(B) 48 grams
(C) 3 grams
(D) 132 grams
(E) 22.4 grams
41. A closed system contains the following reaction at STP: Cl2(g) + 2NO2(g) ←→ 2NO2Cl(g). What is the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction?
(A) 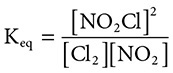
(B) 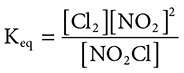
(C) 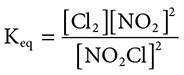
(D) 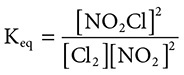
(E) 
42. Referring to the question and choices in question 41, what would be the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
(E) E
43. Which Lewis structure below has been drawn incorrectly in Figure 2?
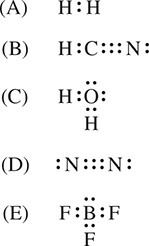
Figure 2
44. Which reaction below demonstrates the Lewis definition of acids and bases?
(A) HCl + NaOH → HOH + NaCl
(B) H2O + NH3 → OH1− + NH41+
(C) NH3 + BF3 → NH3BF3
(D) HI + KOH → H2O + KI
(E) H+ + OH1− → H2O
45. Which sample is a homogeneous mixture?
(A) KI(aq)
(B) Fe(s)
(C) CO2(g)
(D) NH3(l)
(E) NaCl(s)
46. Which pair below represents isomers of the same compound?
(A) CH3CH2CH2OH and HOCH2CH2CH3
(B) CH3CH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2CH3
(C) CH3CH(Cl)CH3 and CH3CH2CH2Cl
(D) CH3COCH3 and CH3CH2CH2CHO
(E) ClCH2CH2Br and BrCH2CH2Cl
47. Which would you never do in a laboratory setting?
I. Eat and drink in the laboratory
II. Push a thermometer through a rubber stopper
III. Remove your goggles to take a better look at a reaction
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
48. How many pi bonds are there in a molecule of N≡≡C—CH2—CH2—CO—NH—CH==CH2?
(A) 7
(B) 4
(C) 12
(D) 10
(E) 5
49. When the equation: C2H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O is completely balanced using the lowest whole number coefficients, the sum of the coefficients will be
(A) 4
(B) 9.5
(C) 19
(D) 15.5
(E) 11
50. From the heats of reaction of these individual reactions:
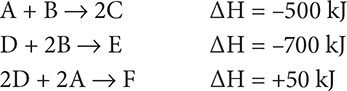
Find the heat of reaction for F + 6B → 2E + 4C.
(A) +450 kJ
(B) −1,100 kJ
(C) +2,350 kJ
(D) −350 kJ
(E) −2,450 kJ
51. Which solutions have a concentration of 1.0 M?
I. 74 grams of calcium hydroxide dissolved to make 1 liter of solution
II. 74.5 grams of potassium chloride dissolved to make 1 liter of solution
III. 87 grams of lithium bromide dissolved to make 1 liter solution
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
52. According to the reaction 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3, how many grams of hydrogen gas and nitrogen gas are needed to make exactly 68 grams of ammonia?
(A) 2 grams of hydrogen gas and 28 grams of nitrogen gas
(B) 3 grams of hydrogen gas and 1 gram of nitrogen gas
(C) 12 grams of hydrogen gas and 56 grams of nitrogen gas
(D) 102 grams of hydrogen gas and 34 grams of nitrogen gas
(E) 6 grams of hydrogen gas and 2 grams of nitrogen gas
53. Which compound is not paired with its correct name?
(A) FeCl2 / iron(II) chloride
(B) K2O / potassium oxide
(C) NO2 / nitrogen dioxide
(D) PCl3 / potassium trichloride
(E) NH4Cl / ammonium chloride
54. A reaction takes place according to the equation H2 + I2 → 2HI. How many grams of HI can be formed from 254 grams of I2 and 6 grams of H2?
(A) 6 grams of HI are made with 248 grams of iodine in excess.
(B) 254 grams of HI are made with 6 grams of hydrogen gas in excess.
(C) 256 grams of HI are made with 4 grams of hydrogen gas in excess.
