
To succeed in the long term, focus on the middle term.
—Geoffrey Moore
The Portfolio Level contains the principles, practices, and roles needed to initiate and govern a set of development Value Streams. This is where strategy and investment funding are defined for value streams and their Solutions. This level also provides Agile portfolio operations and Lean governance for the people and resources needed to deliver solutions.
The portfolio level aligns enterprise strategy to portfolio execution by organizing the Lean-Agile Enterprise around the flow of value through one or more value streams. Delivering the basic budgeting and necessary governance mechanisms, it assures that investment in solutions will provide the return on investment (ROI) the enterprise needs to meet its strategic objectives. In the large enterprise, there may be multiple SAFe portfolios.
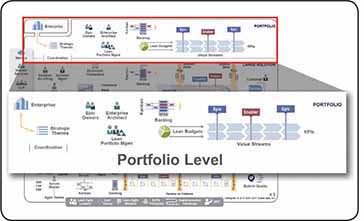
The SAFe portfolio level (Figure 1) contains the people and processes necessary to build the systems and solutions that the Enterprise needs to meet its strategic objectives.
Each SAFe portfolio has a two-way connection to the enterprise. The first way establishes the Strategic Themes for the portfolio that guide it through ever-changing business objectives. The second way provides a constant flow of feedback from the portfolio back to the enterprise stakeholders. This feedback includes:
The current state of the portfolio’s solutions
Value stream key performance indicators (KPIs)
Qualitative assessments of the current solution’s fitness for purpose
Assessments of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats present across the portfolio
Highlights of the portfolio level include:
Lean Budgets – Lean budgeting allows fast and empowered decision-making, with appropriate financial control and accountability.
Value Streams – Every value stream has to fund the people and resources necessary to build Solutions that deliver the value to the business or customer. Each is a long-lived series of steps (system definition, development, and deployment) that build and deploy systems that provide a continuous flow of value.
Portfolio Kanban – The portfolio Kanban system makes the work visible and creates Work-in-Process (WIP) limits to help assure that demand is matched to the actual value stream and Agile Release Train (ART) capacities.
The portfolio-level roles provide the highest level of accountability and governance, including the coordination of multiple value streams.
Lean Portfolio Management (LPM) – This function represents the individuals with the highest level of decision-making and financial accountability for a SAFe portfolio. This group is responsible for three primary areas: strategy and investment funding, Agile portfolio operations, and Lean governance.
Epic Owners – These individuals take responsibility for coordinating portfolio Epics through the portfolio Kanban system.
Enterprise Architect – This person works across value streams and programs to help provide the strategic technical direction that can optimize portfolio outcomes. The Enterprise Architect often may act as an Epic Owner for enabler epics.
The following portfolio-level artifacts help describe the strategic intent of the portfolio solution set:
Business epics – Capture and reflect the new business capabilities that can be provided only through cooperation among value streams.
Enabler epics – Reflect the architectural and other technology initiatives that are necessary to enable new Features and Capabilities.
Strategic themes – Provide specific, itemized business objectives that connect the portfolio to the evolving enterprise business strategy.
Portfolio Backlog – Is the highest-level backlog in SAFe. It holds approved business and enabler epics that are required to create a portfolio solution set. This provides the competitive differentiation and/or operational efficiencies necessary to address the strategic themes and facilitate business success.
LEARN MORE
[1] Leffingwell, Dean. Agile Software Requirements: Lean Requirements Practices for Teams, Programs, and the Portfolio. Addison-Wesley, 2011.