(D) 258 grams of HI are made with 2 grams of hydrogen gas in excess.
(E) 260 grams of HI are made with no excess reactants.
55. 500 mL of a 0.2 M solution has 200 mL of water added to it. What is the new molarity of this solution?
(A) 0.50 M
(B) 0.28 M
(C) 0.70 M
(D) 0.14 M
(E) 0.40 M
56. Which mixture is correctly paired with a method for separation of the mixture?
(A) Oil and water—filter paper
(B) Salt water—distillation
(C) Sand and water—separatory funnel
(D) Sand and sugar—tweezers
(E) Sugar water—filter paper
57. Which reaction between ions does not form a precipitate?
(A) Ag1+ + Cl1−
(B) Pb2+ + 2I1−
(C) Ca2+ + CO32−
(D) Hg2+ + 2Br1−
(E) Na1+ + OH1−
58. Which will happen when sodium sulfate is added to a saturated solution of CaSO4 that is at equilibrium? [CaSO4(s) ←→ Ca2+(aq) + SO42−(aq)]
(A) The solubility of the calcium sulfate will decrease.
(B) The concentration of calcium ions will increase.
(C) The reaction will shift to the right.
(D) The Ksp value will change.
(E) The equilibrium will shift to consume the decrease in sulfate ions.
59. Given the reaction 2A(g) + B(g) + Heat ←→ 3C(g) + D(g), what could be done to the reaction to shift the equilibrium so that more D is made?
(A) Increase the concentration of D.
(B) Increase the concentration of C.
(C) Increase the temperature.
(D) Increase the pressure.
(E) Remove B from the reaction.
60. A 10-gram sample of water at 273K is cooled so that it becomes a completely solid ice cube at 273K. How much heat was released by the sample of water to form this ice cube?
(A) 2,730 J
(B) 4,368 J
(C) 18,258 J
(D) 350 J
(E) 3,336 J
61. Sublimation is the process by which a solid becomes a gas without having a liquid phase. Which of these can sublime?
I. Iodine
II. Naphthalene
III. Carbon dioxide
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) I, II, and III
62. Which of the following will decrease the rate of a reaction?
(A) Using powdered solids instead of whole pieces
(B) Selecting ionic reactants that have been dissolved in water
(C) Decreasing the temperature
(D) Increasing the pressure
(E) Adding a catalyst
63. Three gases are mixed in a sealed container. The container has 0.3 mole of gas A, 0.4 mole of gas B, and 0.3 mole of gas C. The total pressure of the gases is 1,000 torr. What is true about the partial pressures of the gases?
(A) The partial pressure of A is 700 torr.
(B) The partial pressure of B is 600 torr.
(C) The partial pressure of C is the same as B.
(D) Gases A and C have an equal number of gas particles contributing equally to the total pressure.
(E) The partial pressure of C is 700 torr.
Questions 64 and 65 refer to the voltaic cell below in Figure 3:

Figure 3
64. What is the half reaction that occurs at the cathode?
(A) Al → Al3+ + 3e–
(B) Ni2+ + 2e– → Ni
(C) Ni → Ni2+ + 2e–
(D) 2Al3+ + 6e– → 2Al
(E) Al3+ + 3e– → Al
65. Which statement is true about the setup above?
(A) The electrode potential for this cell is 1.40 V.
(B) The electrode potential for this cell is 2.54 V.
(C) Electrons will be carried by the salt bridge.
(D) Ions will be carried through the wire.
(E) The reaction is nonspontaneous.
66. Over a number of years the average pH of a stream changes from a pH of 6.9 to a pH of 5.9 due to acid rain. Which statement is true about the pH of the stream?
(A) The pH of the stream now is one time more acidic than it was years ago.
(B) The stream now has 10 times more hydroxide ions than it did years ago.
(C) The pH of the stream is now 10 times more acidic than it was years ago.
(D) The stream is more basic now than it was years ago.
(E) The concentration of hydronium ion in the stream has decreased over the years.
67. An alkaline earth metal, element M, reacts with oxygen. What is going to be the general formula for the compound formed?
(A) M2O
(B) MO
(C) MO2
(D) M2O3
(E) M3O2
68. Which functional group below does not contain a carbonyl group?
(A) Aldehydes
(B) Ketones
(C) Esters
(D) Ethers
(E) Carboxylic acids
69. Using the bond dissociation energies found in the appendix, calculate the change in the heat of reaction for 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O.
(A) −118 kJ
(B) +118 kJ
(C) −91 kJ
(D) −1,042 kJ
(E) −833 kJ
70. What can we conclude from this graph of the reaction: 2NO + Cl2 → 2NOCl?
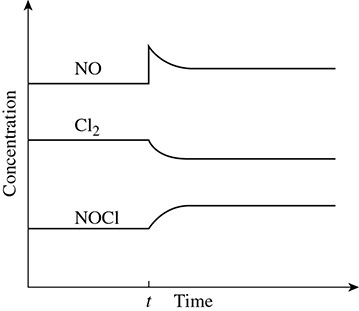
I. More chlorine gas was added to the reaction.
II. An increase in concentration of a reactant leads to more product forming.
III. The equilibrium of a reaction can be stressed but then a new equilibrium can be established.
(A) I and II only
(B) II and III only
(C) I and III only
(D) II only
(E) III only
-------------------------------------------STOP-------------------------------------------
If you finish before time is called, go back and check your work.
Answers and Explanations
Part A
1. (B) The triple point on a phase diagram tells the temperature and pressure needed for a solid, liquid, and gas to exist at the same time.
2. (A) If a system is at equilibrium, adding more reactants will shift the equilibrium to form more products.
3. (E) The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature in which the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
4. (D) The activated complex on the potential energy diagram is where the first appearance of products occurs.
5. (E) Copper sulfate is a blue salt that forms blue solutions.
6. (D) Chlorine is a green gas.
7. (B) Permanganate ion will form a dark purple solution.
8. (C) Bromine is an orange liquid at STP.
9. (B) An electrolytic cell uses an externally applied current to drive a nonspontaneous reaction.
10. (A) The salt bridge in the voltaic cell allows ions to migrate from one half cell to another.
11. (C) The Geiger counter detects radioactive emanations.
12. (E) The lanthanides and actinides are the elements whose valence electrons are located in the f orbitals.
13. (B) The alkali metals have a valence electron configuration of s1 and need to lose just one electron to form a stable, complete, outermost principal energy level.
14. (D) Because the noble gases have very stable electron configurations, it takes much energy to remove an electron from the stable, complete, outermost principal energy level.
15. (A) Fluorine and chlorine are gases at STP, while bromine is a liquid and iodine is a solid.
16. (E) 0.25 moles of O2 will have 0.50 moles of oxygen atoms. 0.50 moles of atoms is the same as 3.01 × 1023 atoms.
17. (D) 3.0 moles of hydrogen gas (molar mass is 2) will have a mass of 6.0 grams.
18. (B) 56 grams of nitrogen gas at STP is 2 moles of nitrogen gas. This sample will occupy 44.8 liters.
19. (A) 96.0 grams of sulfur dioxide (molar mass is 64) is the same as 1.5 moles of sulfur dioxide. This will equal 9.03 × 1023 molecules of sulfur dioxide.
20. (A) Water is the only substance from the list that will exhibit hydrogen bonds. Remember the mnemonic device “FON.”
21. (A) Water is the only substance from the list that is a polar molecule.
22. (D) Argon is monatomic and nonpolar. The noble gases will exhibit dispersion (or Van der Waals) forces between their atoms.
23. (B) Filling in the atomic numbers shows the full reaction: 21884Po → 21885At + X. X has no mass and a negative one charge, 01−X. This makes X a beta particle.
24. (C) Tc-99 did not change in mass or in atomic number. It must have given off something without mass or charge. Energy was released. Gamma radiation is the only energy that is listed among the choices.
25. (D) Filling in the atomic numbers shows the reaction: 1910Ne → 199F + 01+X. X is a particle with zero mass and a 1+ charge, a positron.
Part B
101. (T, F) The number of protons defines the atomic number and the nuclear charge for an element. Neutrons do not have any charge.
102. (T, T, CE) According to the Gibbs Free Energy equation, ΔG = ΔH – TΔS, the favored decrease in enthalpy (ΔH is −) and the favored increase in entropy (ΔS is +); ΔG will have a negative value.
103. (T, F) Conjugate pairs differ by a proton. When an acid loses a proton, it forms a conjugate base.
104. (T, T, CE) The electrolytic cell uses an external power supply to drive a redox reaction that normally has an electrode potential that is negative in value.
105. (T, T, CE) The expression 2n2, where n is the principal energy level number, is used to determine the maximum number of electrons that can be held in a principal energy level. Remember to square the number first, then multiply by 2.
106. (F, F) Kilo- means “one thousand.” 3,000 grams would be equivalent to 3 kilograms.
107. T, T, CE) According to Charles’ Law, as the temperature of a gas increases, the volume of the gas will increase as well. This is a direct relationship.
108. (F, T) While a catalyst can lower the potential energy of the activated complex and activation energy in a reaction, a catalyst will not change the heat of a reaction.
109. (T, T, CE) Dispersion forces increase between nonpolar molecules as the mass increases. Helium is the lightest of the noble gases and has the fewest dispersion forces between its atoms.
110. (T, T, CE) Nitrogen is lighter and less dense than oxygen given equal conditions. This means that the rate of effusion for nitrogen gas will be greater.
111. (T, T, CE) Propane is a compound made up of elements. Compounds can be decomposed in a chemical reaction, whereas elements cannot.
112. (T, T, CE) A distillation uses heat to separate a mixture of liquids based upon their different boiling points.
113. (F, F) Isotopes are the same element with a different number of neutrons and a different mass number.
114. (T, T, CE) The addition reaction allows a diatomic molecule to be added to the double and triple bonds of organic and other compounds.
115. (F, T) When NaCl undergoes hydrolysis, water is added and the original acid and base are formed, NaOH and HCl. Because these are both strong, they will neutralize each other. This means that NaCl is a neutral salt.
Part C
26. (C) As we move from left to right in period 3, the metallic character decreases along with atomic radius. The first ionization energy will increase.
27. (B) Radioisotopes (and radiotracers) can be used to help diagnose problems in certain organs in our bodies. The use of radioisotopes is beneficial if the right dosage is used correctly.
28. (B) Ideally, gas molecules should not have any attractive or repulsive forces between the molecules.
29. (C) There are a number of steps required to balance this redox reaction:
(i) Separate the two half reactions:
Ce4+ → Ce3+ and Bi → BiO1+
(ii) Add water to balance the oxygen atoms:
H2O + Bi → BiO1+
(iii) Add H1+ ions to balance the hydrogen atoms:
H2O + Bi → BiO1+ + 2H1+
(iv) Add electrons to balance the charges:
1e– + Ce4+ → Ce3+ and H2O + Bi → BiO1+ + 2H1+ + 3e–
(v) Use the distributive property to balance the number of electrons:
3(1e– + Ce4+ → Ce3+) becomes 3e– + 3Ce4+ → 3Ce3+
(vi) Add the two reactions together and cancel the common substances:
3Ce4+ + H2O + Bi → 3Ce3+ + BiO1+ + 2H1+
The coefficient before the cesium ions is 3.
30. (D) When multiplying and dividing, the final answer contains the same number of significant figures as the number with the fewest significant figures.
31. (E) Ethane is a hydrocarbon with all single bonds. This means that the two carbon atoms will both be sp3 hybridized.
32. (E) There are three steps in completing this problem:
(i) Change the percent sign to grams (assume a 100-gram sample):
12.1 grams of C, 71.7 grams Cl, and 16.2 grams of O.
(ii) Convert the grams of each element to moles:
1 mole of C, 2 moles of Cl, and 1 mole of O.
(iii) Divide by the lowest number of moles:
In this case it is the number “1.” The empirical formula will be CCl2O.
33. (B) The total mass of this compound is 180. The oxygen makes up 96 of the 180 which is about 53%.
34. (E) The positive value for the change in entropy means that there will be more disorder. An expanding universe and a food fight are sure signs of more disorder.
35. (C) Carbon dioxide and water can react to produce carbonic acid. CFCs are responsible for causing a hole in the ozone layer and methane is a greenhouse gas that can trap heat on earth.
36. (C) Because the gas pressure inside the manometer is pushing the level of mercury higher and toward the opening of the tube, the pressure inside the manometer must be greater than the atmospheric pressure. The mercury rose to a level that is 65 mm above the height of the bulb in the manometer. This means that the atmospheric pressure is 65 mm lower than the pressure of the gas. 815 − 65 = 750 torr.
37. (D) 2.5 molal NaCl will be, in effect, 5.0 molal because 1 mole of sodium chloride yields 2 moles of ions. This is the highest concentration of any of the choices and will have the greatest effect on the boiling and freezing points of water.
38. (A) A stronger acid or base will also be a better electrolyte because more ions will be released into solution. The greatest value listed is 1.0 × 10−2.
39. (D) Gases, like HCl, will experience a decrease in solubility as the temperature of the solution they are dissolved in increases. The solids will all have an increase in solubility as the temperature increases.
40. (B) 67.2 liters of carbon dioxide equates to 3 moles of carbon dioxide. Because carbon dioxide and methane are in a 1:1 ratio, for each mole of carbon dioxide produced, 1 mole of methane reacted. This means that 3 moles of methane were burned. Because the molar mass of methane is 16, 3 moles of methane would weigh 48 grams.
41. (D) Remember for equilibrium constants, “Products over reactants, coefficients become powers.” This is demonstrated by choice D.
42. (C) To write the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction, one must reciprocate the numerator and denominator.
43. (E) Boron will not form an octet, as shown correctly in the other four choices. Boron prefers six electrons in its outermost principal energy level.
44. (C) The Lewis definition of acids states that acids are electron pair acceptors while bases are electron pair donors. Choices A, D, and E show the Arrhenius definition whereas choice B shows the Brønsted-Lowry definition.
45. (A) By definition, an aqueous solution must be homogeneous. The KI(aq) tells that there is a homogeneous solution of water and KI.
46. (C) Isomers have the same molecular formula but a different structure. This also means that isomers will have different names. The isomers in this question are 2-chloropropane and 1-chlorpropane.
47. (E) Eating, drinking, and removing one’s goggles are all unsafe in the laboratory setting. Pushing a glass thermometer through a rubber stopper is also dangerous and should be done by a trained laboratory specialist.
48. (B) There are 4 pi bonds in this molecule. Two of them are between the N and C. One is between the two carbon atoms that have a double bond. The last pi bond is between the C and the O. When C and O are written as shown in this problem, it means that a double bond is present. A double bond has 1 pi bond.
49. (C) When balancing a reaction, leave the simplest substance for last. In this case it will be the oxygen gas. Balancing the carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms gives C2H6 + O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O. Balancing the oxygen atoms gives C2H6 + 3.5O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O. To get whole number coefficients, multiply the entire equation by 2: 2C2H6 + 7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O.
50. (E) First, double the reaction for A, B and C so that 4C ends up on the product side:
2A + 2B → 4C ΔH = −1,000 kJ
Next, double the second reaction so that 2E can be produced:
2D + 4B → 2E ΔH = −1400 kJ
Finally, switch the last reaction so that F appears on the reactant side:
F → 2D + 2A ΔH = −50 kJ
Adding up the three steps shows that the heat of reaction is −2,450 kJ.
51. (E) All three masses given are equivalent to 1 mole of the compounds in question. Because the 1 mole samples are all dissolved to make 1 liter of solution, each solution is 1 molar.
52. (C) 68 grams of ammonia (molar mass is 17) is 4 moles of ammonia. Setting up a proportion, you see that 6 moles of hydrogen gas and 2 moles of nitrogen gas are needed: 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3 is doubled and becomes 6H2 + 2N2 → 4NH3. 6 moles of hydrogen gas (molar mass is 2) is 12 grams of hydrogen gas. 2 moles of nitrogen gas (molar mass is 28) is 56 grams of nitrogen gas.
53. (D) Although it does use the prefix “tri-” correctly for a covalent compound, PCl3 is phosphorus trichloride.
54. (C) In this reaction 254 grams of I2 (one mole of I2) are reacted with 6 grams of H2 (three moles of H2). However, because the mole ratio is one to one, just one mole (2 grams) of the three moles of hydrogen will be used. This means that two moles of HI (256 grams of HI) are produced and that two moles of hydrogen gas (4 grams of H2) are in excess.
55. (D) The initial volume, V1, is 500 mL and the initial molarity, M1, is 0.2 M. The new volume, V2, is 700 mL because 200 mL of water were added to the original 500 mL. Using the equation M1V1 = M2V2 substitute and find that (0.2)(500) = (M2)(700). Solving for M2 you see that the concentration has decreased as it should when diluted: M2 is 0.14 M.
56. (B) A distillation can boil the solution and drive off the water from the solution. The water vapor will then enter a condenser where it is cooled and turns back into a liquid. This separates the water from the salt that will be left behind.
57. (E) Halides of lead, mercury, and silver will form precipitates, so choices A, B, and D are all precipitates. Calcium carbonate is also a solid. Sodium hydroxide is soluble in water.
58. (A) Because there were already sulfate ions in solution and more sulfate ions were added, sulfate ion is called the common ion. Adding sodium sulfate to the solution increases the concentration of sulfate ion in solution driving the reverse reaction. This is called the common ion effect and more of the solid calcium sulfate will be made. If the solid is being formed that means that it is not dissolving and the solubility has decreased.
59. (C) An increase in temperature will increase the amount of heat, which is one of the reactants. Because a reactant was added, more products will be made.
60. (E) This calculation requires using the heat of fusion of water. The equation is q = Hfm. Substitution gives q = (333.6 J/g)(10 g) = 3,336 joules of heat.
61. (E) All three substances can sublime. Naphthalene is the substance that is used to make mothballs. Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice. Iodine is a purple solid that can sublime as well.
62. (C) A decrease in temperature will cause the molecules to move with less kinetic energy. This means that the collisions will occur less frequently and will not be as effective.
63. (D) An equal number of moles of a gas will contain an equal number of gas molecules. An equal number of gas molecules will contribute to the pressure equally. Mathematically, the other choices do not make sense.
64. (B) Looking at the two reactions as oxidations shows that Al → Al3+ + 3e– has a potential of +1.66 V while Ni → Ni2+ + 2e– has a potential of +0.26 V. This indicates that the loss of electrons from Al is more of a spontaneous process than the loss of electrons from Ni. Al has a more positive electrode potential and will lose electrons to the Ni. Al will lose electrons and be the anode. The Ni electrode will gain electrons and be the cathode. At the cathode there is a gain of electrons for the ions that are in the solution where the cathode is located. The electrons will react with the Ni2+ ions according to the reaction Ni2+ + 2e– → Ni.
65. (A) From above we have the two half reactions:
Al → Al3+ + 3e– +1.66 V
Ni2+ + 2e– → Ni −0.26 V
The total is 1.40 V. Also remember that the electrode potential is never multiplied by any coefficients in a balanced equation.
66. (C) Remember that pH is based upon logarithms and base-10. Because the pH changed by a value of 1.0, it has changed by a power of 10. Because the pH value dropped, the stream has become more acidic.
67. (B) An alkaline earth metal is found in group 2 of the periodic table. This means that it will have two valance electrons and form an ion with a charge of 2+. When it reacts with oxygen’s ionic charge of 2−, the two ions will combine in a 1:1 ratio.
68. (D) A carbonyl group is characterized by a C==O. Ethers have an oxygen atom but the oxygen has only single bonds, R—O—R.
69. (E) Set up this problem:
[2(H—H) + 1(O—O)] − [4(H—O)]. Use the reference tables and substitute to get:
[2(435) + 1(145)] – [4(462)] =
[870 + 145] − [1,848] =
[1,015] − [1,848] = −833 kJ.
70. (B) The addition of NO did cause more NOCl to form. When the reaction is stressed the equilibrium will shift as to relieve this stress and the concentrations will become constant again.
Score Sheet

